By Wilson and Womersley 1968, the project architect was John Sheard.
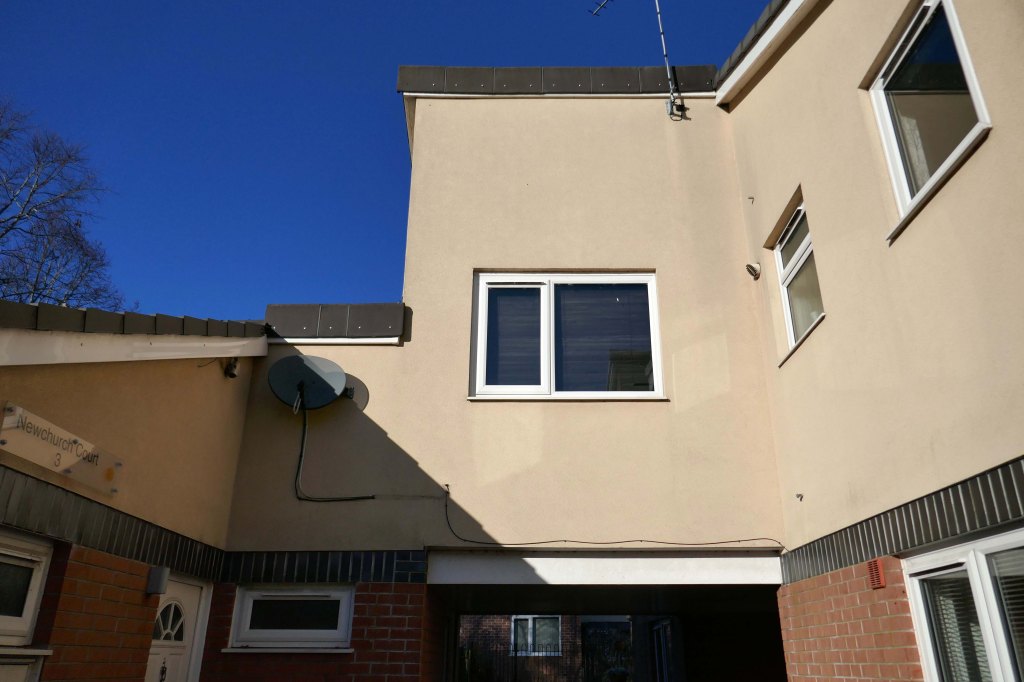
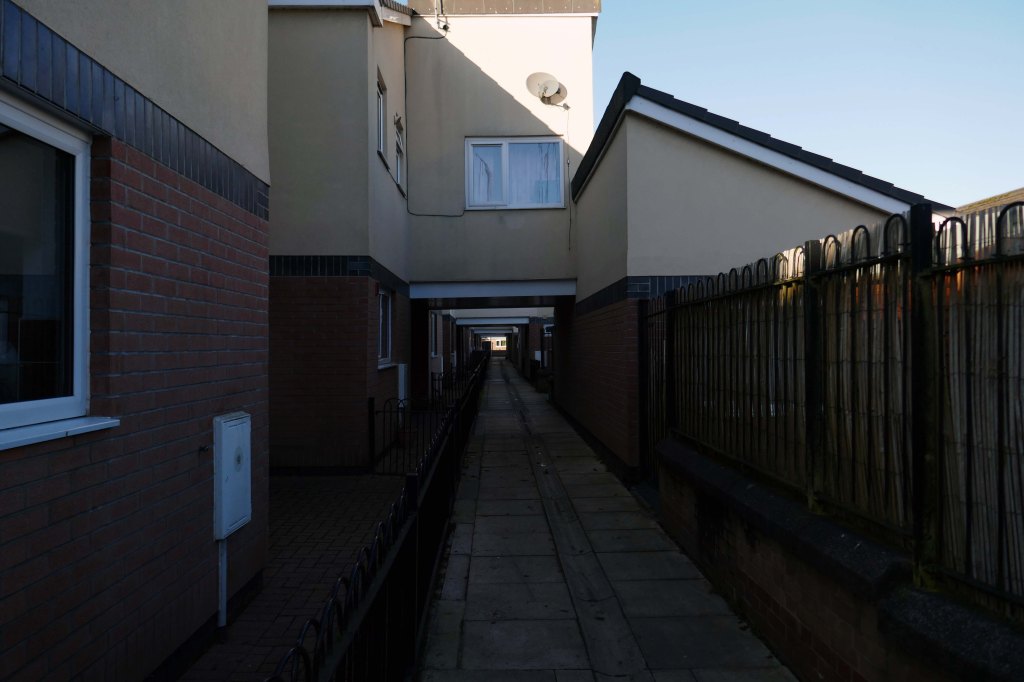
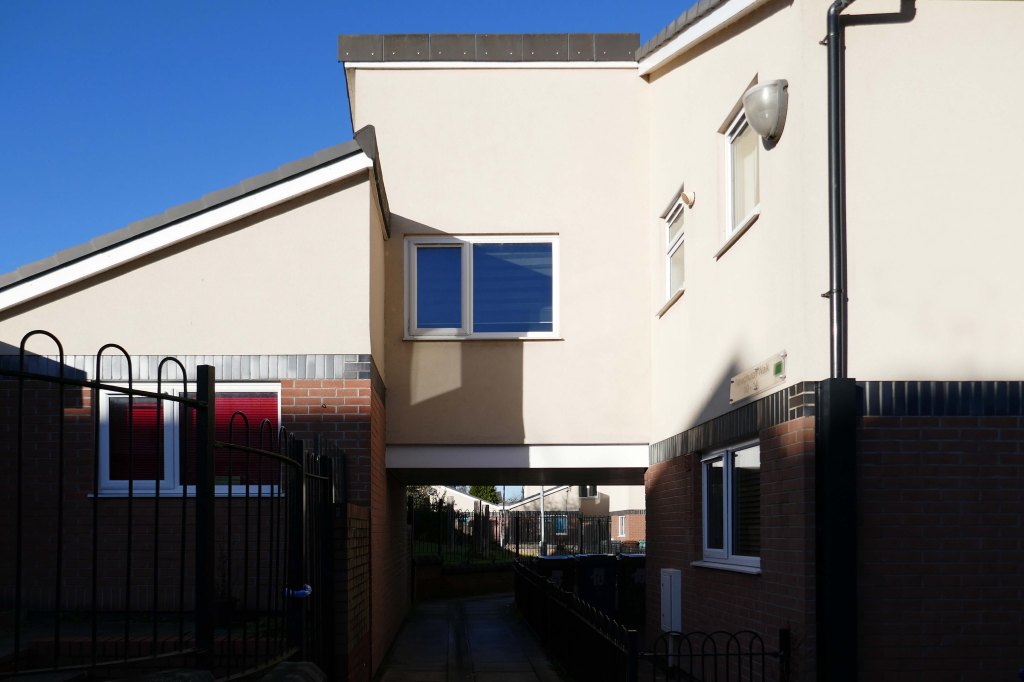
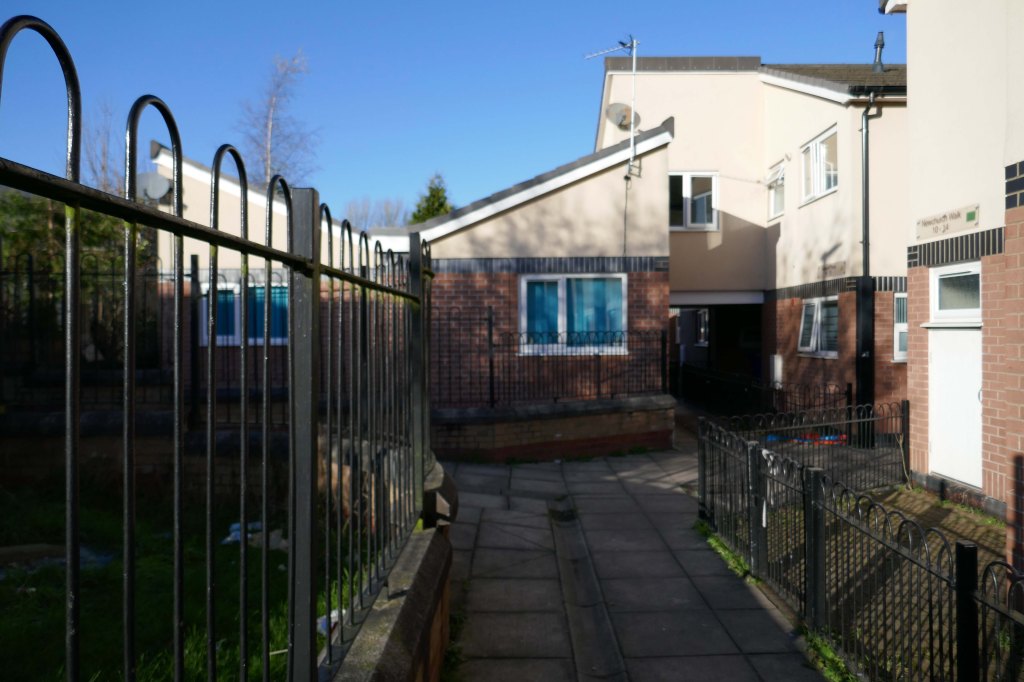
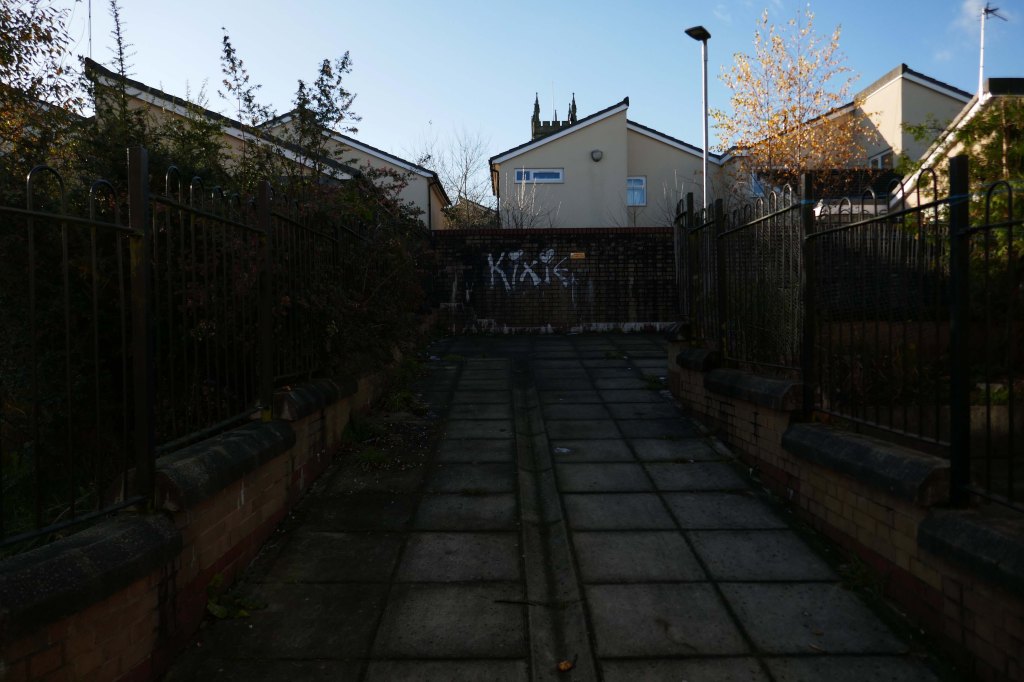
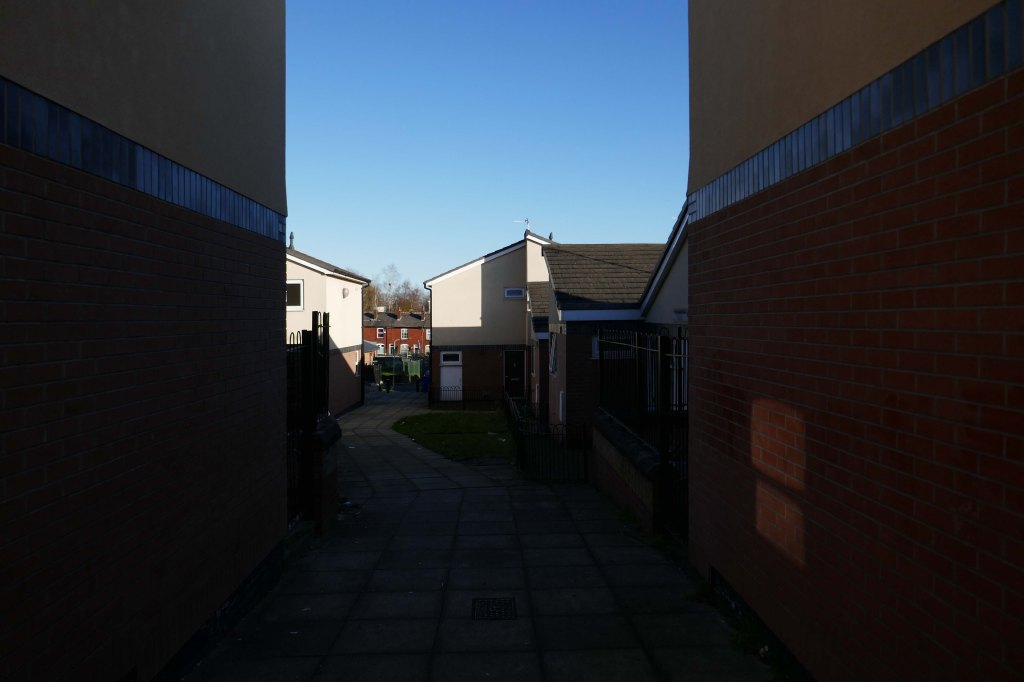
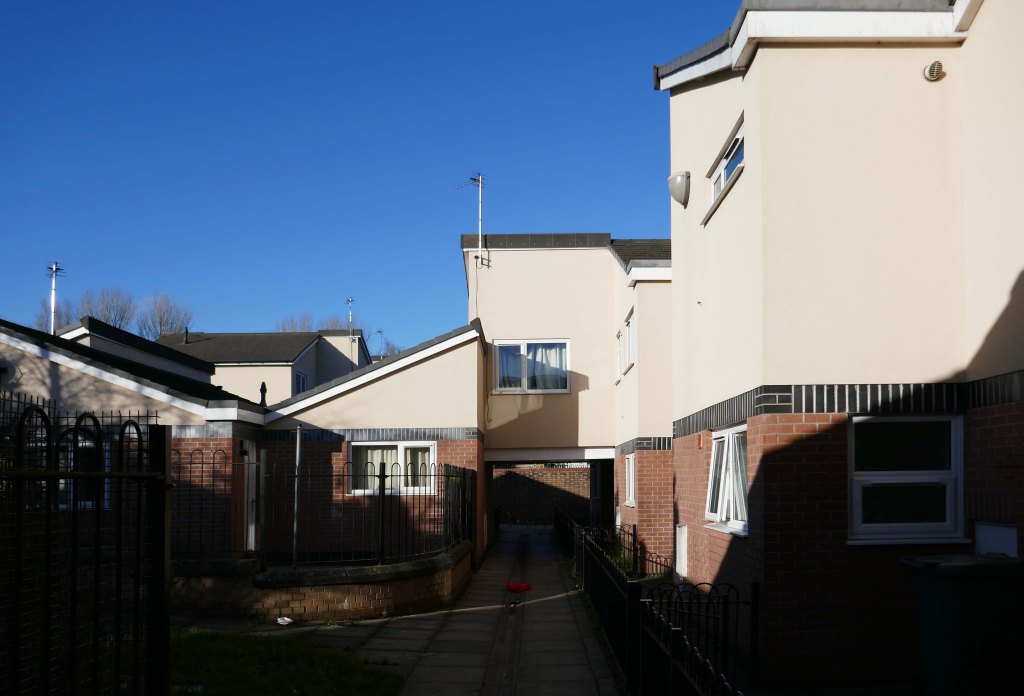
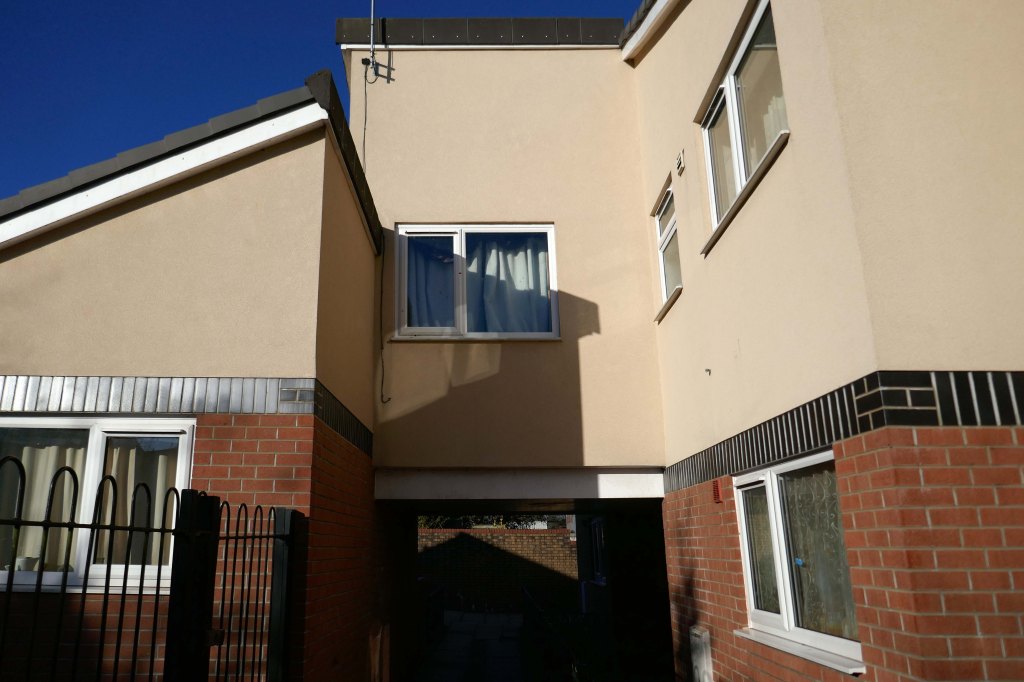
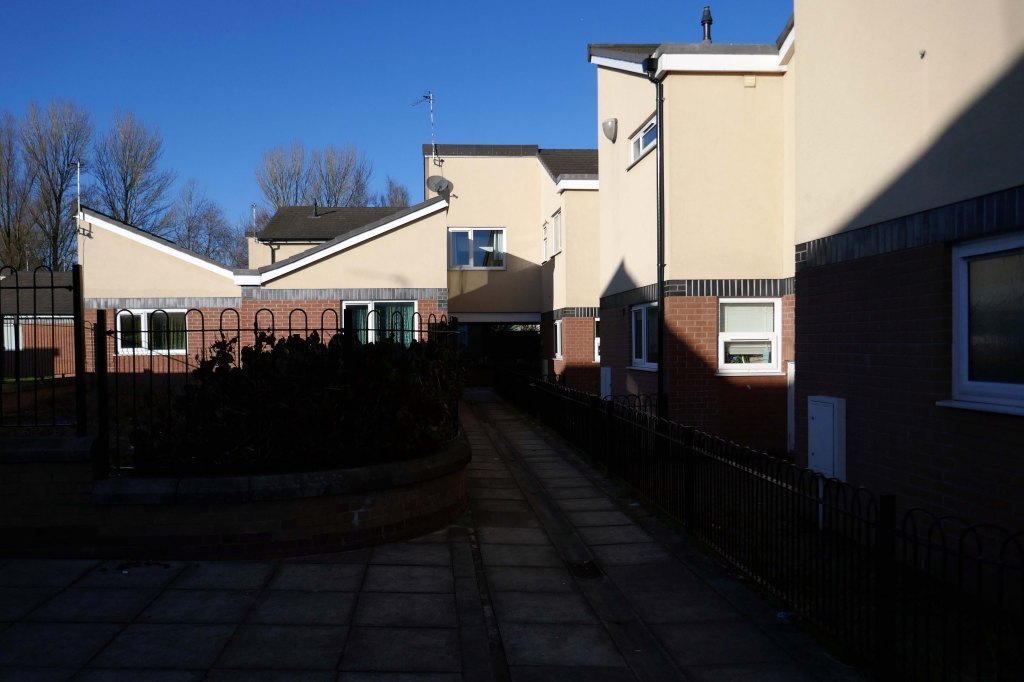
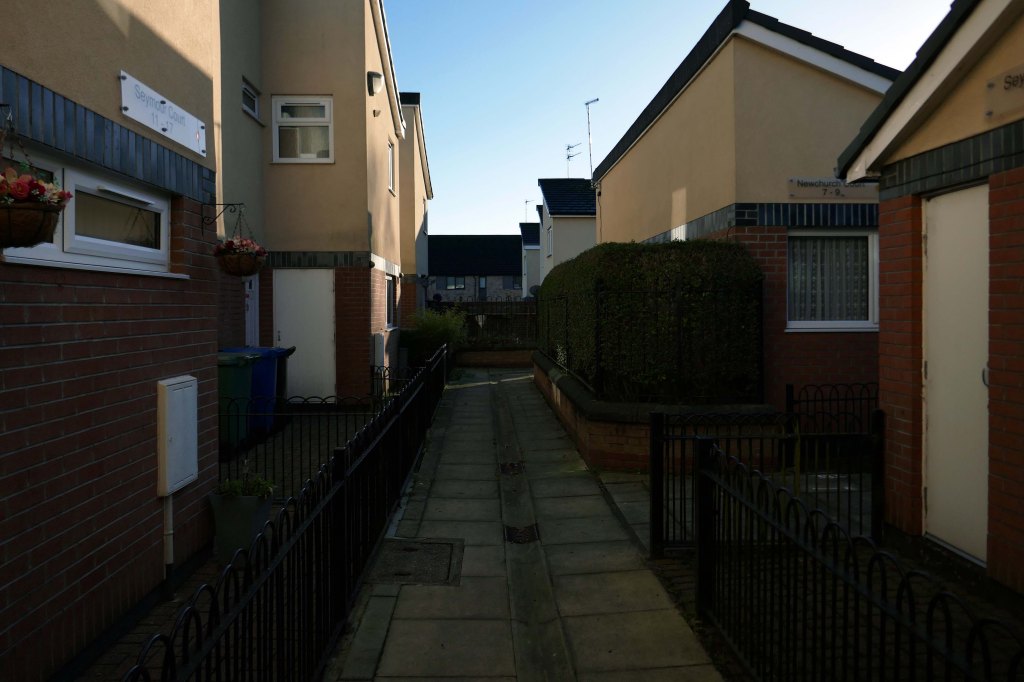
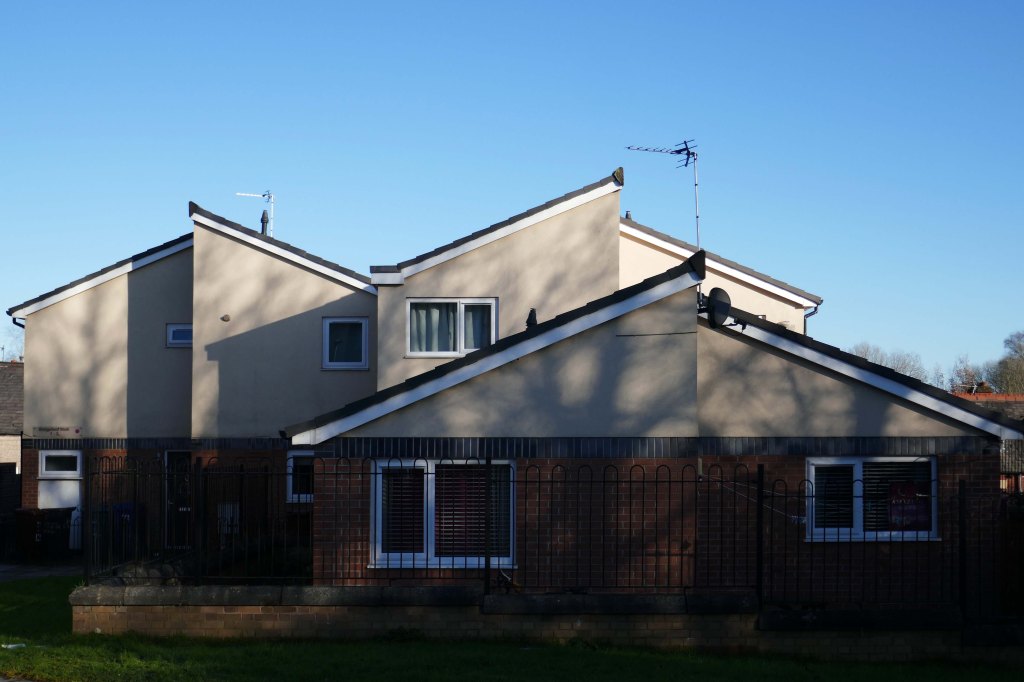
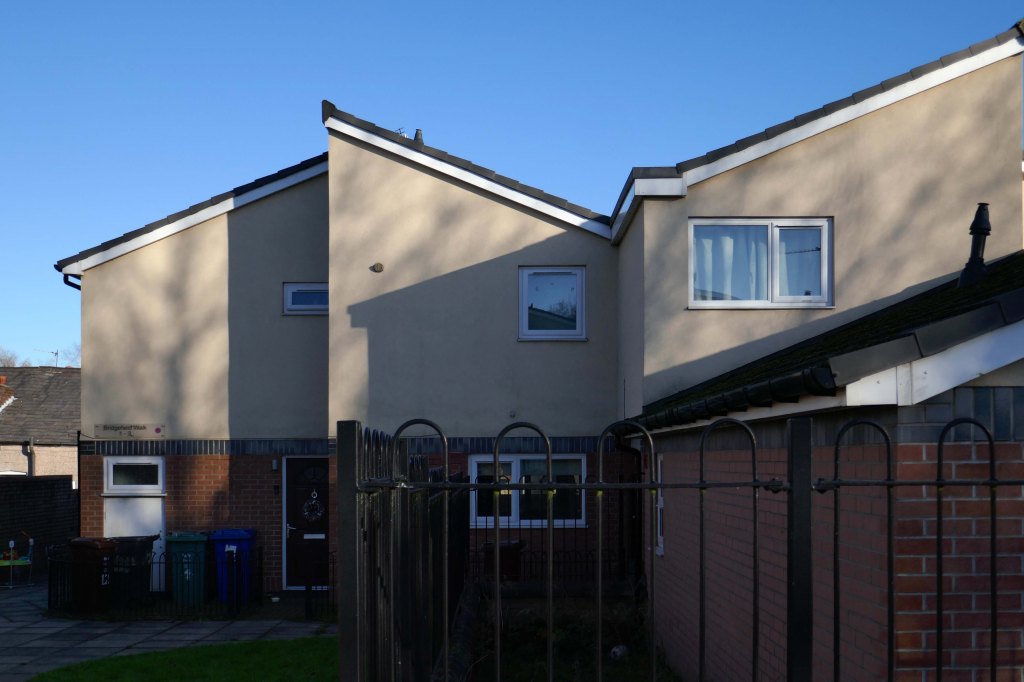
New-towny, dense low-rise housing irregularly grouped around and over pedestrian access paths.
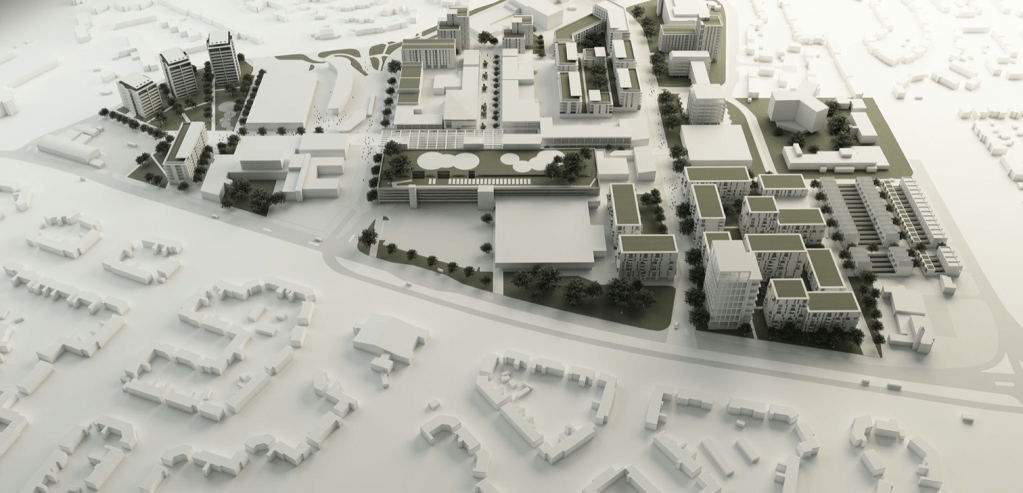
The 2003 masterplan recommence its removal.
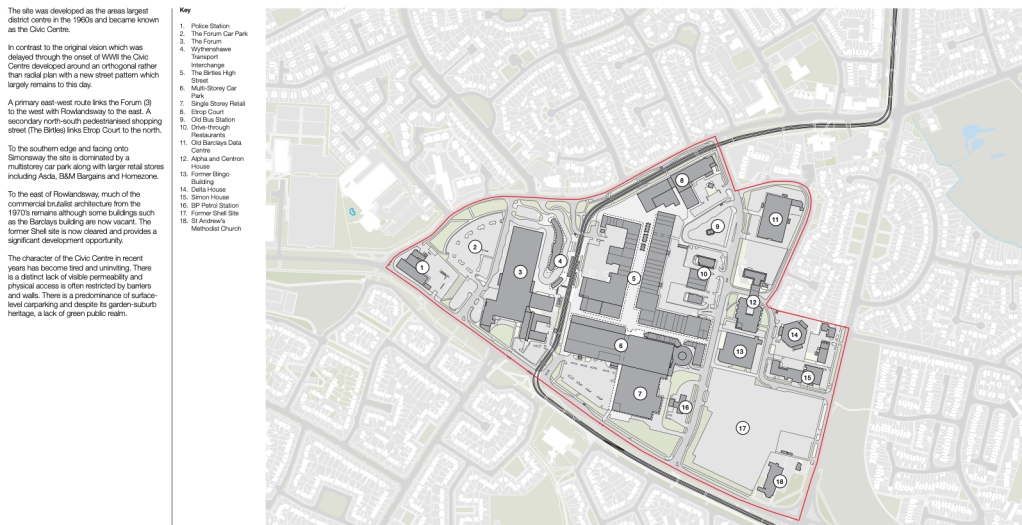
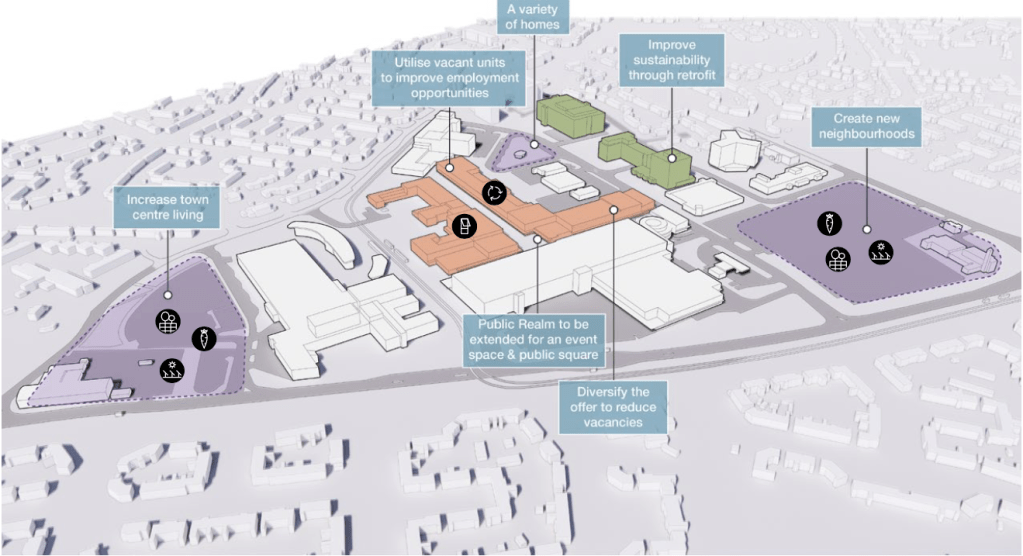
The masterplan states that Radcliffe has many unattractive buildings and few architectural assets. But this could work to its advantage as a lack of protected or noteworthy buildings makes it easier to replace them with contemporary structures.
This could include demolishing the “unwelcoming” St Thomas Estate and replacing it with a mix of private and social housing on the old street layout. Existing tenants would be rehoused in the new houses so that the community would not be broken up.
JL Womersely famously Sheffield City Architect:
During his term, Sheffield’s housing grew upwards with multi-storey flats constructed at Low Edges, Park Hill, Hyde Park, Netherthorpe and Woodside. It was Womersley’s response to 13,000 families on the council’s waiting list and 10,000 condemned properties waiting to be demolished.
Wilson and Womersley were responsible for the Hulme Crescents and Manchester Arndale.
In the space of a decade they shaped Manchester’s urban fabric, leaving a questionable legacy. The technical quality of their buildings was undoubtedly poor, but their qualities – bold forms, monolithic materiality and streets-in-the-sky – were of the moment, and captured a particular brand of urban renewal, imported from North America and inflected through British post-war planning.
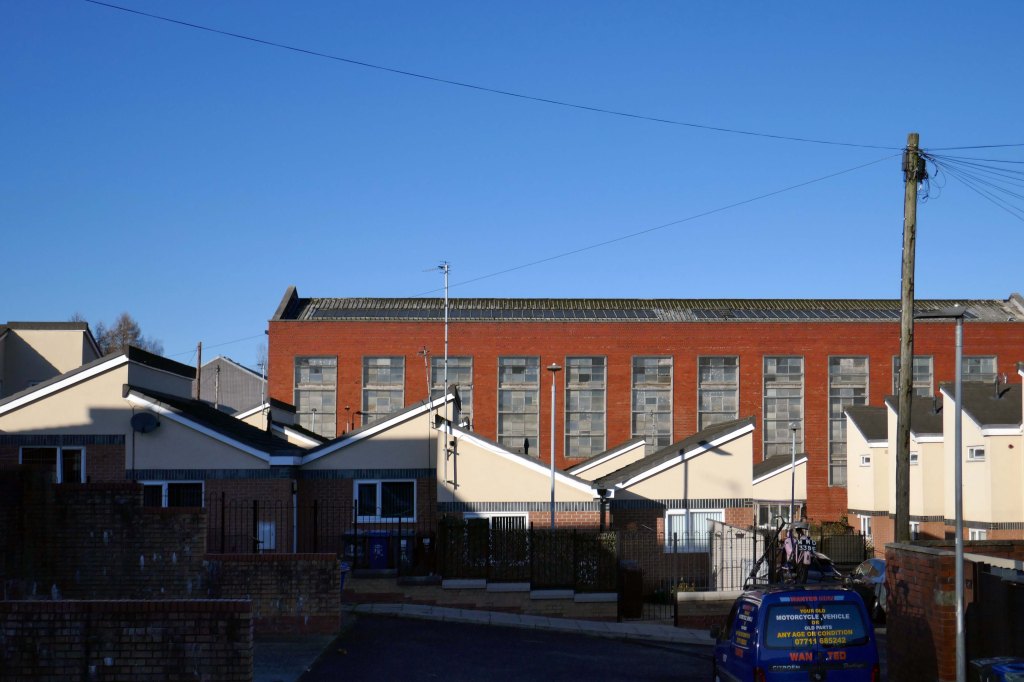
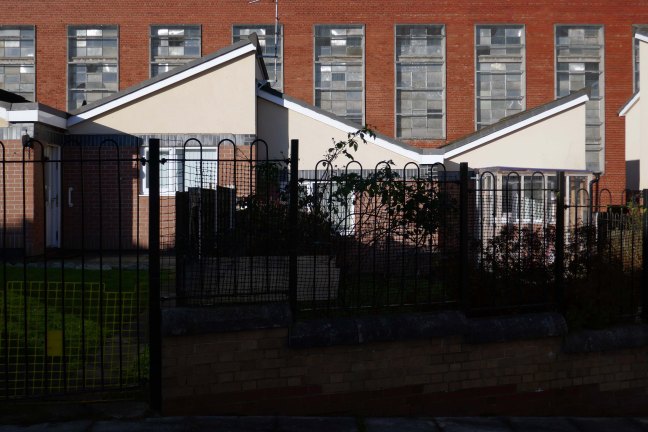
Social housing has been, and continues to be, a contentious arena. This seemingly well-constructed estate was once deemed unfit for habitation by its residents.
Tenants of the St Thomas’ Estate in the town centre allege they have been forgotten by Six Town Housing, which manages the properties.
Magda Csatlos, former chairman of the now disbanded Tenants and Residents Association said rotten bricks with visible gaps between them, badly-designed leaking roofs and damp and mouldy conditions plague many of the 90 homes.
Happily the Local Authority are able to remedy the problem.
After some residents on the estate, who were visited by Bury South MP Ivan Lewis, called for the properties to be “condemned”, the Council agreed to invest £2 million to bring the homes up to standard.
A total of 90 social housing properties on St Thomas Estate have been provided with new external rendering, roofing, windows, doors, insulation and brick cladding.
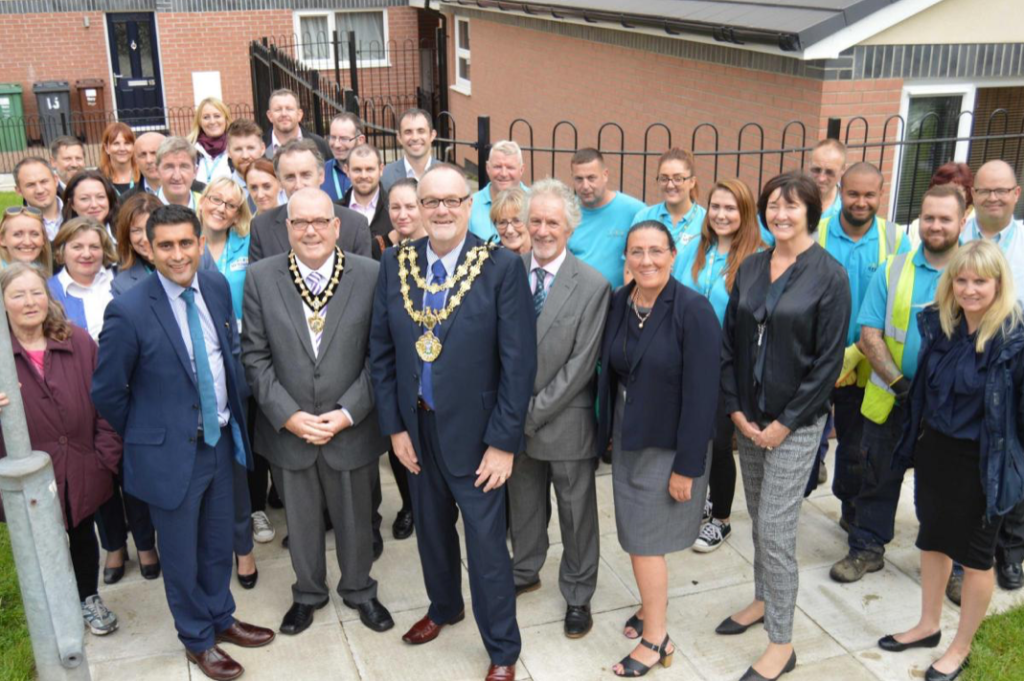

On the day of my visit the long term tenants with whom I spoke were happily, happy with their homes.

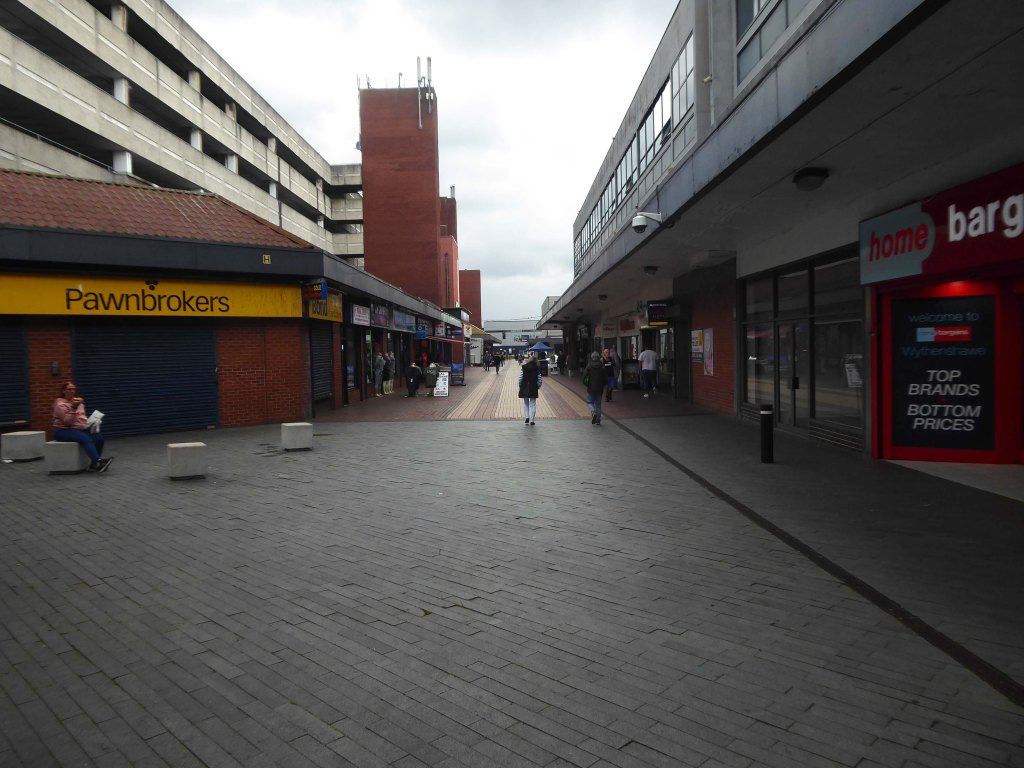
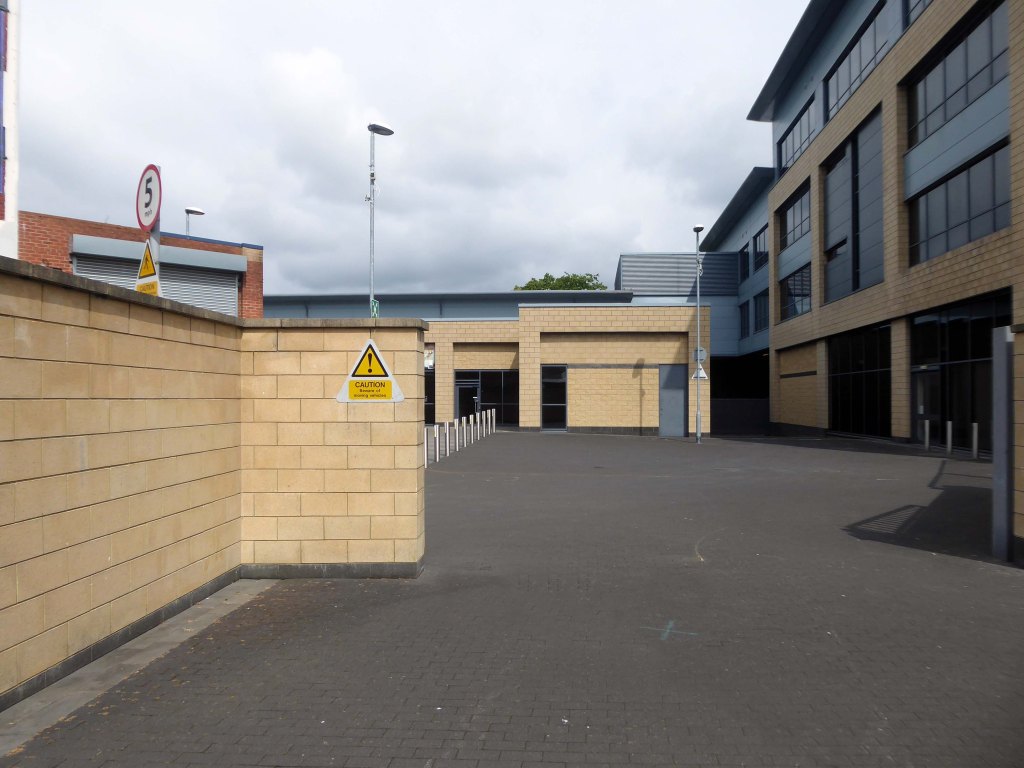
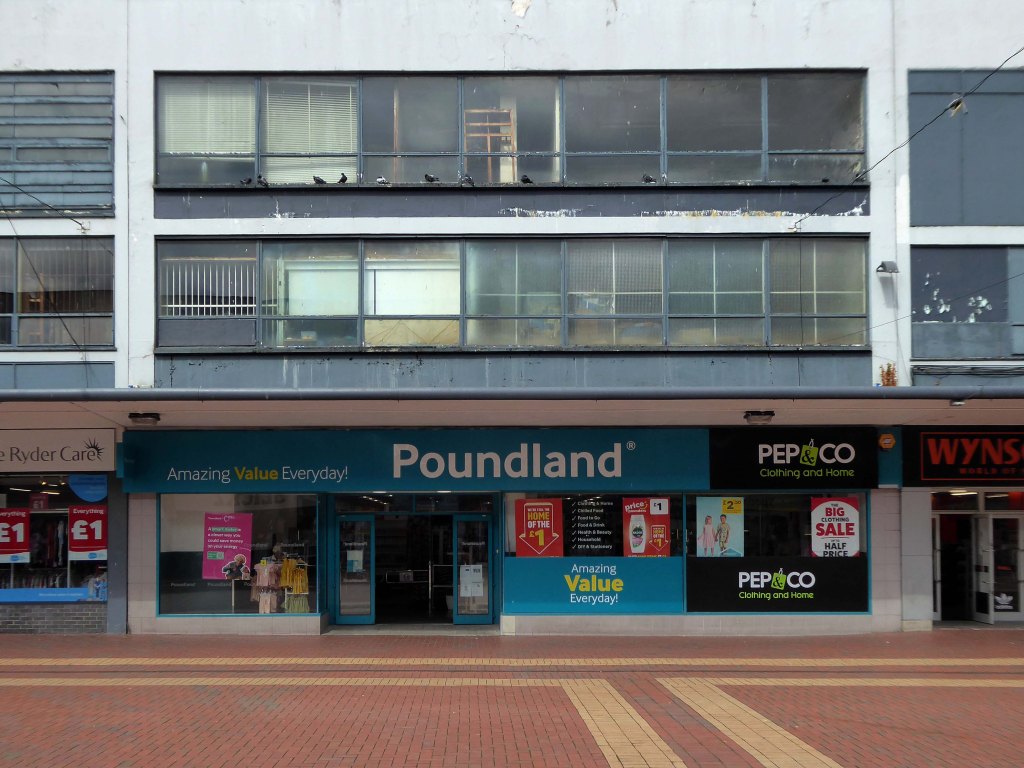
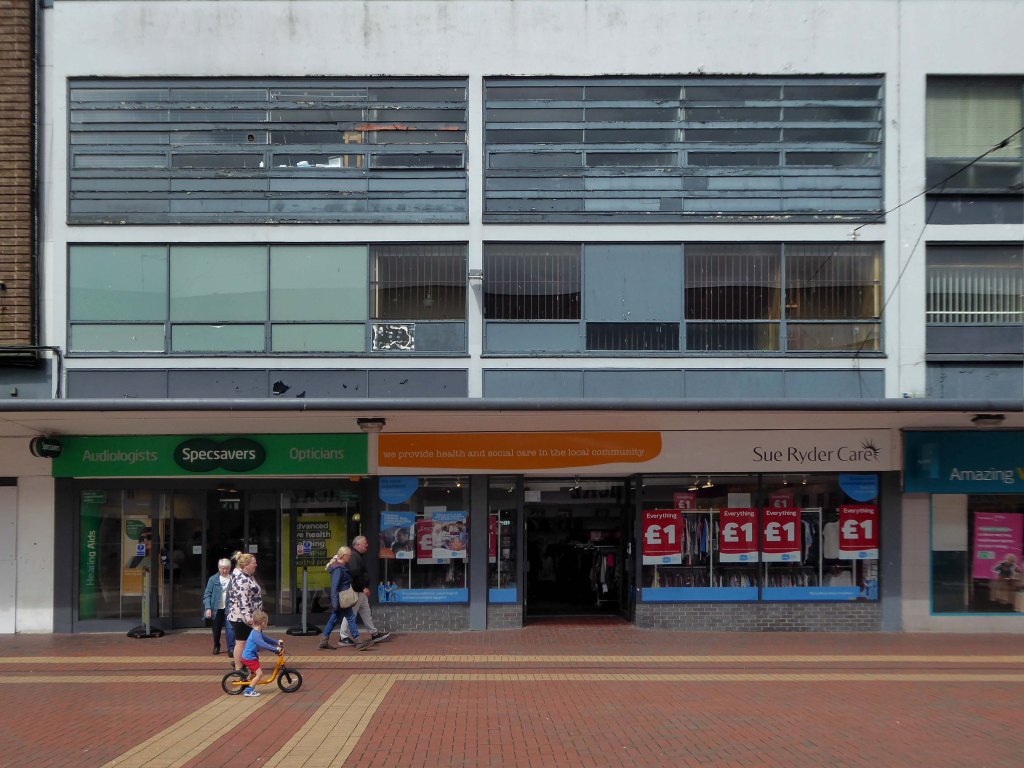
Here are some photographs, taken under the watchful golden eye of a low winter sun, hence the dramatic light and shade.