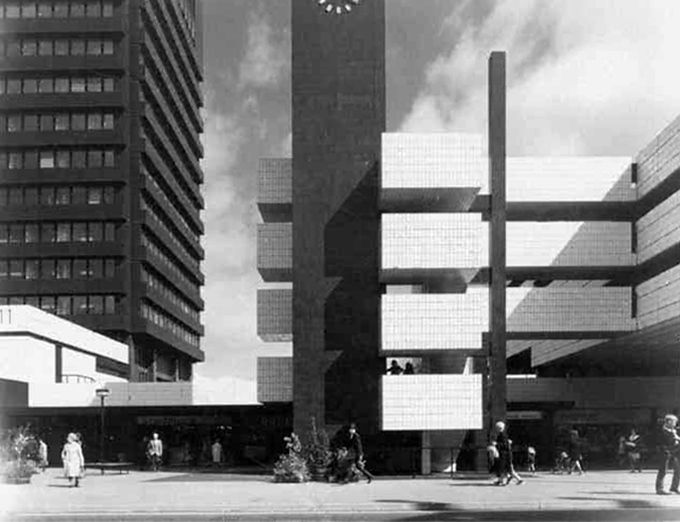
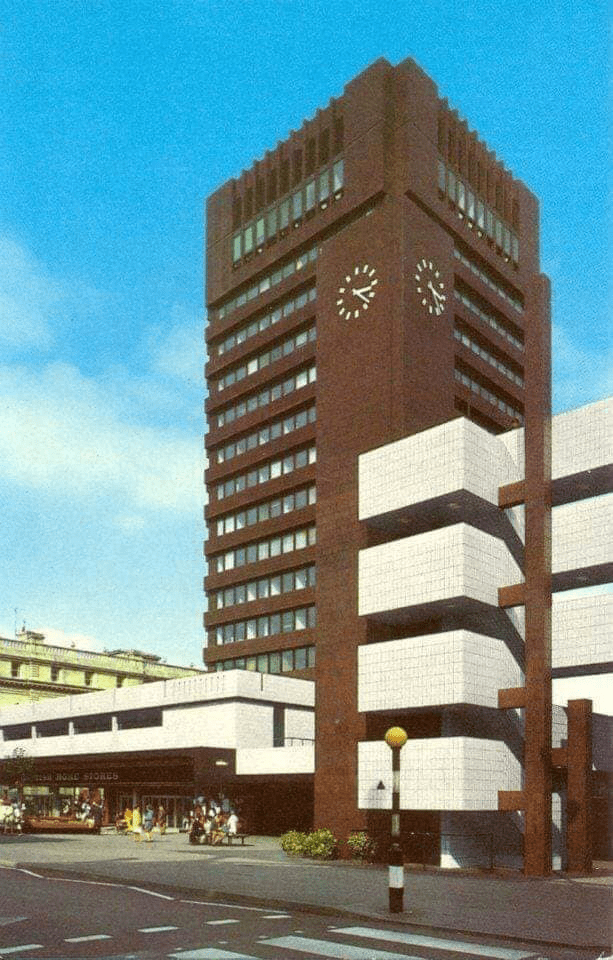
Though plans for a university in York first appeared as early as 1617, it would be over three centuries before they came to fruition. In 1960, permission was finally granted for the University of York to be built, marking the beginning of our journey.
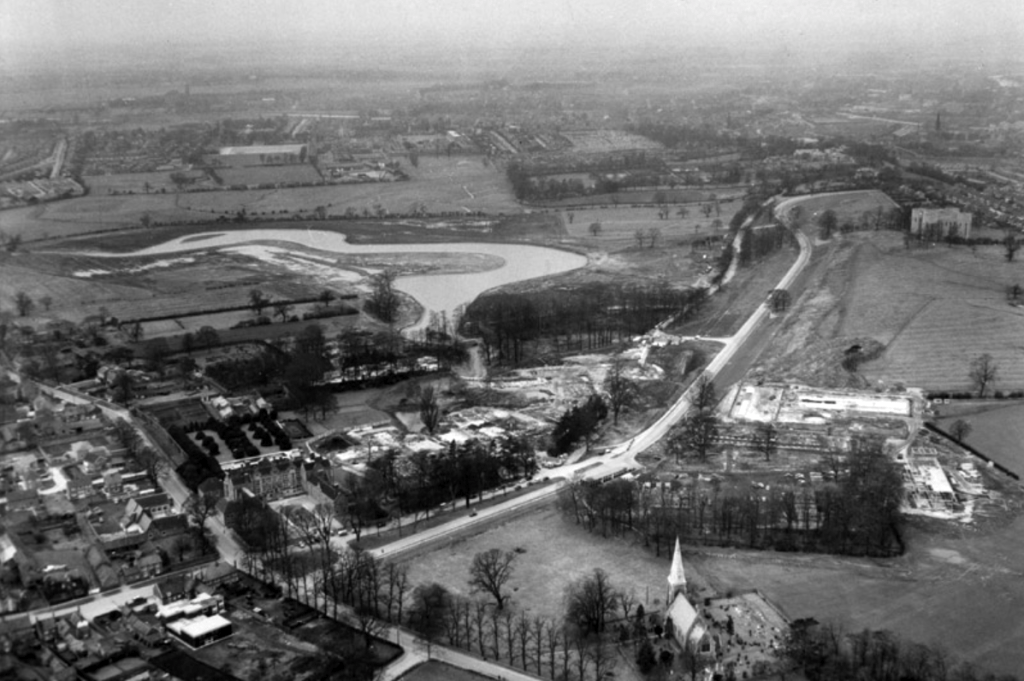
Before the Second World War, Heslington was a quiet rural retreat with a local aristocracy, and a working agricultural village.
Fresh, young, forward-looking and enthusiastic, the University of York was known for its friendly atmosphere before it even opened its doors.

Planning and building the University happened with astonishing speed. In April 1960 the Government approved the establishment and less than three years, on 9 October 1963, the first students walked through the gates of Heslington Hall.
In the 1970s, college social life began to blossom.
Central Hall was the venue for The Who, The Kinks, Fairport Convention, John Martyn, Ian Dury and the Blockheads, Hot Chocolate, Humphrey Littleton, Acker Bilk, Paul Tortelier, Julian Bream, John Williams and others.
Paul and Linda McCartney appeared one day out of the blue with their new band Wings and performed a concert in Goodricke College Dining Room.
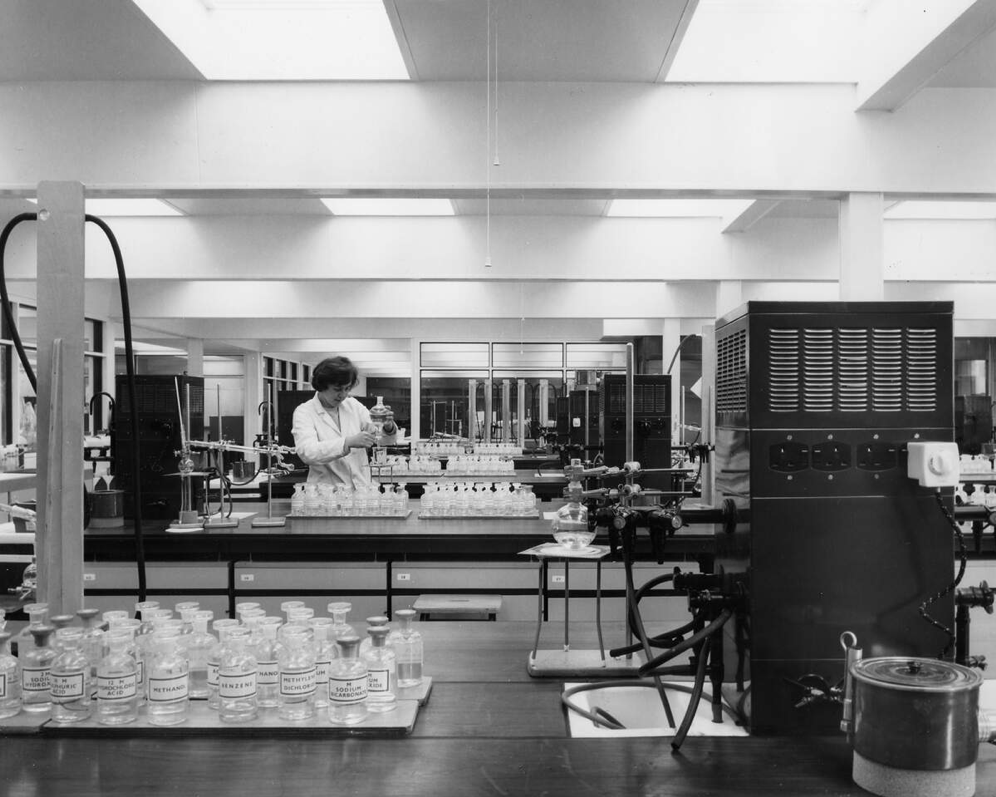

The beginning of the 1980s came with significant challenges for the University.
The decade saw the start of cuts across higher education. Staff were exhorted to make economies including turning down their thermostats, recycling, and making telephone calls as short as possible. There was also a fire in the Department of Chemistry.
In 1990, the Vice-Chancellor, Berrick Saul, recounted to court that York had been described by a senior member of the Universities Funding Council as “a well-run university with a relatively low profile.”
What a difference a decade makes.
By the end of the 1990s, York was dominating national league tables for research and teaching and was receiving international press coverage for achievement across the disciplines.
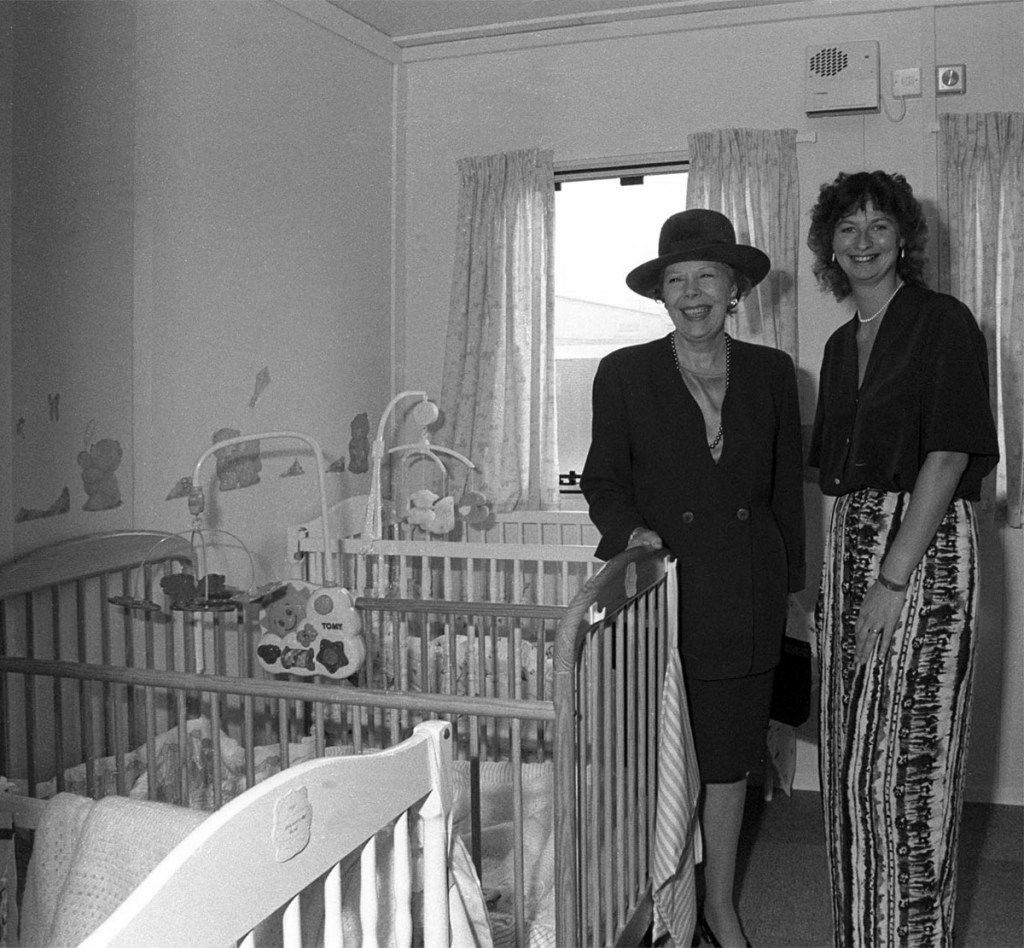

University Chancellor Dame Janet Baker at the opening of the University’s Baby Unit, October 1994 – York Digital Library
The 90s was characterised by advancement and recognition. York remained a popular choice among prospective students growing from 4,300 to 8,500 students without compromising its high entry standards. As the Sunday Times pointed out, “elitism does not appear to be the price of excellence at York”. York was one of only very few universities whose entry from state schools and colleges (around 80 per cent) was the same as the proportion of A-level students in the state system.
The introduction of official quality assessments and the proliferation of newspaper league tables saw the University’s stock rocket. After years of academic advancement, York began to get the recognition it deserved. National recognition attracted additional funding and investment. Research grants rose to over £20m per annum, and the University enjoyed one of the highest incomes per researcher in the higher education sector.

The Sir Jack Lyons Music Research Centre is opened by Roger Wright, controller of BBC Radio 3, 2004
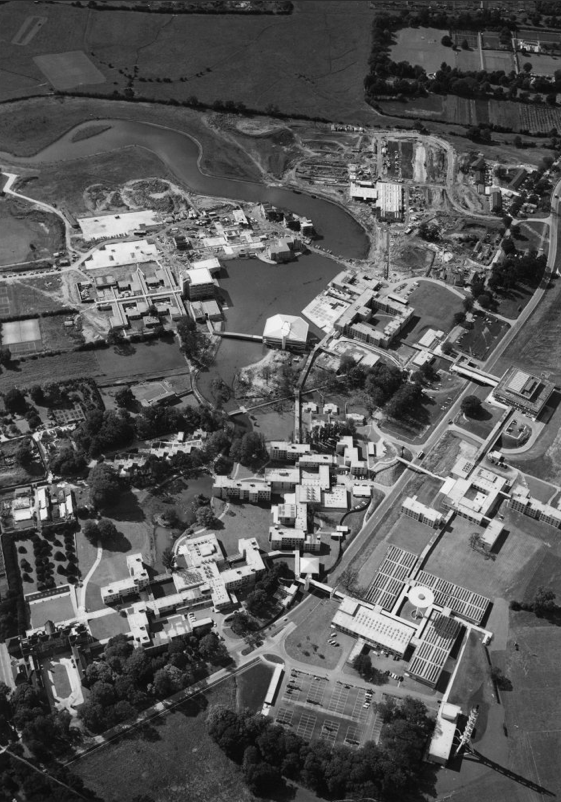
The planning for Heslington East began in earnest in 2002 with the arrival of Brian Cantor as Vice-Chancellor. It took years of master-planning, liaison with interest groups, negotiations with land-owners and local communities, an 8-hour city planning meeting and a Public Inquiry to achieve the purchase of land and complex planning permissions for a site equal to the size of the original Heslington West campus. In 2009, the new Goodricke College opened as the first building on Heslington East.
At the time of the 40th anniversary in 2003, we wrote about Heslington East:
It will be everything that the designers of the original campus hoped for – integrated, landscaped and traffic-free, with a large expanse of water, and a very eager populace.
On 25th November 2010, we were named “University of the Year” at the Times Higher Education Awards, achieving praise from the judges for our “success in combining academic excellence with social inclusion, as well as its record in scientific discovery”.
The development of Campus East continued throughout the decade, with four new sites to accommodate academic departments and a variety of support and social buildings, including the Ron Cooke Hub and York Sports Village.
Campus West also saw much expansion and redevelopment during the 2010s, with the opening of the £13.8m Spring Lane Learning and Teaching Building and £16m Biology teaching and laboratory facility in 2016.
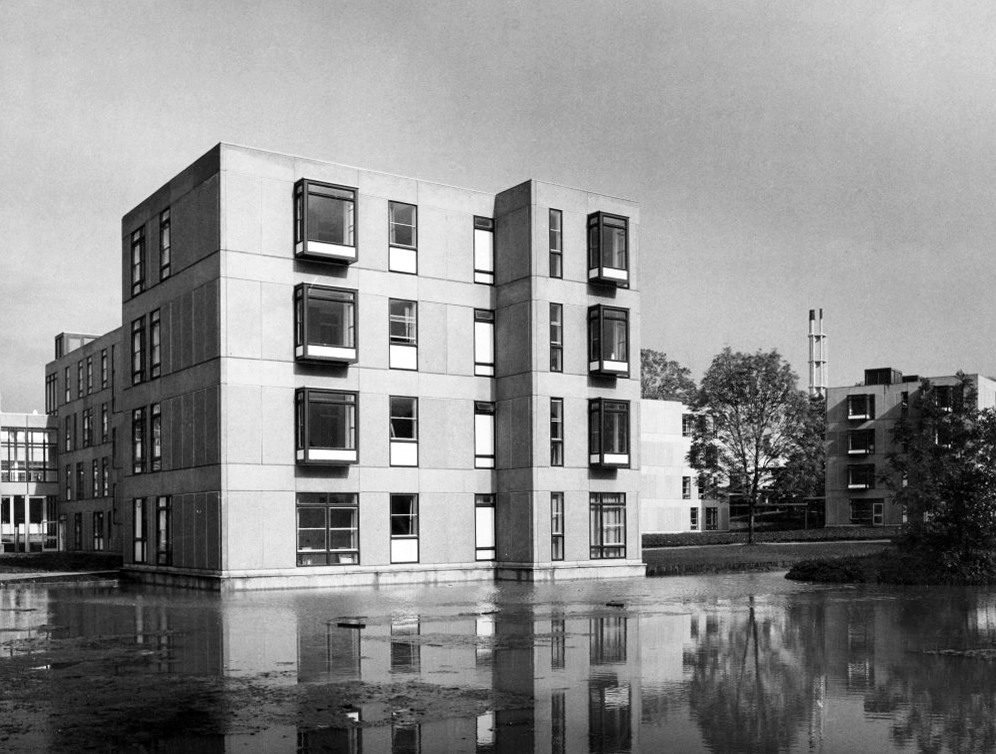
The University of York was founded in 1963 and work on its campus facilities in the grounds of Heslington Hall was begun in 1964. The first two colleges, Langwith and Derwent, accepted residential students for the autumn term of 1965. The original buildings were designed by Sir Andrew Derbyshire of Robert Matthew Johnson-Marshall & Partners, and assembled using the CLASP system of prefabricated construction.
RIBA

Founded in 1956 by architects Robert Matthew and Stirrat Johnson-Marshall, RMJM’s first offices were based in London and Edinburgh.
RMJM is now one of the largest architecture and design networks in the world. Services include architecture, development management, engineering, interior design, landscape design, lead consultancy, master planning, product design, specialist advisory services, and urban design

Langwith College 1965 – photo Reginald Hugo de Burgh Galwey
Constructed using the Consortium of Local Authorities Special Programme – CLASP system, formed in 1957 by Local Authorities in England to develop a shared prefabricated system for the construction of school buildings. The resulting CLASP building system was initially developed by Charles Herbert Aslin, the county architect for Hertfordshire.
CLASP’s popularity in coal mining areas was in part because the system permitted fairly straightforward replacement of subsidence-damaged sections of building, and the lightness of the structures. The system was also later used for the construction of railway stations, offices, university buildings, and churches until the late 1970s.
Today, 3000 examples are still in use.
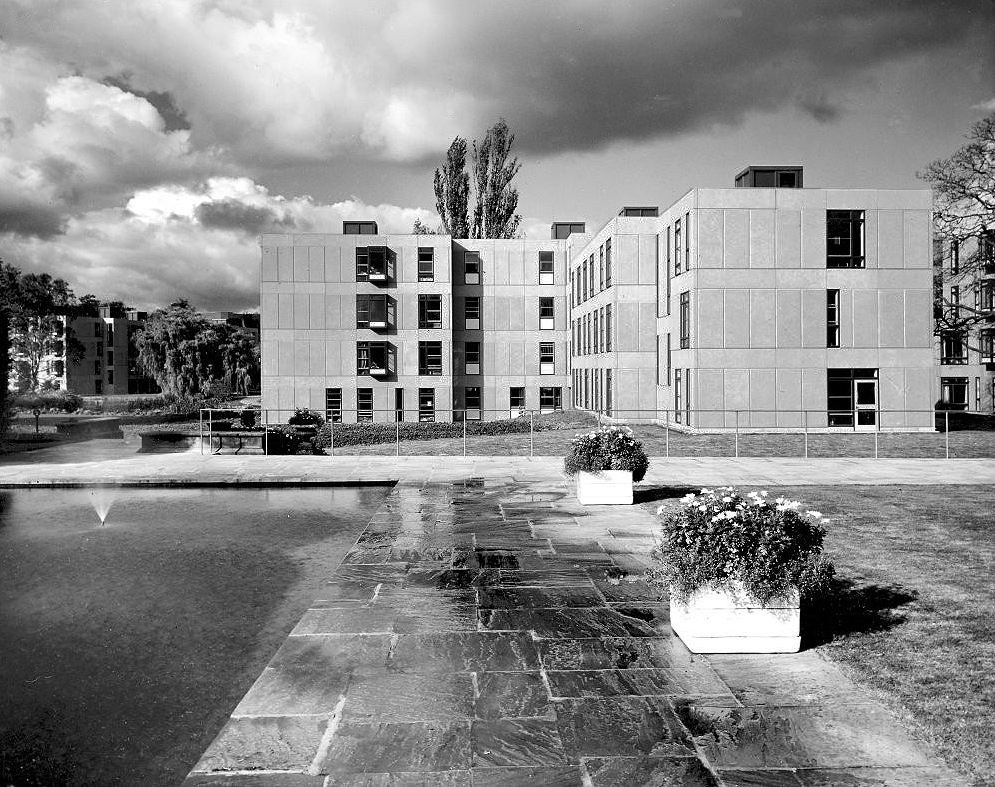

Photo – Keith Gibson 1965
The system utilised prefabricated light gauge steel frames which could be built economically up to a maximum of four storeys. The frames were finished in a variety of claddings and their modular nature could be employed to produce architecturally satisfying buildings. Initially developed solely for schools, the system was also used to provide offices and housing.
The cynics’ definition of the CLASP acronym, circulating in the 1970s, was:
collection of loosely assembled steel parts.
CLASP buildings fell out of favour in the late 1970s. Budgetary advances and changing architectural tastes made the scheme obsolete.
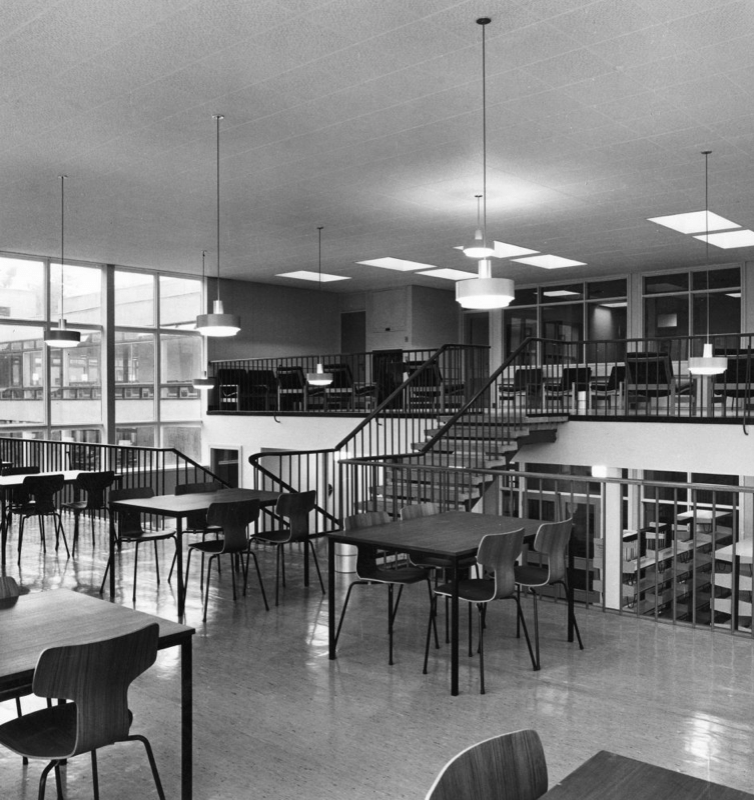
Upper Level reading rooms Langwith College.

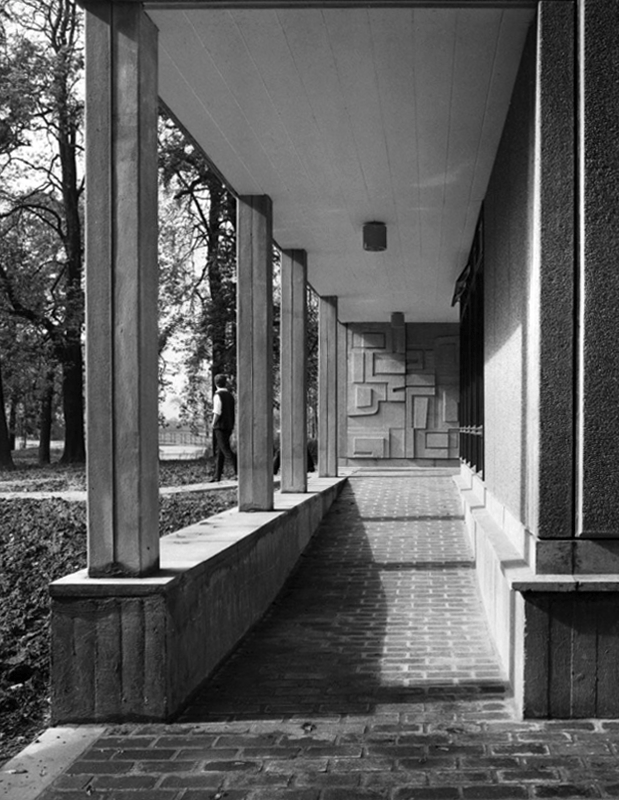
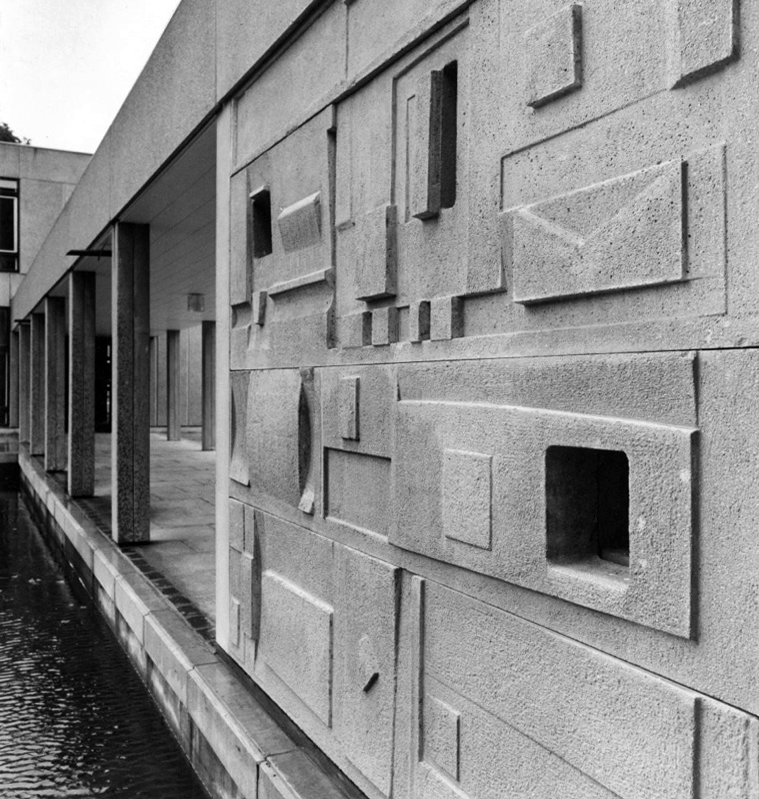
Walkway Derwent College with concrete relief by Fred Millett 1965
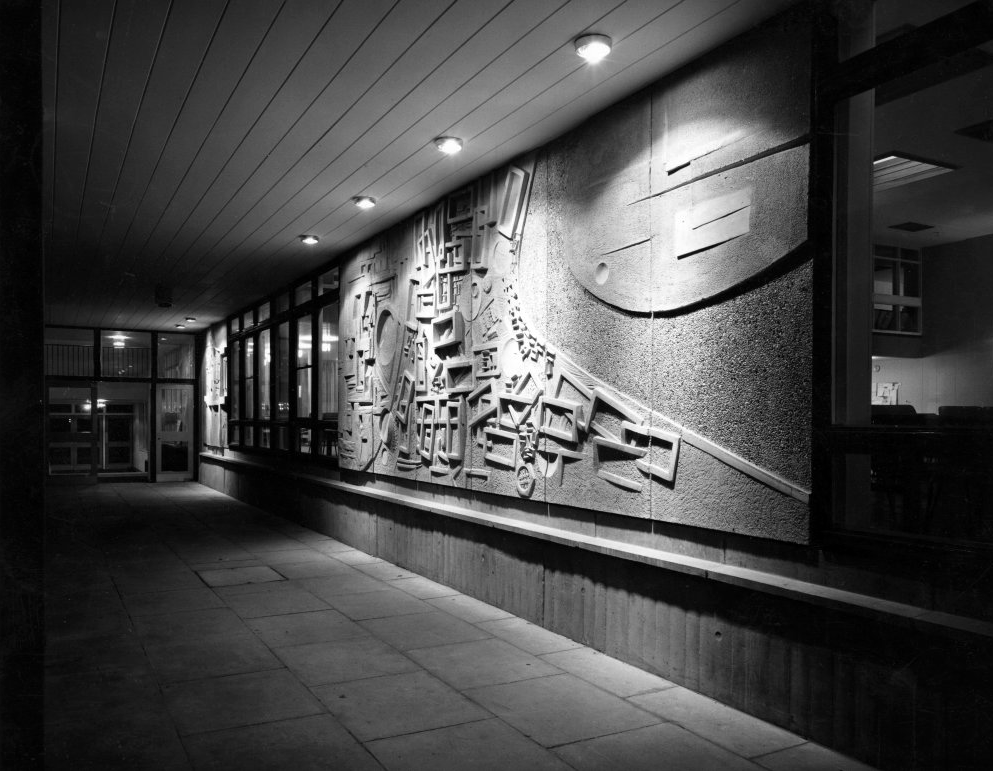
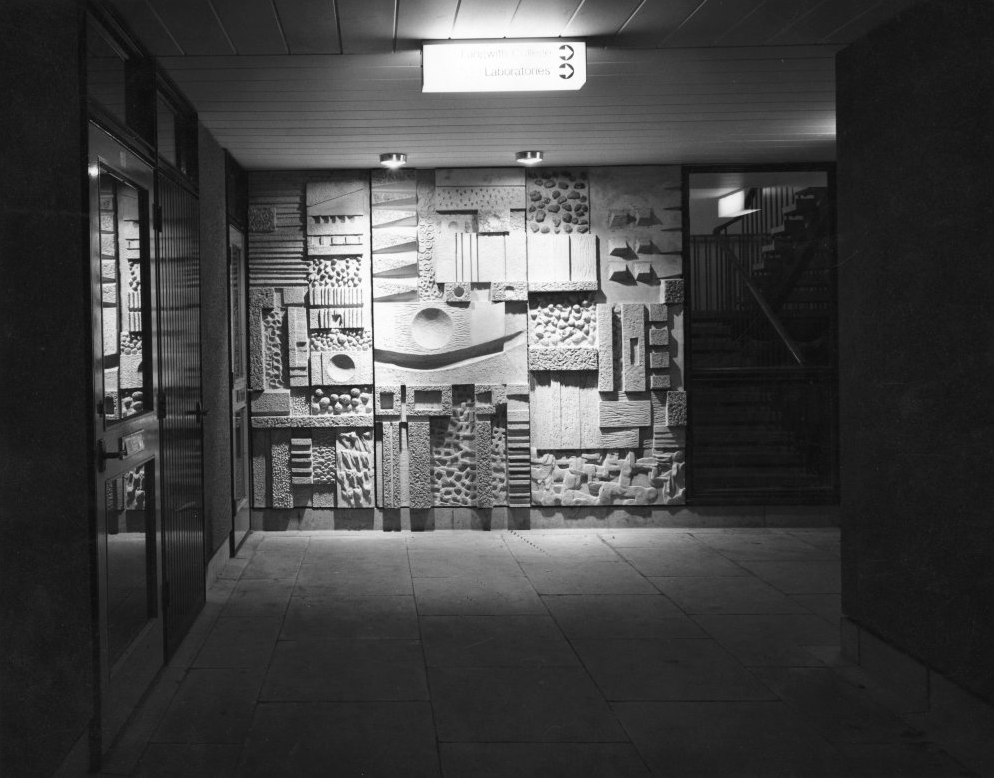




Photos 1965 Bill Toomey
Fred Millett 1920–1980 was a muralist and poster artist who exhibited at the Festival of Britain and was commissioned by London Transport, National Westminster Bank, University of York and the General Post Office. He also taught Perception and Communication at the Polytechnic of Central London.
Fred Millett – Sculpted Wall Raglan Estate Camden 1965
Originally part of the children’s playground, the work is a feature of a post war estate designed by Frank Scarlett in Kentish Town
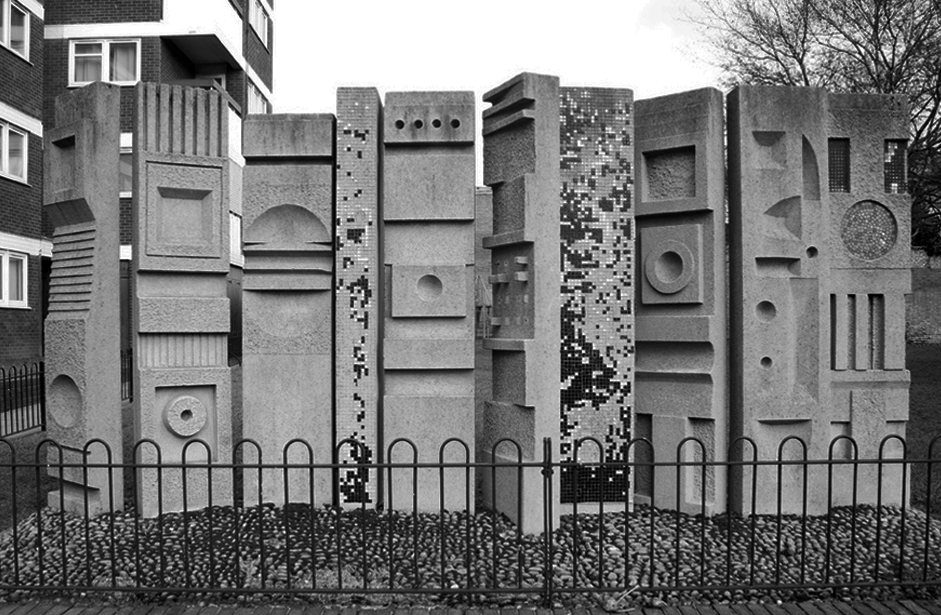

Fred Millett – London Transport 1968

Covered walkway Derwent College.
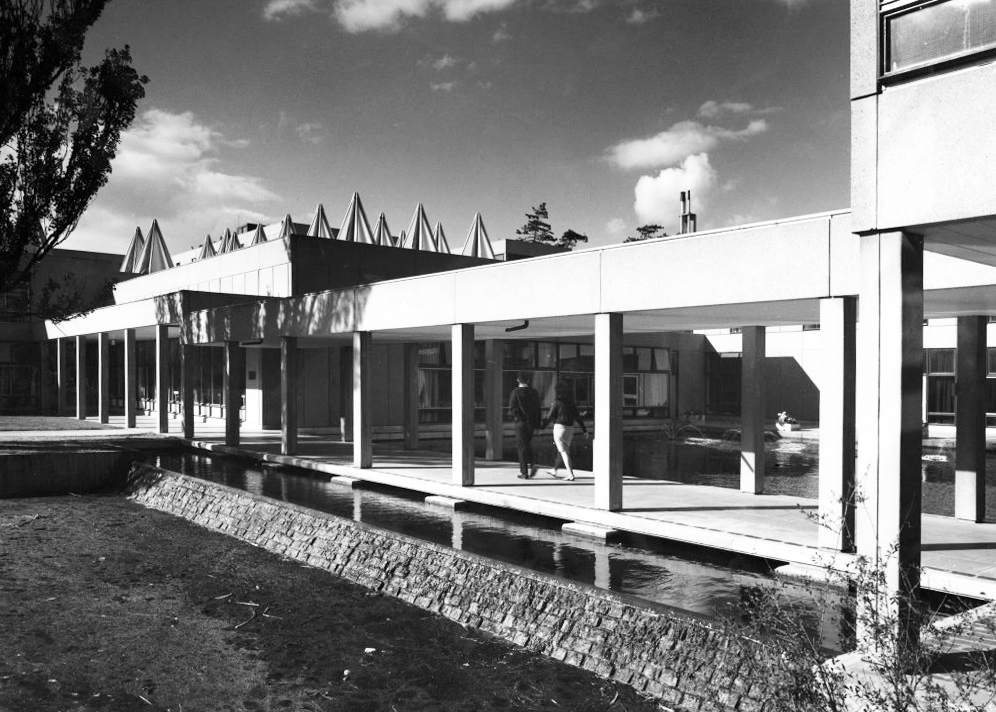

Photo 1965 Reginald Hugo de Burgh Galwey
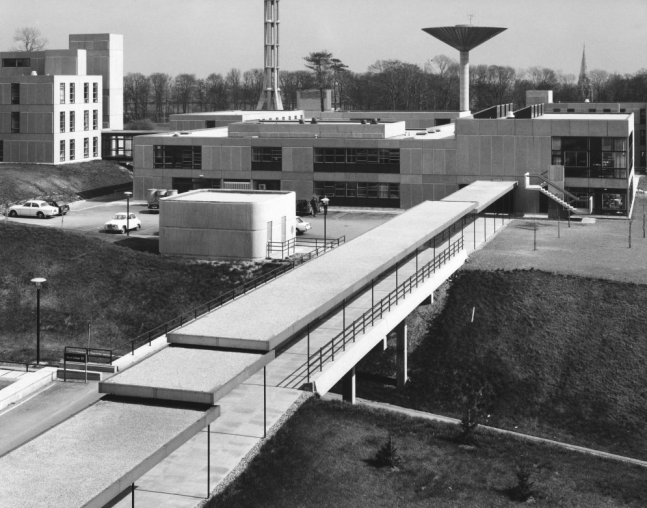
JB Morrell Library seen from the south side of Heslington Road with linking pedestrian bridge and ramp in foreground and cast aluminium sculpture by Austin Wright.
Austin Wright 1911-1997 is a significant post-war sculptor whose personal and professional lives were deeply intertwined with the city of York.
He was born on 4th June 1911 in Chester but spent his childhood in Cardiff. Though a largely self-taught artist, Austin took evening classes at Cardiff Art School. Austin attended New College, University of Oxford for his degree in Modern Languages before he started his teacher training. His first job as a teacher started in 1934 at The Downs, Malvern in Worcestershire. The school attracted artistic people. W.H. Auden taught English for example, and the art master organised a Dada exhibition one year. Here, Austin taught painting and sculpture as well as French and German.
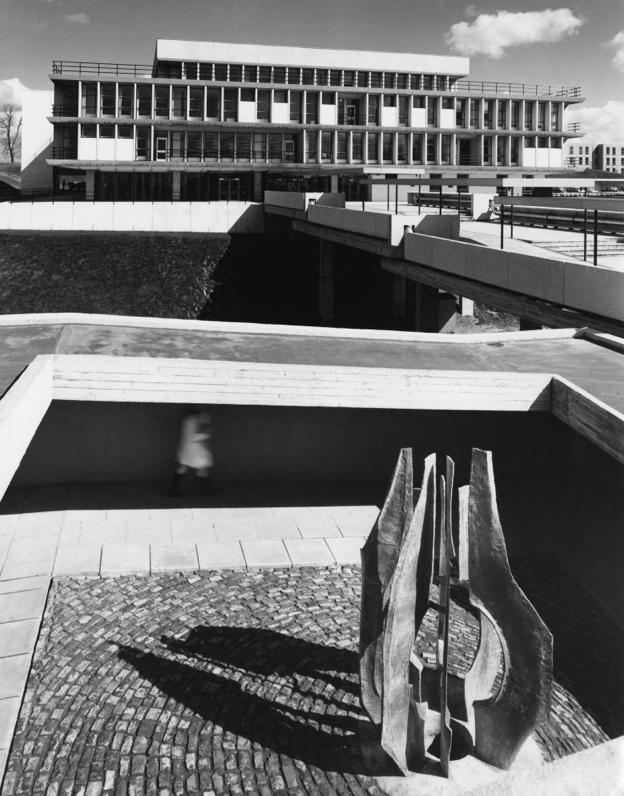

Photo 1968 Keith Gibson
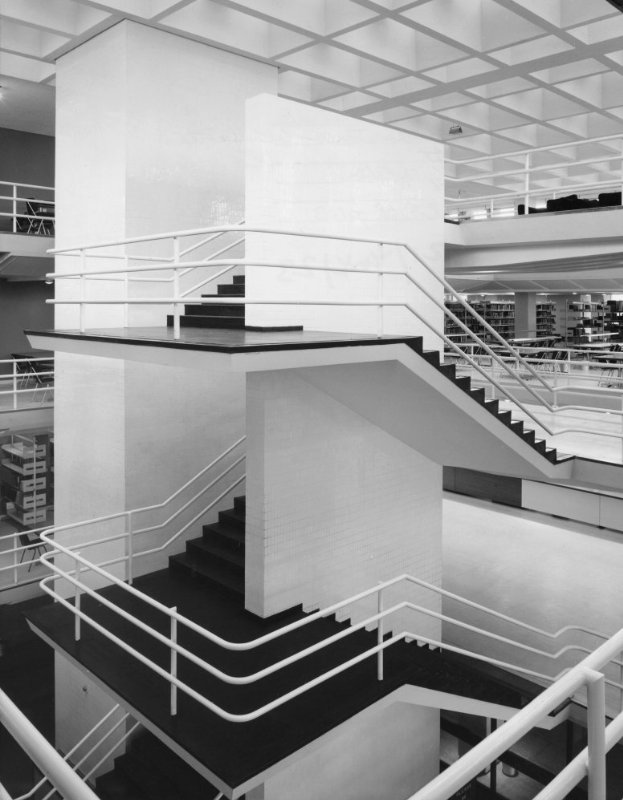
Library central stairway and lift shaft.

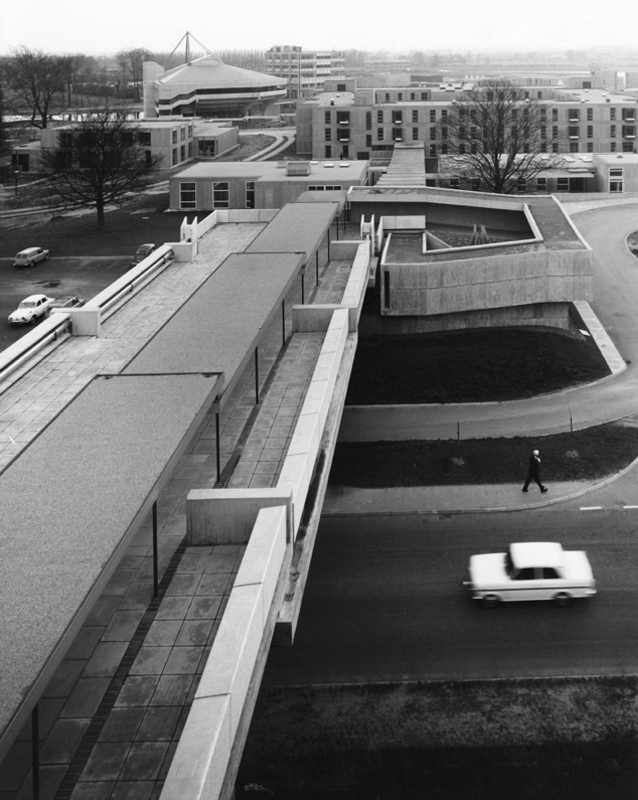
Covered pedestrian bridge linking the southern side of the campus to the JB Morrell Library on the north side.

Central Hall
Colloquially known as The Spaceship designed by John Speight, constructed in 1966–1968. The hall is seen as a tour de force of the university, appearing on merchandise and often used as a background for university publicity.
Central lecture and recreation hall to the University of York, 1966-1968 by Robert Matthew, Johnson-Marshall & Partners with Stirrat Johnson-Marshall and Andrew Derbyshire as partners in charge, and John Speight as job architect.
* it forms part of a wave of seven new universities that improved access to higher education and marked the high point of publicly-funded architecture in post-war Britain;
* it is a physical manifestation of the University of York Development Plan, which was heralded as the beginning of contemporary university planning in Britain;
* it continues a historic tradition established by late-C19/early-C20 ‘red brick’ universities of featuring a great hall for special events.
* it has an imaginative and bold design with a striking architectural form and massing that is the focus of the most dramatic views across the campus lake;
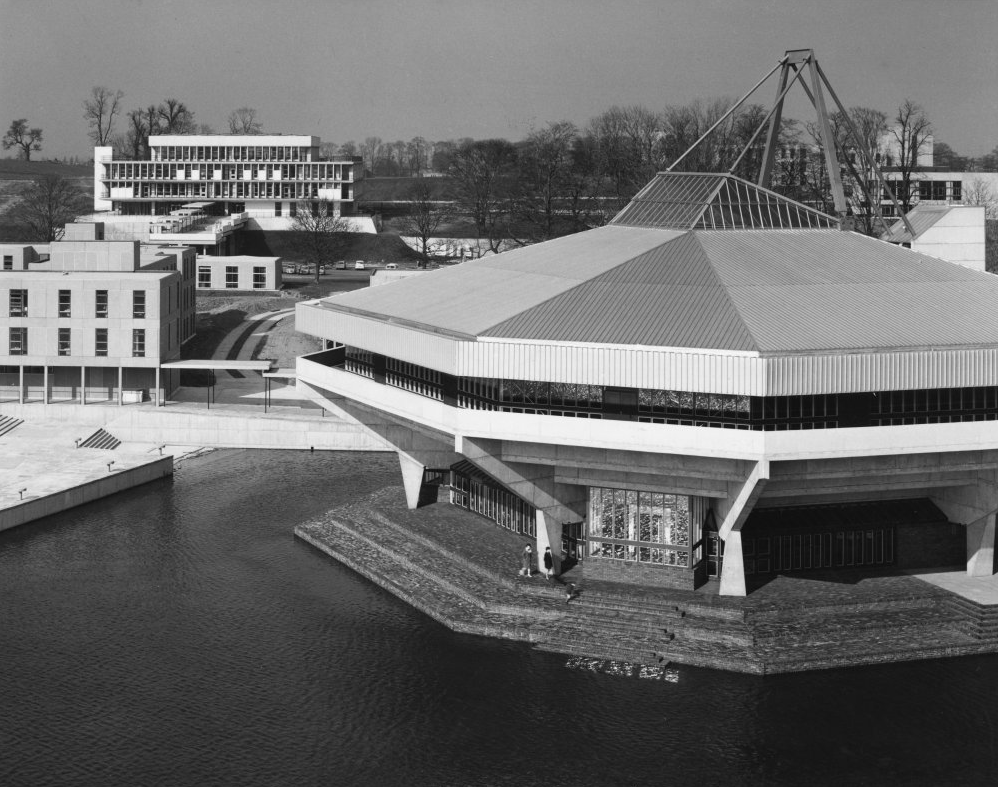

Photo 1968 Keith Gibson
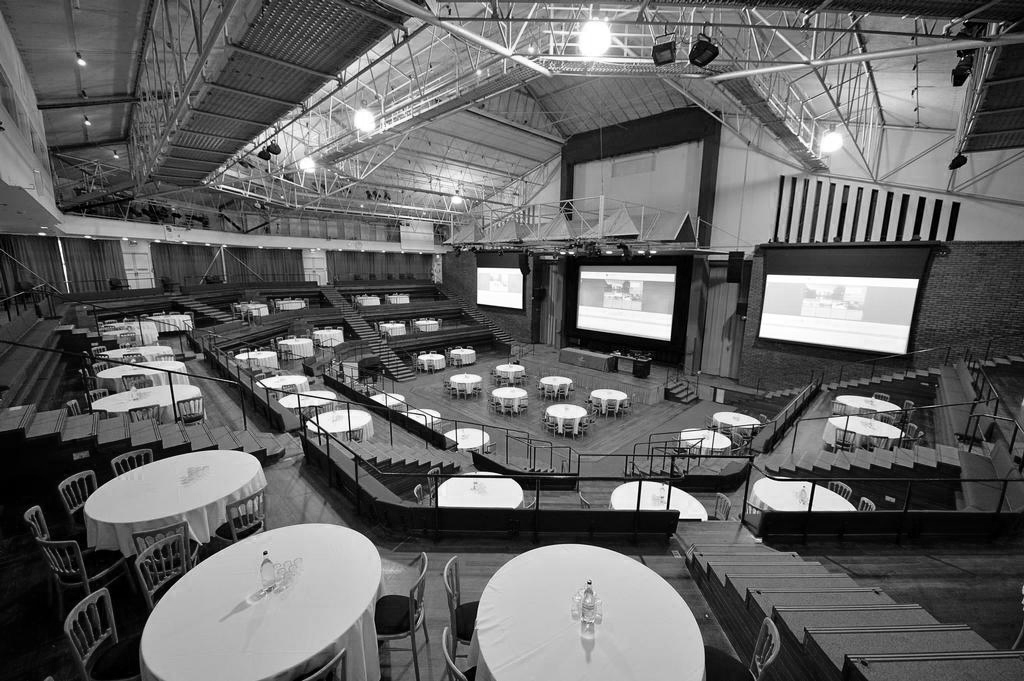

Photo University of York
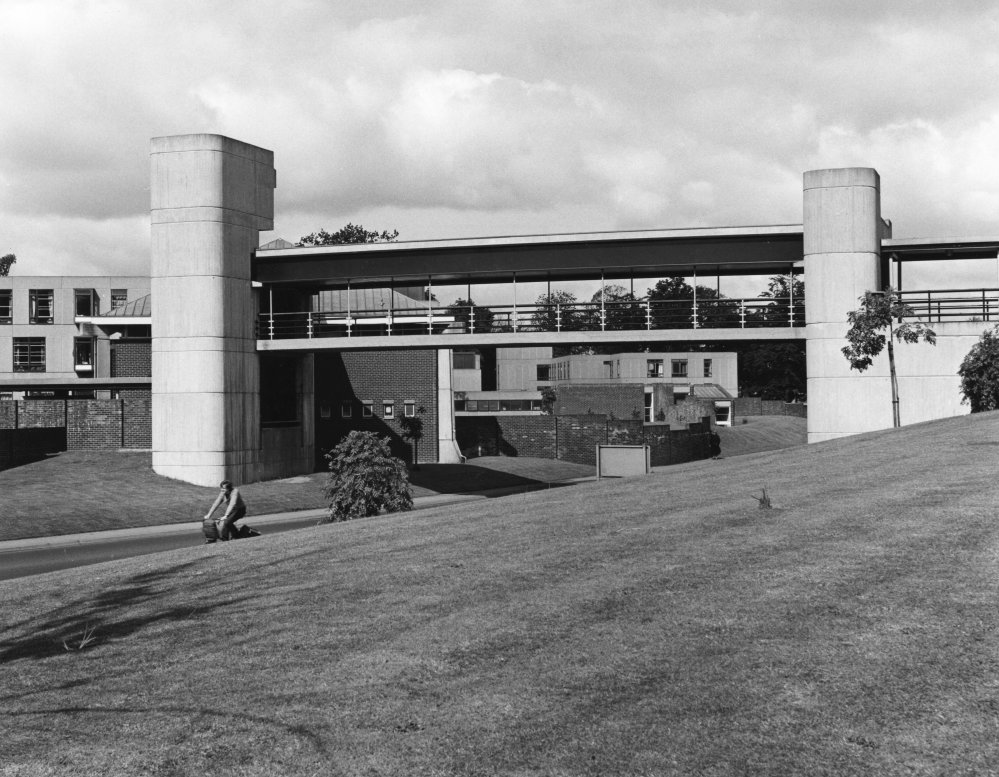
Concrete Linkbridge.

David Brown Laboratories the fluestack and water tower rising above the laboratory blocks.
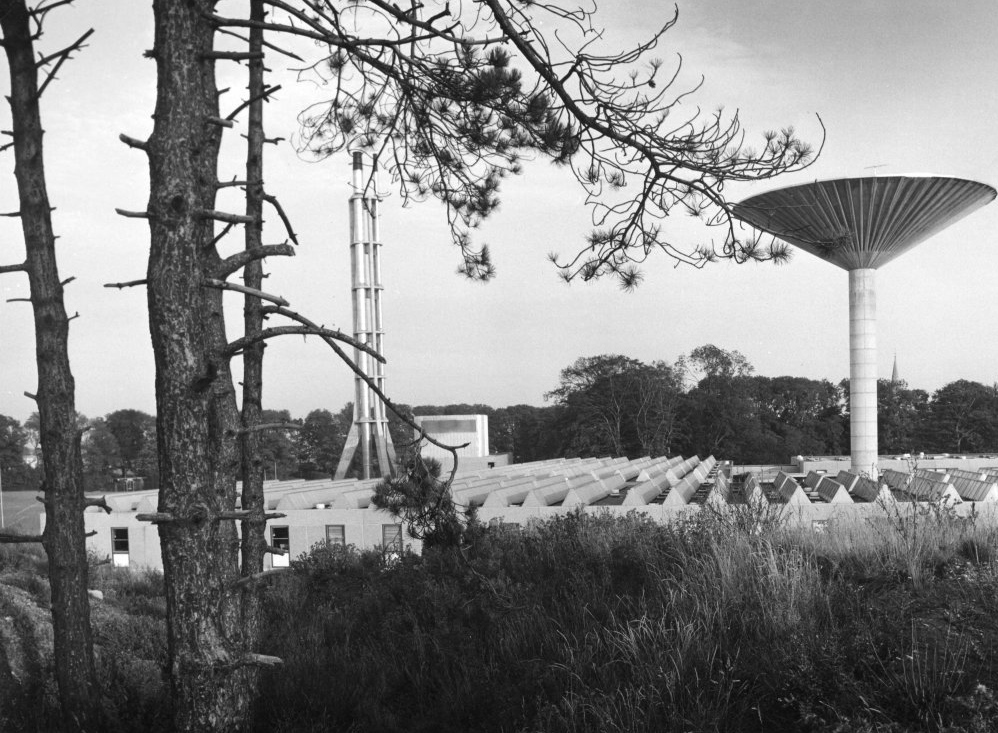

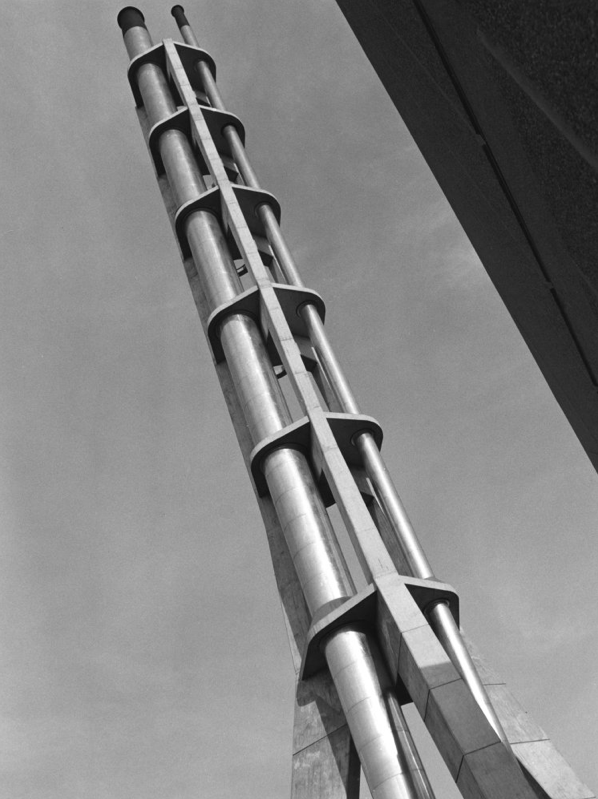
Fluestack – extant.
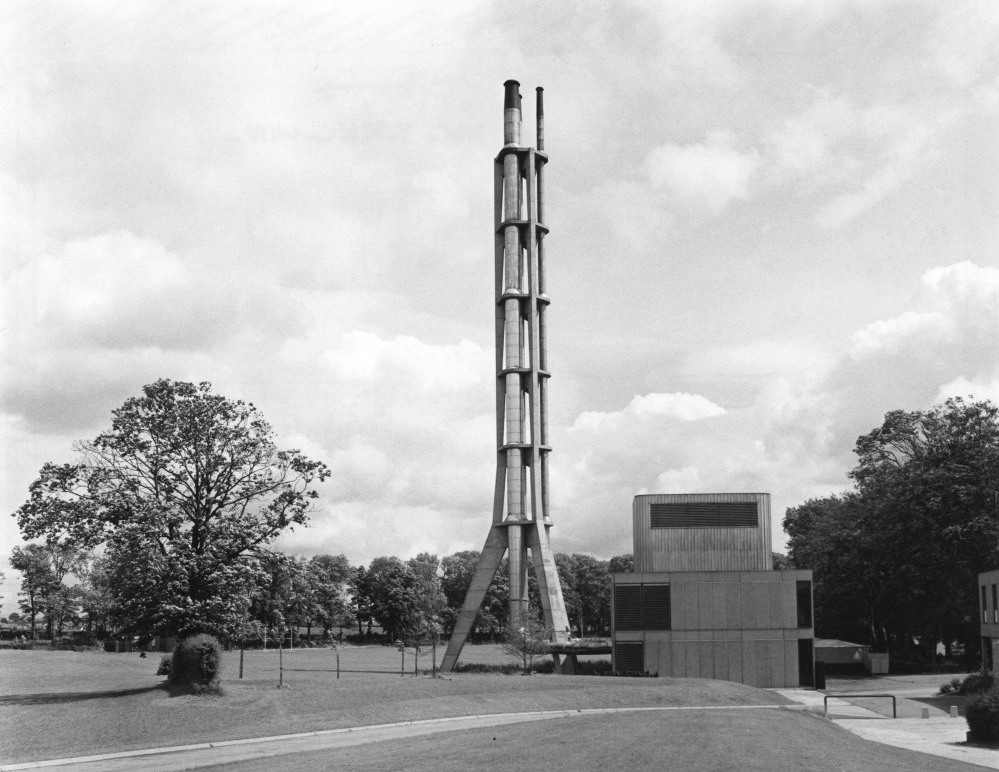


Water Tower – demolished
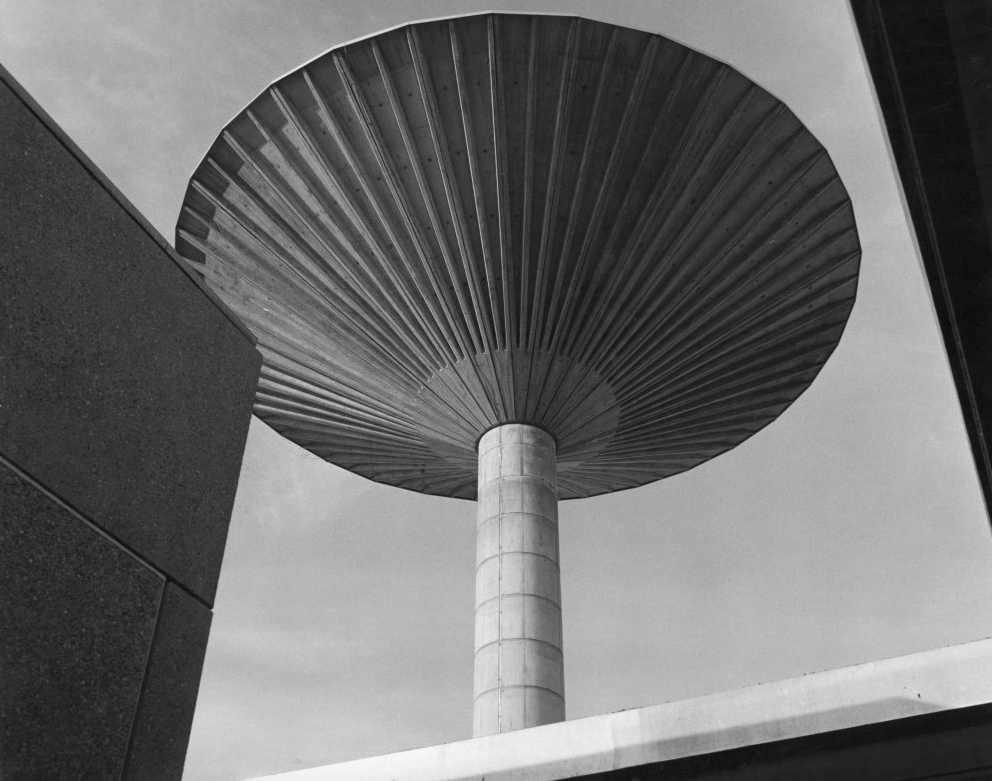

Archive photographs RIBA pix.
Further information can be found here.