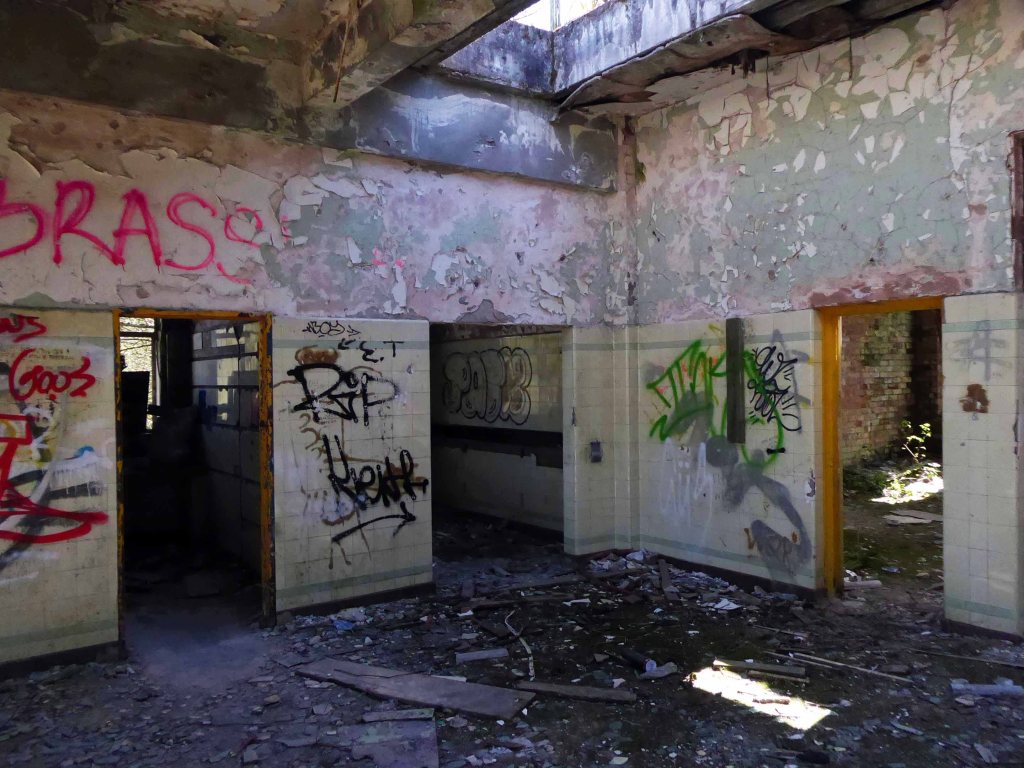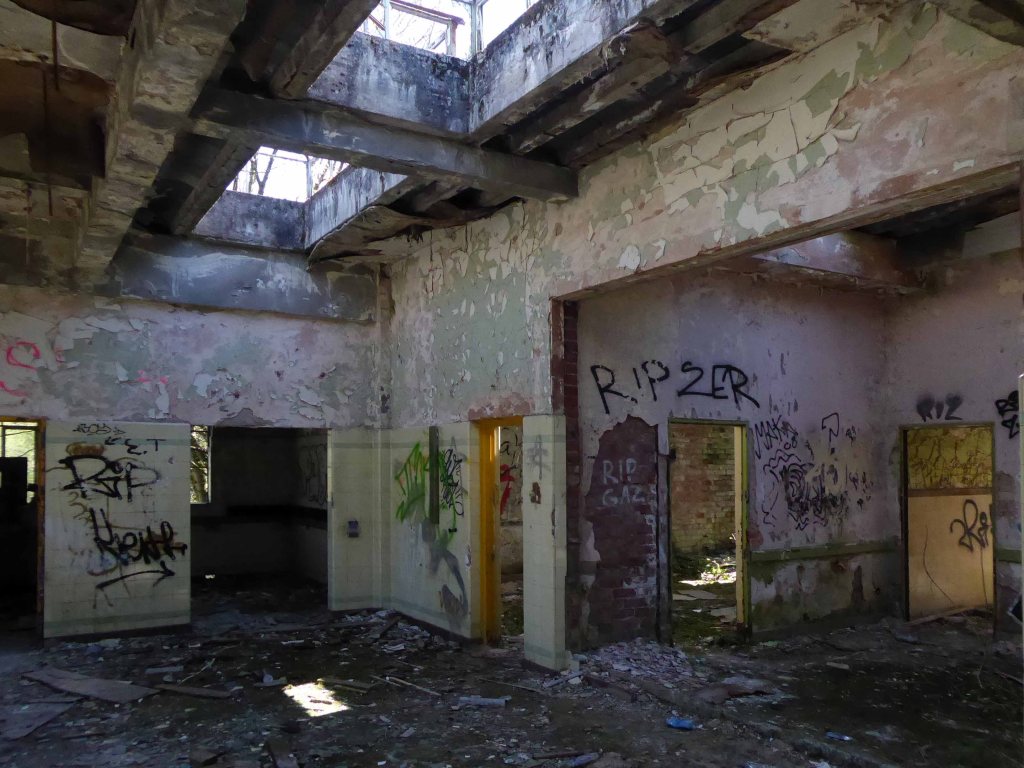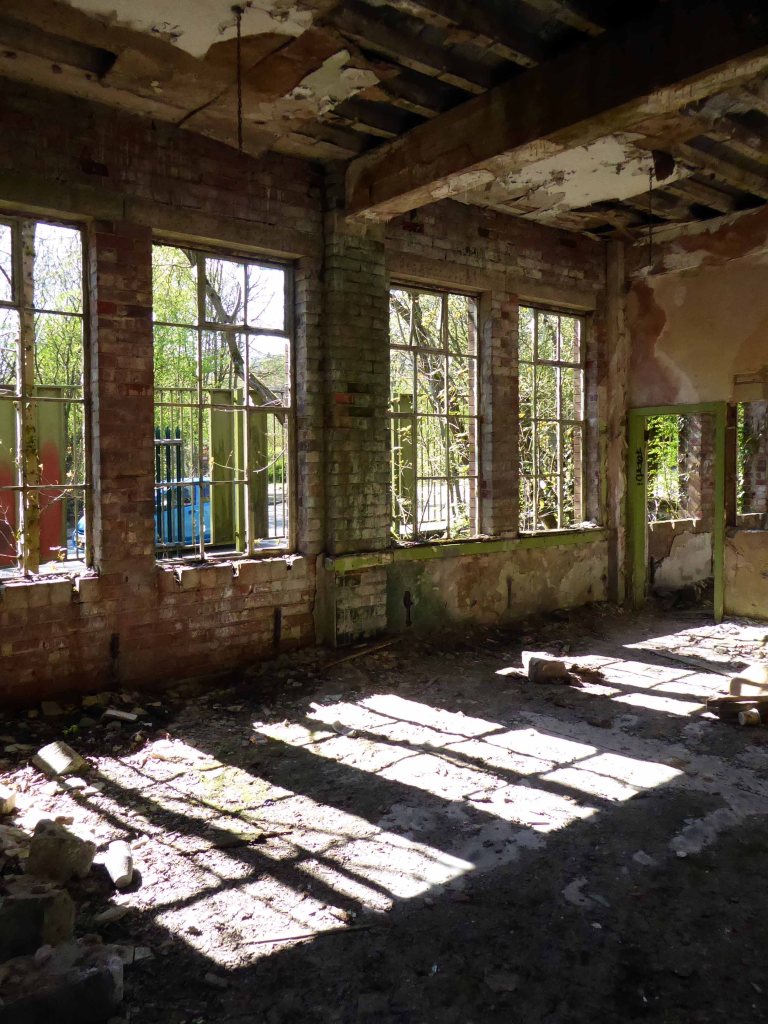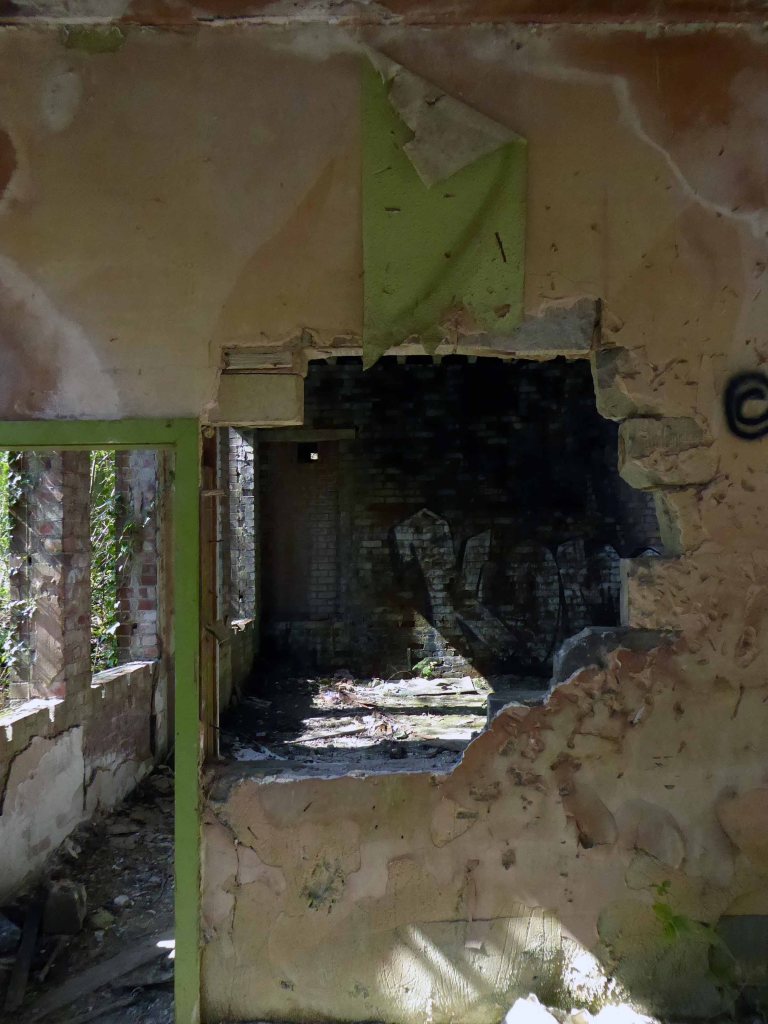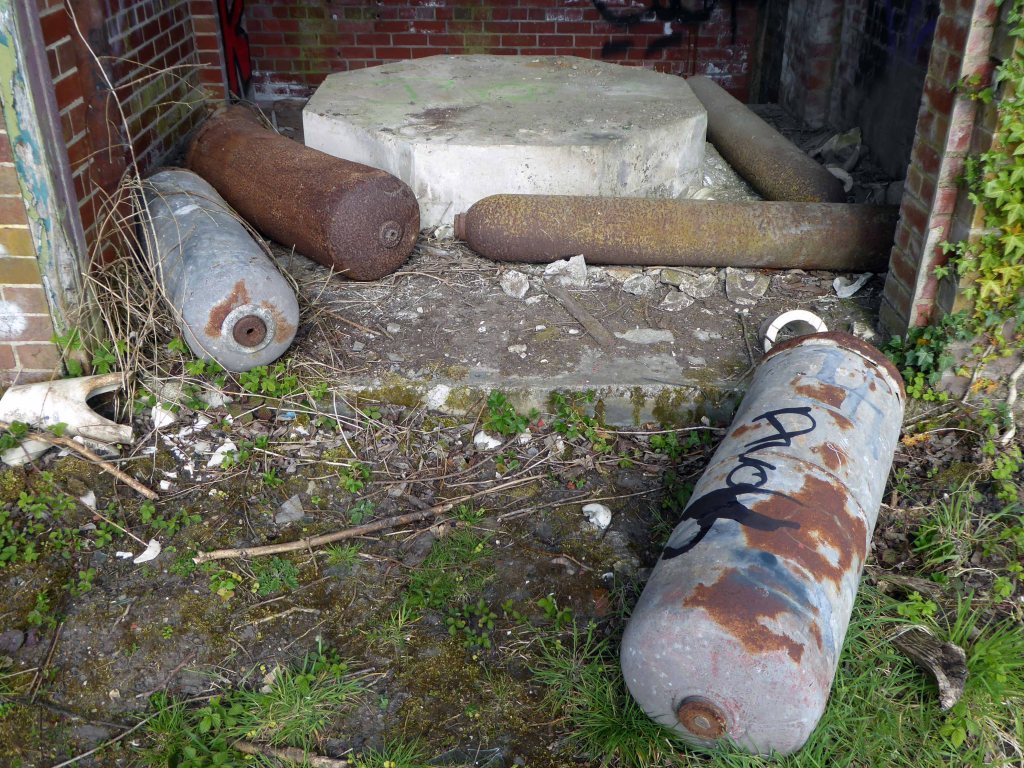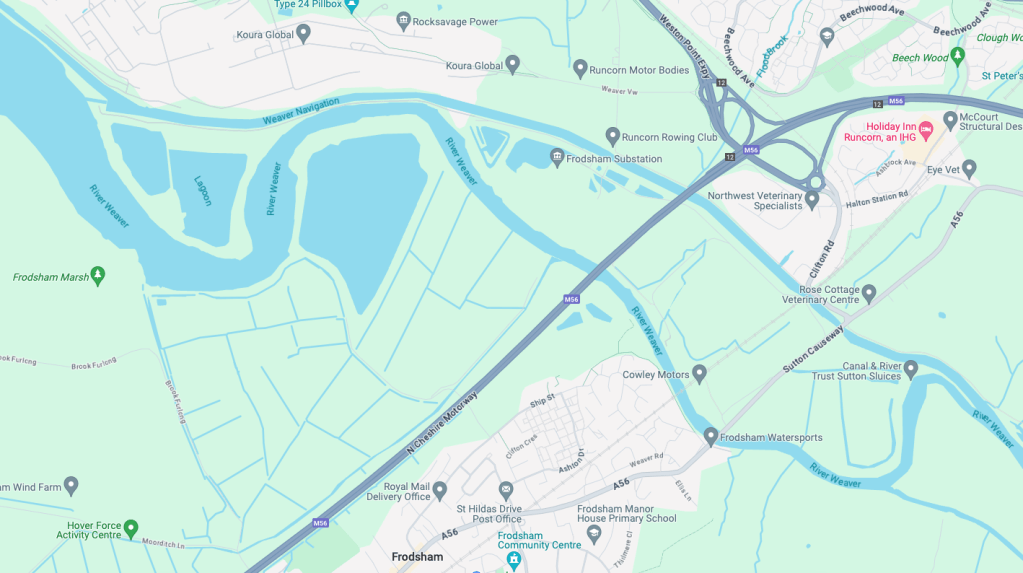
Along with my almost lifelong friend Mr Tim Rushton – I took a trip along a short stretch of the River Weaver, walking from east to west.
River Weaver – rising on the boundary between the counties of Shropshire and Cheshire and then flowing 45 miles north to reach the Irish Sea estuary of the River Mersey to the west of Runcorn.
Below Winsford, the course of the river has been altered several times, by the construction of cuts and locks, to enable small ships to trade on it. The river formerly joined the River Mersey at Weston Marsh, but since the construction of the Manchester Ship Canal, begun in 1887, it has flowed into the canal, from where surplus water enters the Mersey by the Weaver sluices, just upstream of the junction. The tidal river section below Frodsham has been bypassed by the Weston Canal since 1810 and is no longer navigable, as Frodsham Lock is derelict.





Railway viaduct over River Weaver and adjoining land by A Rendel Engineer and Thomas Brassey, contractor 1848-1850 – for Birkenhead Lancs & Cheshire Junction Railway Co.
Red sandstone, brown brick and cast iron, two segmental-arched iron spans of circa thirty metres over river; two round arches on west bank and twenty one on east bank. Piers to iron spans are rusticated tooled ashlar; the other spans have rusticated voussoirs, pier faces and quoins and rock-faced spandrels with brick reveals, cornice to iron-span piers, plainer imposts to others.
Top of central pier to river modified to take mid C20 concrete track bed.


Weaver Viaduct is one of the outstanding features of M56 and its design was approved by the Royal Fine Arts Commission. The three-quarter mile of elevated motorway and approach embankments over the River Weaver and Weaver Navigation Canal opened on 21 February 1971.
Design was by Husband and Co of Sheffield – acting for Department of Environment, who also supervised the project. The contractor was Christiani Shand with a tender price of £3,146,387 in March 1968.
Work began in April 1968 – the eventual cost was put at £3.5 million.
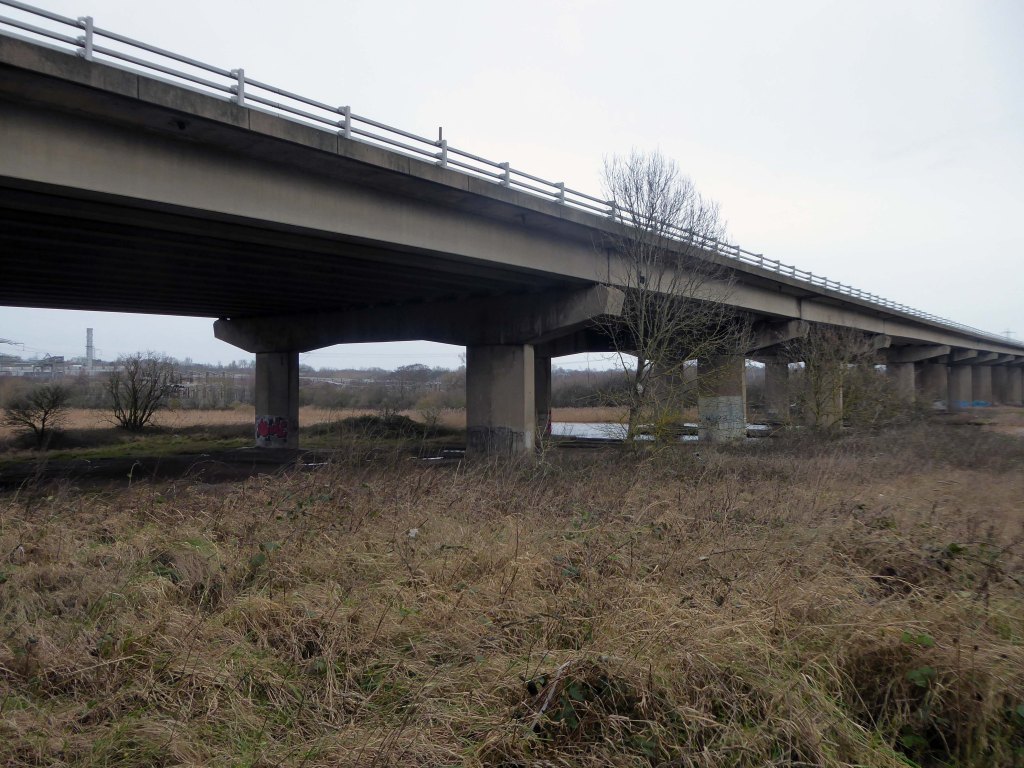
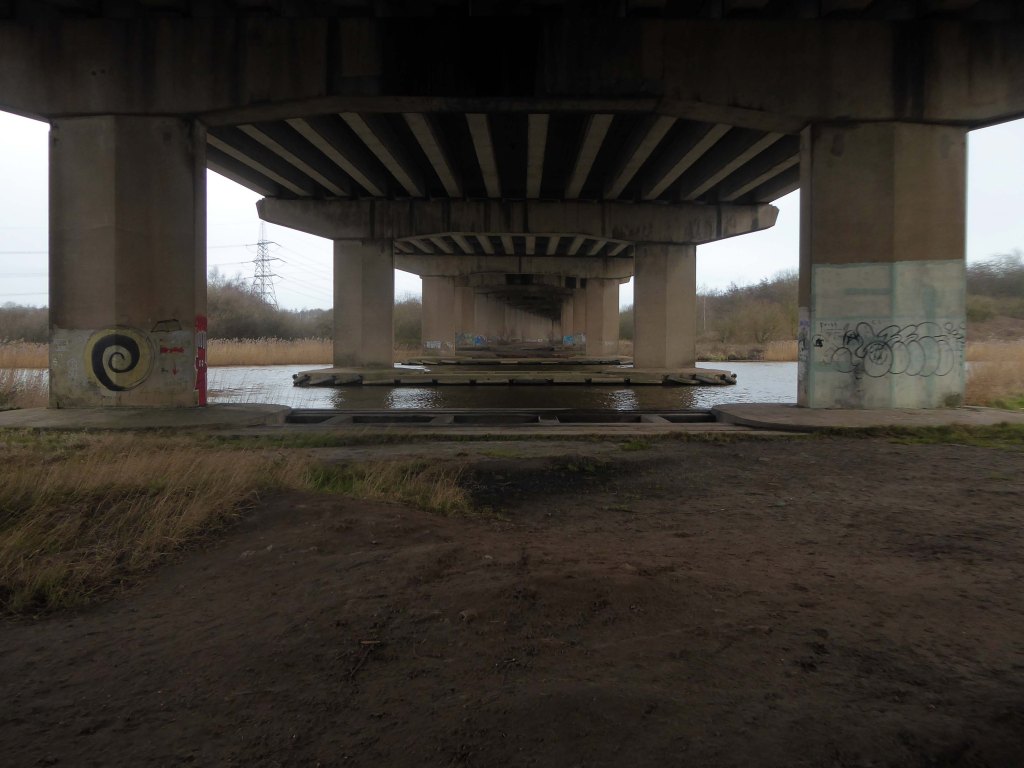




Thirty two 125-foot concrete 100-tonne beams were put into place in July 1970; the concrete beams were made by Matthews & Mumby of Windmill Lane Denton.


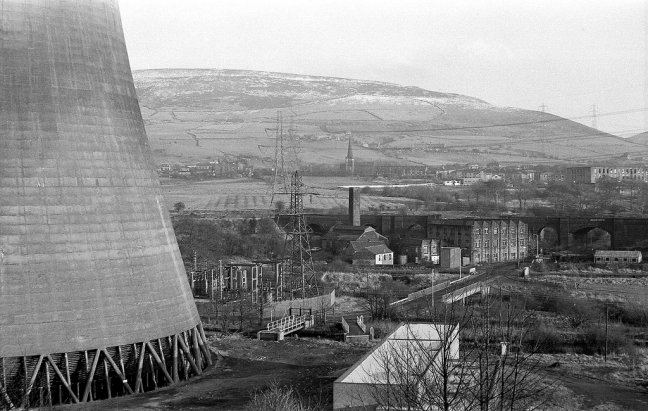
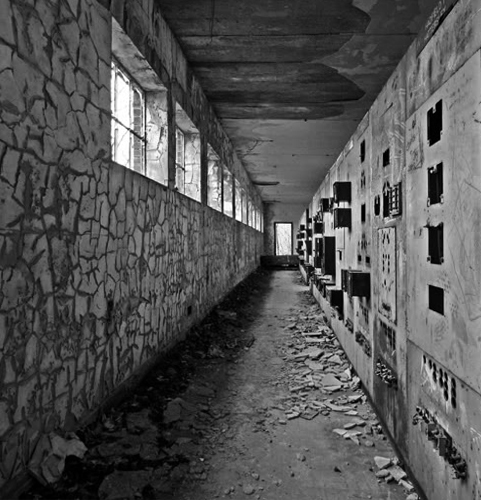
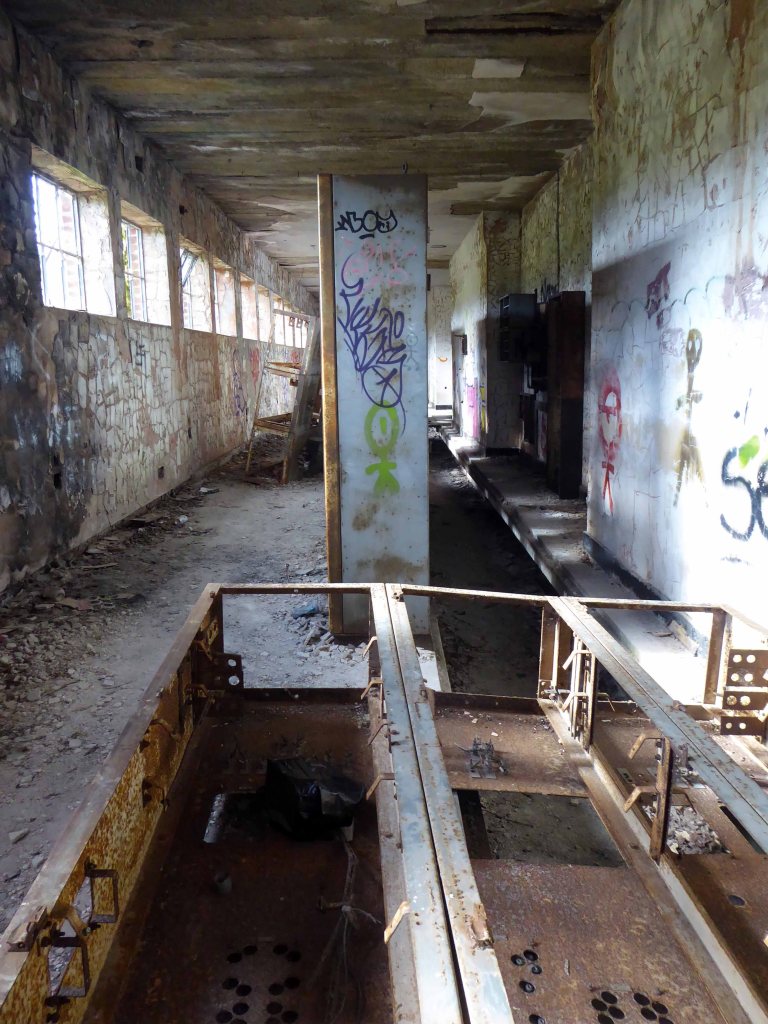
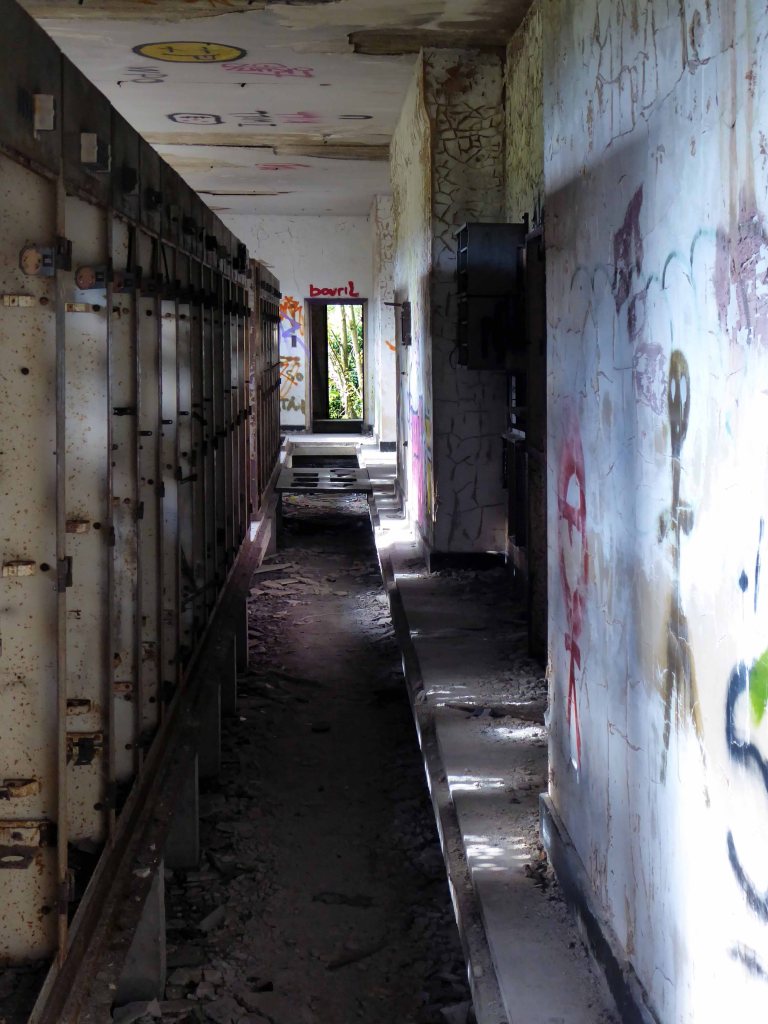
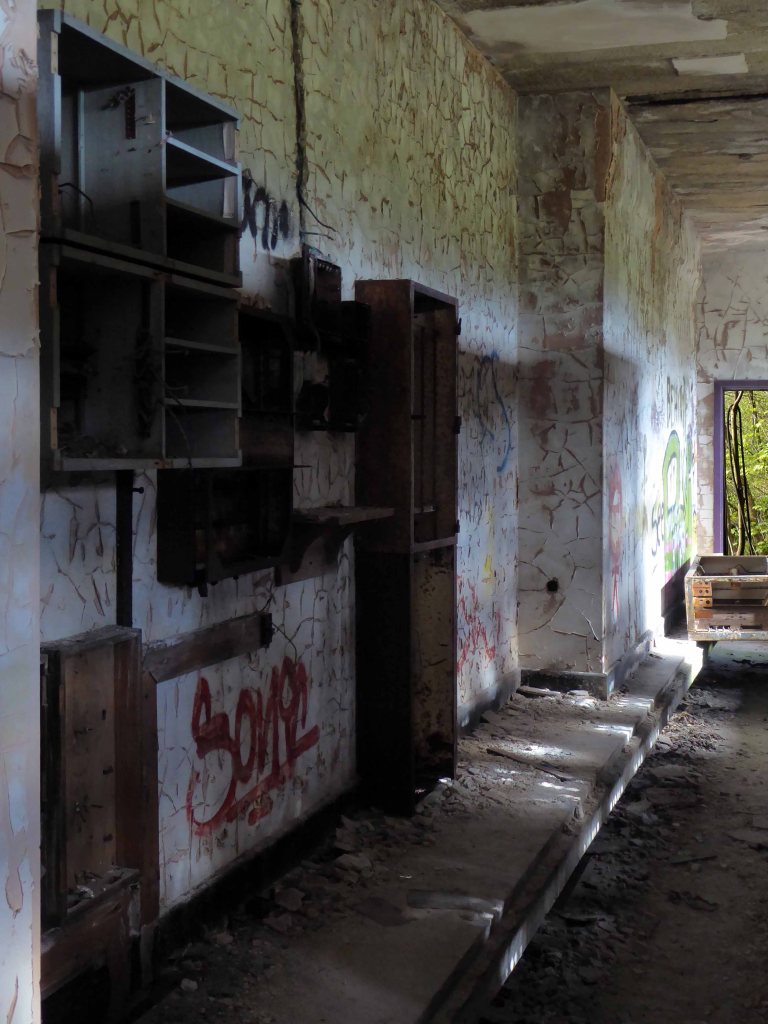
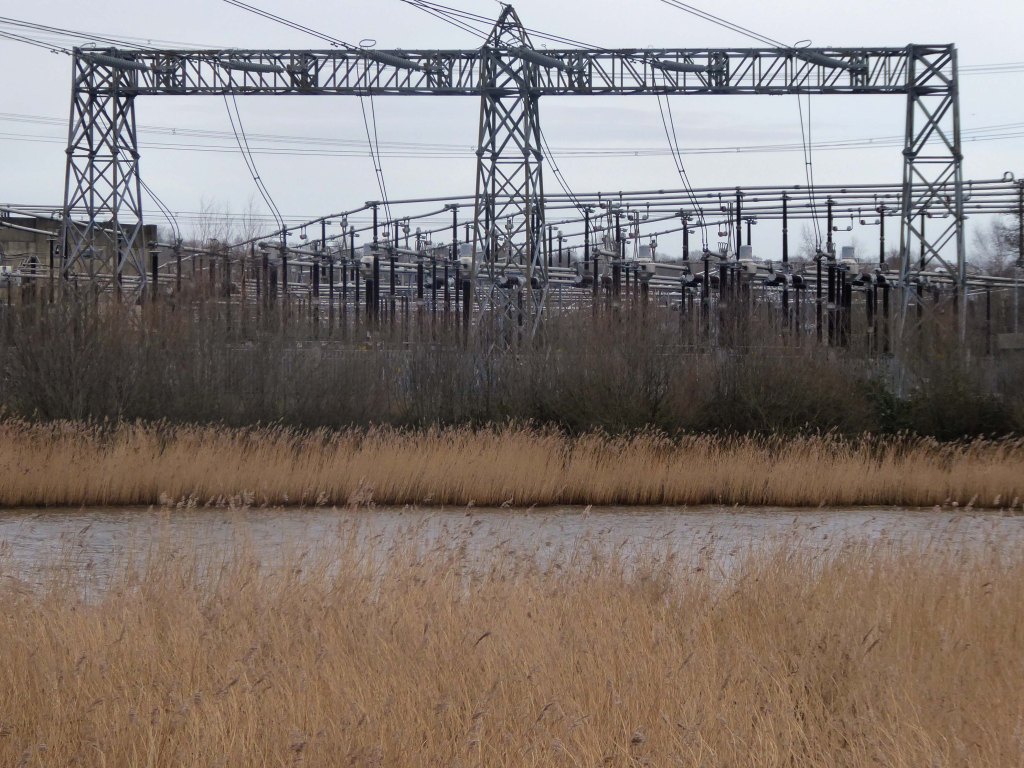
High-Voltage Frodsham Substation – Rock Savage power station
Rock Savage Power Station is an 800 MWe gas-fired power station.
It was opened by Queen Elizabeth II on 31 July 1998, and owned by InterGen, a company that is now jointly owned by Ontario Teachers’ Pension Plan and China Huaneng Group, it cost £375m.
It sponsors the Runcorn Jets baseball club, the Highfield Male Voice Choir and the Weston Angling Club.
The name comes from the nearby ruined Elizabethan mansion – Rocksavage.
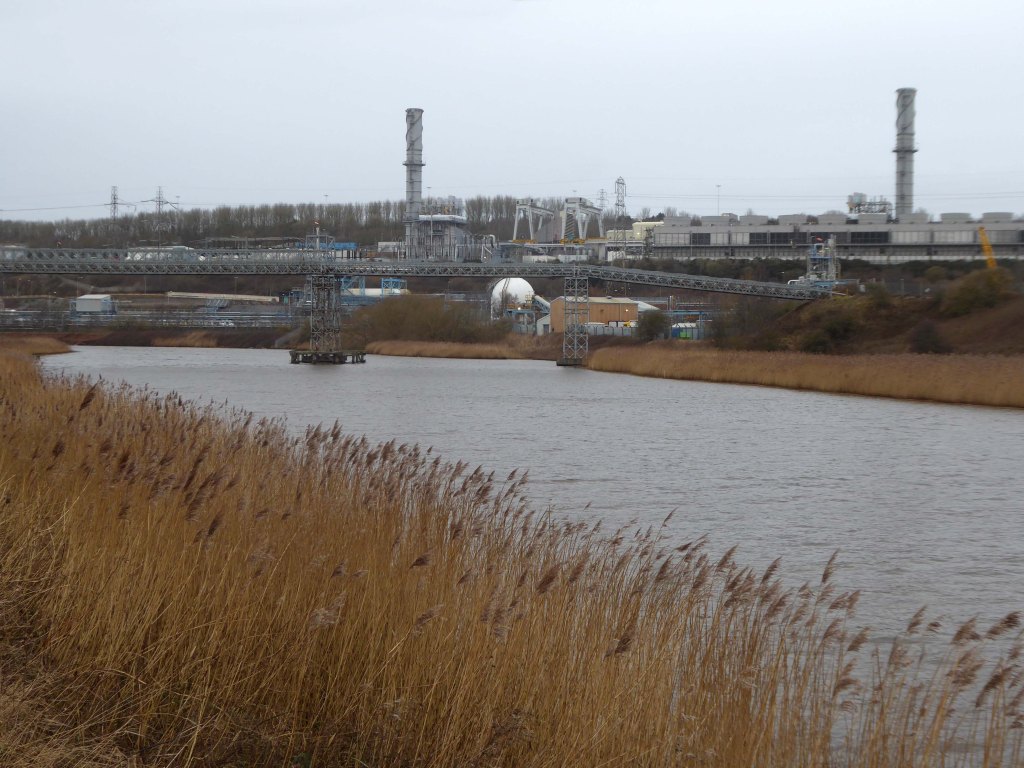





Koura Global – leader in the development, manufacture, and supply of fluoro products and technologies, opened a new HFA 152a production facility at their Runcorn site in the UK.
Chiesi, the international research-focused pharmaceuticals and healthcare group, signed a commercial agreement to use the new low carbon footprint medical propellant for inhalation product development and clinical trials in 2019.

Britain from Above 1948
Ineos Chemical Complex formerly ICI Rocksavage Works on the banks of the River Mersey River Weaver and Manchester Ship Canal in Runcorn formerly ICI works of Rocksavage and Castner Kelner Works which produced fluorcarbons such as aerosol propellants dry cleaning solvents and chlorine UK January 2007
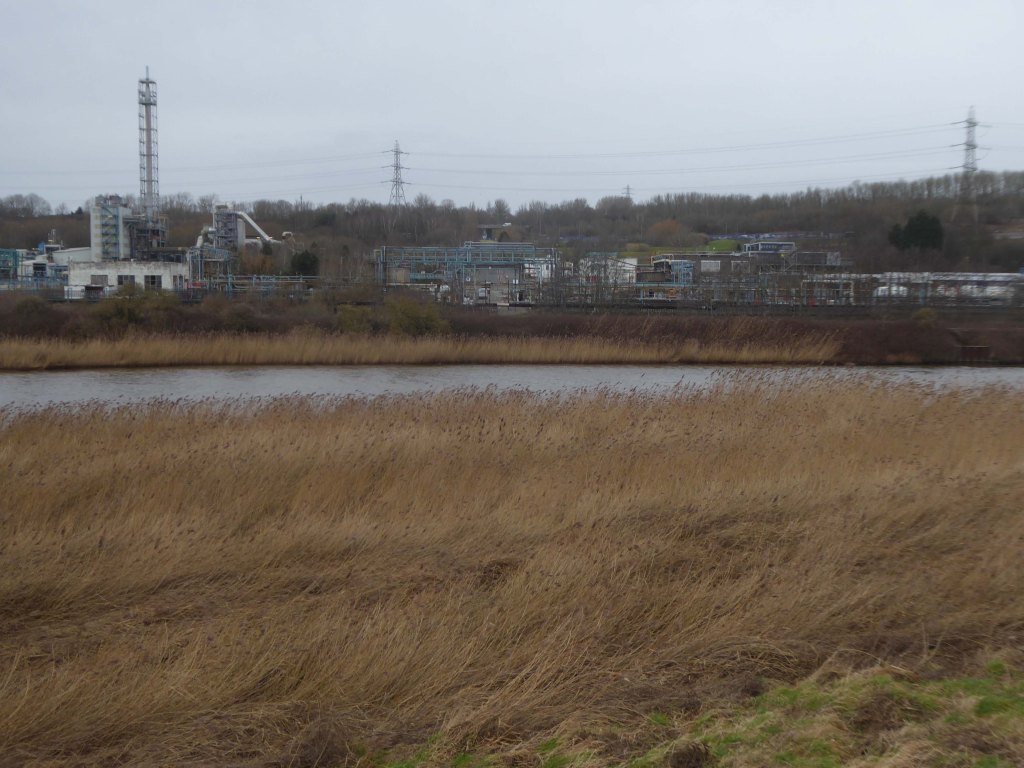
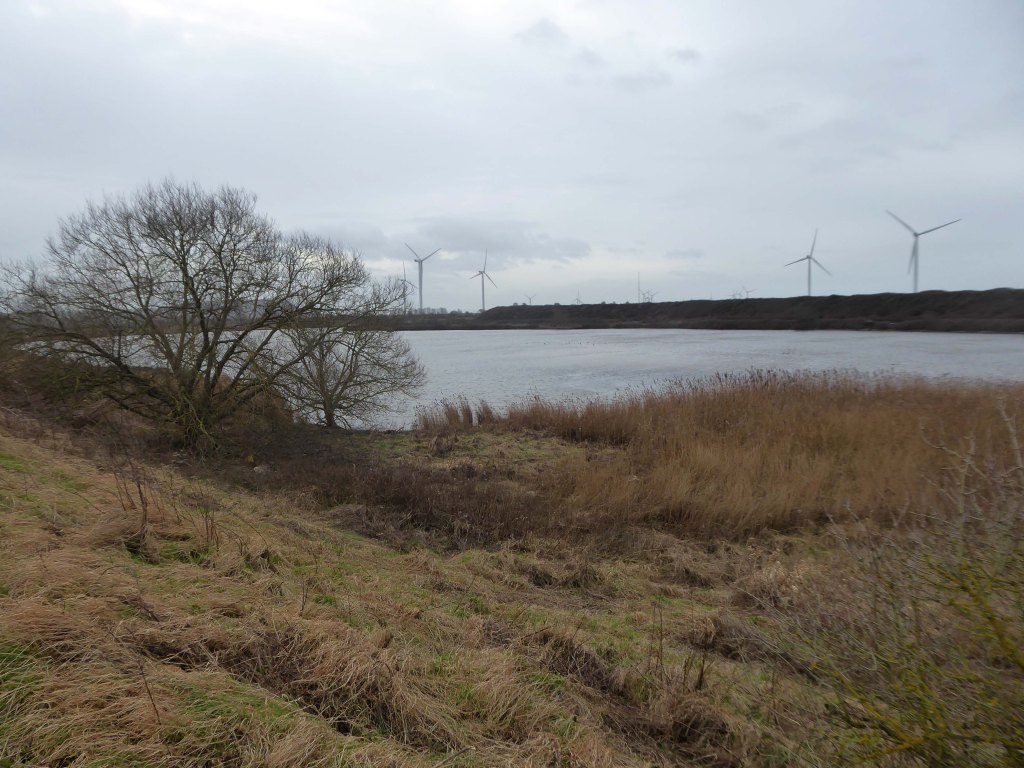
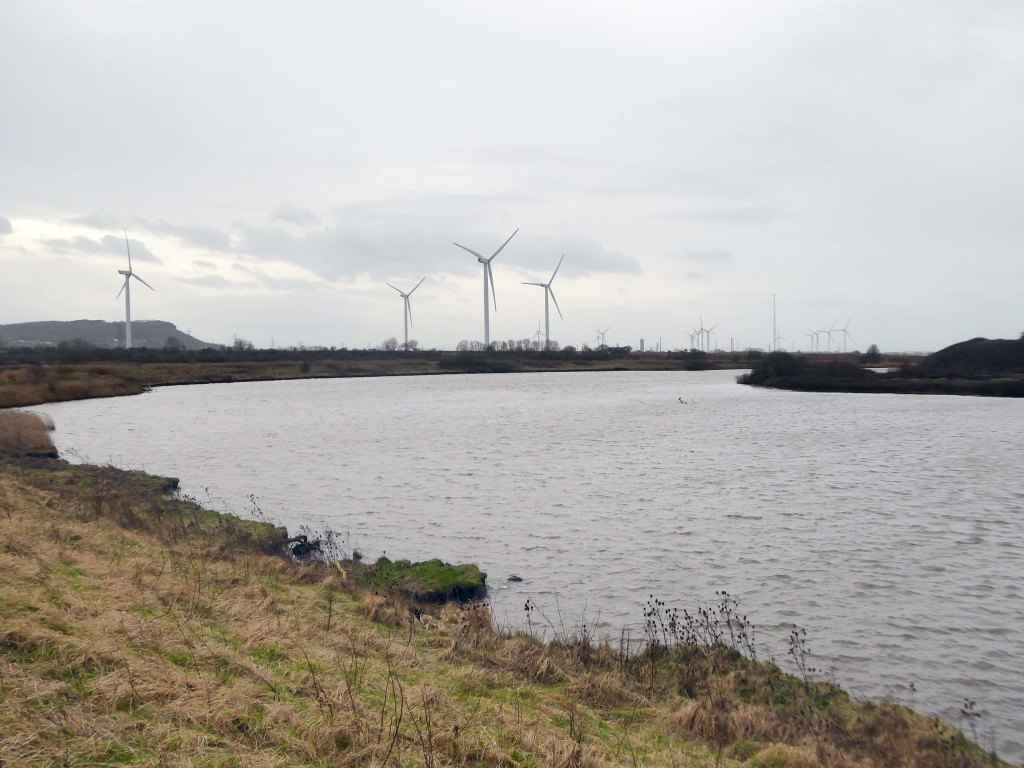
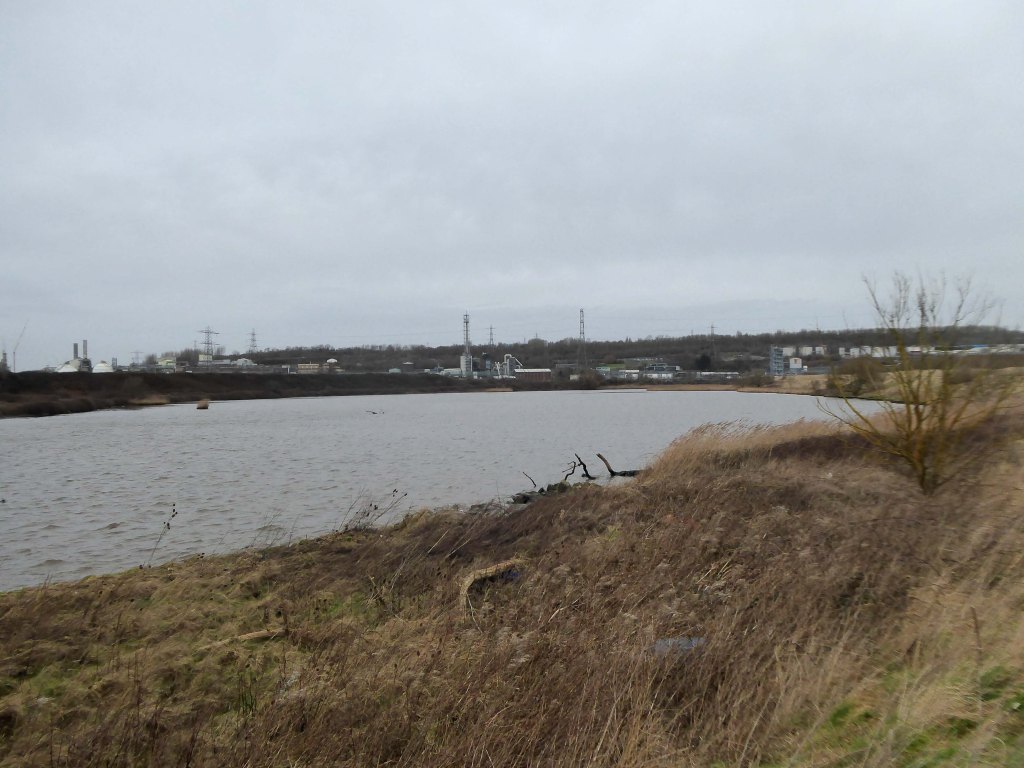
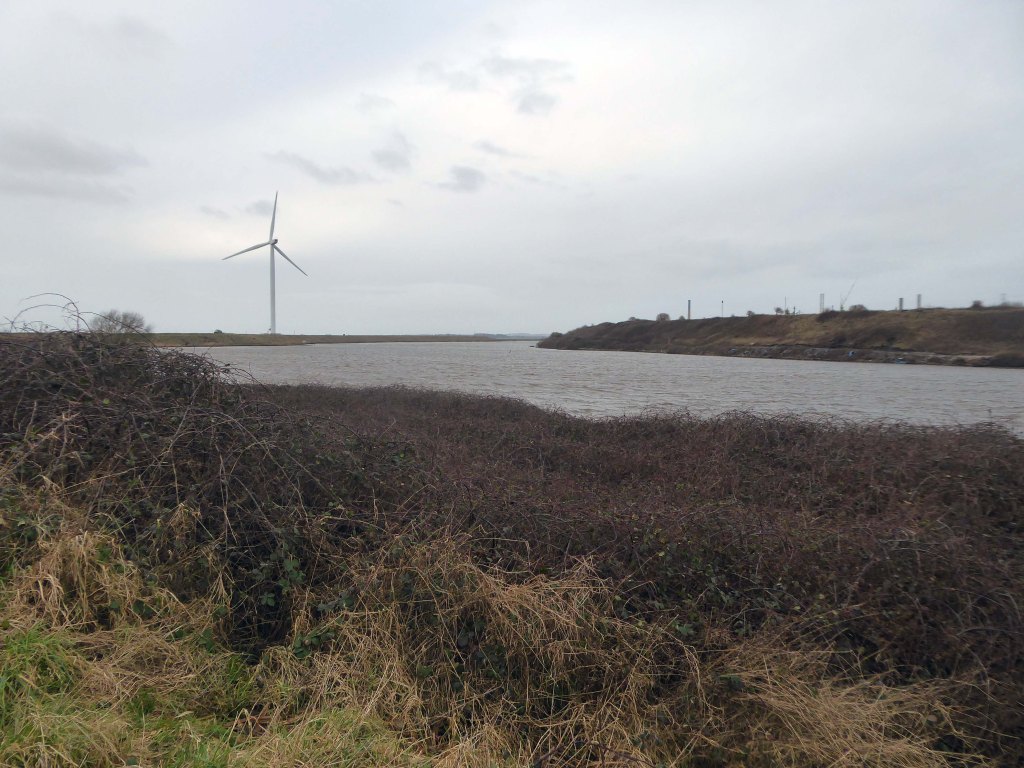









Frodsham Wind Farm is one of England’s largest onshore generating stations, and the largest in the Cheshire region, with an installed capacity of more than 50 MW. Construction of the wind farm began in March 2015 and became fully operational in February 2017.