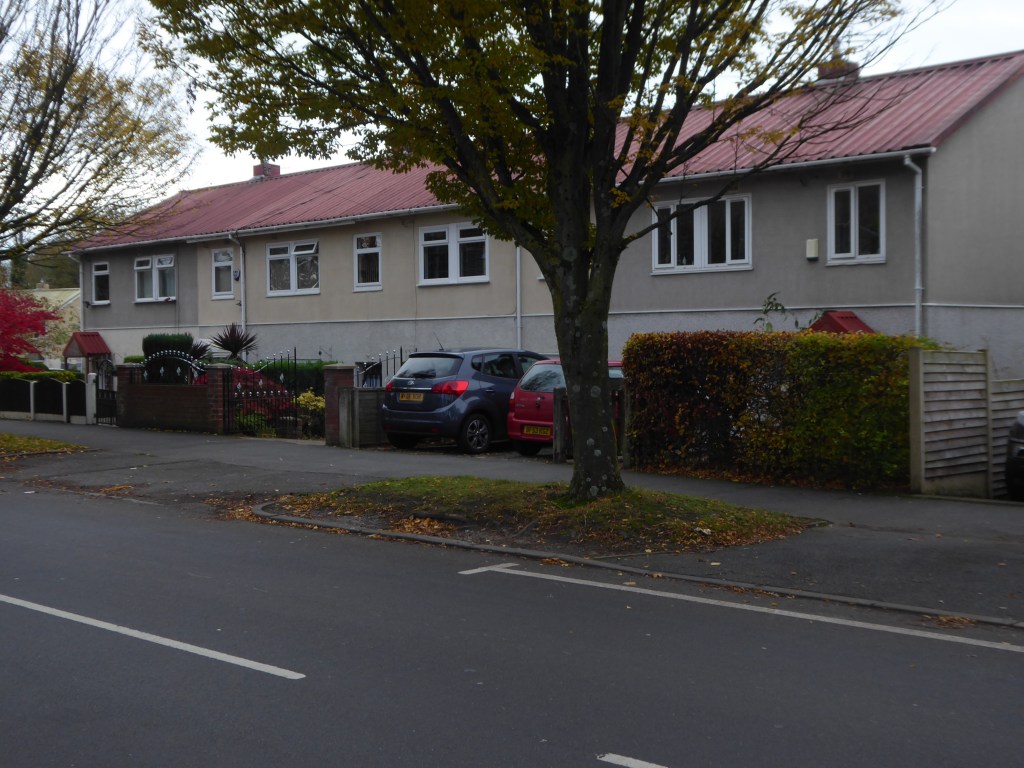
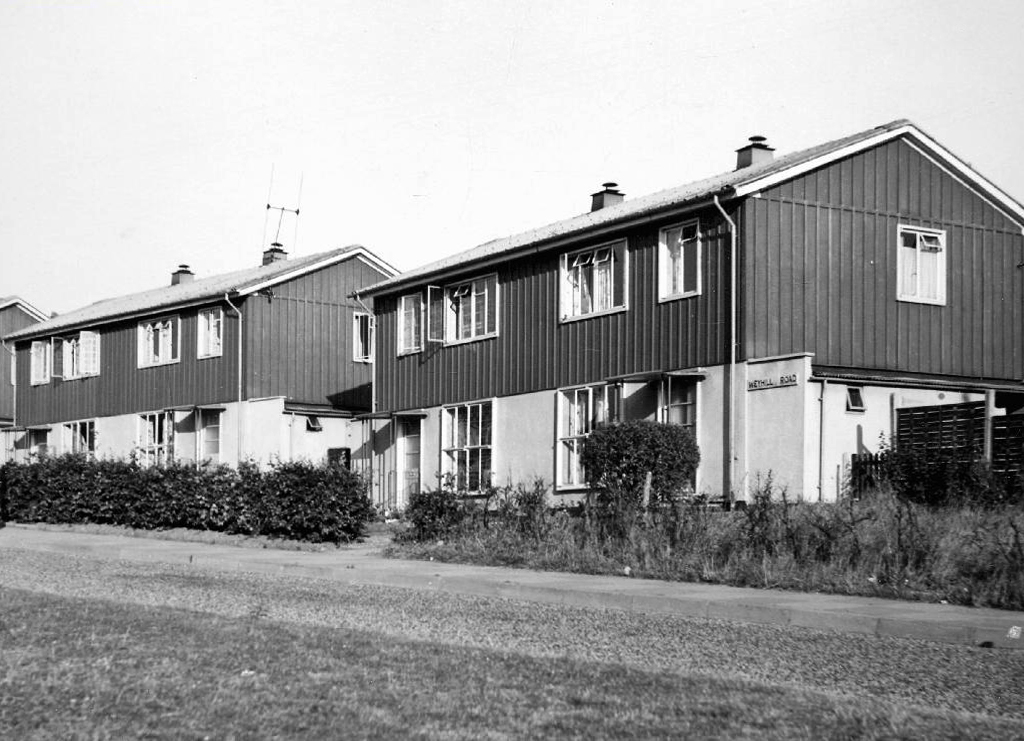
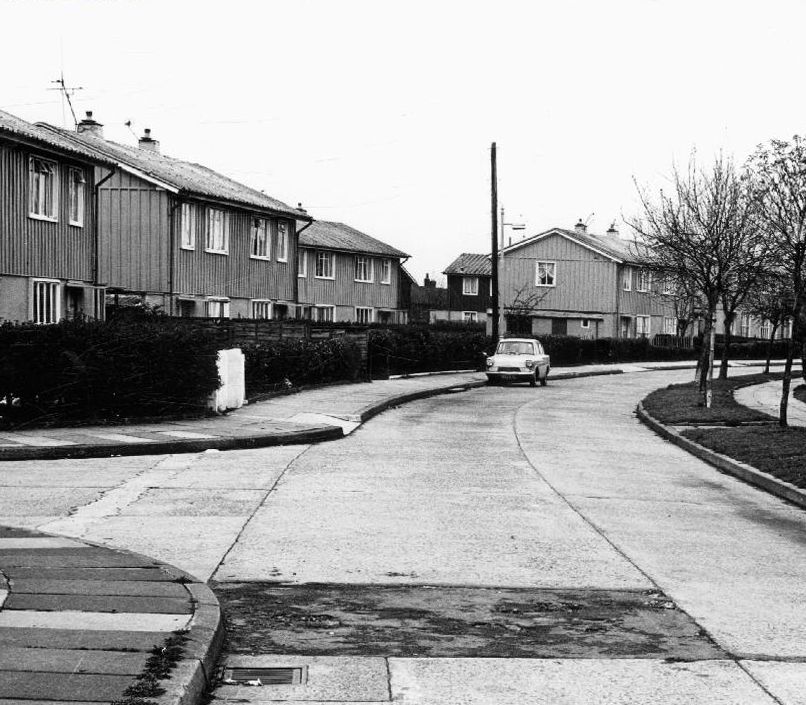
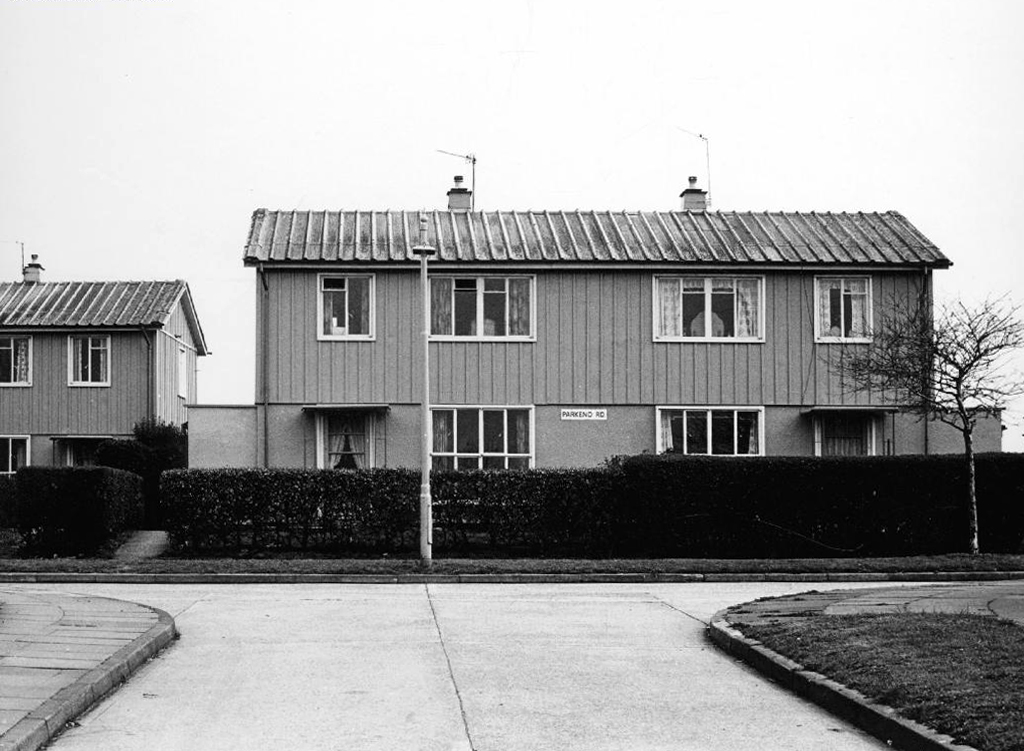
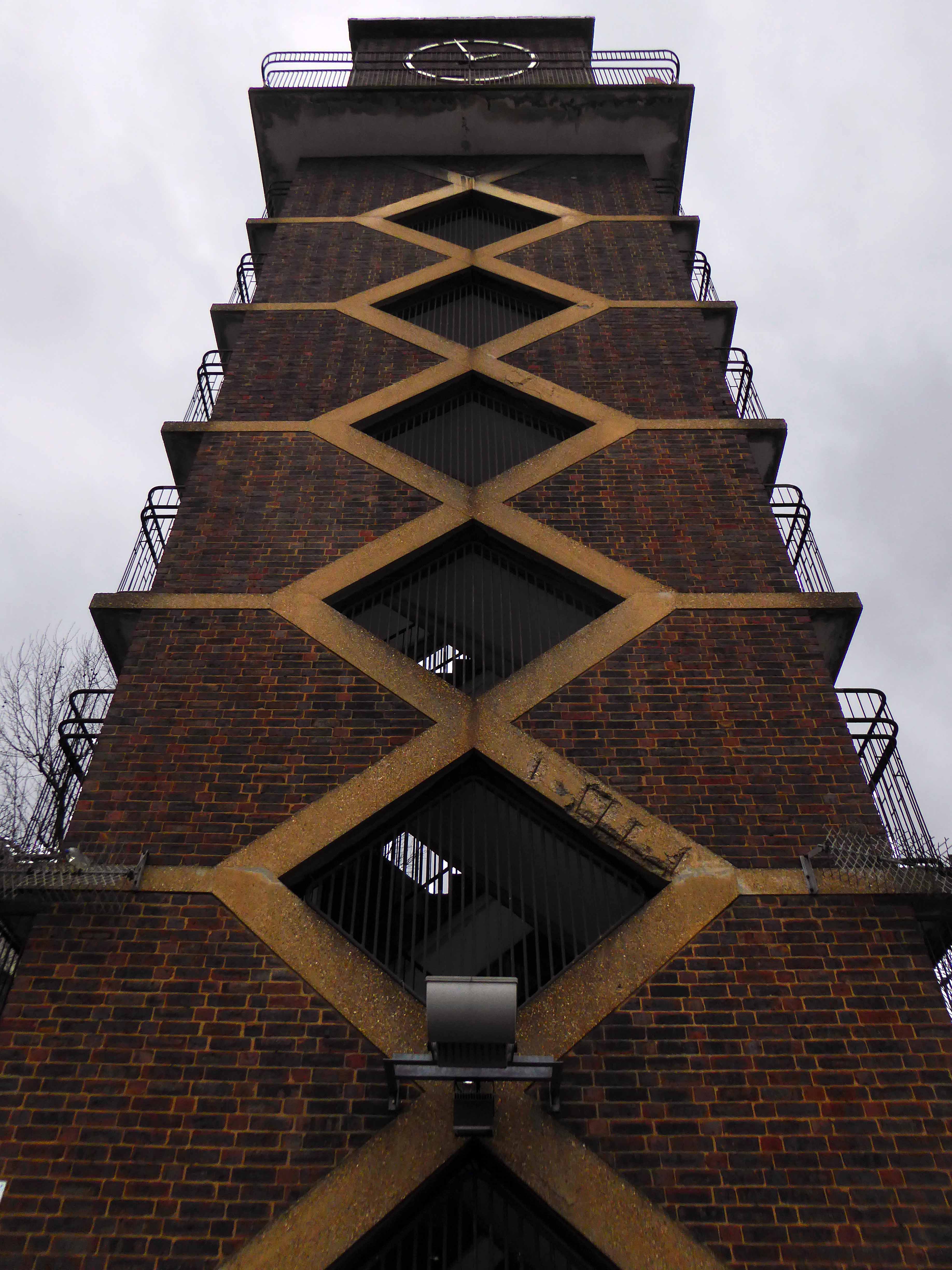
The third time by the banks of the Don – first time around in May 2019, subsequently in October 2020.
So much can change in so short a time, post-pandemic and every town is doing its level best to build back better.
The vision includes:
- Ensuring the centre is a focus for business and enterprise.
- Building on the success of the current markets and raising the aspirations and functions of the markets.
- Recognising the city core as the heart of the economy and the borough and the place where the image of Doncaster is most clearly reflected.
- Enhancing green spaces and waterways to create a better setting for visitors, investments and city heritage.
- Developing the civic and cultural quarter and reinforcing the retail and leisure core through better links and public space improvements.
- Developing city-scale functions and assets, to become a stronger draw for business, workers, visitors and inward investment.
- Developing and bidding for new city-wide cultural venues, a University and Research and Development facilities.
- Rebranding Doncaster as a location of choice for regional businesses.
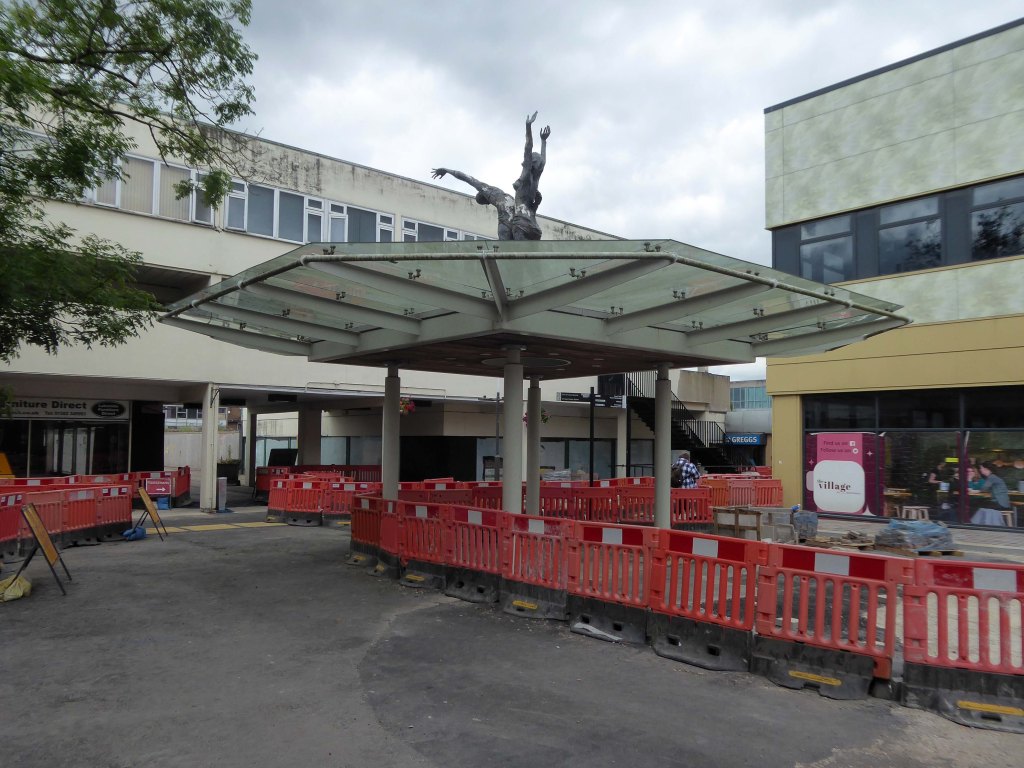
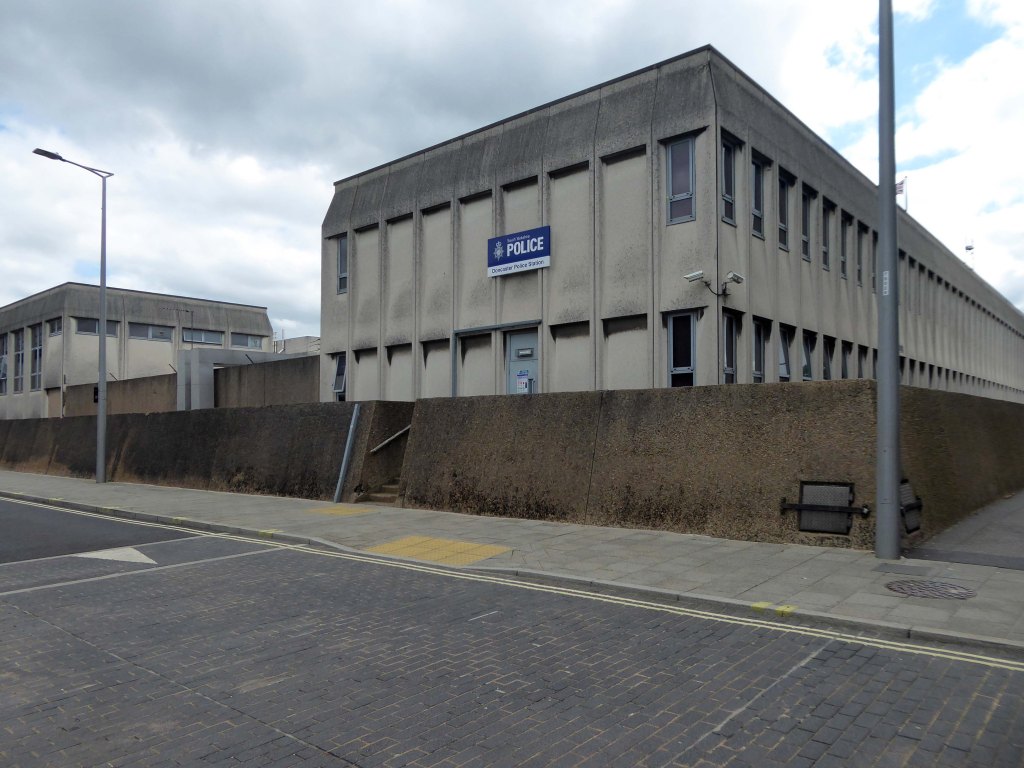
Arriving by train and ascending into the light – here’s the station lights.
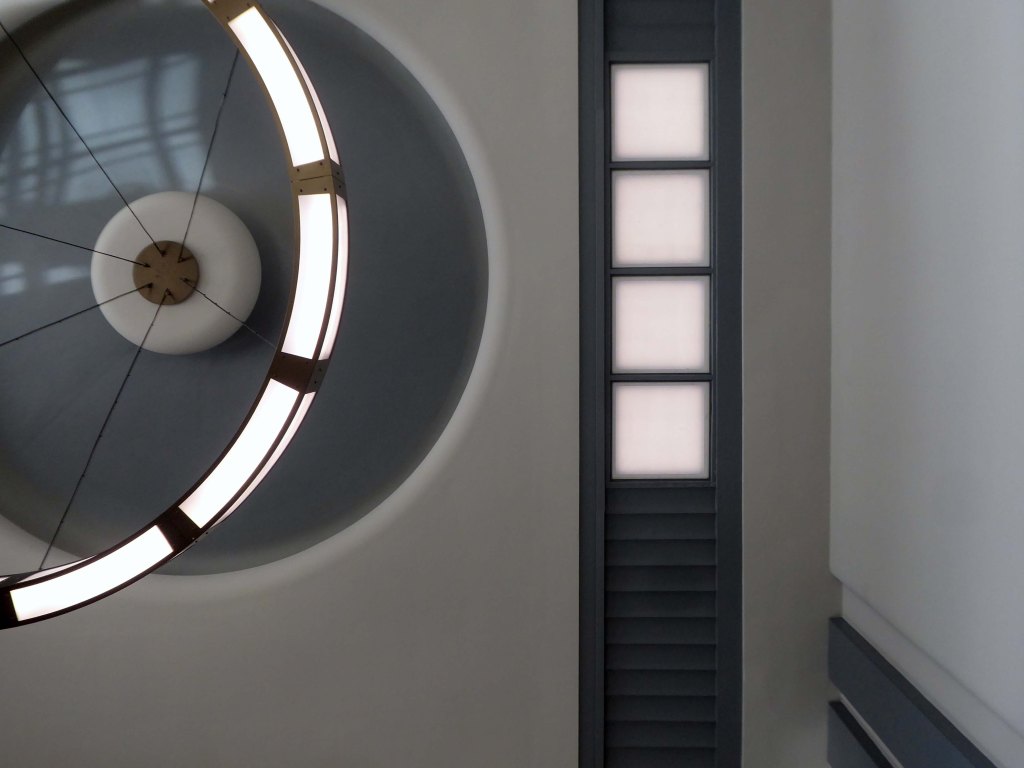

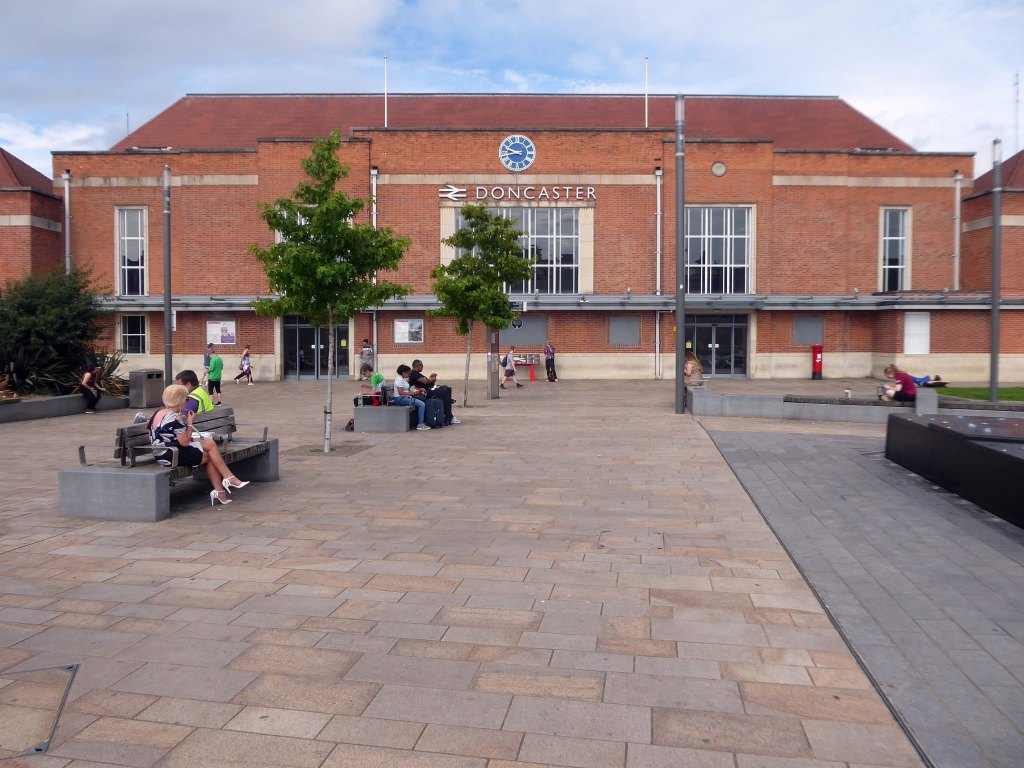
The railway station has sharpened up its apron and facade.
We have transformed the station forecourt. It has become a quality gateway which delivers a great first impression for visitors arriving in Doncaster by train. This will help stimulate interest from investors and developers, helping to attract new investment and create jobs for the borough and wider region.

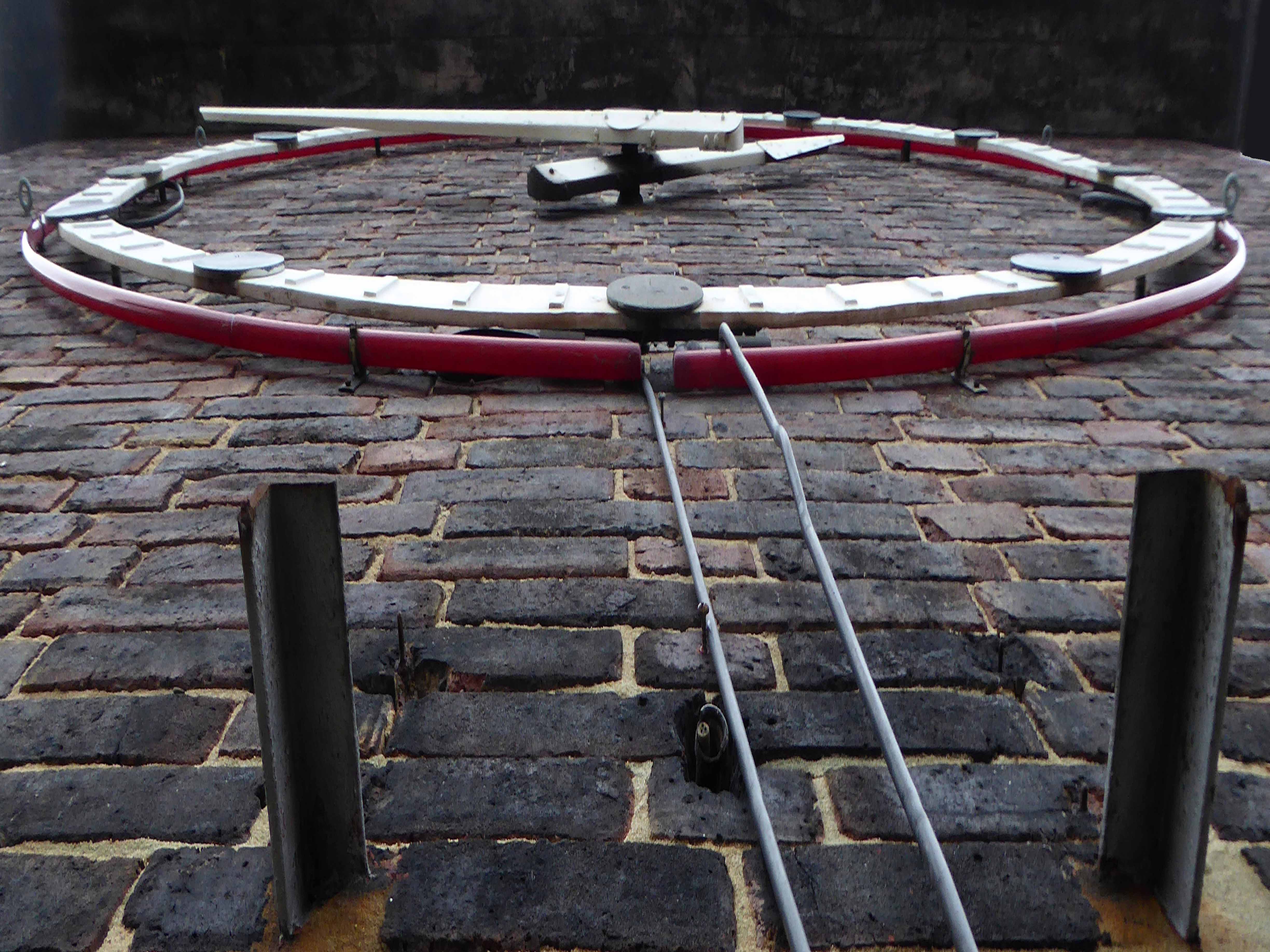
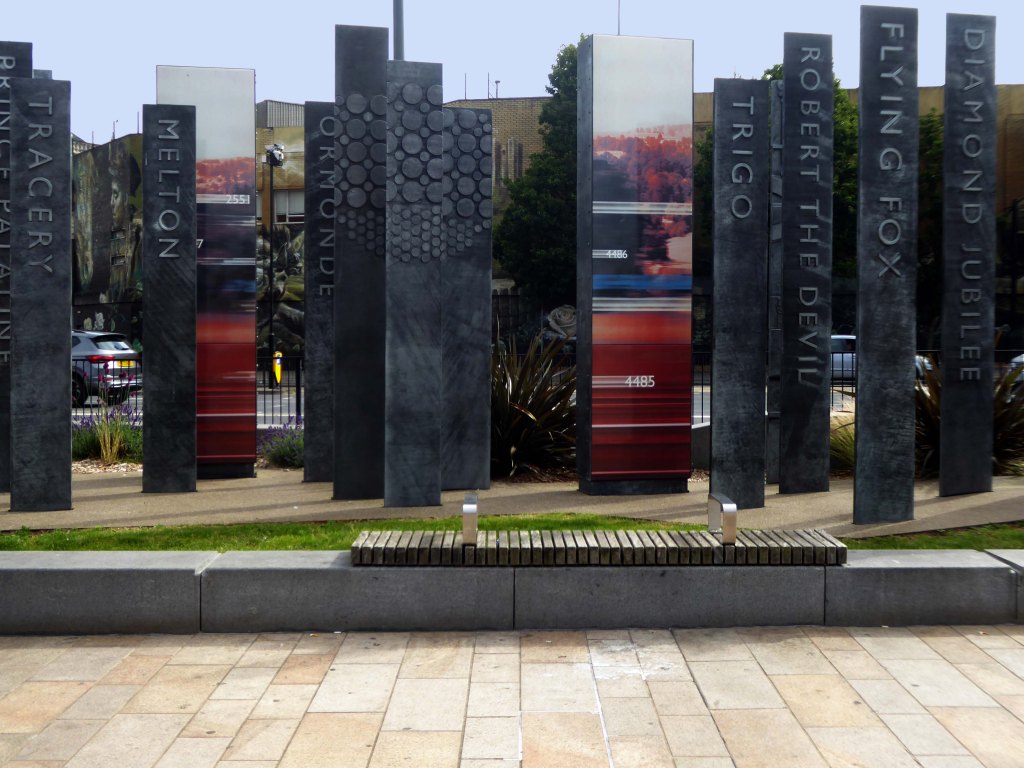
Celebrating engineering, speed and connectivity and stretching forty metres in length the public art at Doncaster Station consists of forty seven monoliths which are a nod to Doncaster’s past, present and future. With a fountain and three impressive water walls, the art takes centre stage in the new public space as you step out of the train station and head into the town centre.
The concept was devised by Doncaster Council and further developed by Chris Brammall.
CB Arts manufactured and installed the piece

Typically the high and low streets of Britain’s industrial towns and cities, are an amalgam of architectural style and fashion, spanning at least two or three centuries.
Faience fronted interwar developments abound.
Neo-classical speculative shopping arcades.

Revamped Victorian pub facades.
Behind the buff faience frontage is a lovely, small two-room pub with a well preserved interior created under plans of 1934. It was remodelled by the Grimsby brewers Hewitt Brothers Ltd who were Doncaster’s biggest pub owners for many years.

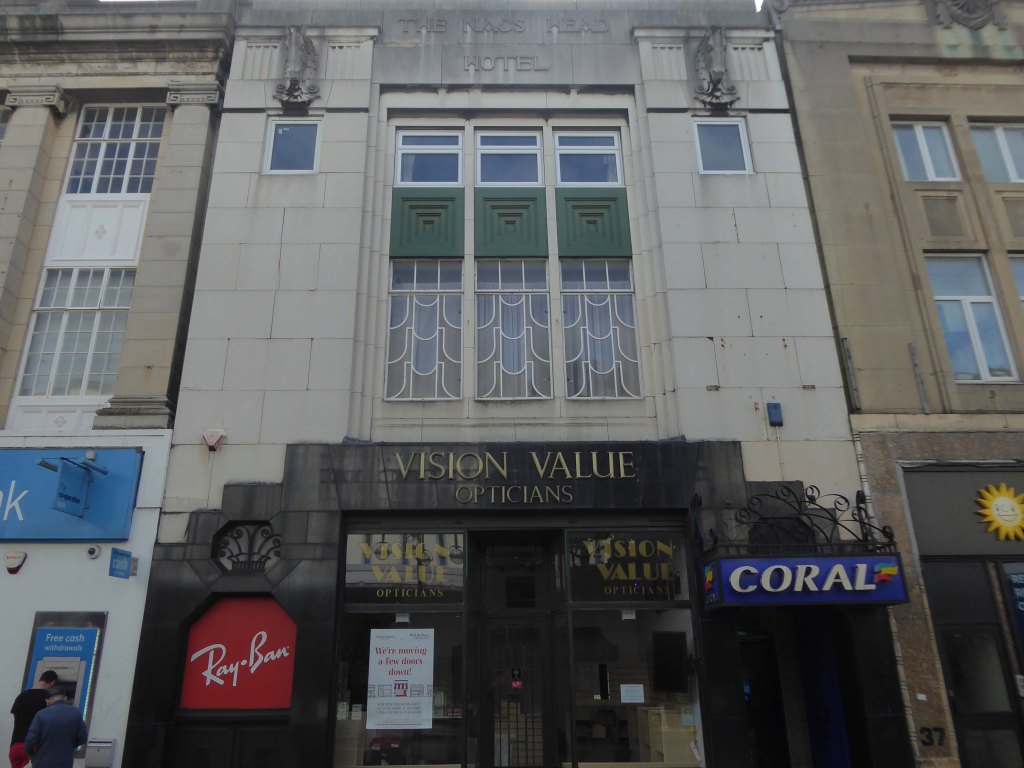
Originally a Gent’s Outfitters, this deco-gem was topped off with the Nags Head Hotel.
This grade II listed pub is now in retail use, though Vision Value, are it seems, on the move.

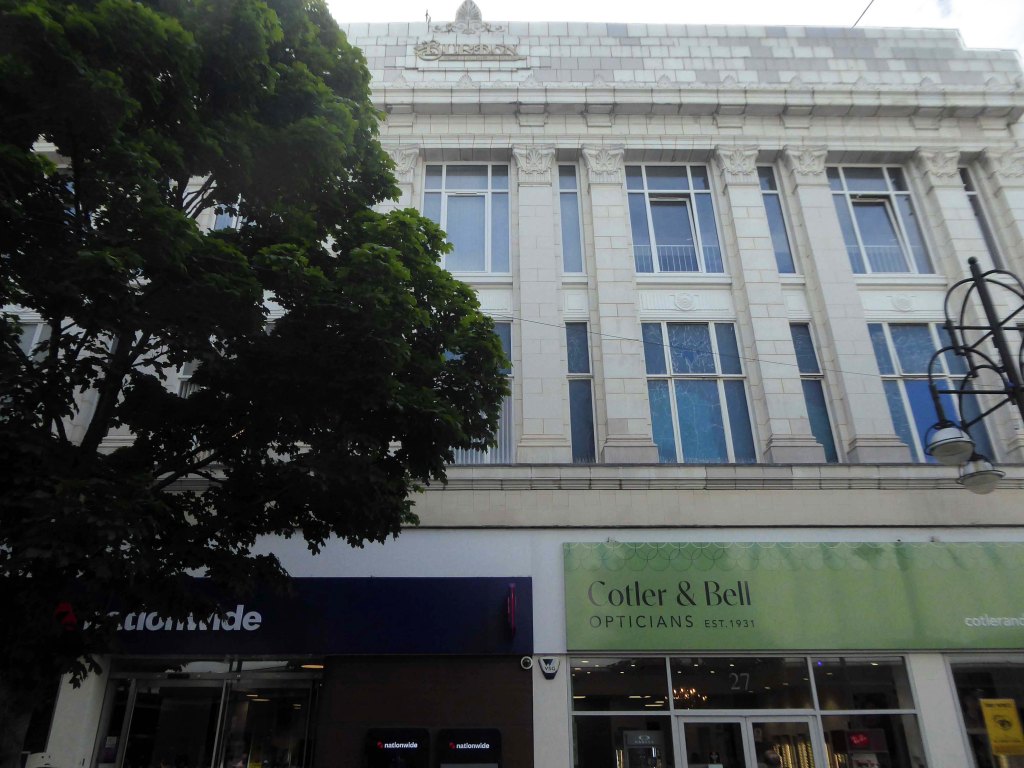
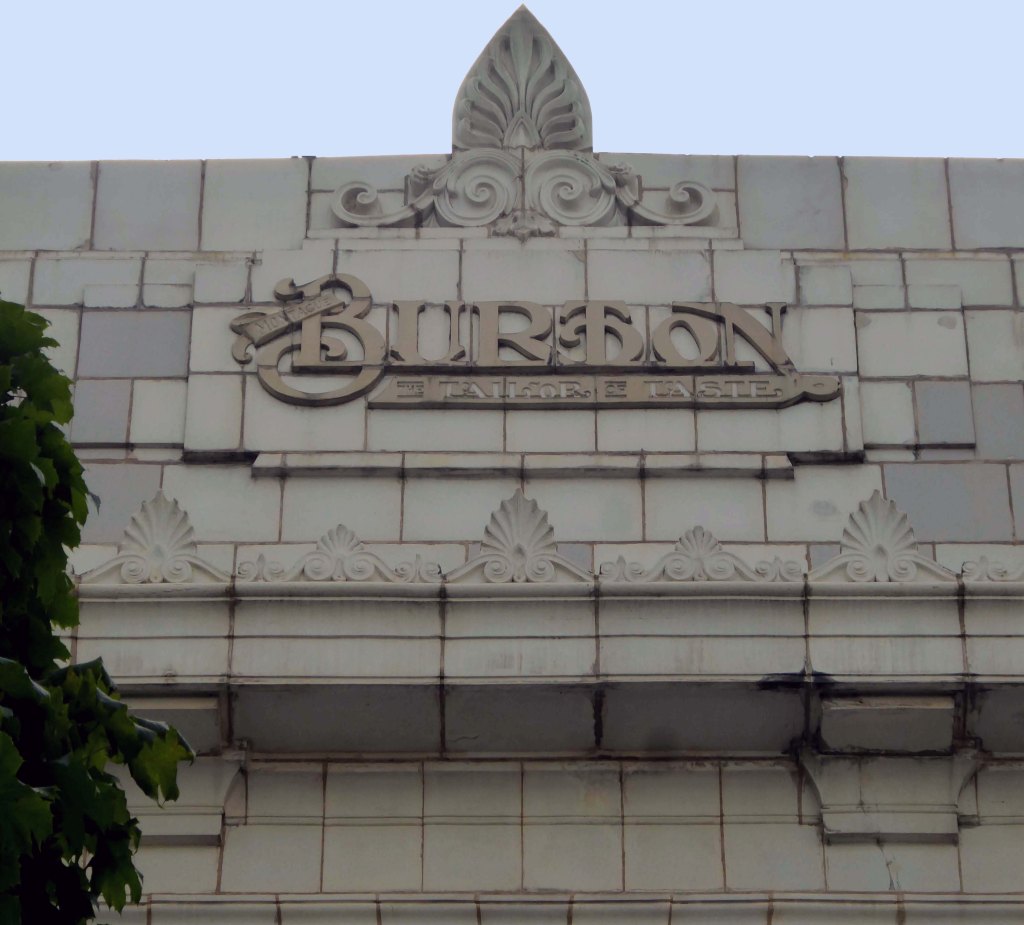
Of course, every town had a Burton’s – the tailor of taste.


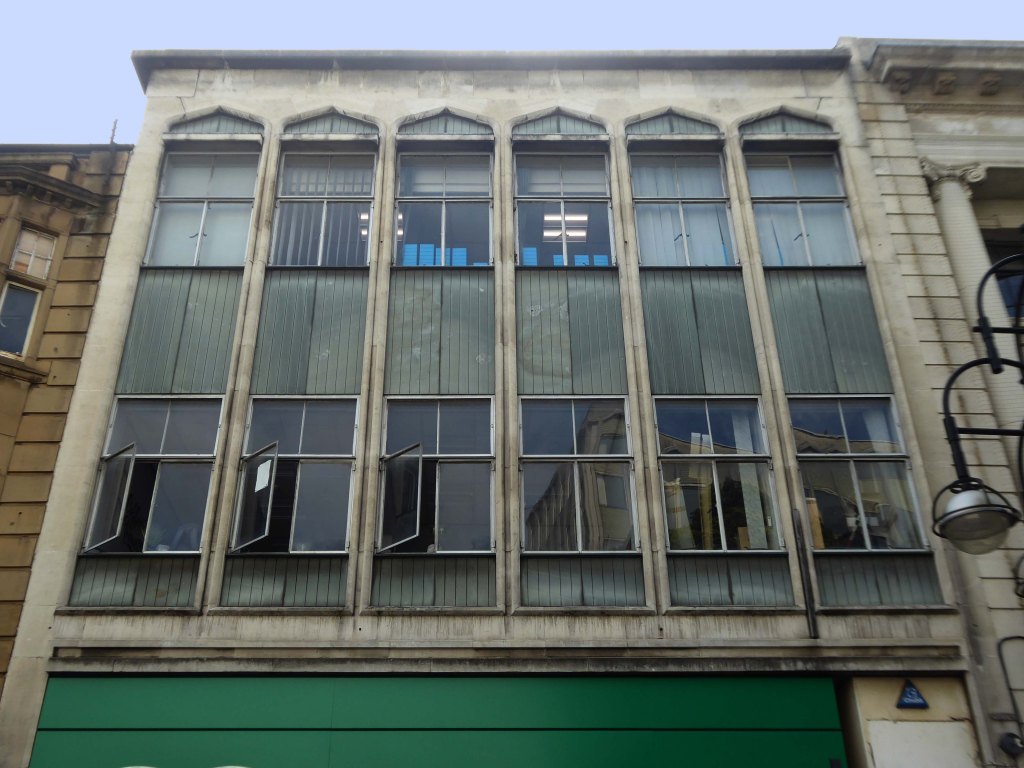
This post war infill has that distinctive Festival of Britain feel, original metal window frames, Portland stone and blueish slate like panels.

The revamped Frenchgate Shopping Centre, officially opened on October 4th 1968, has in places an upper tier, resistant to zinc over cladding.
The centre has been the heart of the city for over 40 years and was originally called the Arndale Centre because it was built, owned and managed by the Arndale Group. It was renamed in 1988 after a change of ownership, with the new name reflecting the name of the street which passes to the east of the centre and which is one of Doncaster’s main shopping streets.
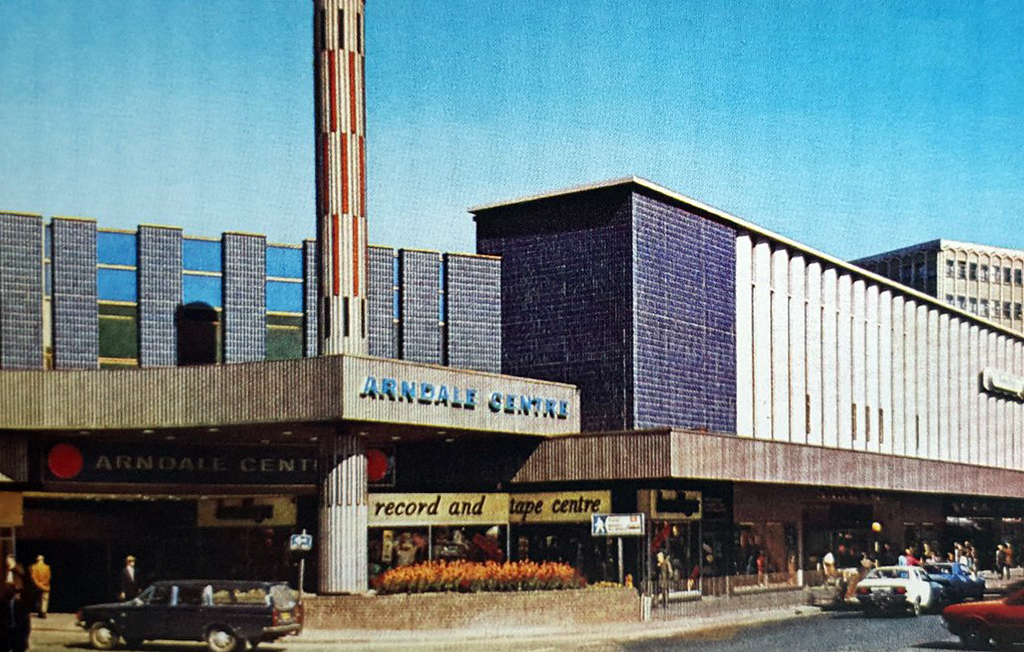

The sale of the centre came just a year after Frenchgate had undergone a £200 million facelift to transform it into the country’s first shopping centre with integrated public transport and retail interchange.
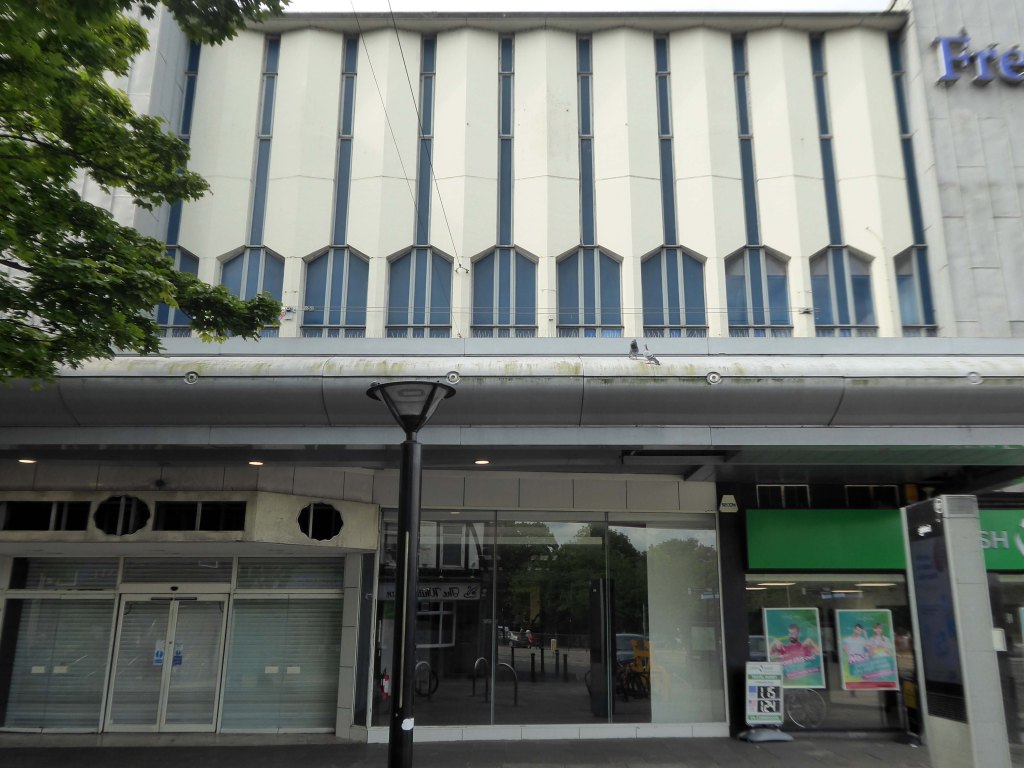

There are plans to rework the shopping centre.
We propose this is fundamentally transformed though the addition of apartments that wrap along the back of the first-floor retail with a further 2.5 new storeys placed on top. We also feel additional height -up to seven or eight storeys, is justifiable to the corner of Frenchgate and Trafford Way.
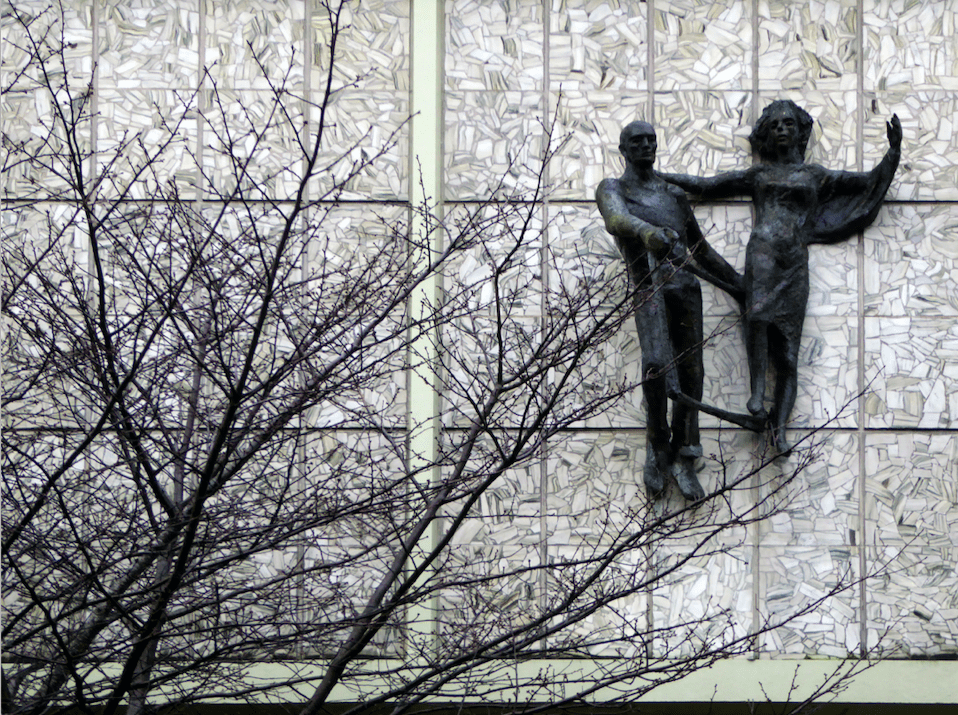
The Lovers were once located in the Arndale, removed to a local garden, unloved – then later reinstated in the Waterdale Centre, where we will embrace them a little later.
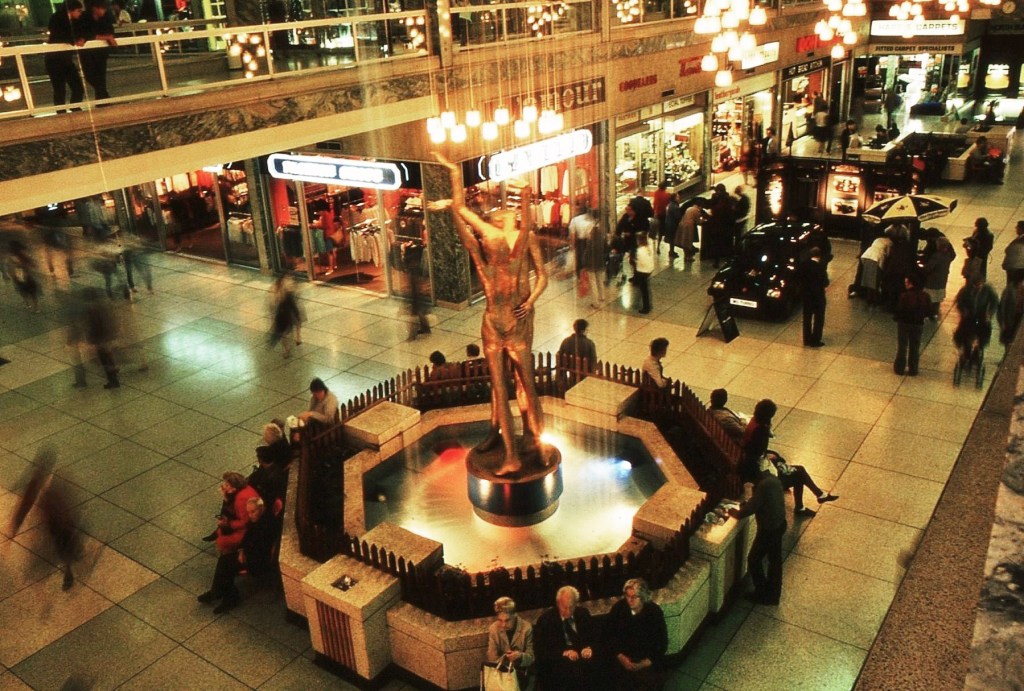

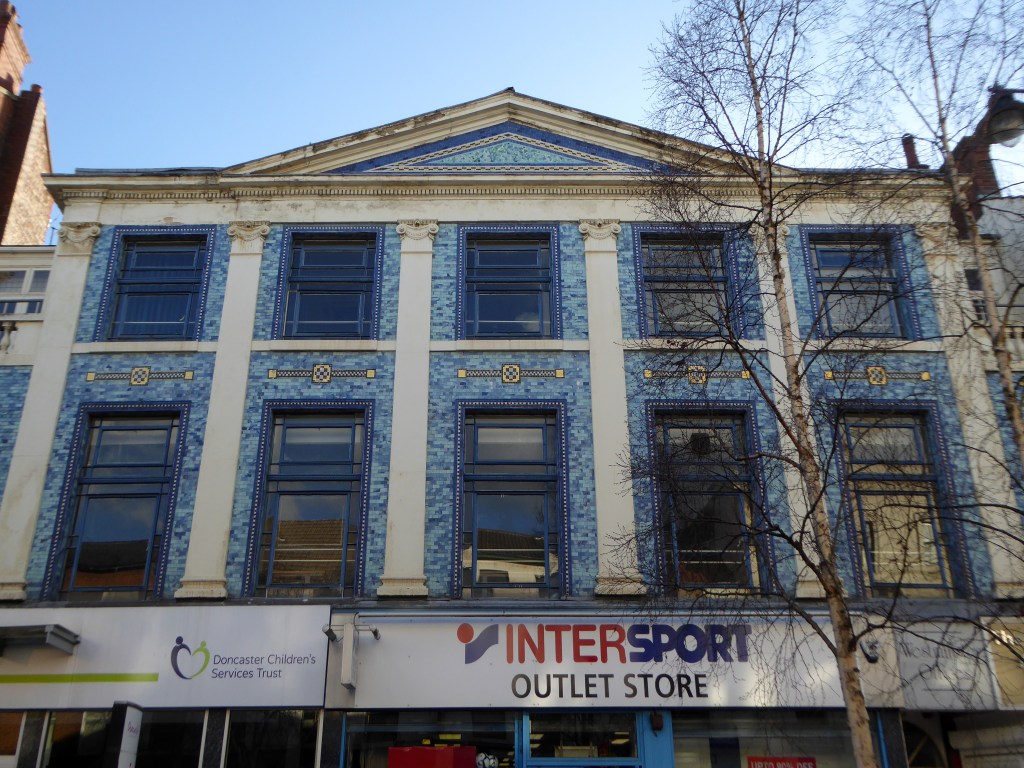
Turn right to take in the 1920s mosaic remake remodel of the Grade II listed Blue Building.
The Blue Building which used to be the Doncaster Design Centre and Tourist Information Centre was originally the home of John Whitaker, a wine merchant, and son of James Whitaker who was Mayor of Doncaster in 1758.
In 1925 the complete building was demolished apart from the facade which was retained and given a facing of decorative blue tiles. The intention was to build a shopping arcade from High Street to Printing Office Street. Only part of the arcade, known as the Westminster Arcade was built. It had a number of shops, the largest being that of Woodhouse & Co Furnishers.

Two adjacent 60s extensions – to the right a redundant post office to the left an almost redundant telephone exchange, with the earlier brick built exchange in smack dab the middle.
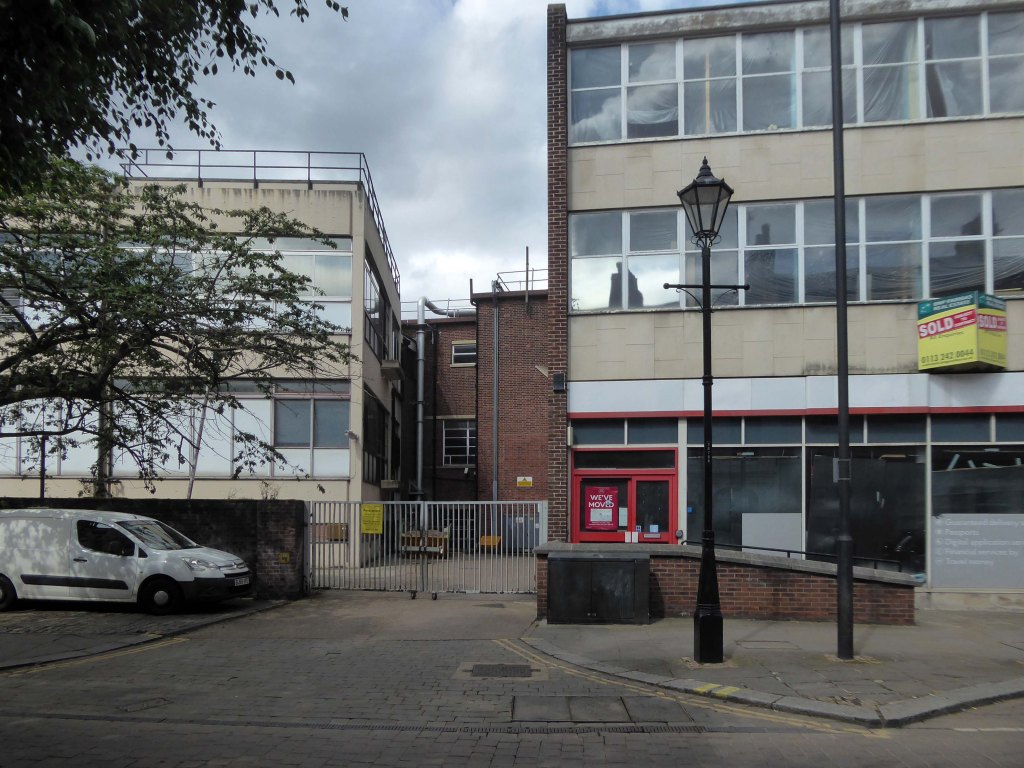

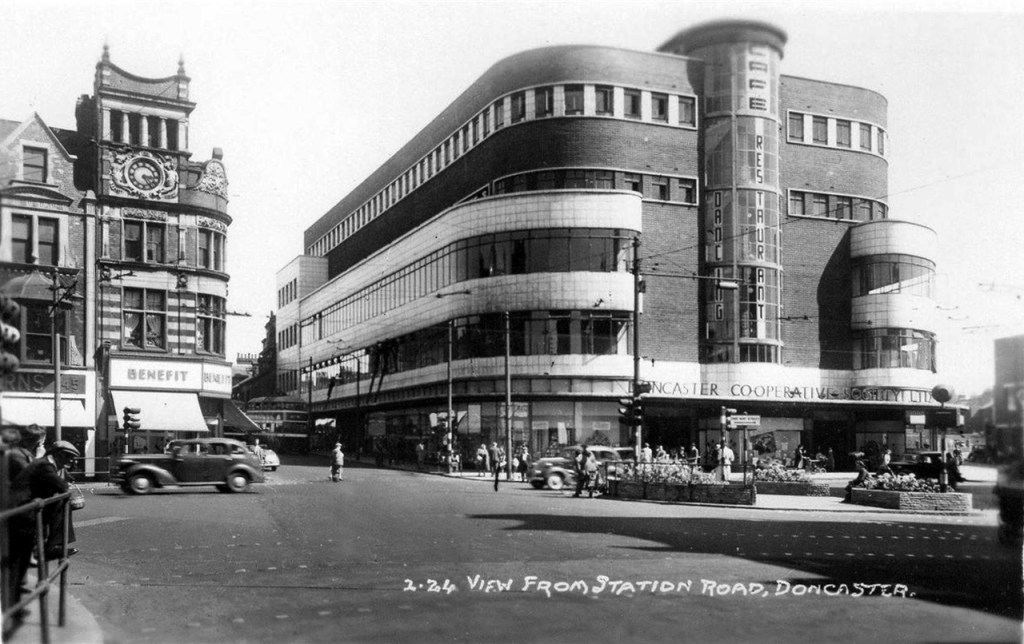
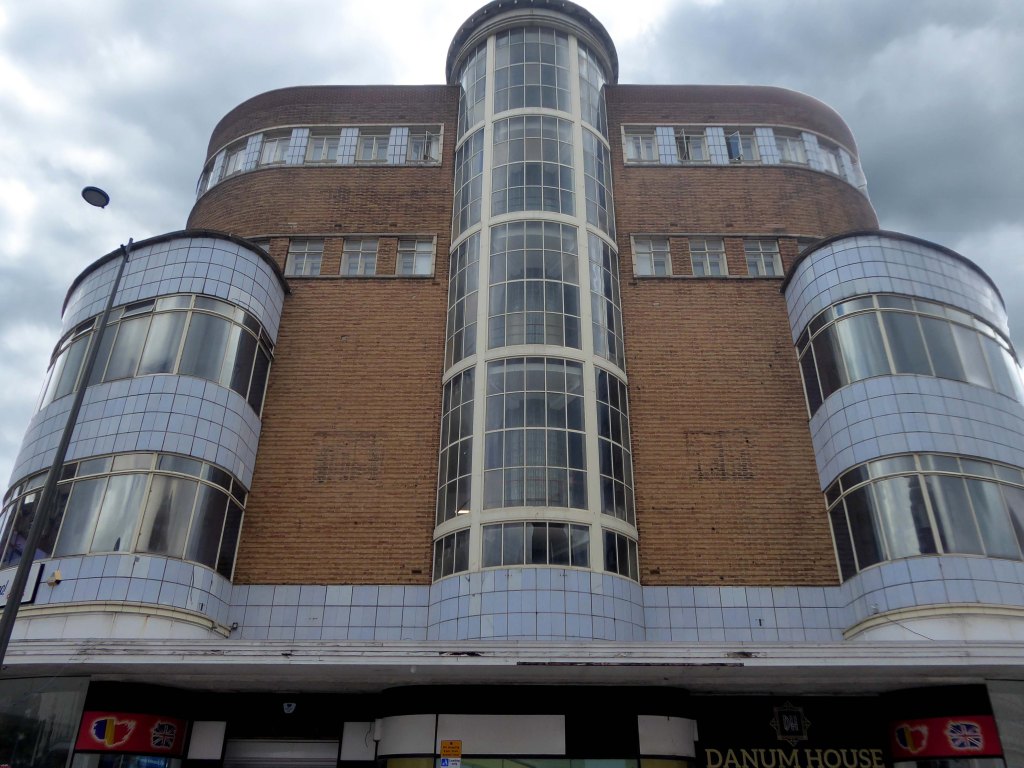
Turn another corner and it’s all at the Co-op now – the Grade II listed Danum Co-operativeBuilding, department store and offices: 1938-40 designed by T H Johnson & Son for the Doncaster Co-operative Society Ltd.


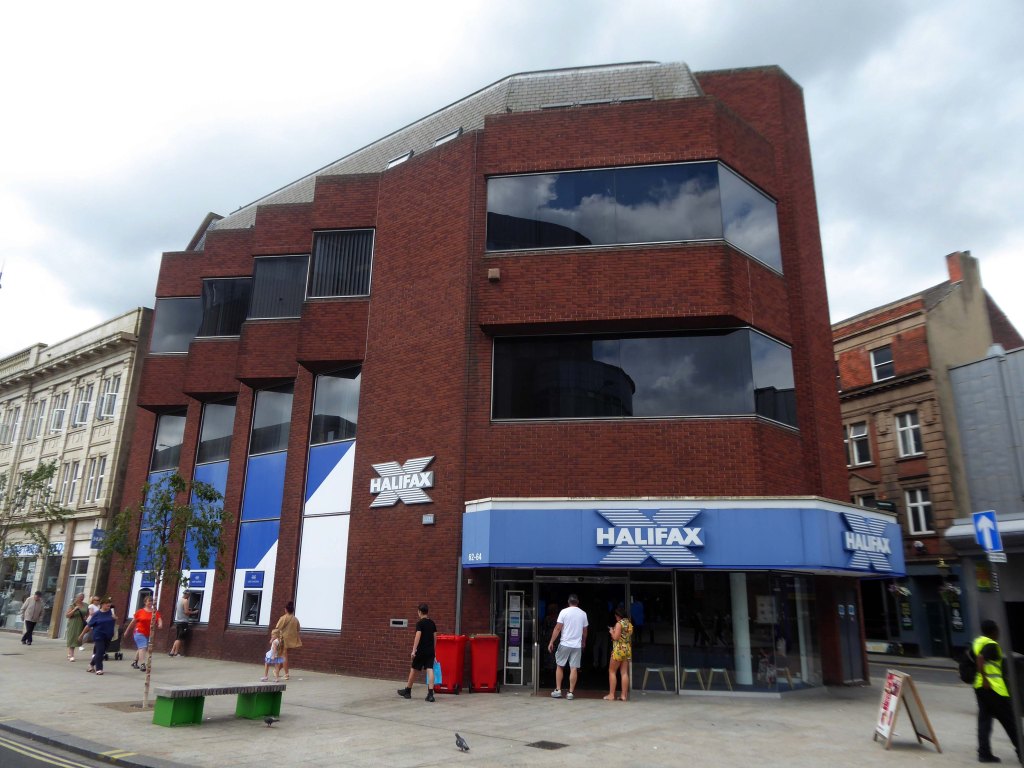
Over the road a zig-zag Halifax Building Society branch, tightly contorted by its corner footprint.

To the right of the Danum, this former Boyes store, having relocated to the Wilko site, the building is ripe for residential conversion.
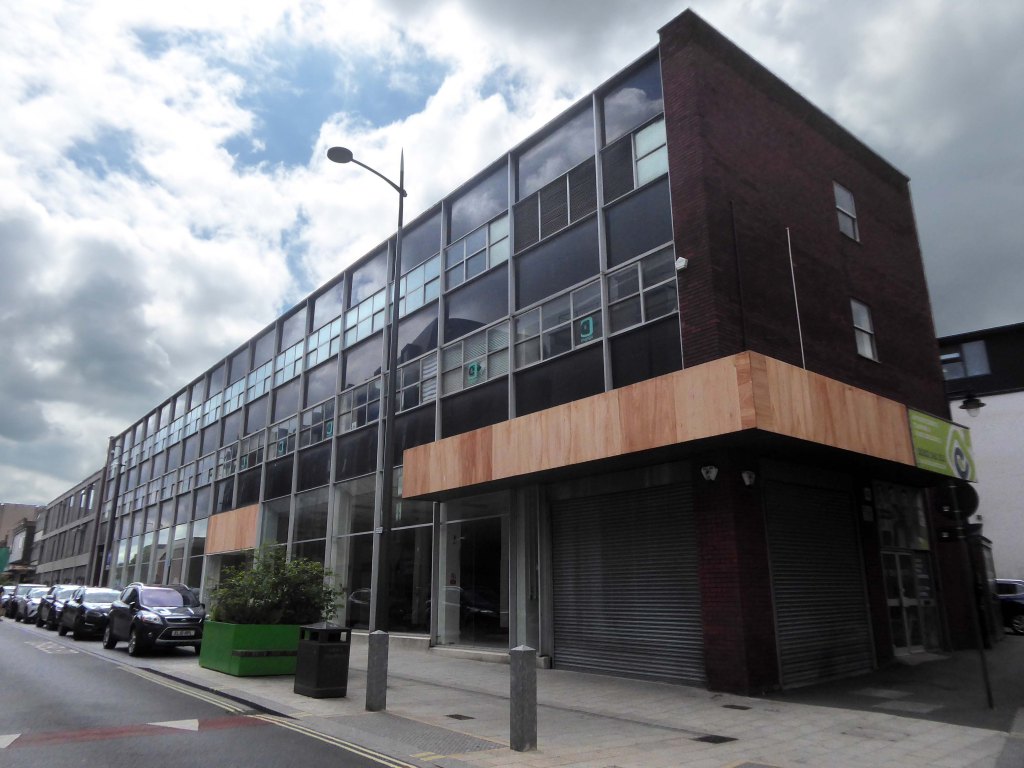

To the left the Colonnades Shopping Centre a fierce angular glass and brick bunker of mixed office and retail space – the sole occupant seeming to be Home Bargains.
A £3.3m makeover of the Colonnades shopping mall in Doncaster town centre was completed in 2019.
The scheme of works was co-ordinated by Doncaster Council and funded by the Sheffield City Region Local Growth Fund.
Built in the 1980s, the brick built building received a major overhaul. The investment saw the visual appearance enhanced inside and out. The five floors were transformed into the prime office space needed in the town centre and the enhancements to the retail area were also finished.
The shift in the town’s axis to the Frenchgate and Market areas, seems to have taken the wind out of its sails.
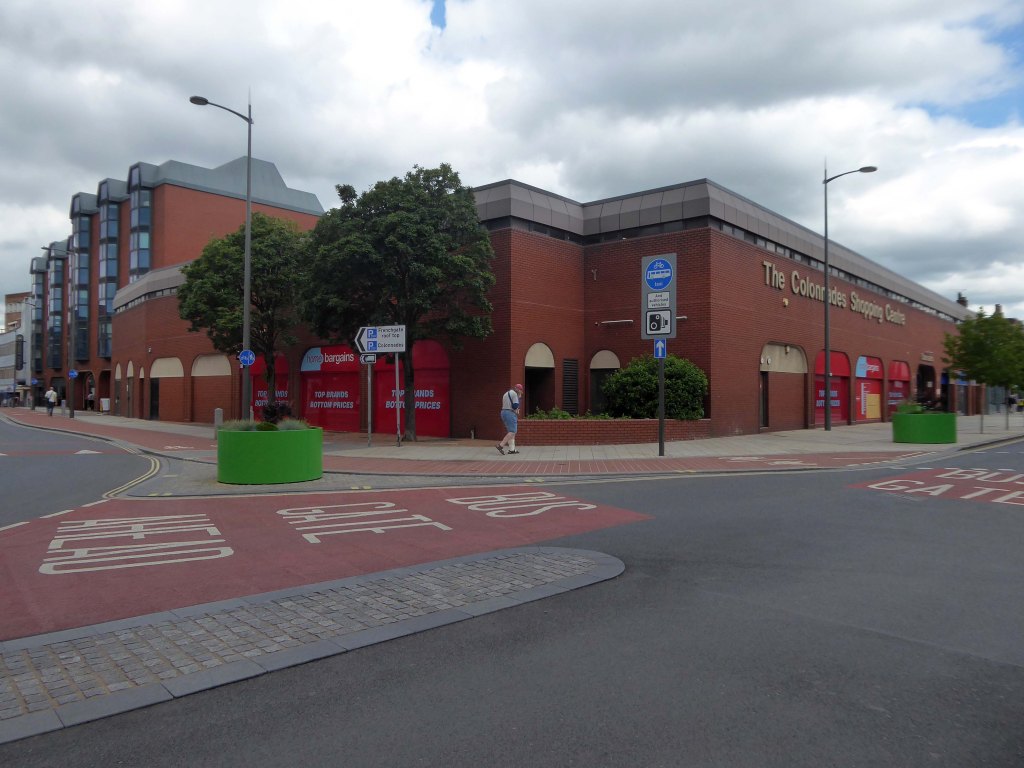

The former flicks now a redundant pale brick behemoth – no more and ABC.
Architects: C Jack Foster and Alan Morgan
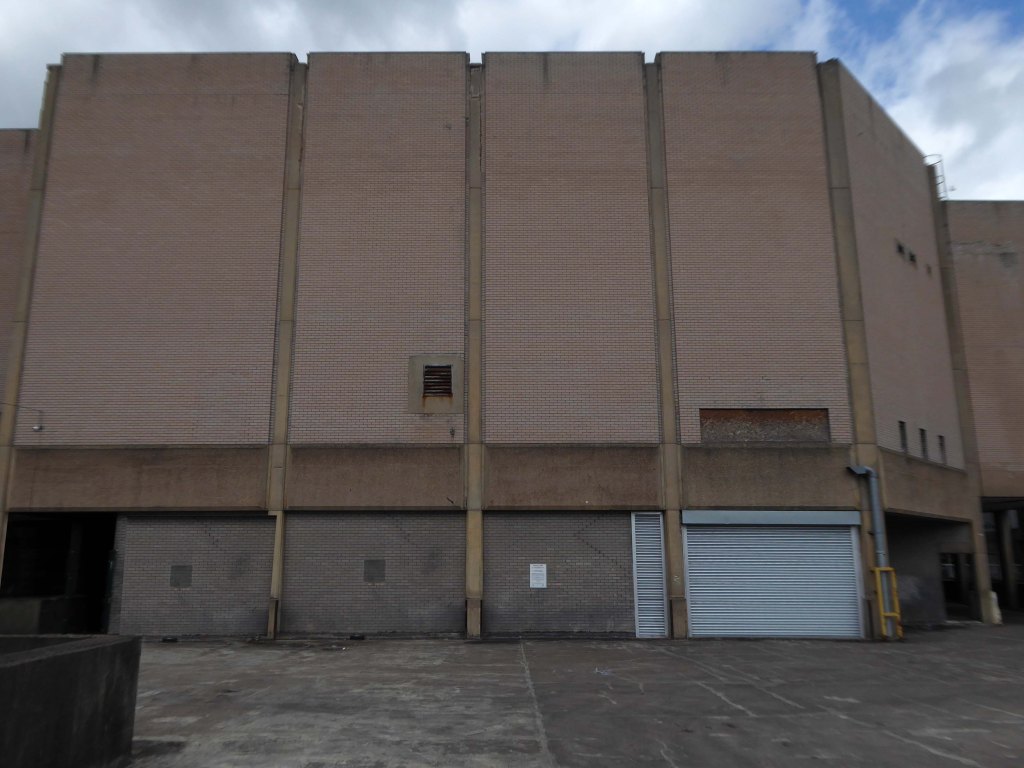

Doncaster’s new £250,000 ABC cinema, part of the Golden Acres development near the town centre, was opened on May 18th 1967.
Closed in January 1981 for conversion into a triple screen it re-opened on 9th April 1981 with seating in the three screens for 477, 201 and 135.
The Cannon Group took control in the mid-1980’s and it was re-named Cannon and it closed on 18th June 1992, screening its opening film Doctor Zhivago.
Cinema Treasures

The Golden Acres development seemed to have morphed into the Waterdale Centre.
It is currently being reshaped to provide a line of desire twixt the Civic and Cultural areas, from the town centre. There are still the remnants of homes, shops and a pub amongst the demolition – almost inevitably there is new paving.
Waterdale is a well-known part of Doncaster’s town centre. During its heyday it was a bustling area with people flocking to shops and the like – it was a place you had to visit while you were in town. However, it had suffered a steady decline which continued when the southern bus station closed – Frenchgate Interchange opening, and Doncaster College moved to the Hub at the Waterfront. With limited public transport entering the area and no student population on its doorstep, less people had reason to pass through.
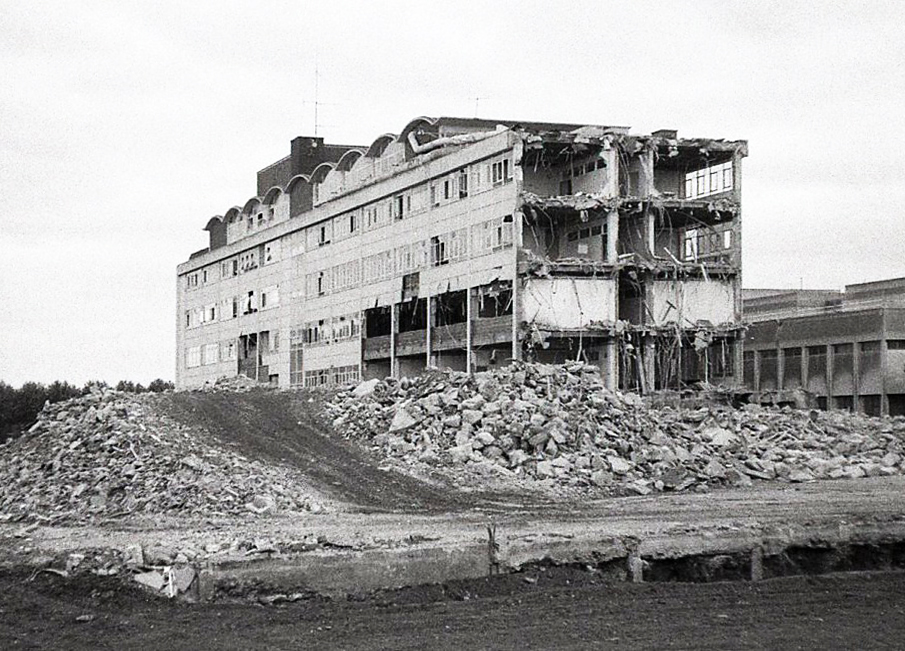

Demolition of the College.
The Civic and Cultural Quarter is transforming Waterdale reconnecting it to the town centre. The quality and content of the plans is raising the profile of this part of town to new levels. The carefully thought out layout and consistent building design is giving the area a clear identity. It is already becoming a big attraction that draws people in and encourages redevelopment in the neighbouring areas.
The relocated Lovers are still in love.


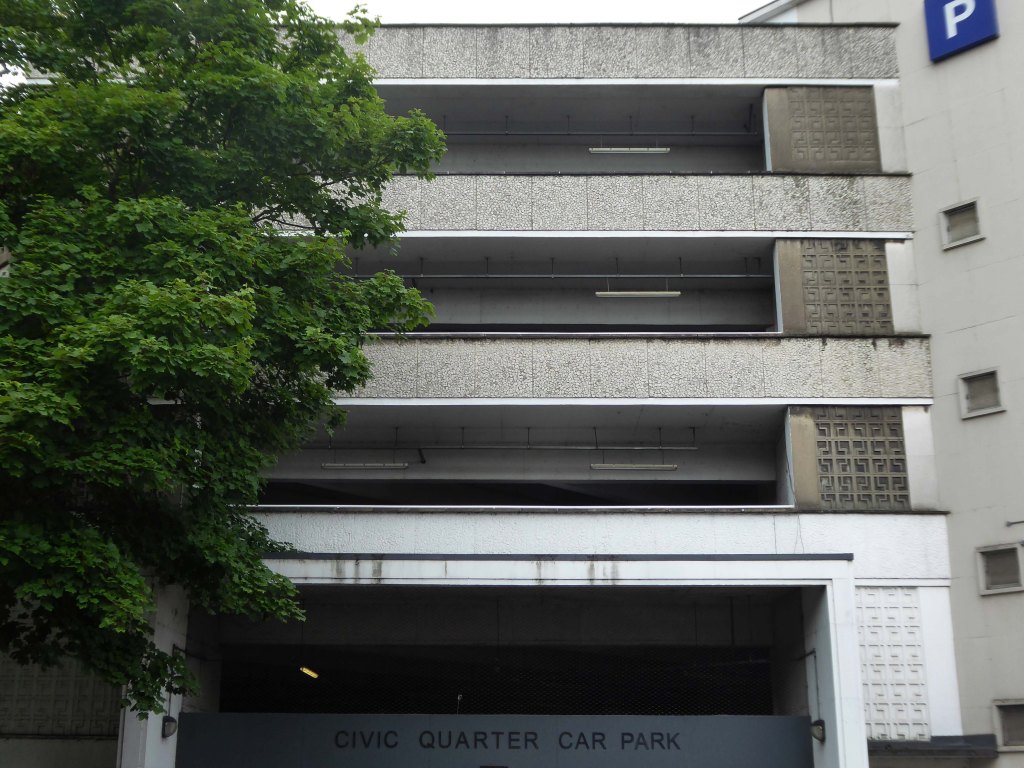
The weary walker is diverted toward the Civic Quarter Car Park.

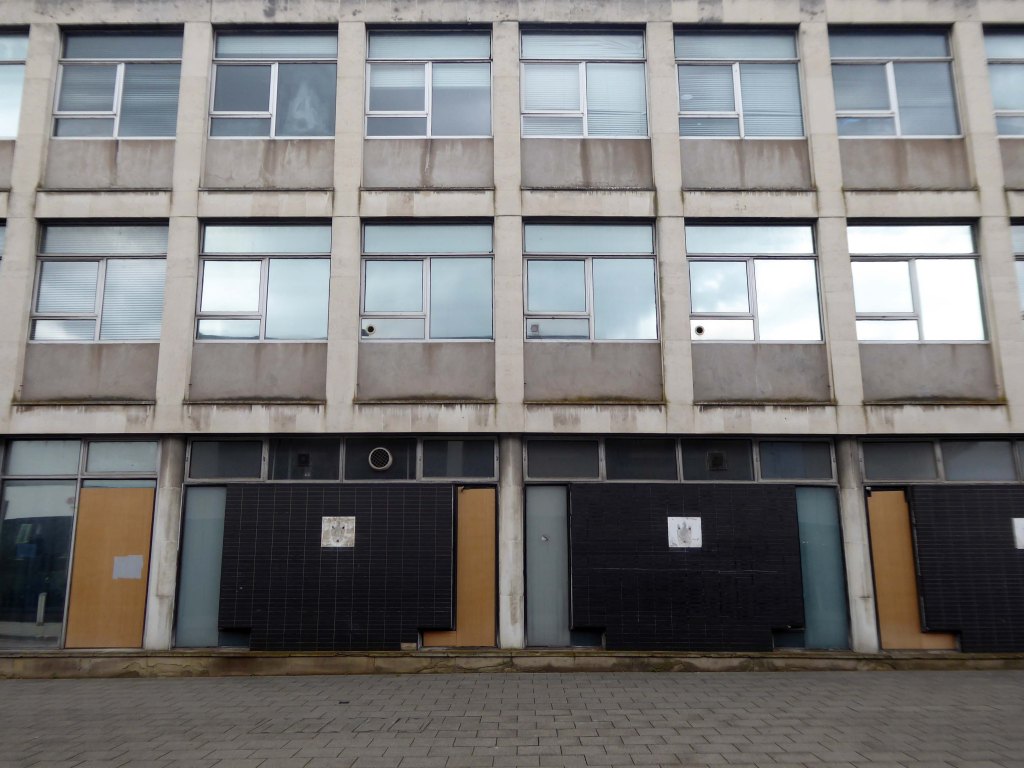
The former Civic Offices are to be demolished.

Demolition of the Central Library is well under way.
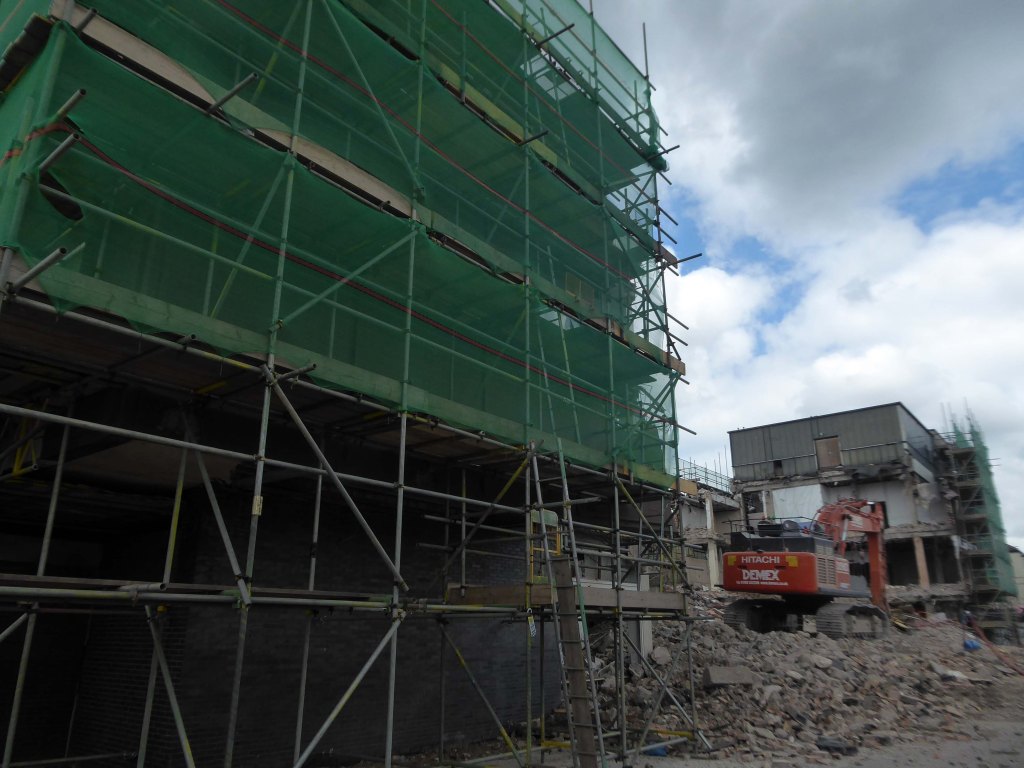

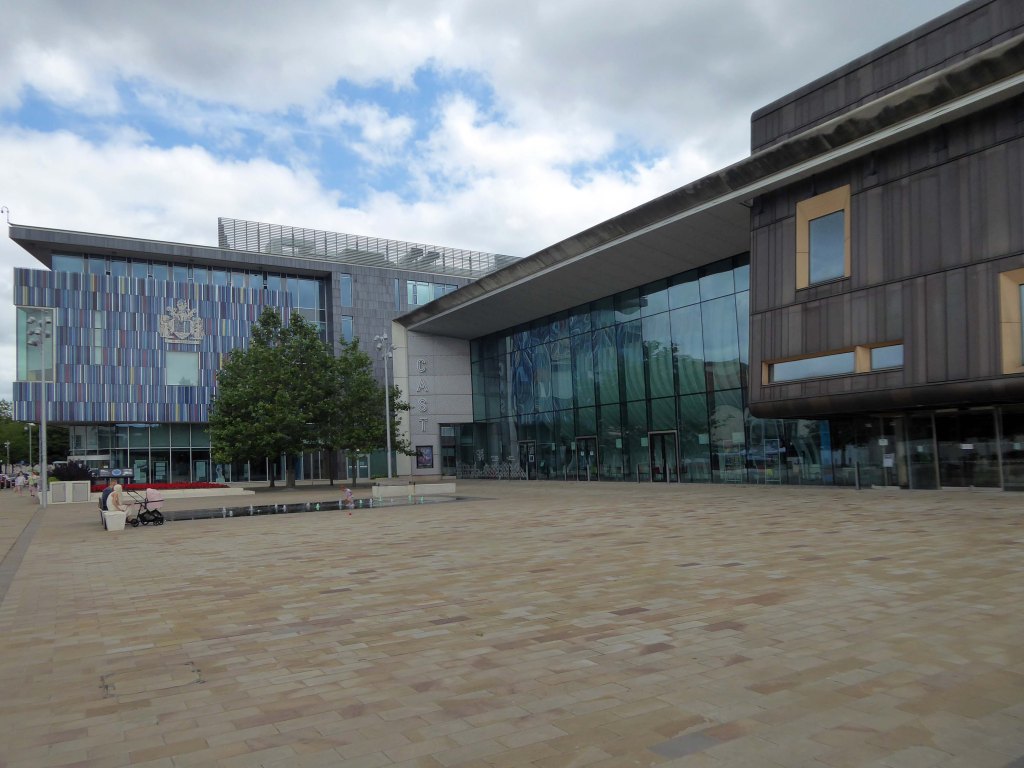
Facing the former library we find the CAST Theatre, Civic Buildings and Savoy Cinema, grouped around Sir Nigel Gresley Square.

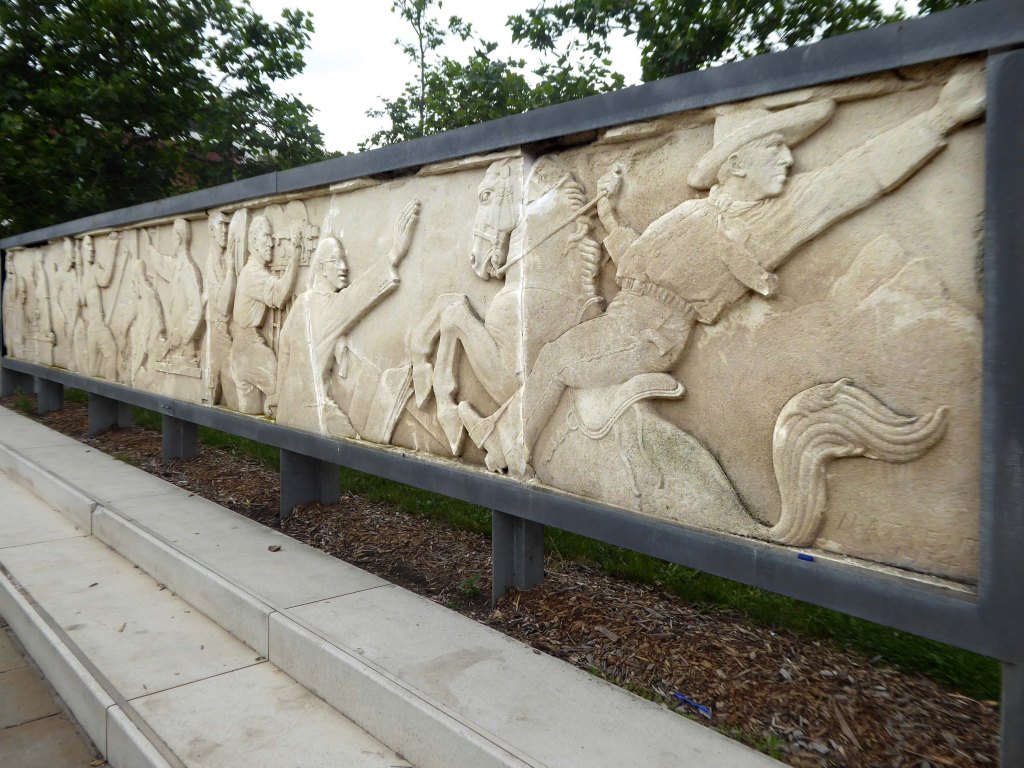
Within the square is a frieze, salvaged from the former Gaumont Cinema, the work of sculptor Newbury Abbot Trent.

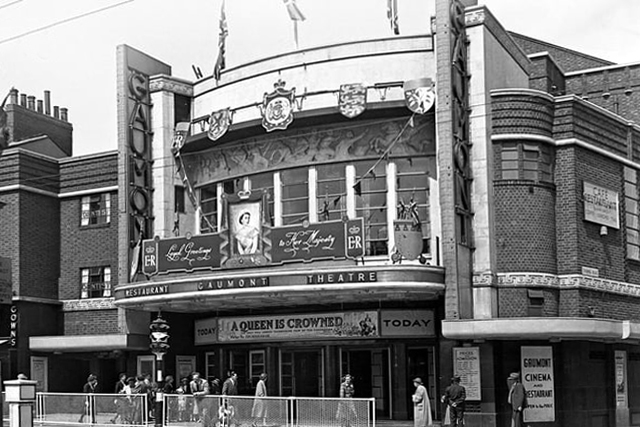
The Gaumont Palace Theatre in Hall Gate at the corner of Thorne Road, Doncaster opened on 3rd September 1934 with Jesse Matthews in Evergreen.
It was designed by architects WE Trent and W Sydney Trent.

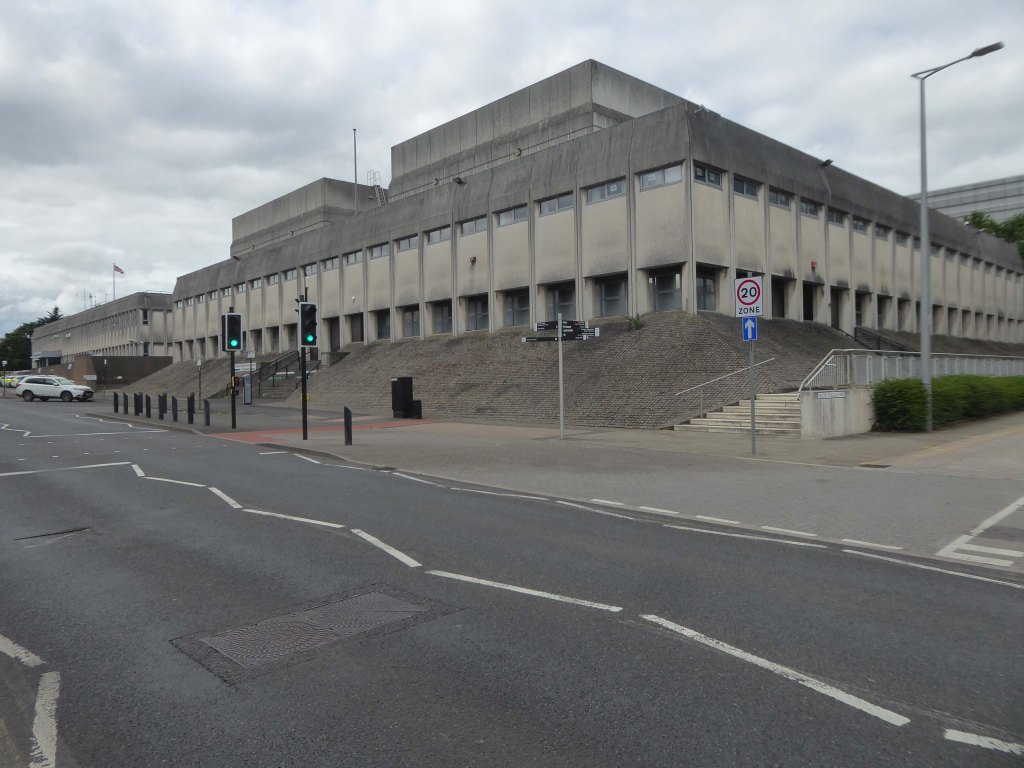
In 1949 WH Price the Borough Surveyor produced an outline plan for the area, with a green space at its heart, it was never realised. In 1955 Frederick Gibberd produced his plan to include a ten storey Town Hall, Art School, Technical College and Civic Theatre, revised and reduced in 1963 – eventually his Police Station and Law Courts were completed in 1969.


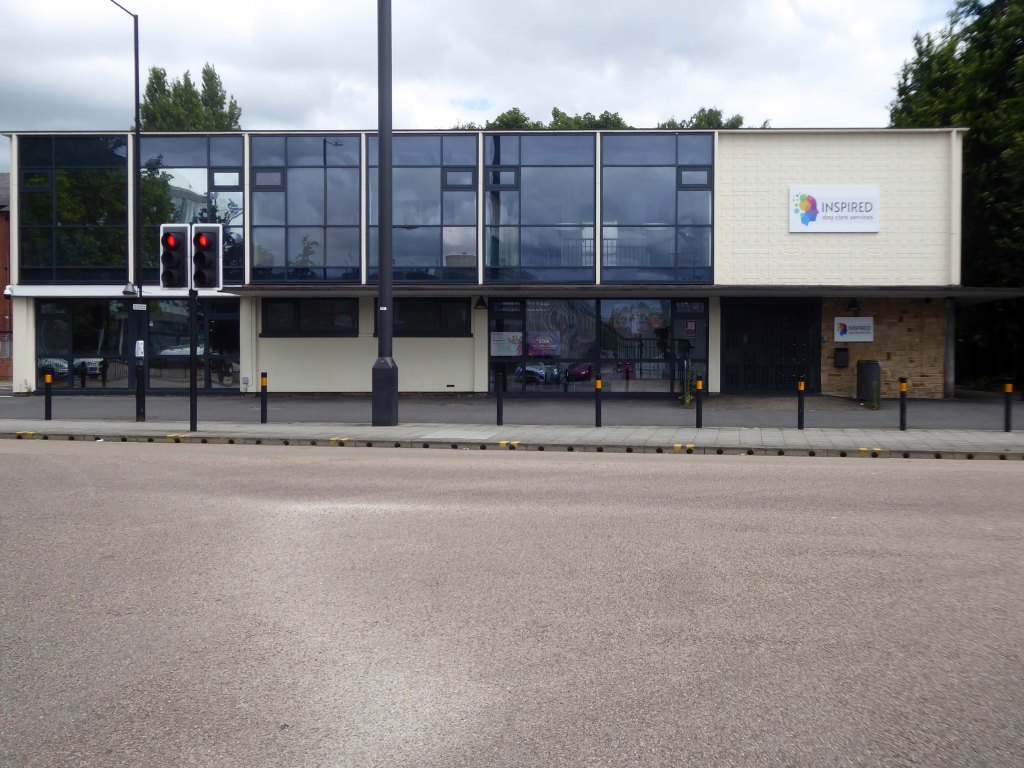
The former NHS Clinic at the ‘T Junction’ is transformed into a day care service.

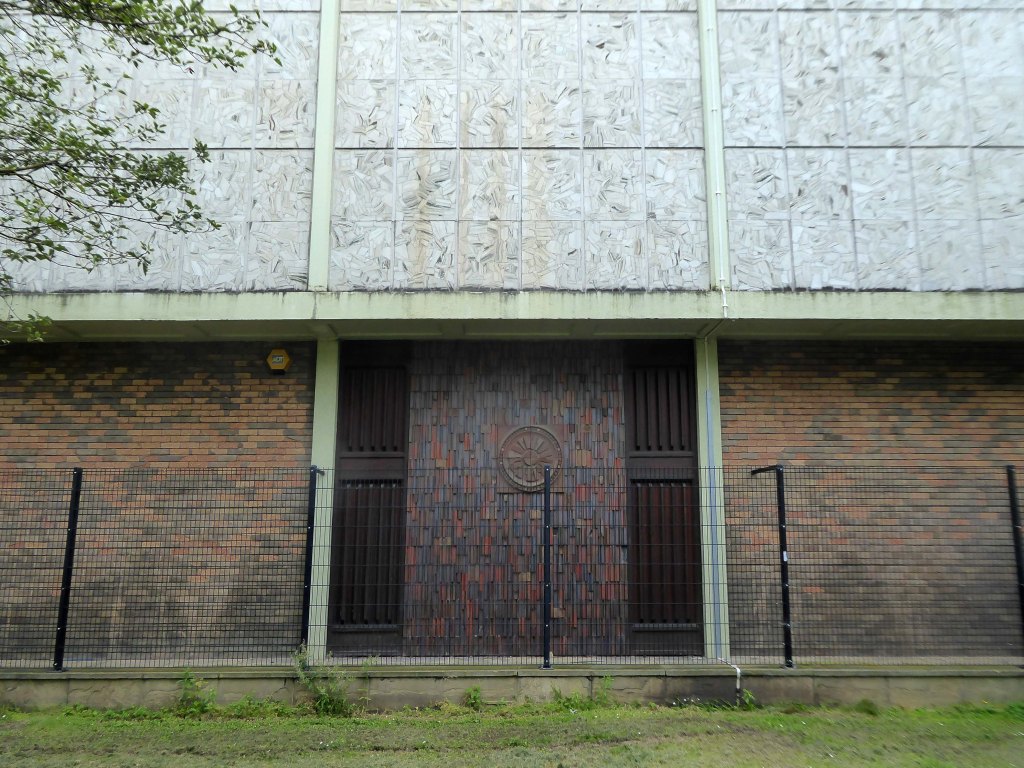
The former Museum and Art Gallery now an archive and local studies centre.
The building was designed in the office of the Doncaster Borough Architect’s Department in a team led by borough architect Mr LJ Tucker.
The ceramic designs were a later addition when it was discovered that the large open areas of glass overheated almost everything inside, the work was undertaken by LJ Tucker and family.

The sculptural work by Franta Belsky, now has a skip for company.

As a footnote the work by Fabio Barraclough reveals a murky past.
Barraclough was born in Madrid in 1923, to a Spanish mother and Yorkshire father who founded Madrid’s Chamber of Commerce. He moved to London with his family in the 1930s as a refugee from Francoist Spain. He taught fine art and sculpture at Rugby School, where colleagues considered him “highly entertaining, a most unorthodox and highly gifted” teacher. He established himself during the 1960s and early 1970s as an authority on sculpture, publishing in academic journals and becoming a member of the Royal British Society of Sculptors.
In 2000, it was revealed that Barraclough, while outwardly living the life of anti-apartheid activist since the 1970s, had been a paid informant of the South African state security police. The media was used to promote his image as a “brilliant, liberal artist with apparently impeccable credentials” in order to gain public trust, while he was funnelling money from anti-apartheid groups to the police. He died on 6th January 2019.
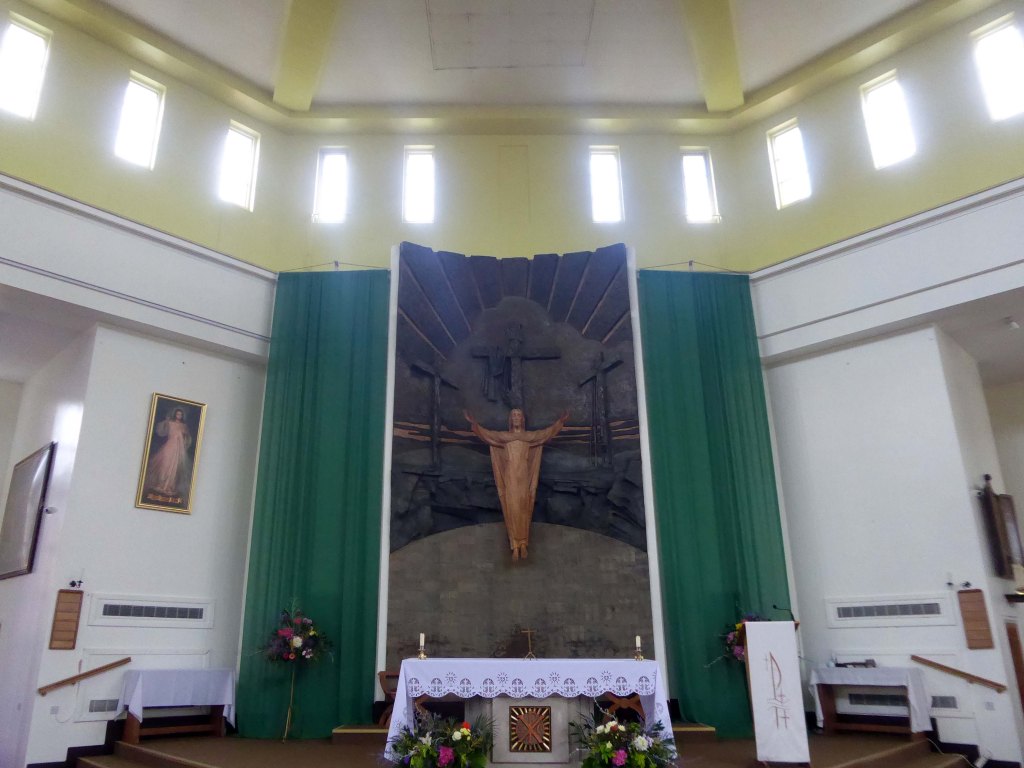
Over the way faros the green sward is St Peter in Chains RC – A large and striking design by JH Langtry-Langton, incorporating important furnishings by J F Bentley from the predecessor church, along with good furnishings of the 1970s. The churches houses the modern successor to the medieval shrine of Our Lady of Doncaster.
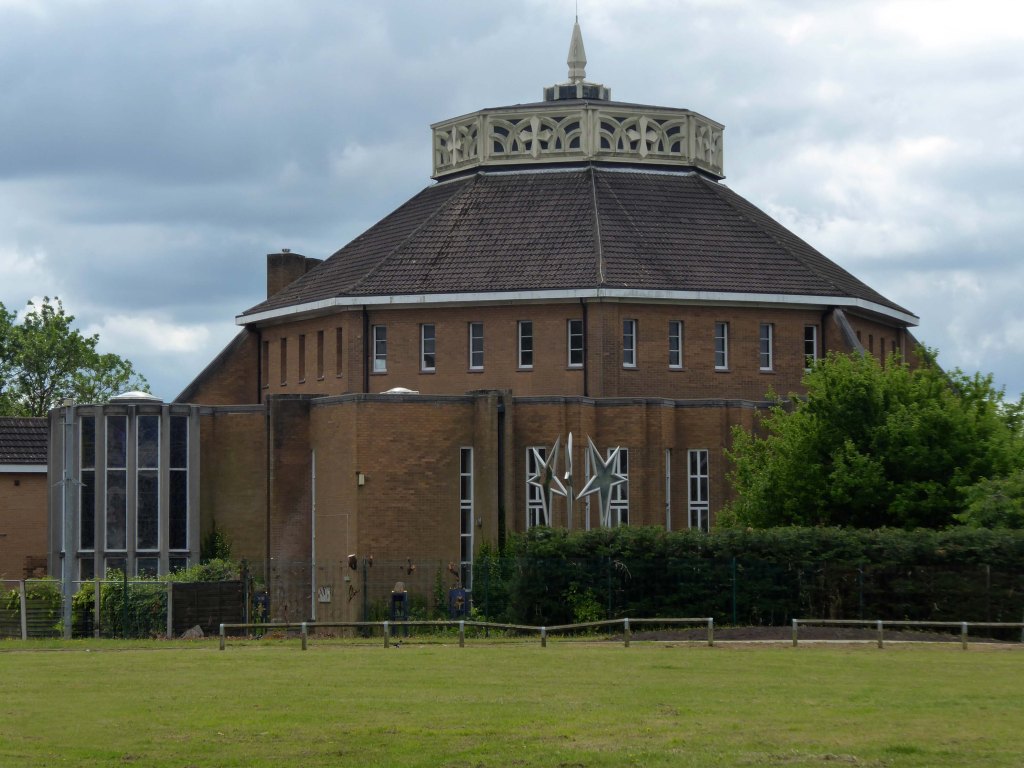


Figurative stained glass by Patrick Feeny for Hardman in 1973 and abstract glass fitted in 2000 as part of reordering and revival of the shrine.
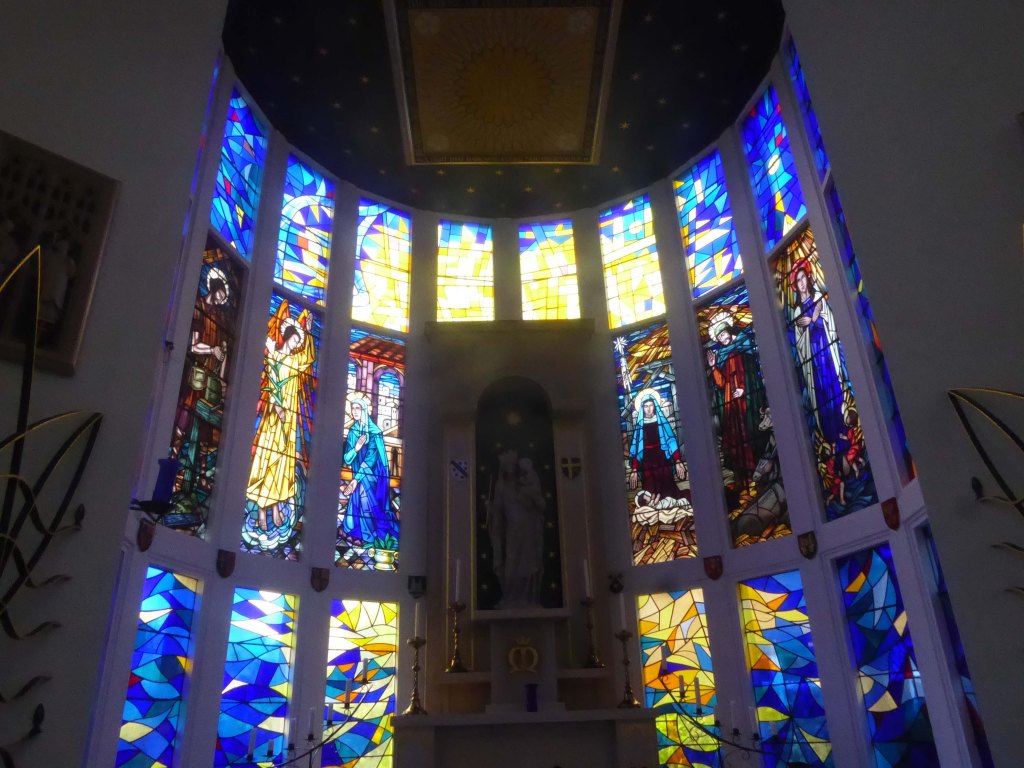

Further information on Taking Stock.
A special mention for the Danum Cultural Hub
Designed by architects Bond Bryan and built by main contractor Willmott Dixon, the new cultural and learning hub has been created following the restoration of four existing buildings.
A key focal point of the scheme is the restored frontage of the Edwardian former Doncaster High School for Girls, which has been framed by Senior’s slimline SF52 aluminium curtain wall and showcased within a new steel-frame building. The glazed facade, which was fabricated and installed by Senior’s supply chain partner Chemplas, also features Senior’s aluminium commercial doors.
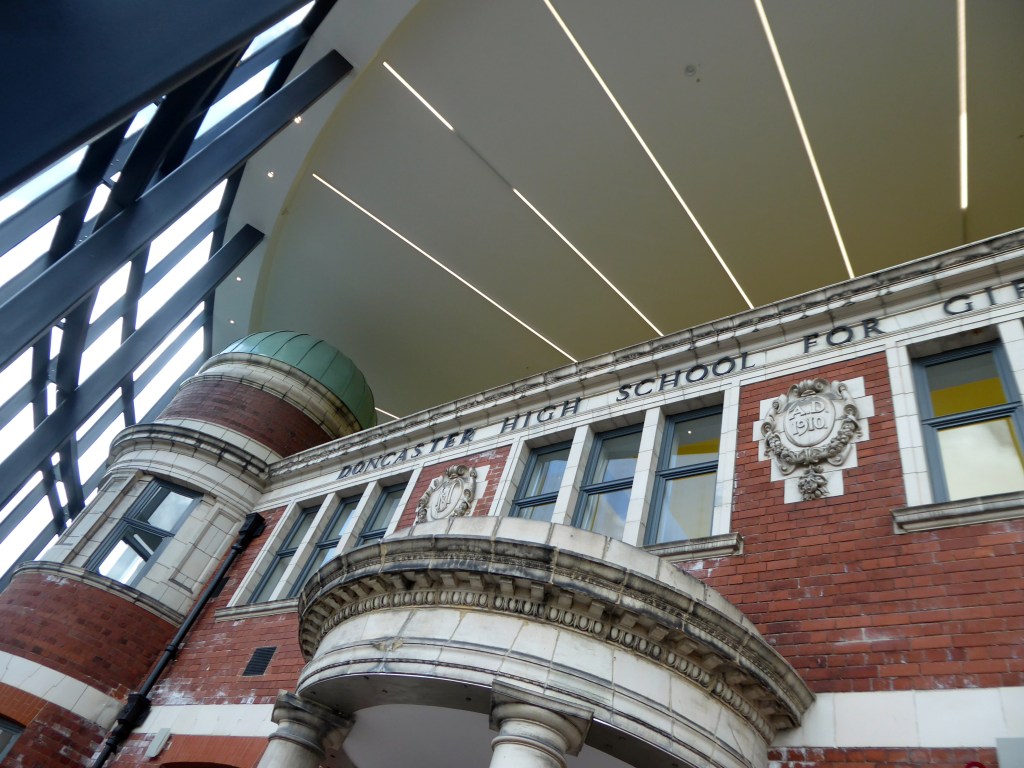

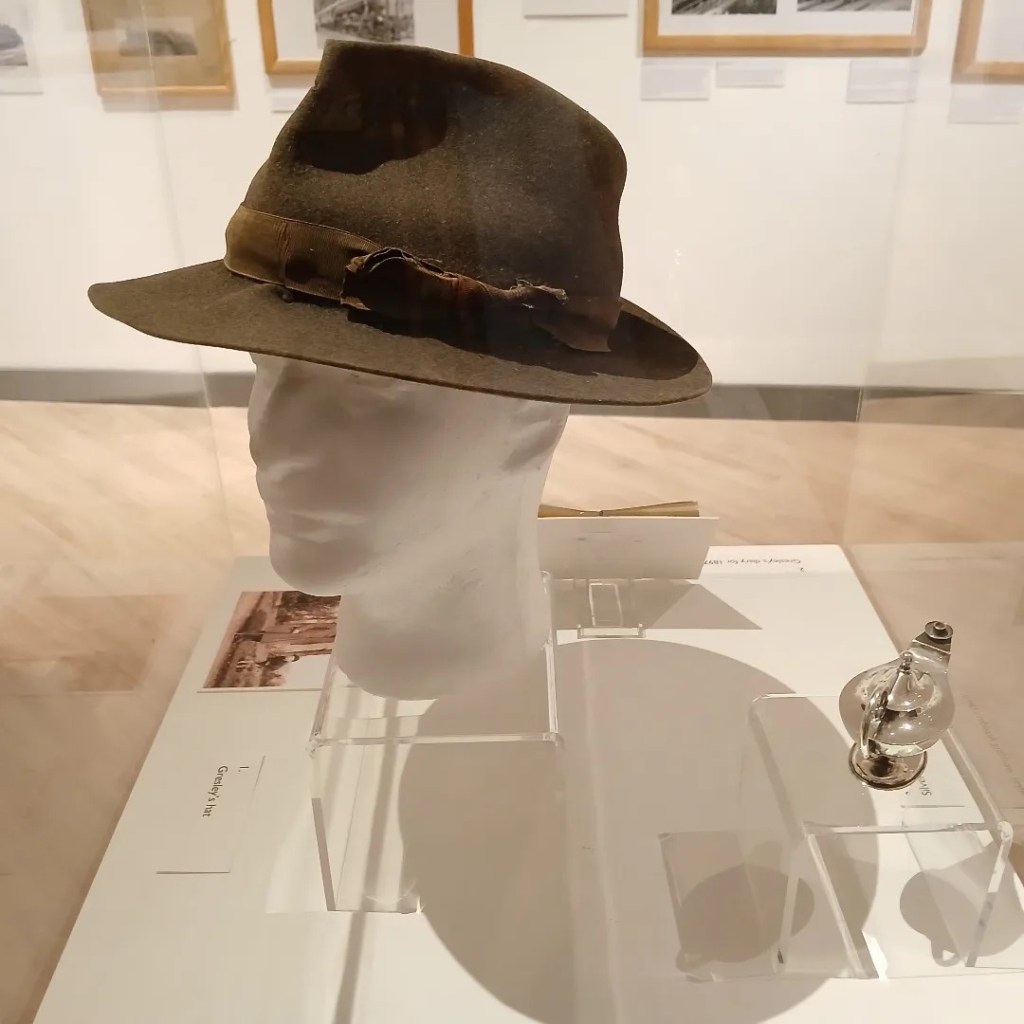
Where I was delighted to see Sir Nigel Gresley’s hat.