My baby takes the morning train
He works from nine till five and then
He takes another home again
To find me waitin’ for him
Sheena Easton
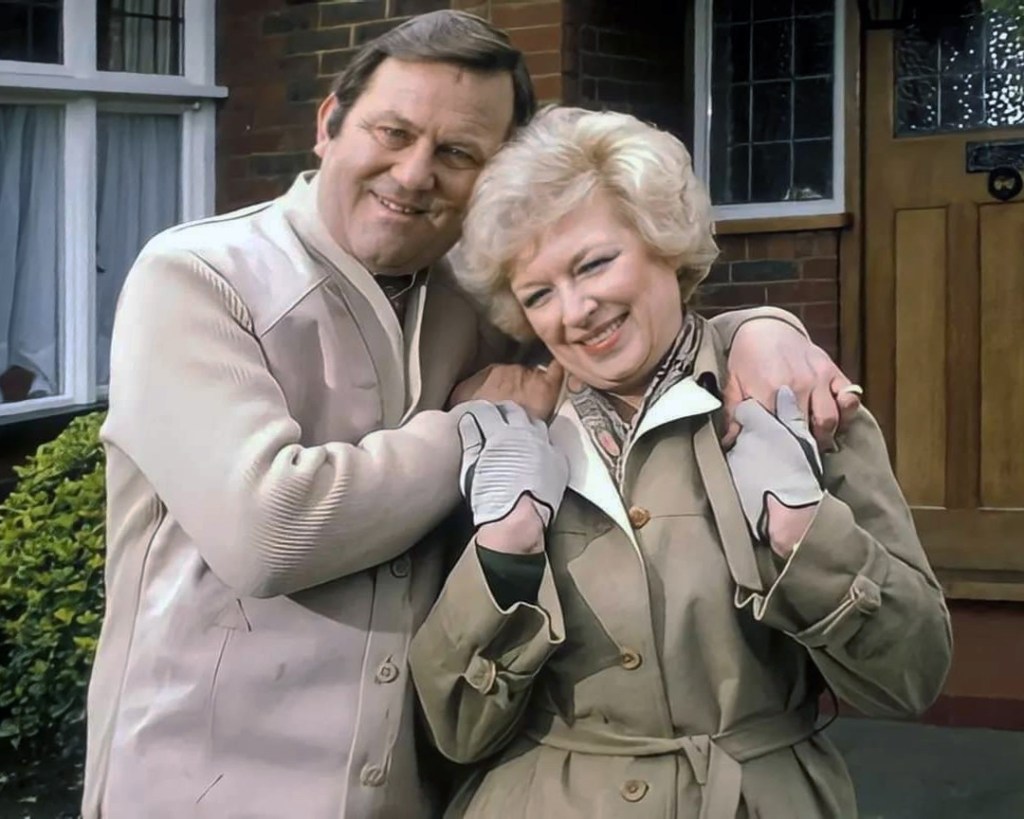
Welcome to the land of Terry and June – the seemingly complacent home to the newly aspirational classes, anathema to those thrill seeking Modernists, embracing the dynamism of the city, or those Ruralists protecting the integrity of the countryside.
Tradition has broken down. Taste is utterly debased, the town, long since degraded, is now being annihilated by a flabby, shoddy, romantic nature worship. That romantic nature worship is destroying also the object of its adoration, the countryside.
Thomas Sharp – Town Planner

Welcome to the land of the Lucie Attwell Bicky House biscuit tin money box.
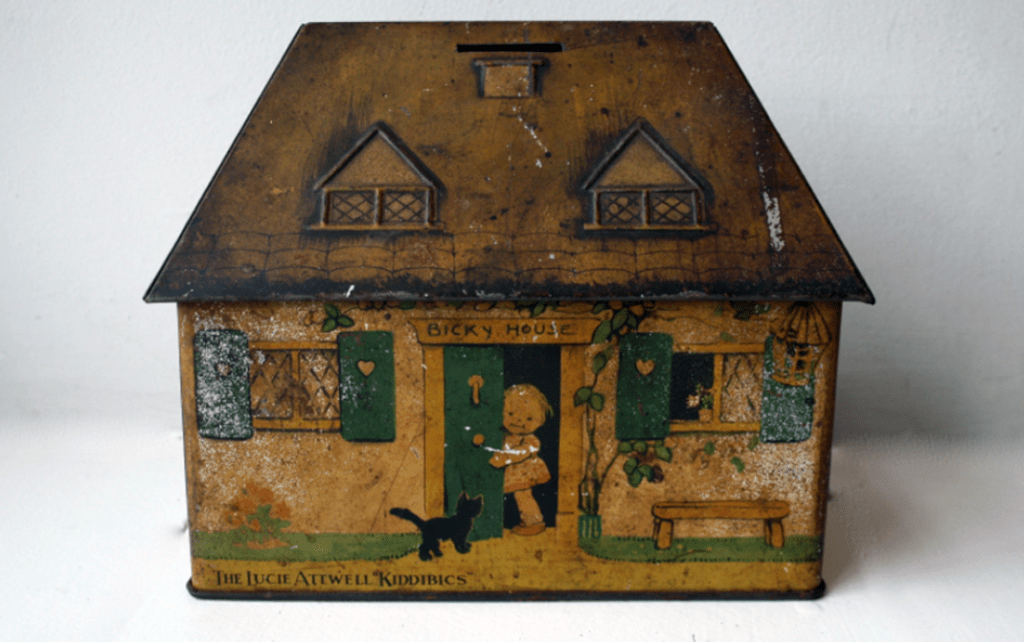

The perfect model home for the modern model family.

In Coming up for Air, George Orwell describes a suburban road as:
A prison with cells in a row. A line of semi-detached torture chambers.
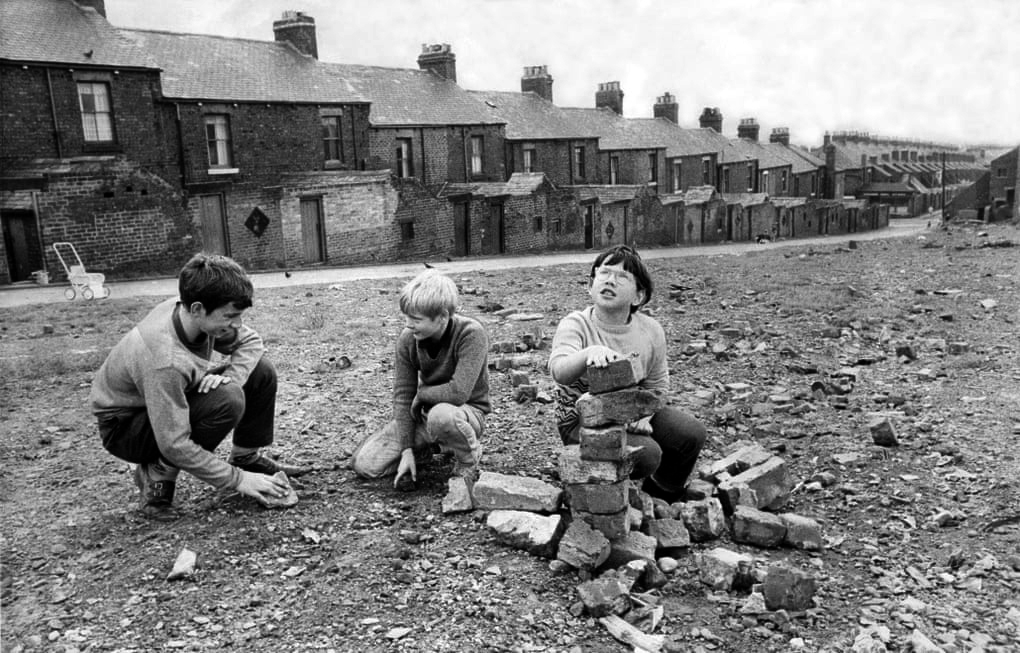
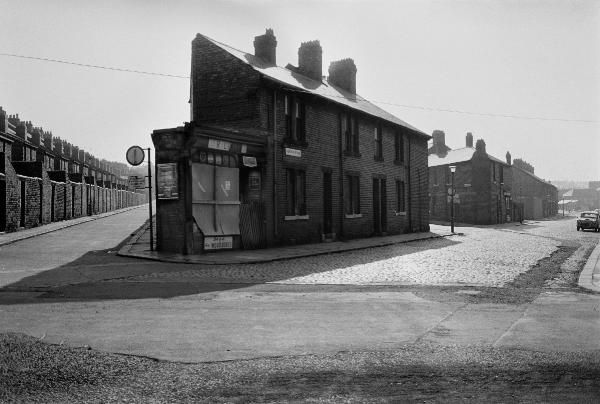
The growth of British towns and cities, from the onset of the Industrial Revolution, created a demand for new homes, the earliest developments were close to the centres of production and administration. Followed by the creation of outlying estates for the fleeing middle classes, as the smoke began to billow and the trains and buses began to run.
Originally the work of speculative private enterprise, followed by homes built by the local authority along with charitable institutions.
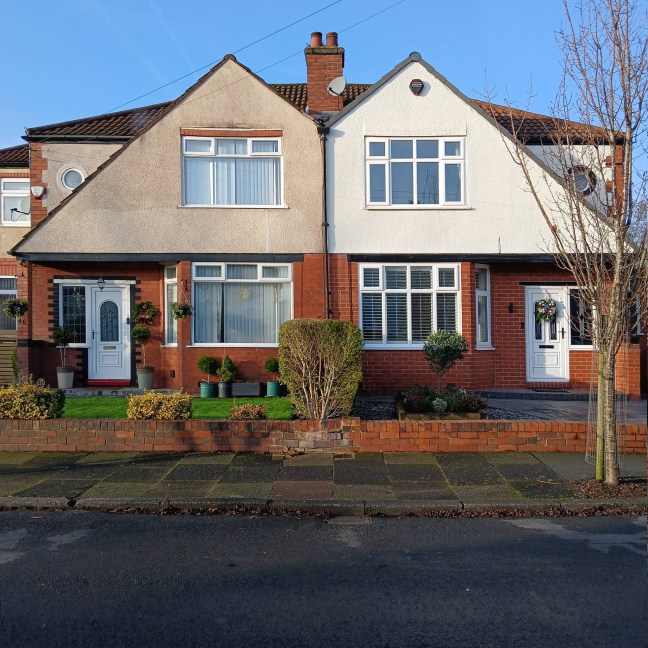
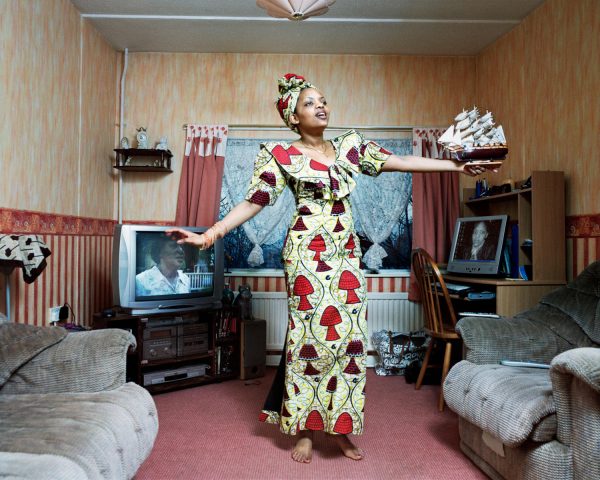
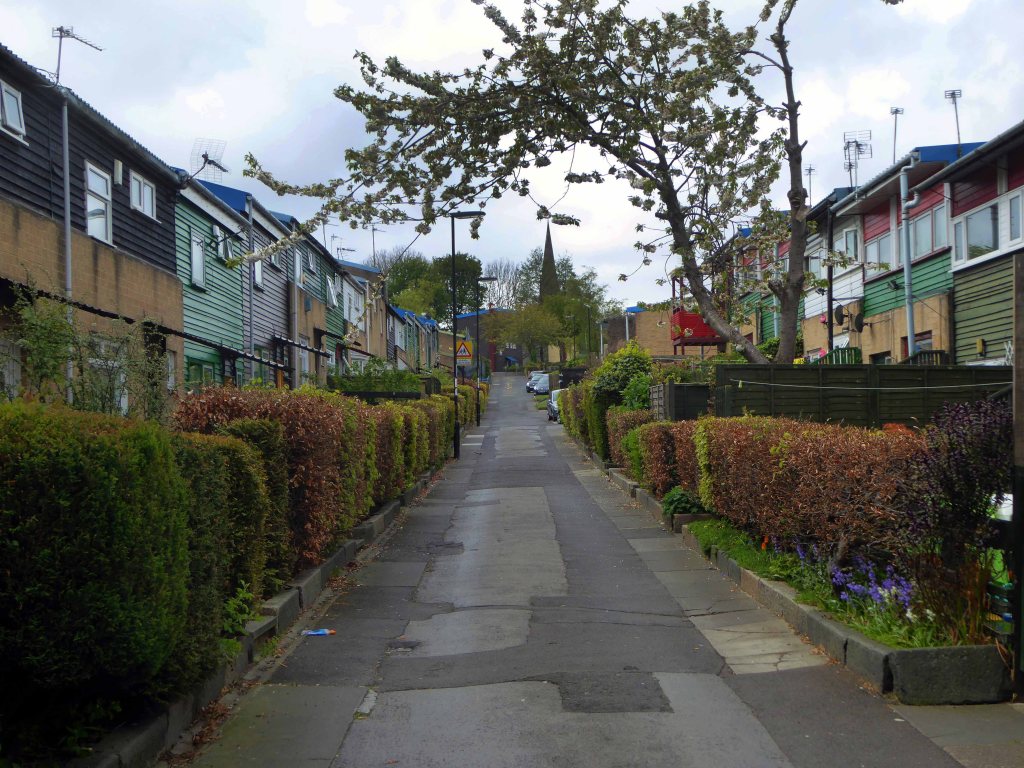
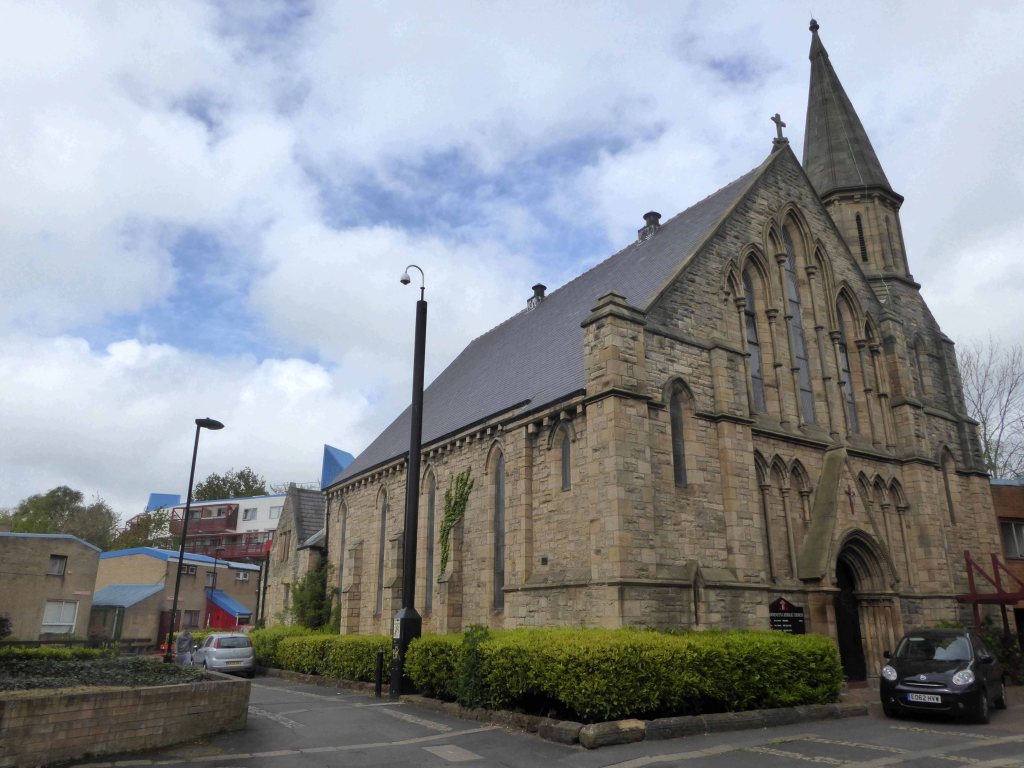
My own experience has taught me that Suburbia is architecturally diverse, socially less so, as various areas are segregated by class, and perhaps less so by ethnicity and/or culture.
The majority of the population live in Suburbia it seems, there now follows a selection of the suburban sites which I have visited in the last ten years or so.
In search of Suburbia.
There are areas of Victorian terraced housing Manchester which survived clearance – such as Jetson Street in Abbey Hey.

Many early estates of the early Twentieth Century where heavily influenced by the Garden City Movement , exemplified by the Burnage Garden Village.

And similar in design Ford Lane Didsbury.

By 1931 1.1 million council houses were built and 2.8 million privately owned homes.
Post WW2 the emphasis was on an expansion of social housing, along with a growth in privately owned property – detailed information and analysis of social housing can be found here at Municipal Dreams.
These homes were at times both temporary and of non-standard construction.
This prefabricated house was originally built for the good folk of Doncaster, later finding itself in Humberston Fitties
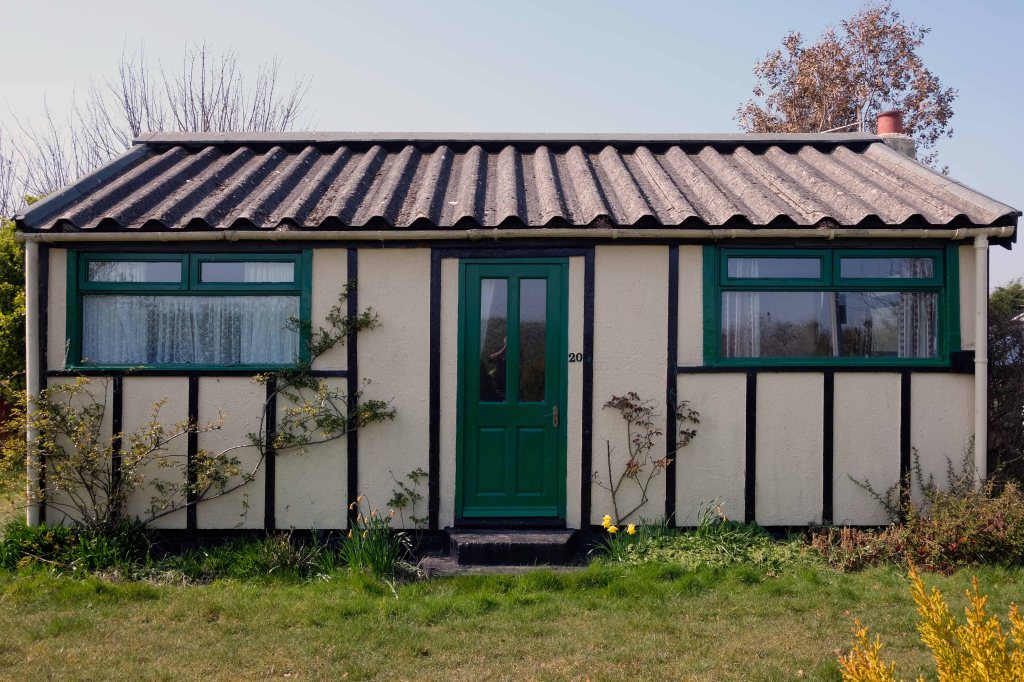

These Wythenshawe BISF Homes designed by Frederick Gibberd, the so-called Tin Town are still very much habitable homes.

Likewise these examples in Hebden Bridge.

The Pre-Fab Museum is a treasure trove of information, along with Non Standard House Construction.
Post war development was inextricably linked to the New Towns.
The new towns in the United Kingdom were planned under the powers of the New Towns Act 1946 and later acts to relocate people from poor or bombed-out housing following World War II. Designated new towns were placed under the supervision of a development corporation, and were developed in three waves. Later developments included the “expanded towns”: existing towns which were substantially expanded to accommodate what was called the “overspill” population from densely populated areas of deprivation.
One such New Town was Peterlee, in the north east of England, where I visited in 2021 and 2025.
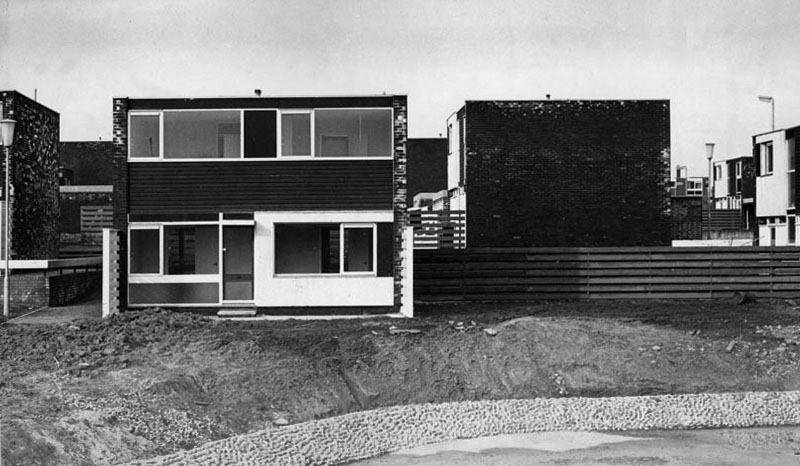

Along with Cumbernauld in Scotland.
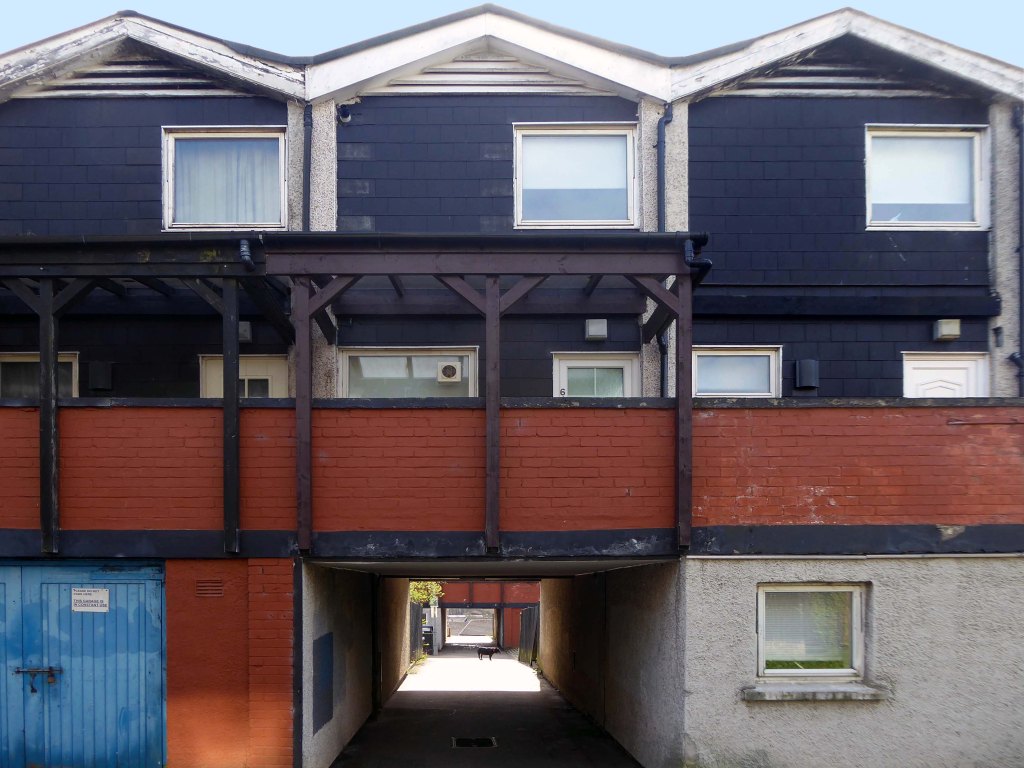

Cwmbran in south Wales.
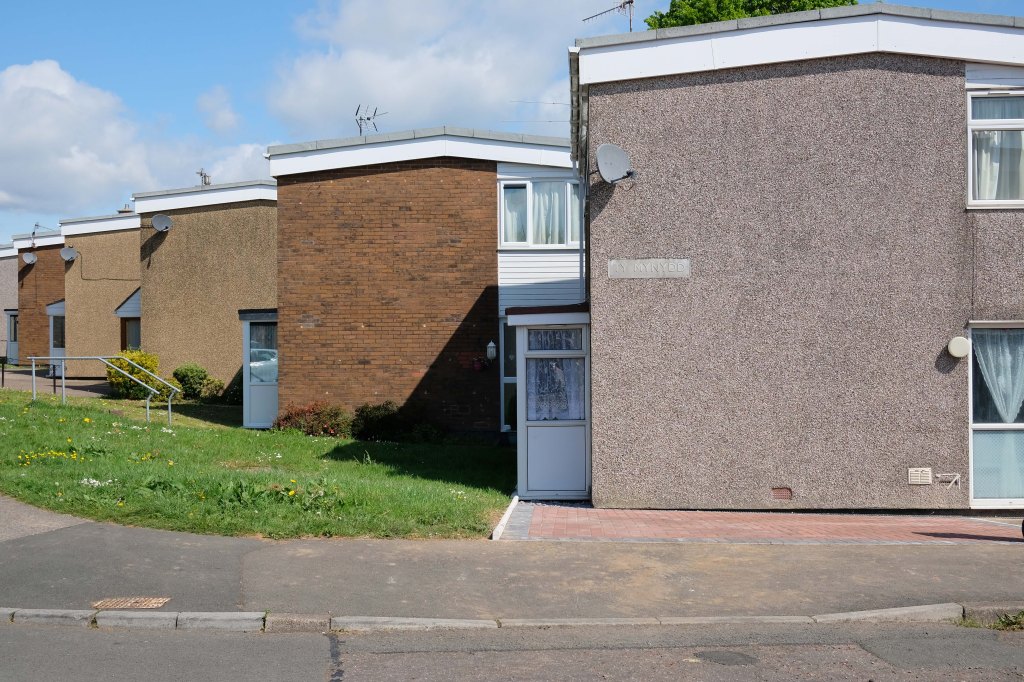

In addition there are examples of European influence in the design of inter and post WW2 housing.
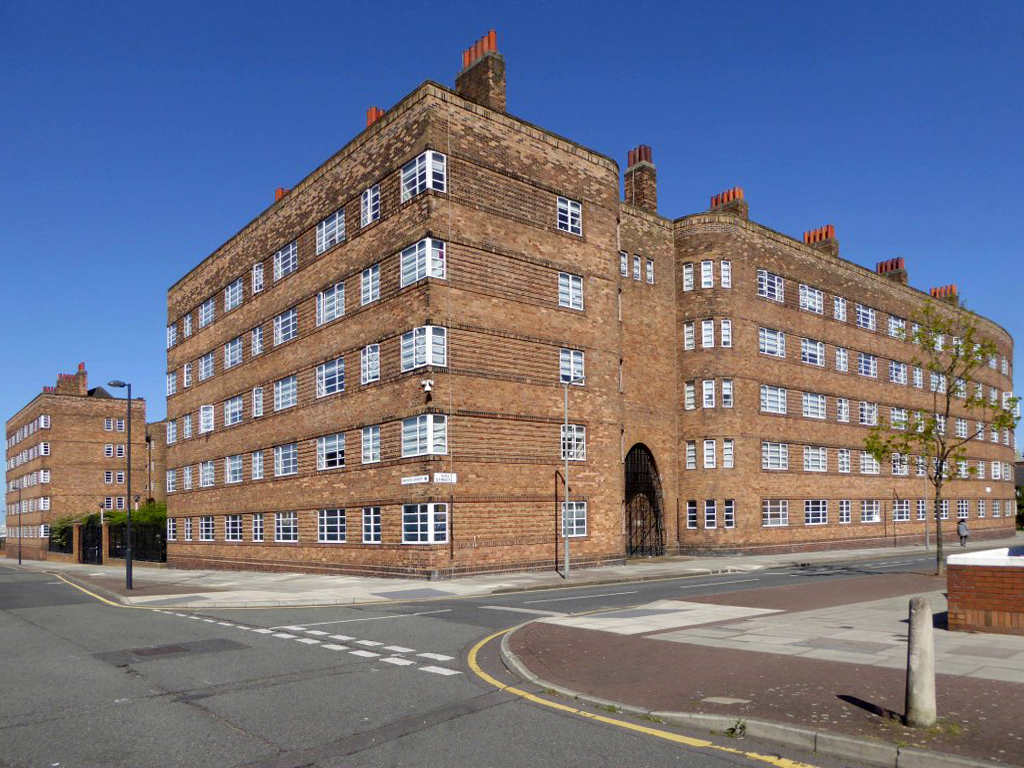
The Bull Ring Liverpool 1935.

Leo Fitzgerald House of 1940 in Dublin displays a similar European influence.
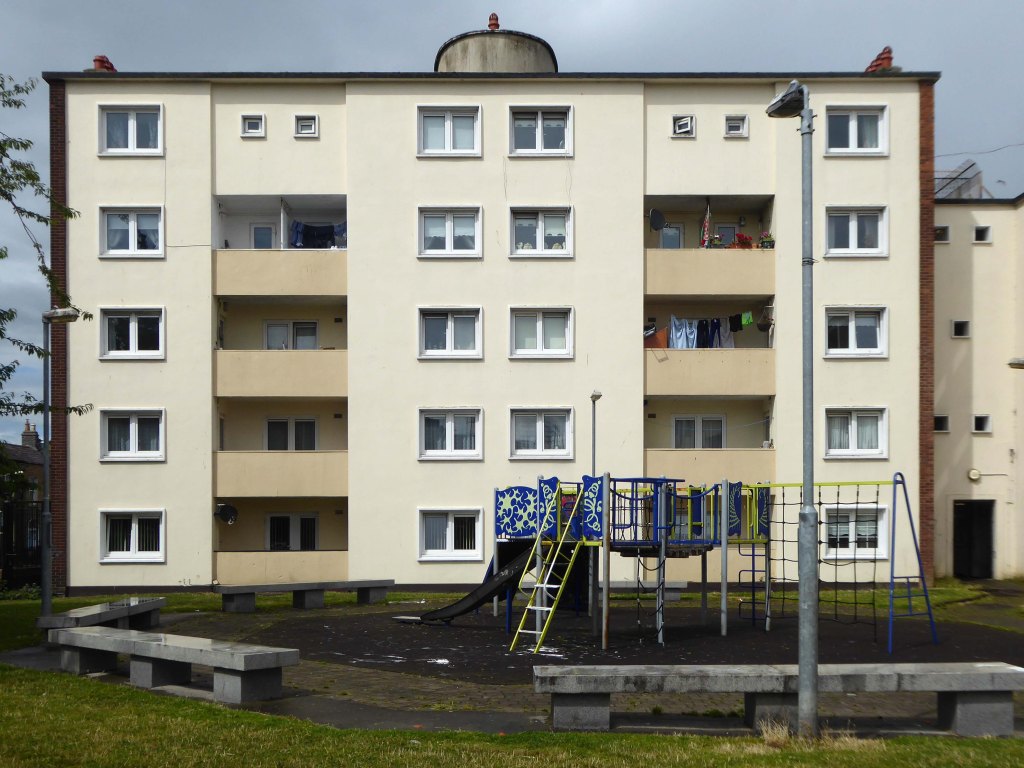

Corporation Street Flats Stafford 1951-52
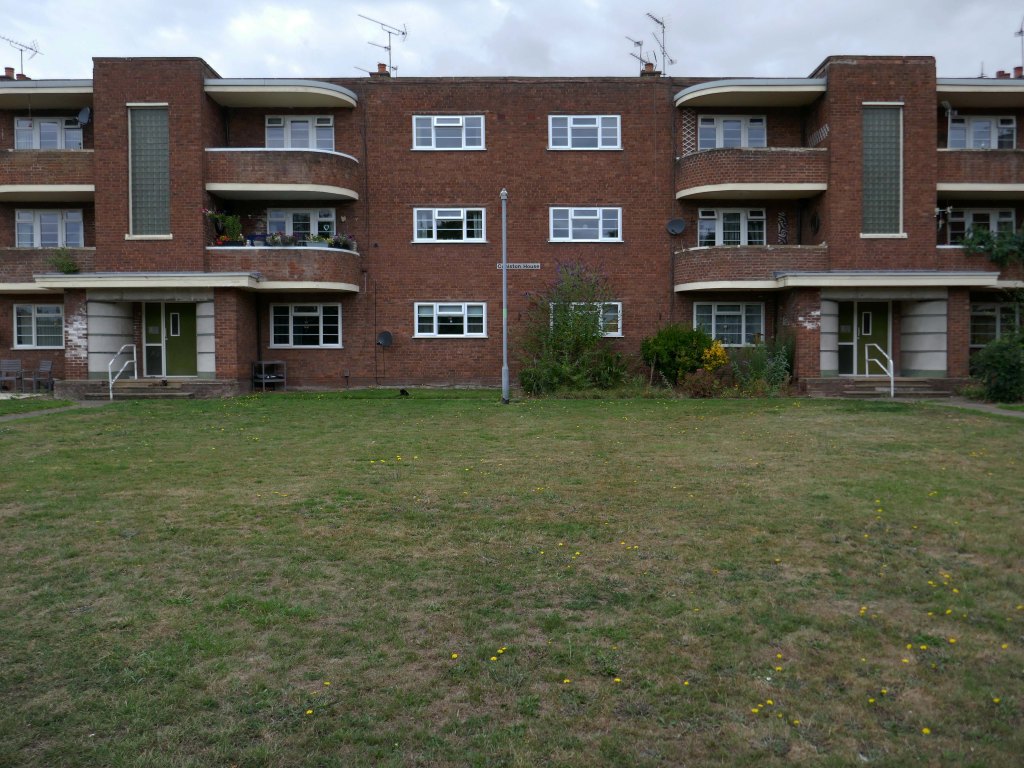

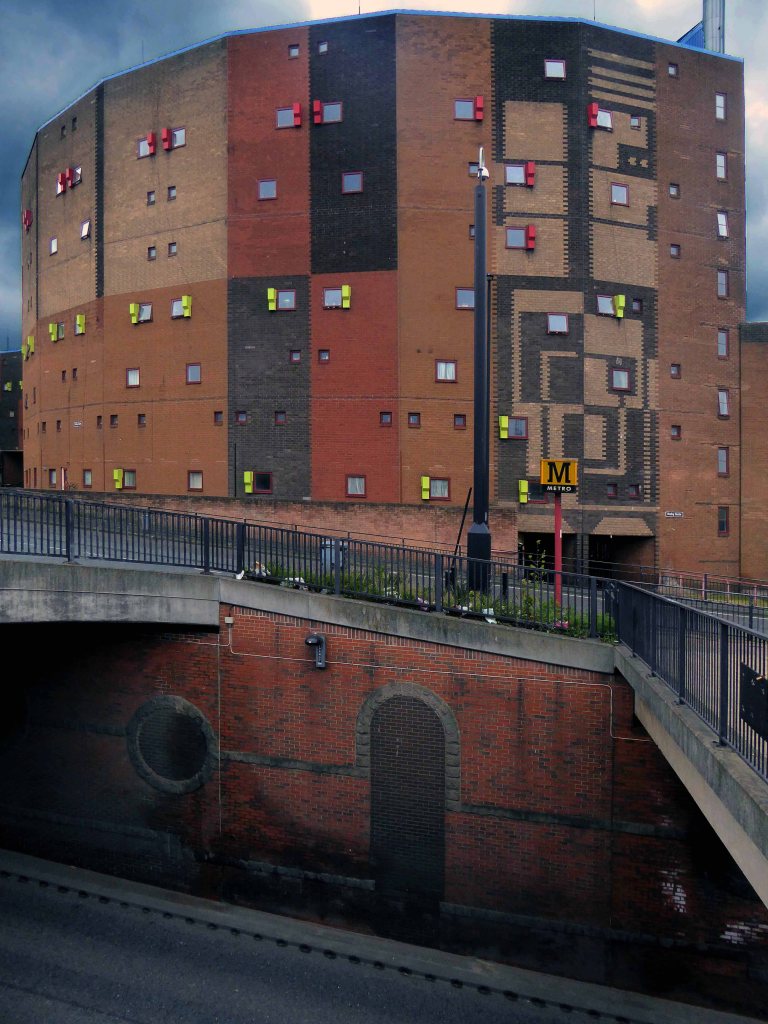
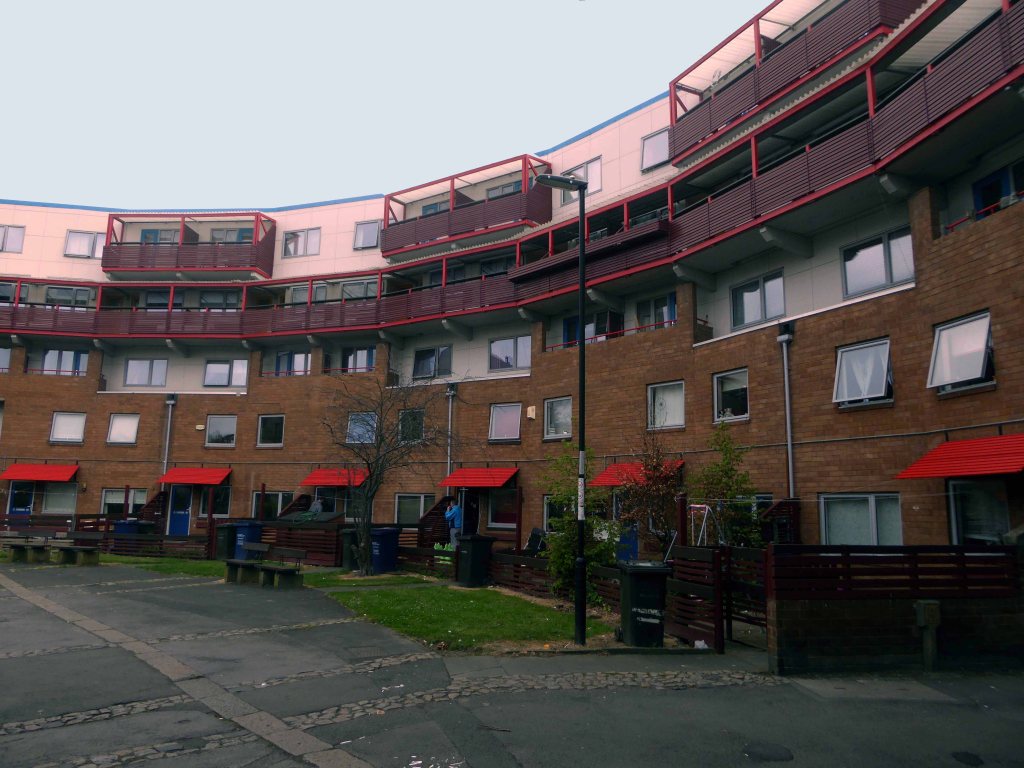
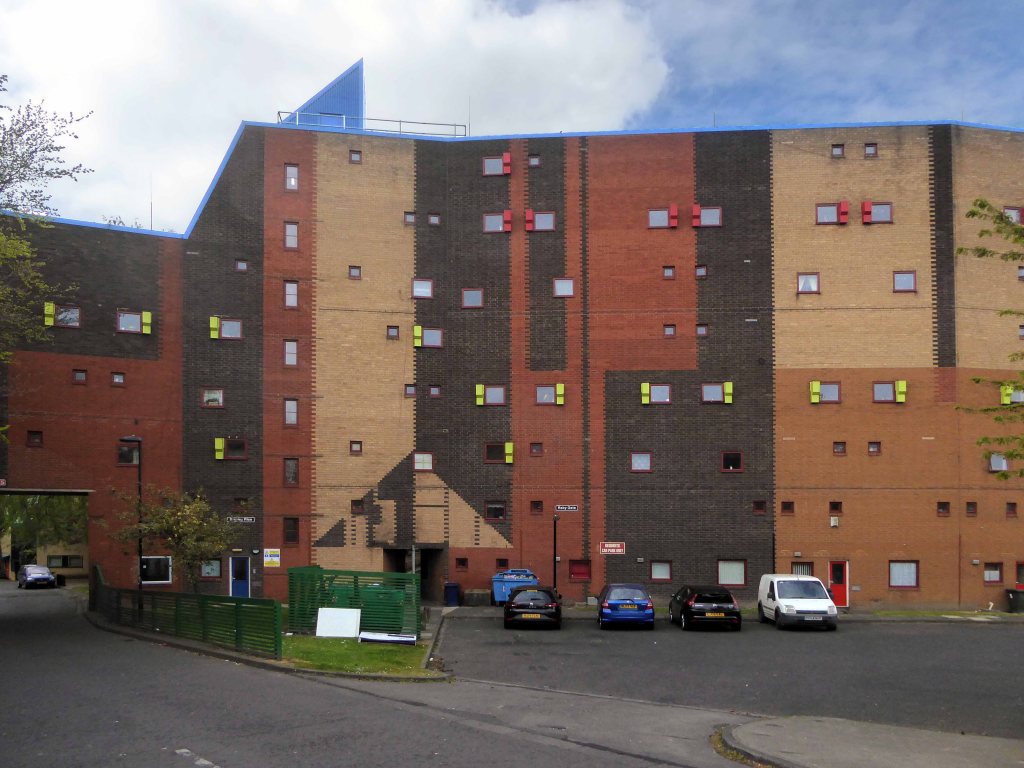
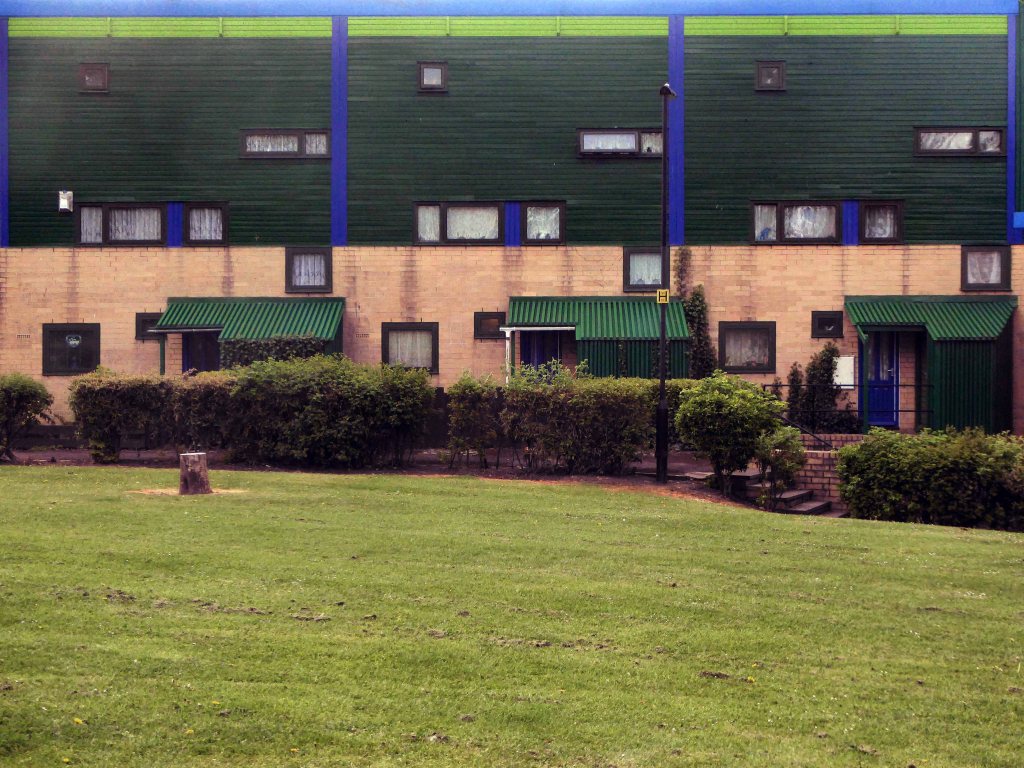
Later examples such as Fort Ardwick in Manchester proved to be badly built and ill advised choices for social housing.
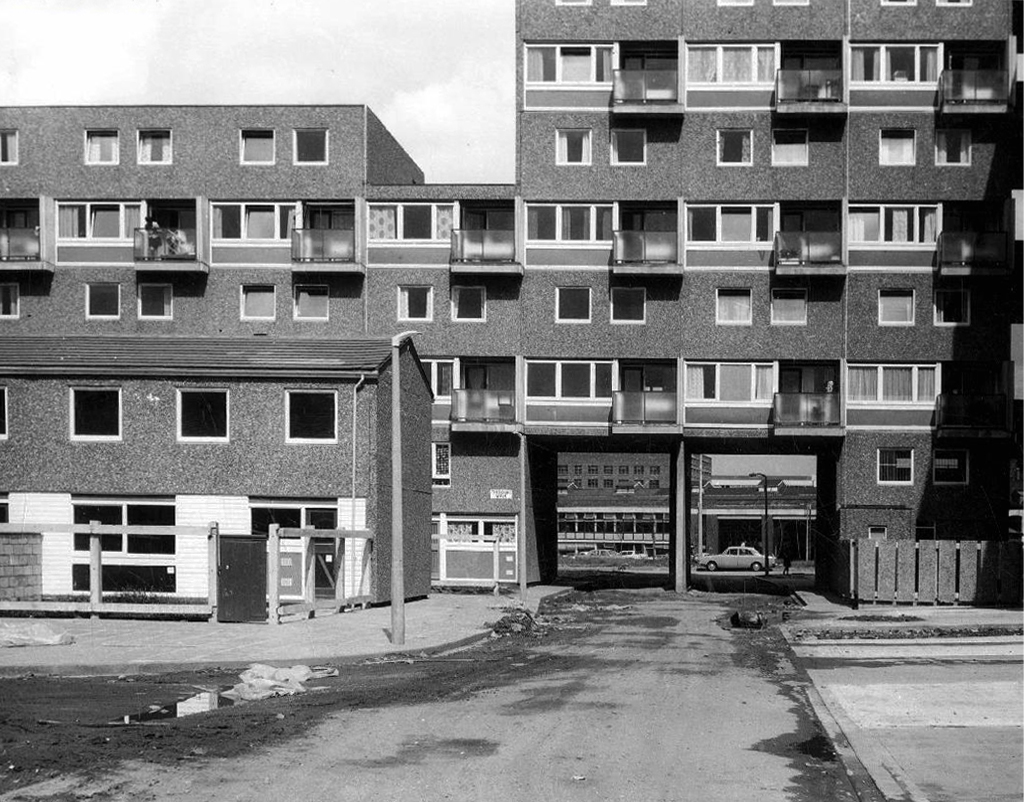

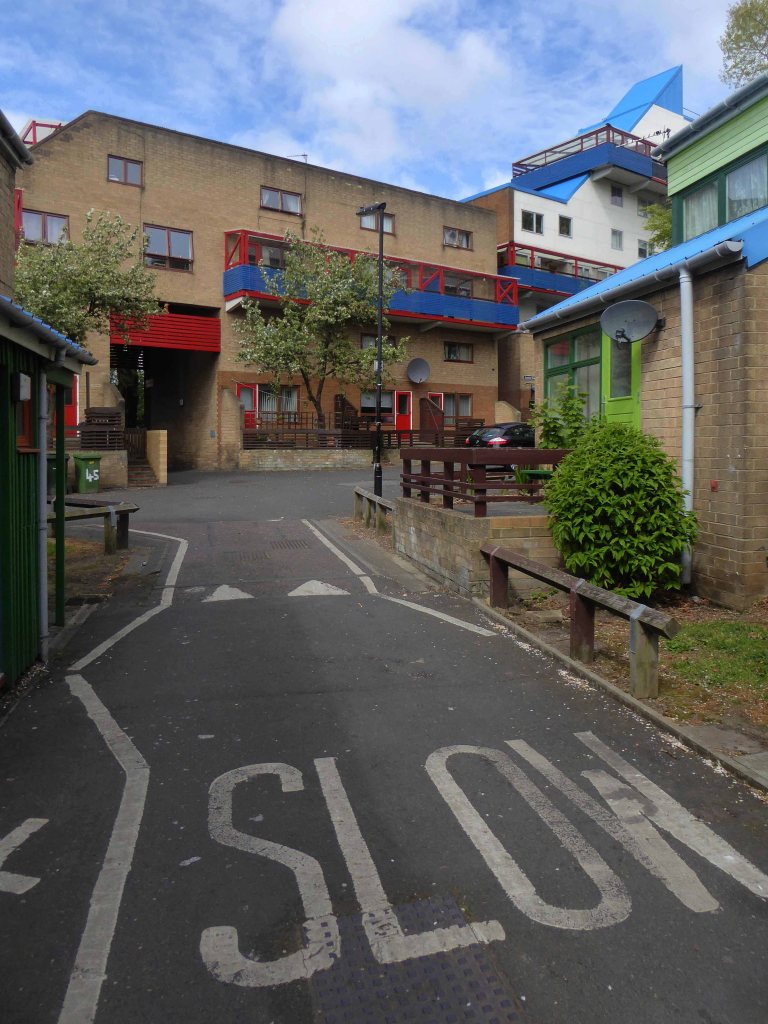
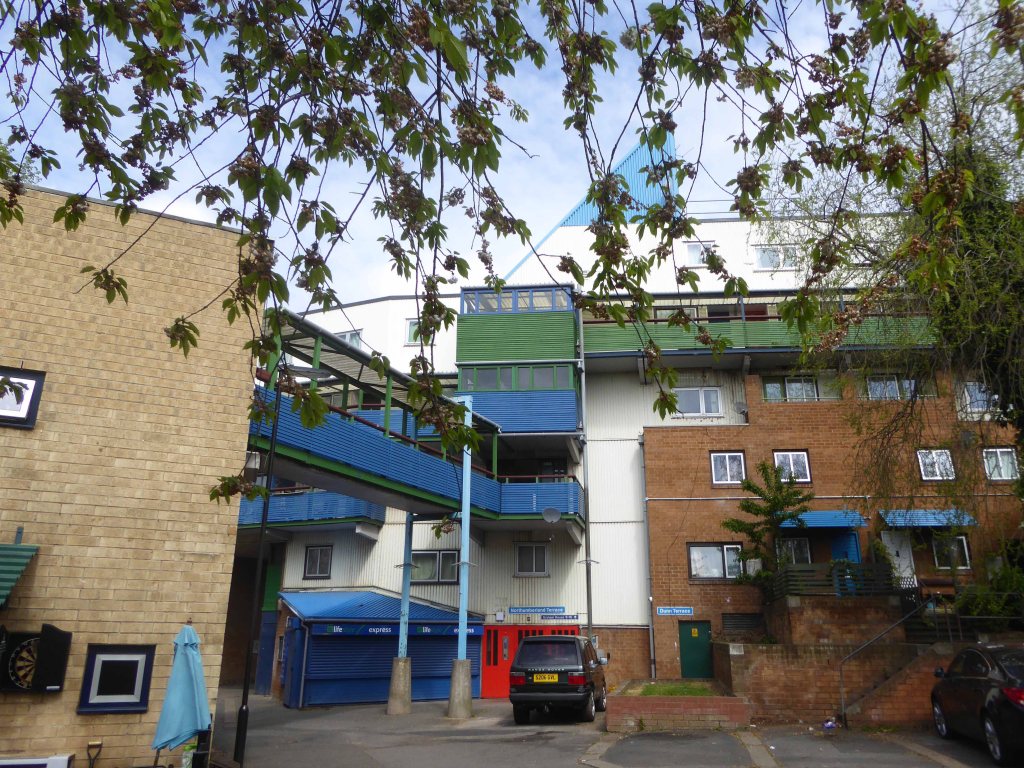
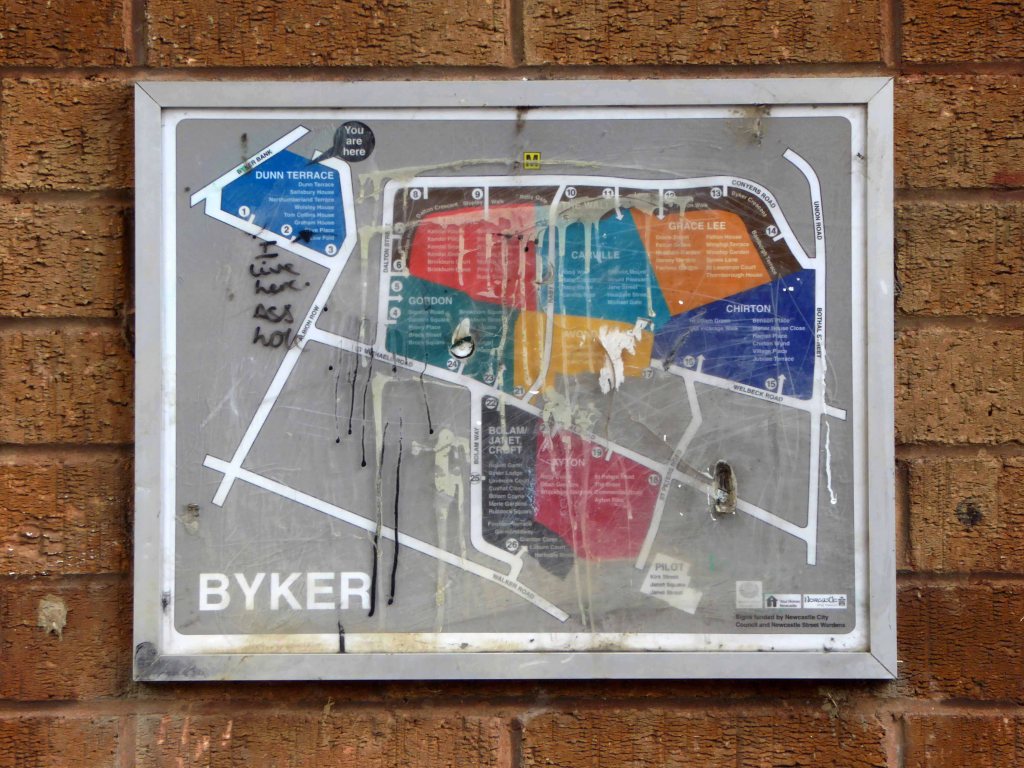
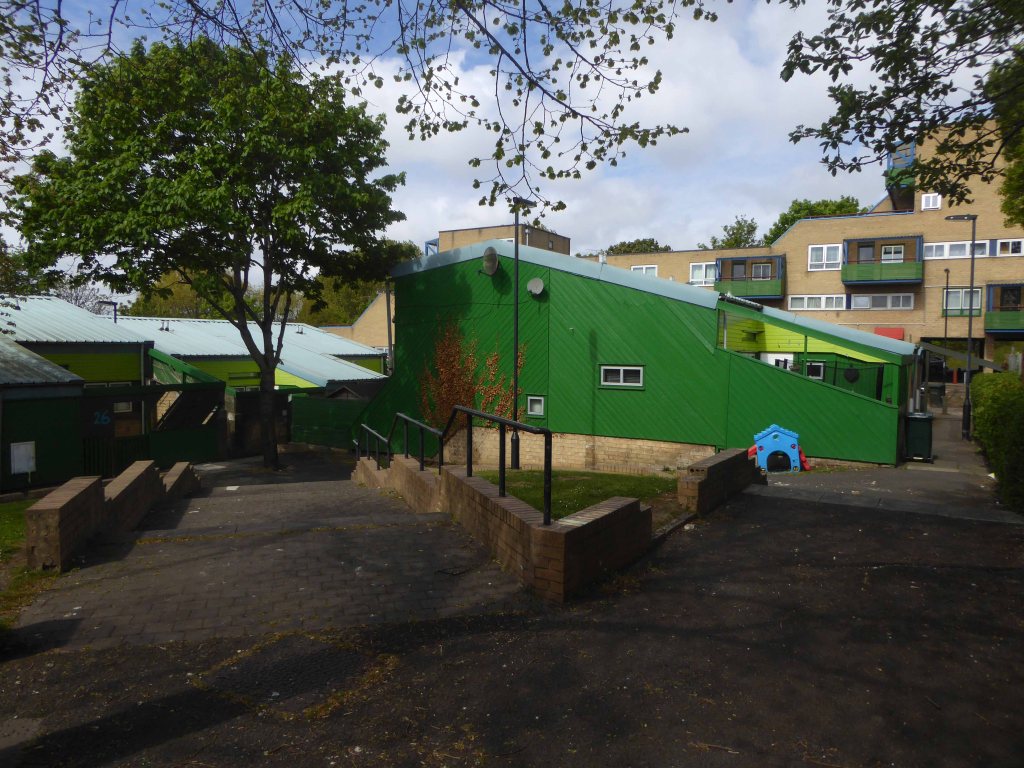
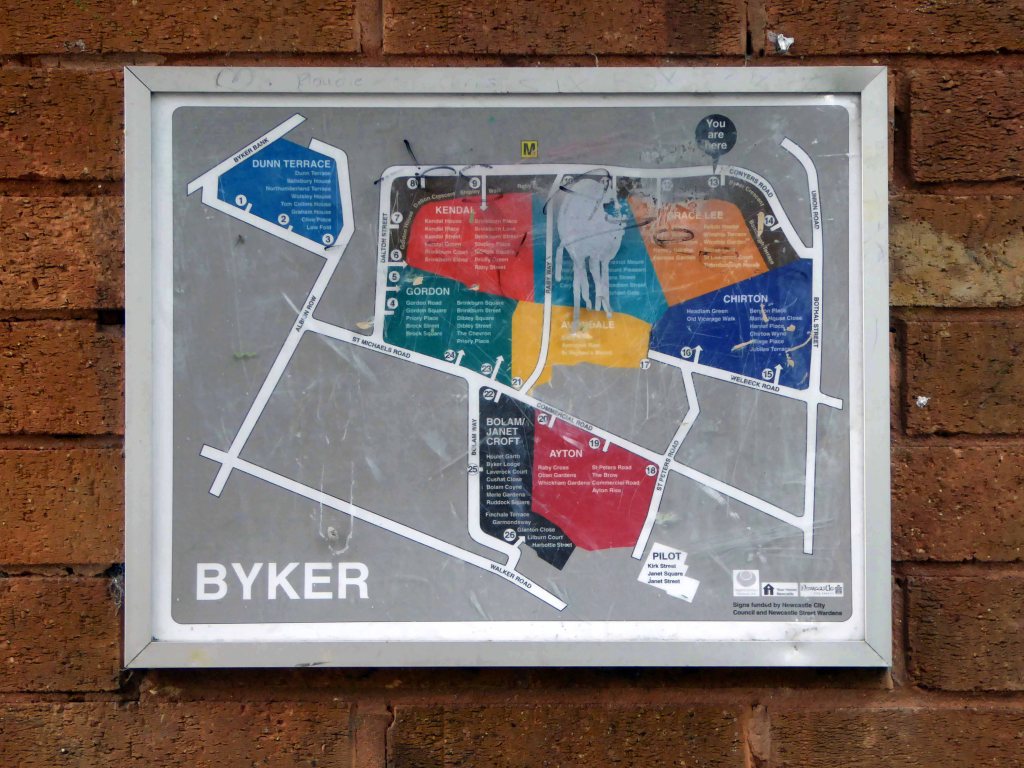
The Byker Estate has proved to be much more durable.
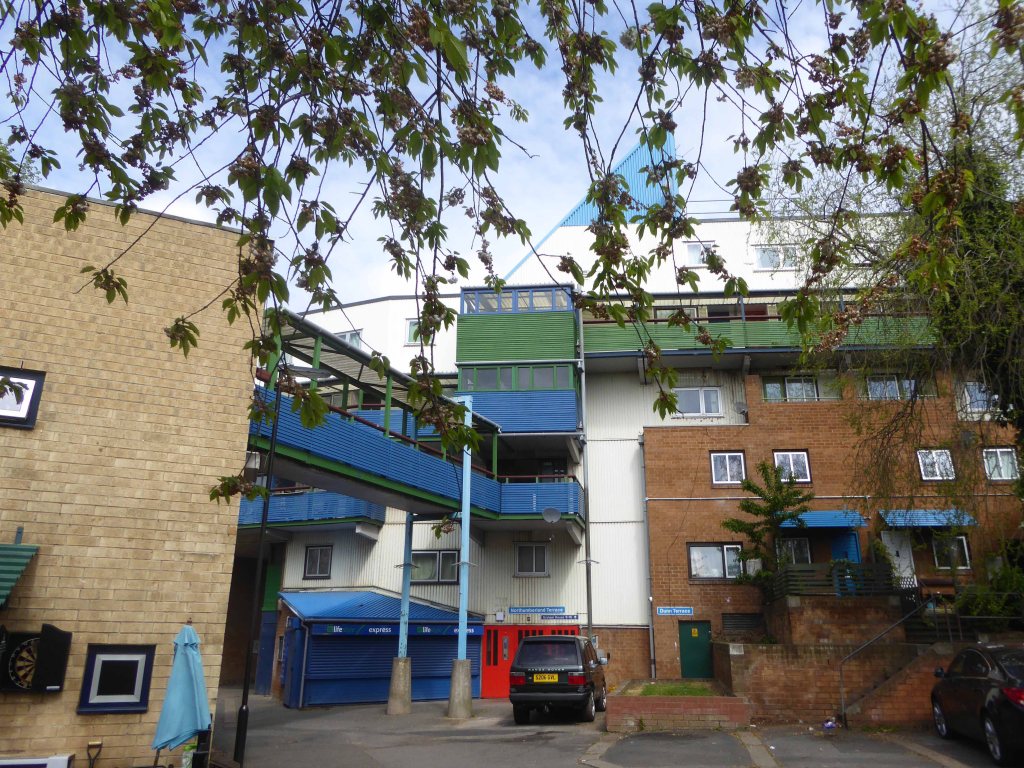

Whilst Park Hill has undergone a change from social housing to largely private ownership and rental.

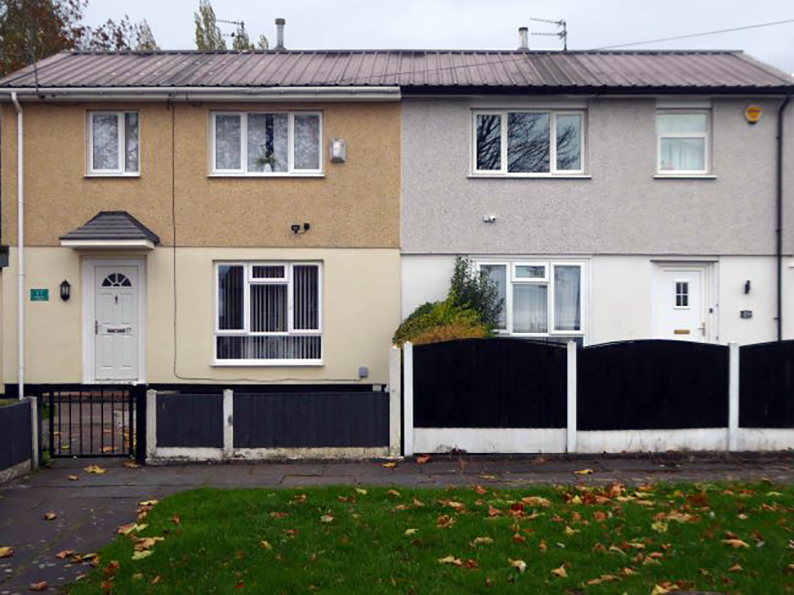
The St Thomas Estate in Radcliffe, mixes the traditional terrace with a modern twist on social housing.
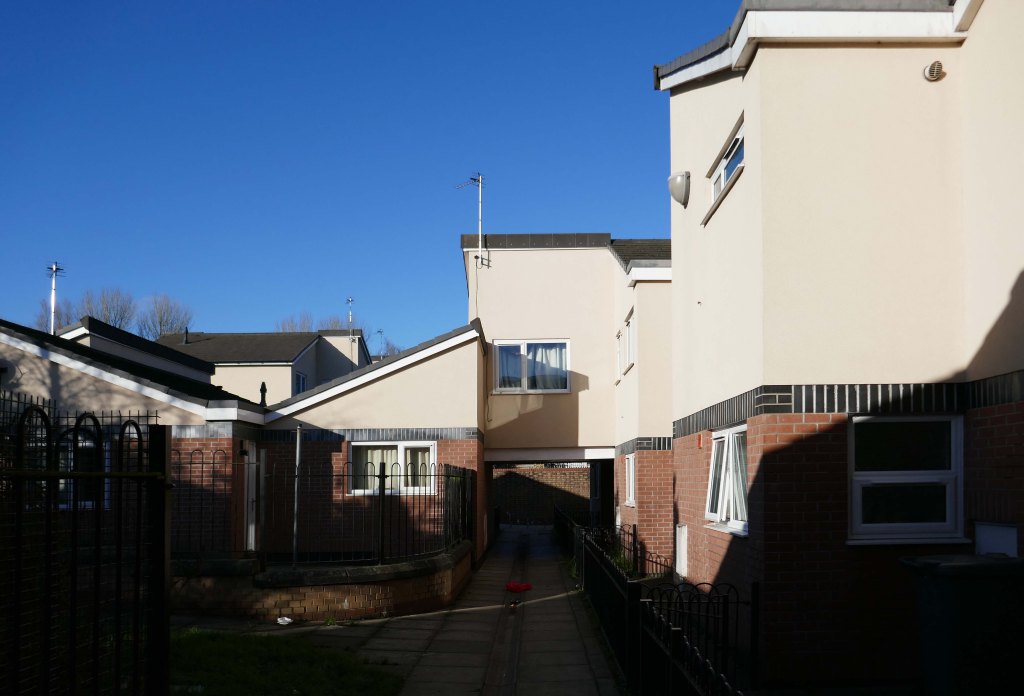

Private developers opted for Span style homes, such as these at Deneway Stockport 1964
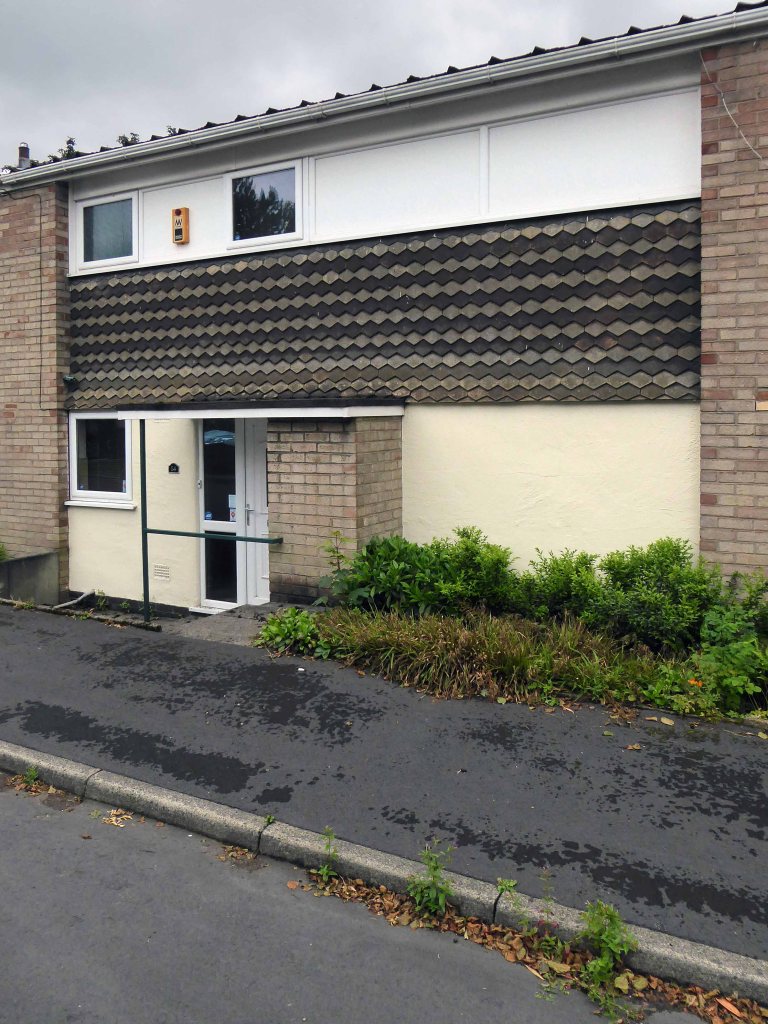

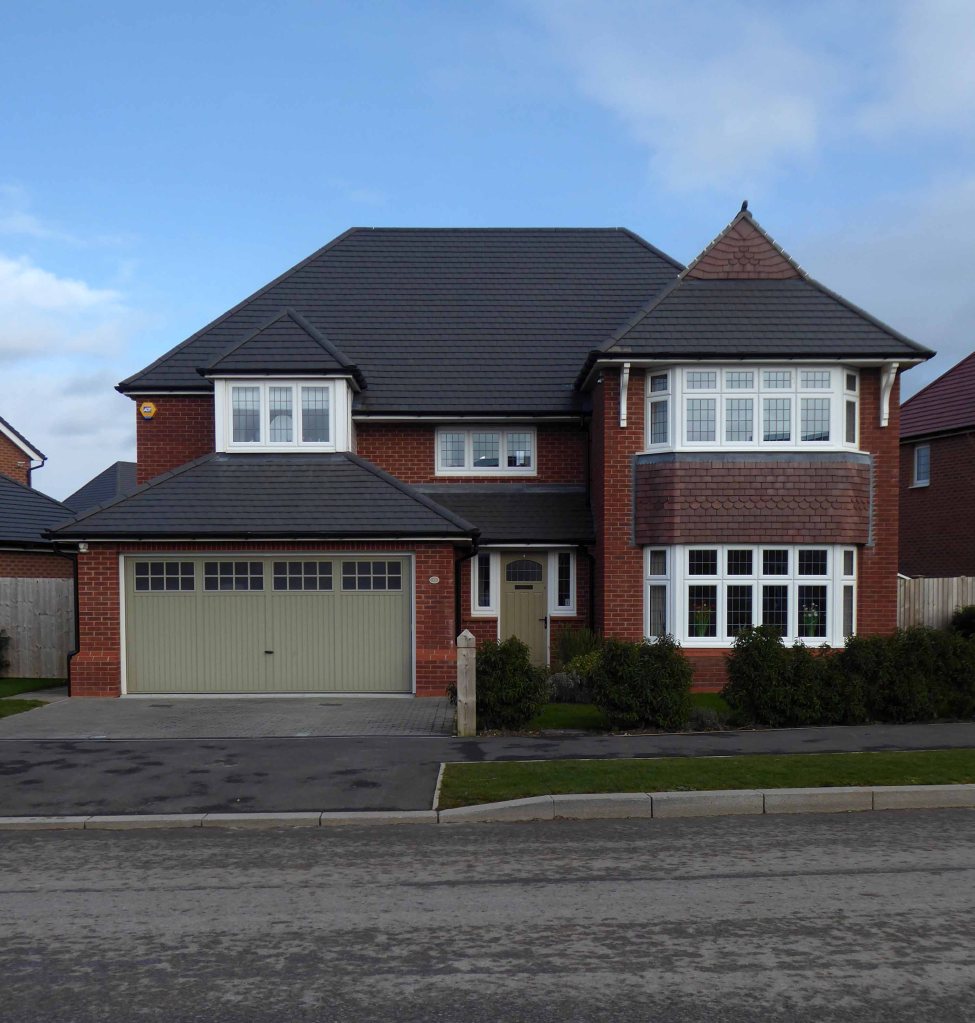
Further afield in the former fields of Cheshire are the out of the way, not way out, Woodford executive homes.

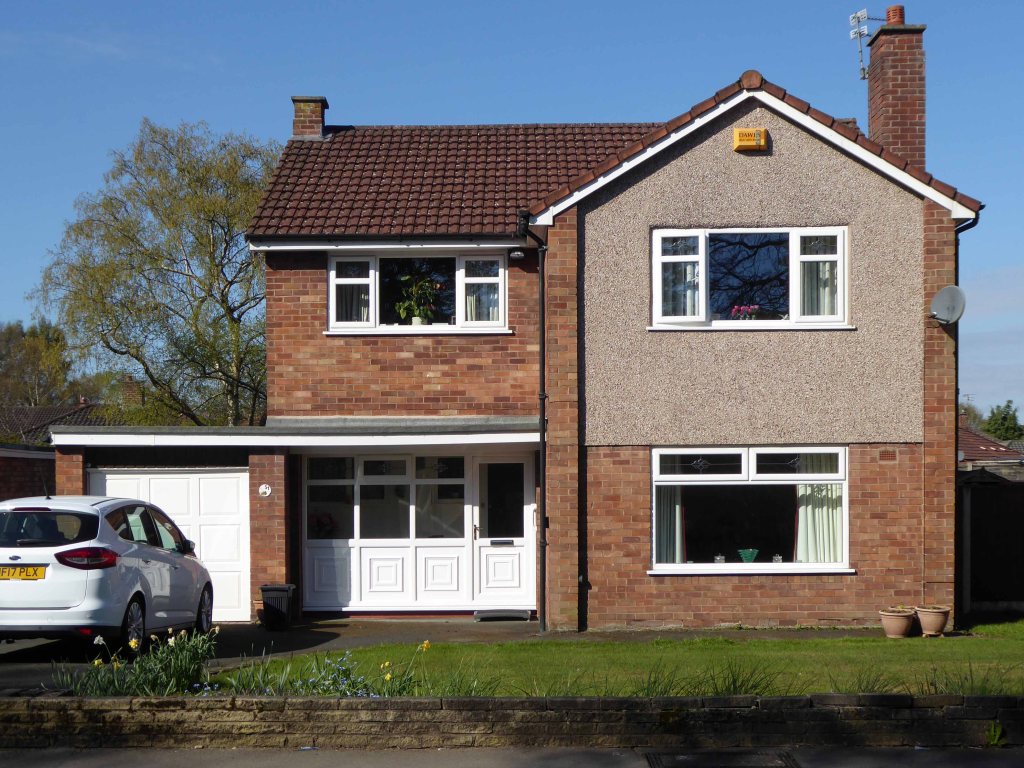
In Heald Green we find the slightly less executive homes.

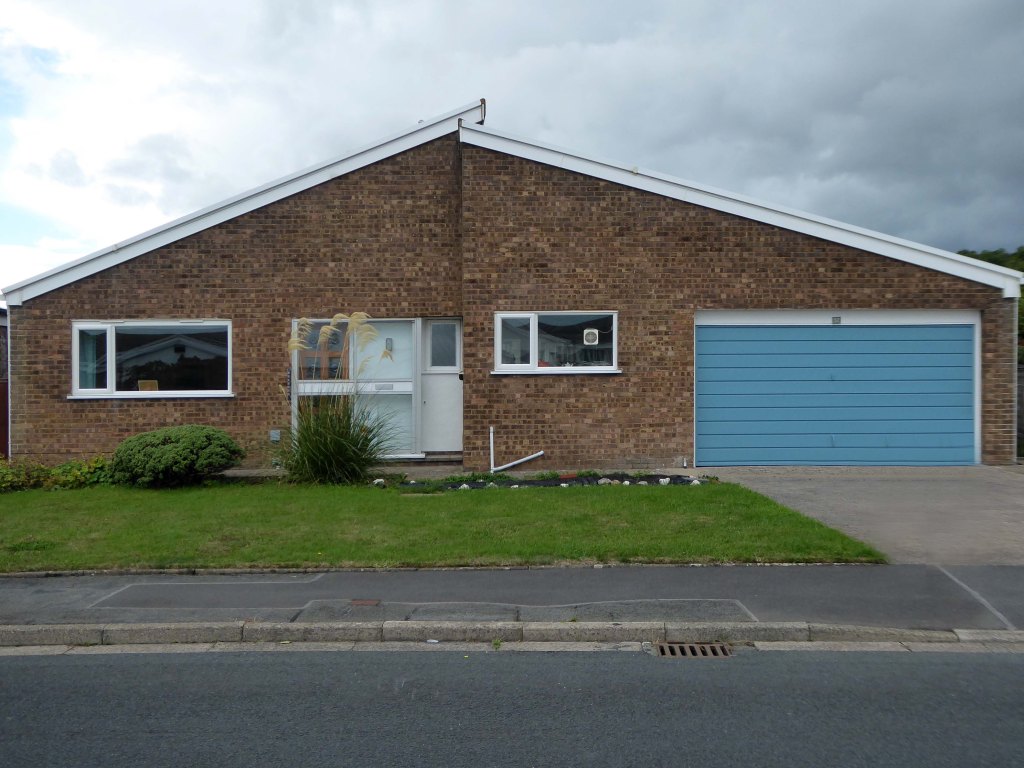
Even further afield the seaside enclave of Penrhyn Bay.

Prompted by a recent viewing of Graham Williamson’s Suburban film, I decided to undertake further in depth research around my own suburban locale.
Here is my first day’s findings in the West Heatons – followed by the next day in the West Heatons.