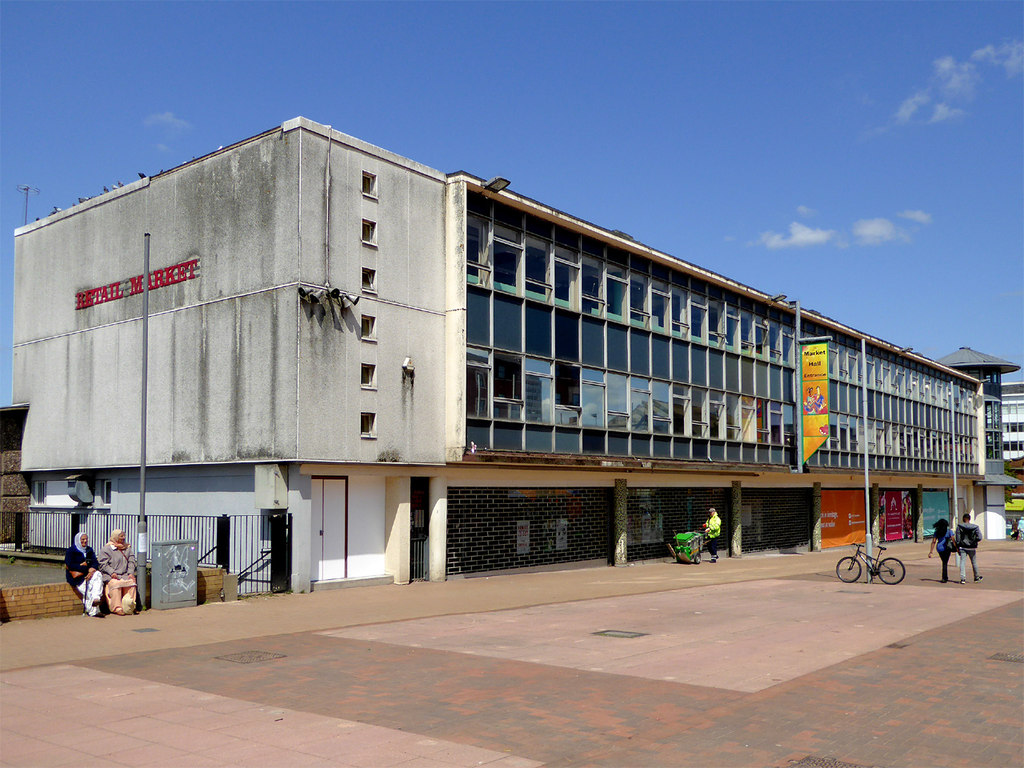
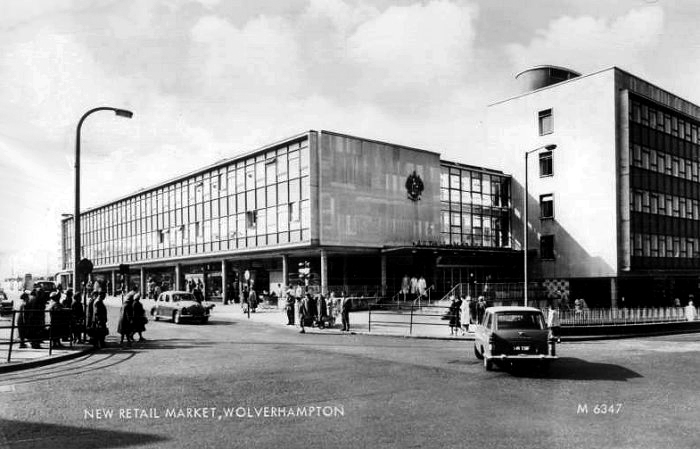
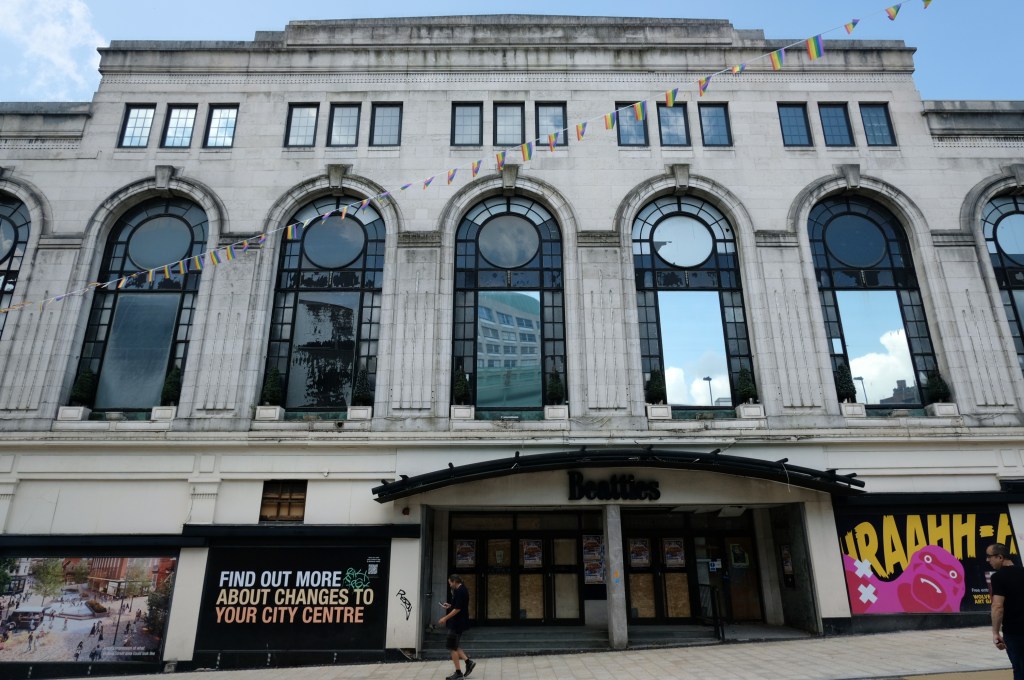
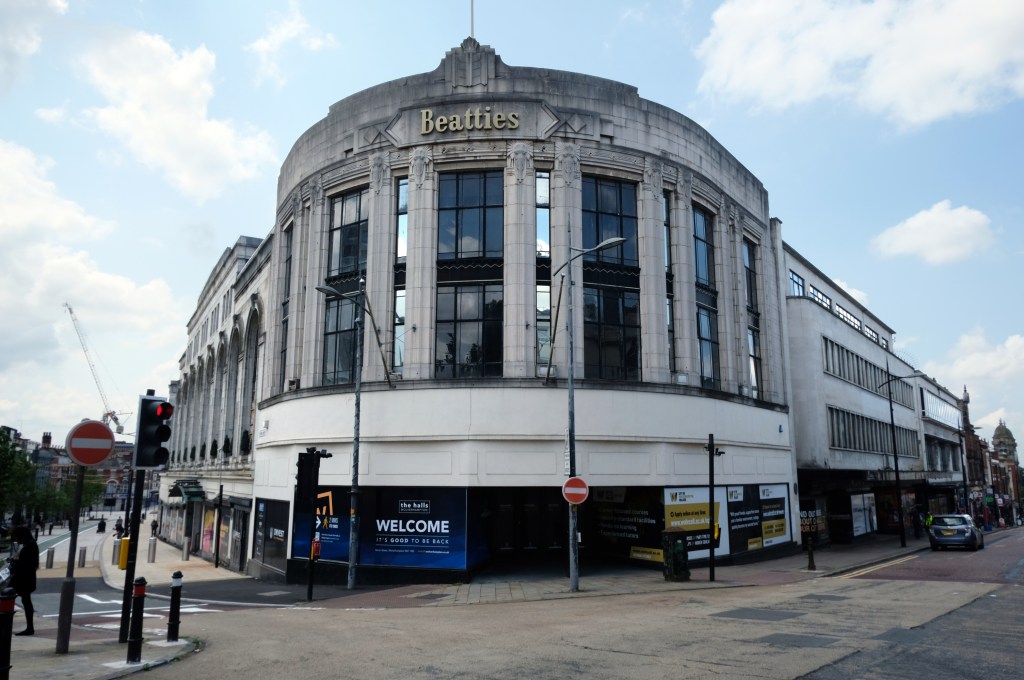
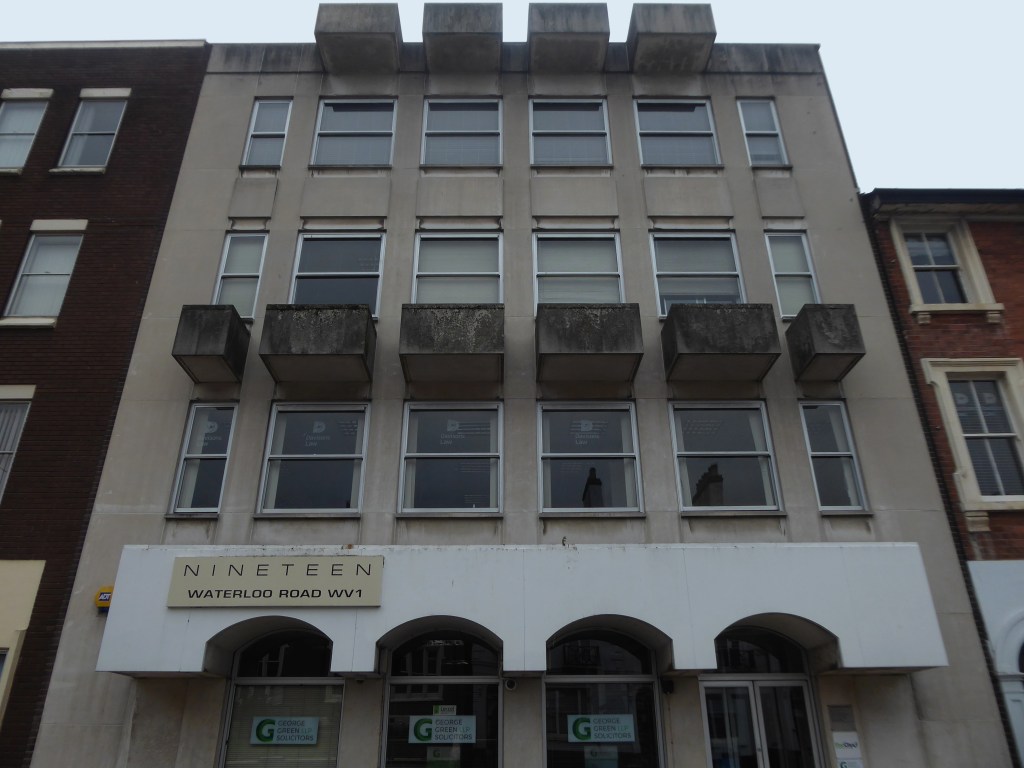
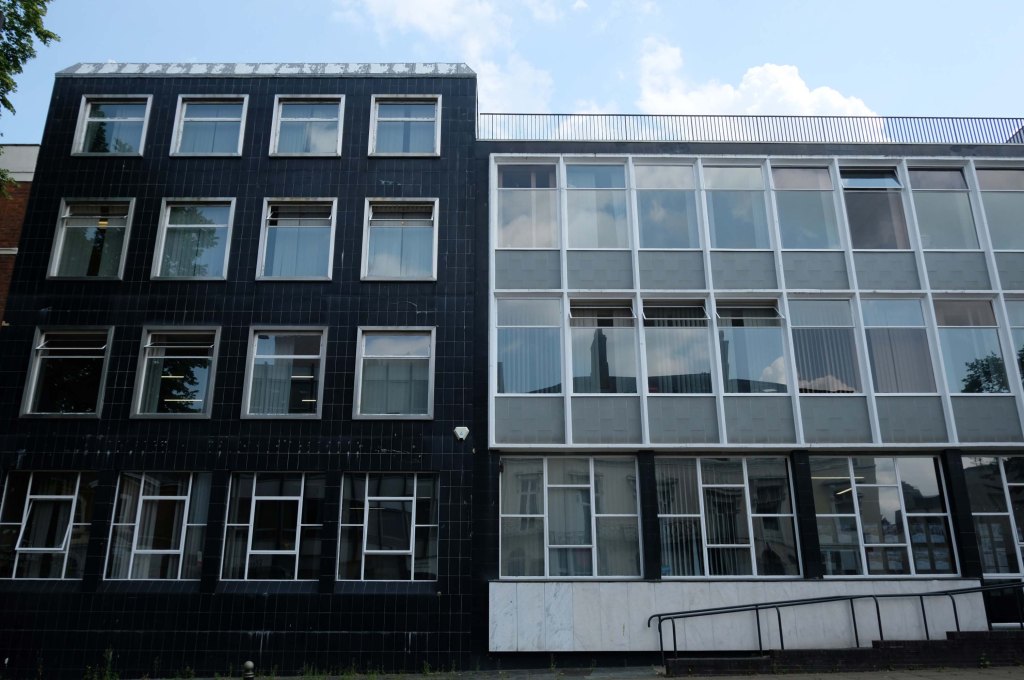
To begin at the beginning – to begin at the Telephone Exchange.
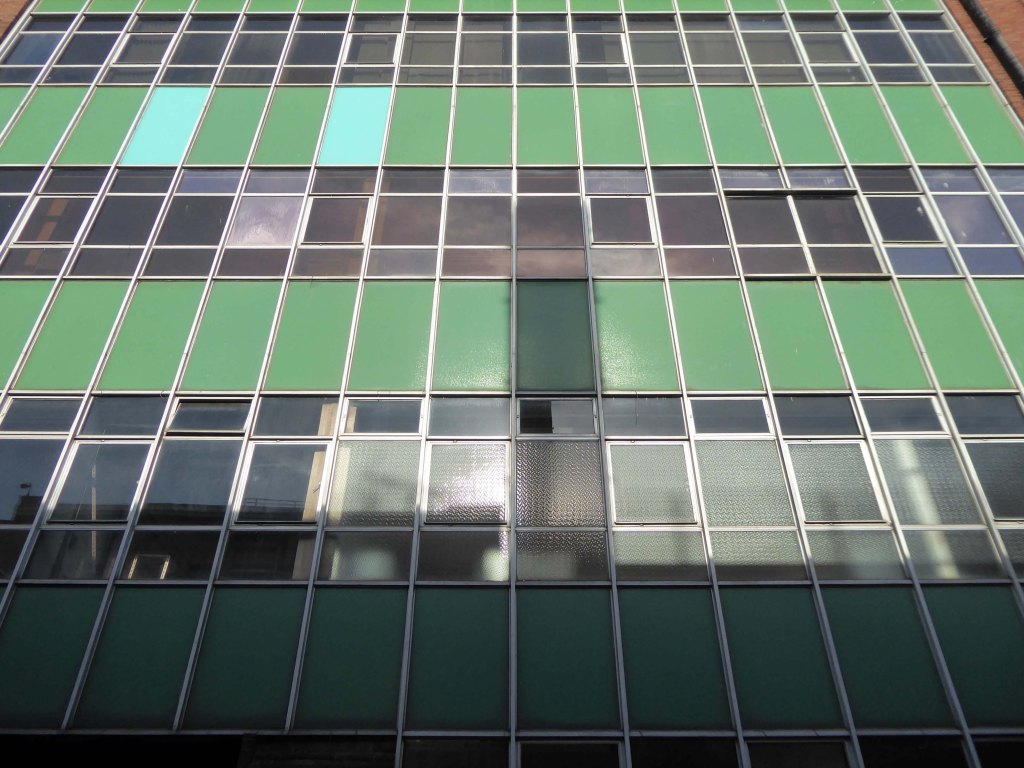
A plethora of surface textures and a purposely restrained palette, well suited to the architecture of infrastructure.


Around the corner the Royal Mail Sorting Office.


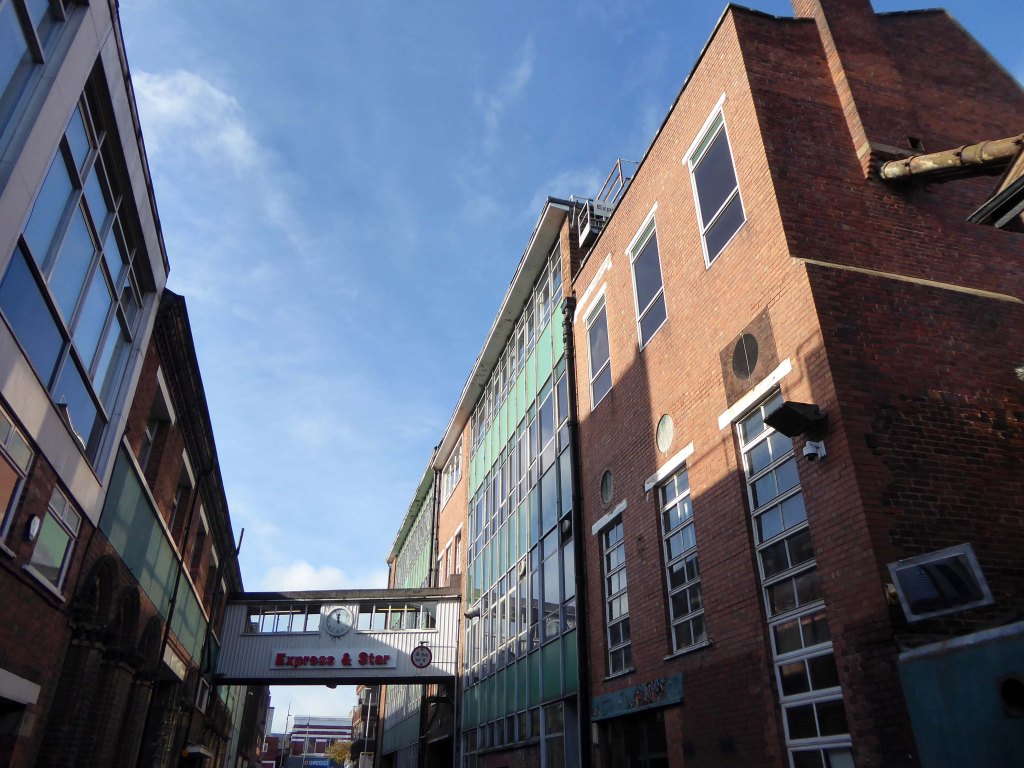
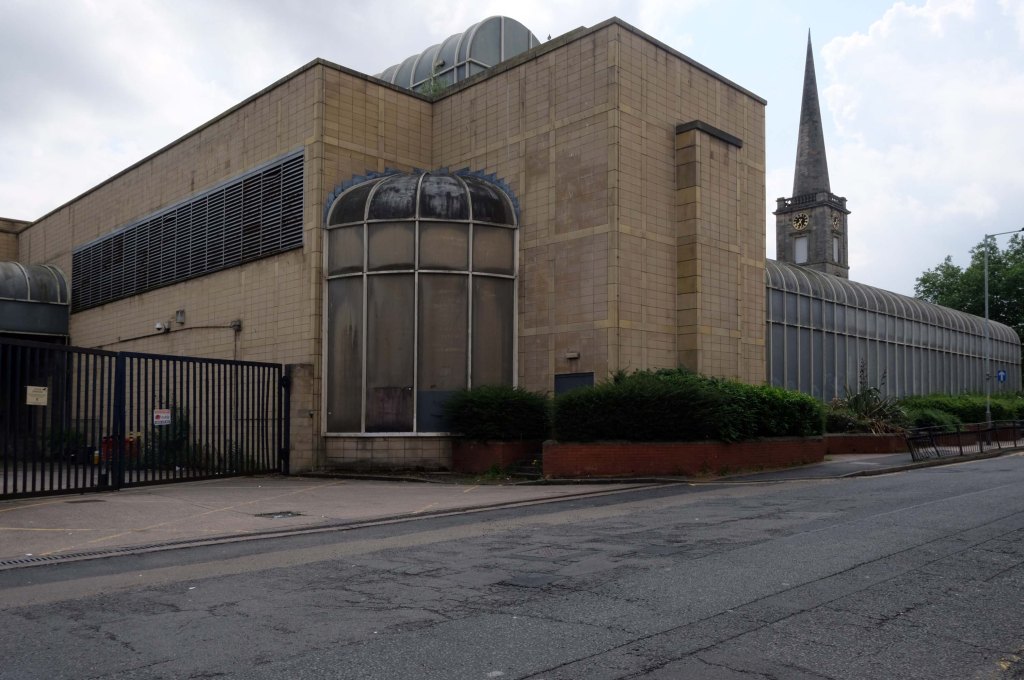
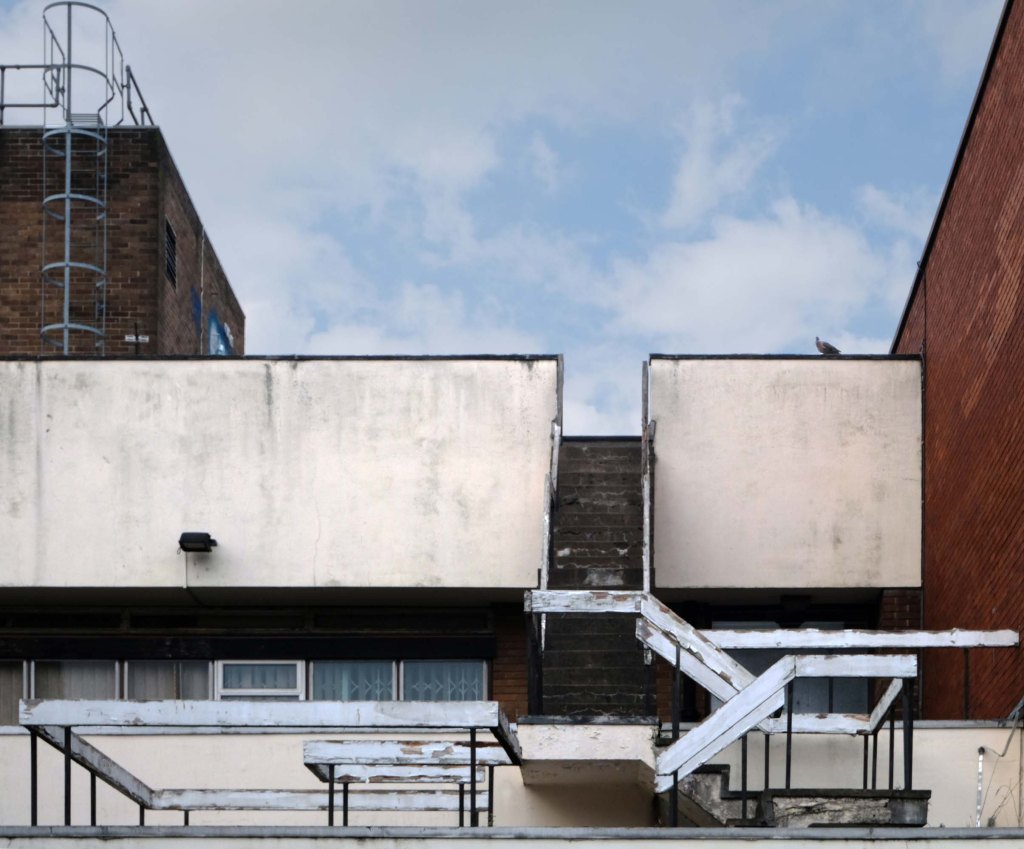
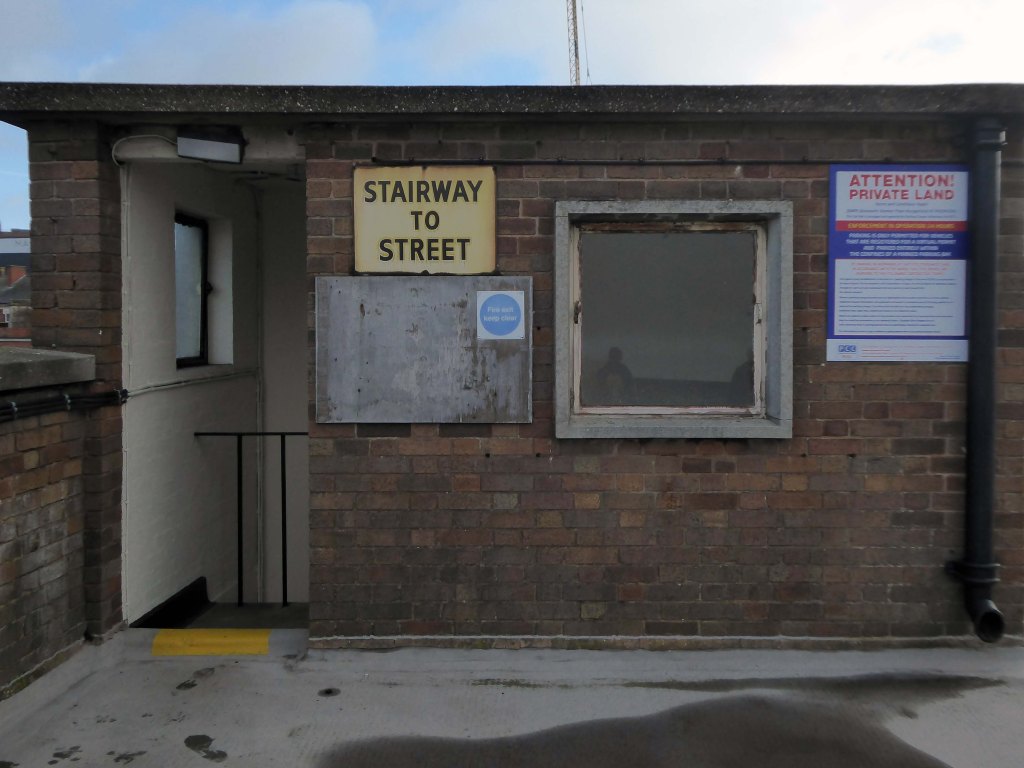
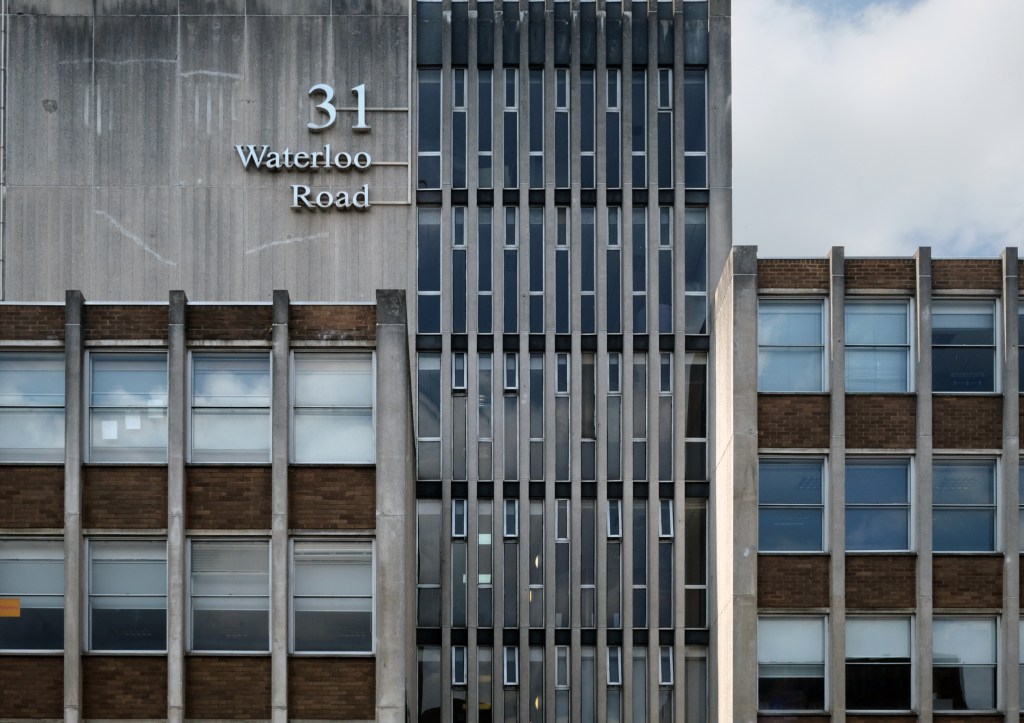
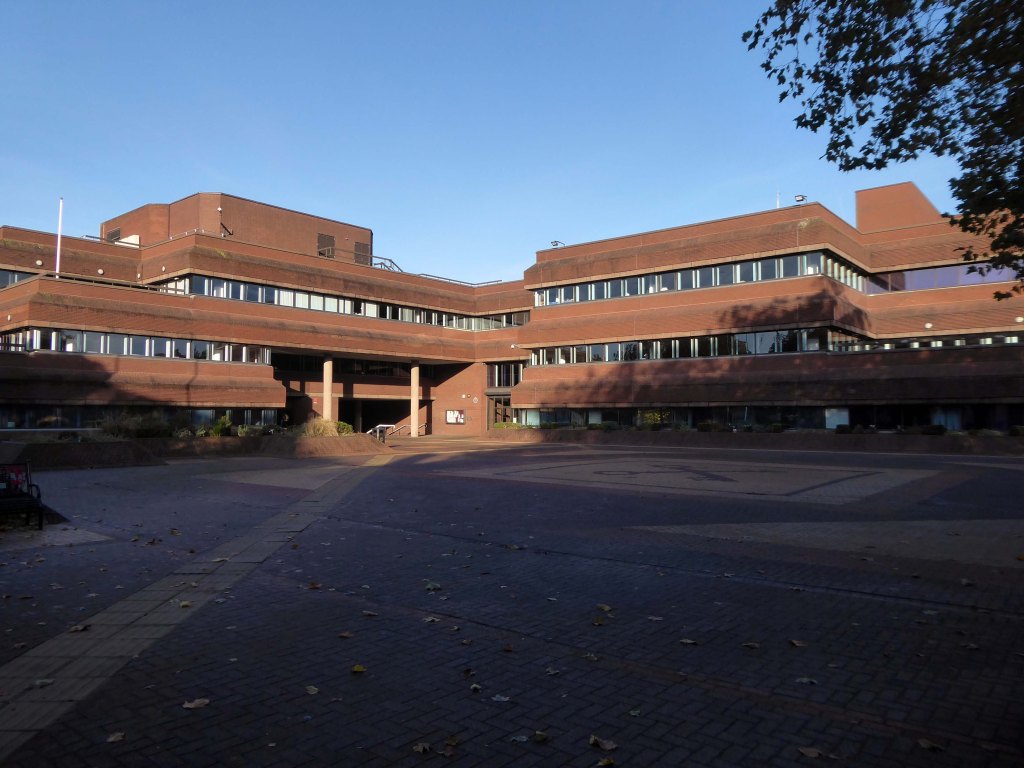
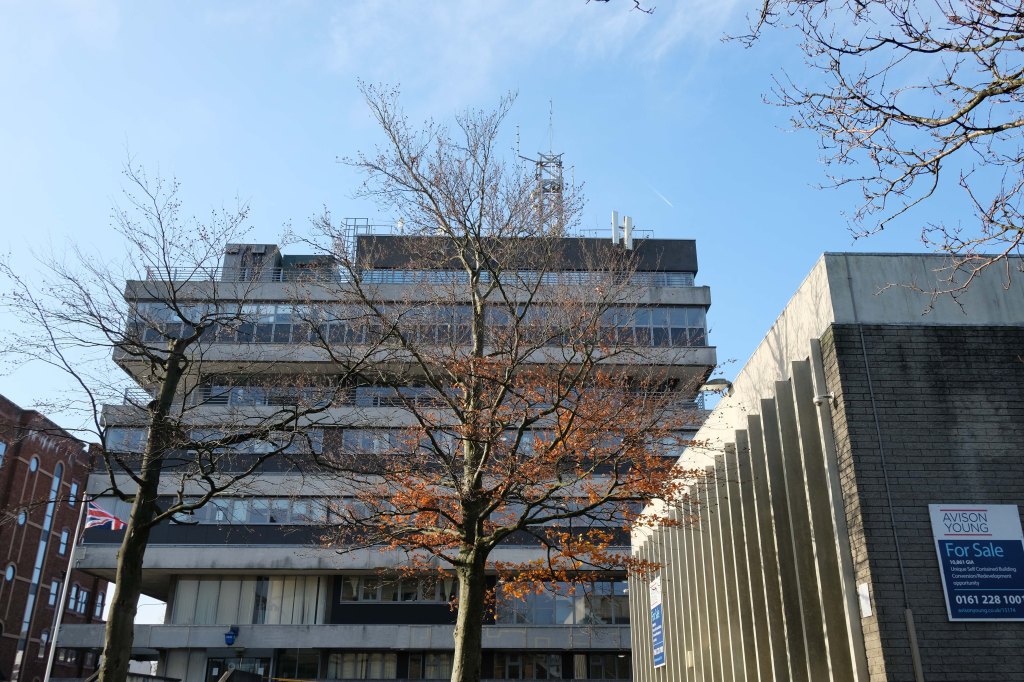
Next door the Telephone Exchange, drawings of the building are dated around 1937 and are simply signed by the Ministry of Works, Preston.
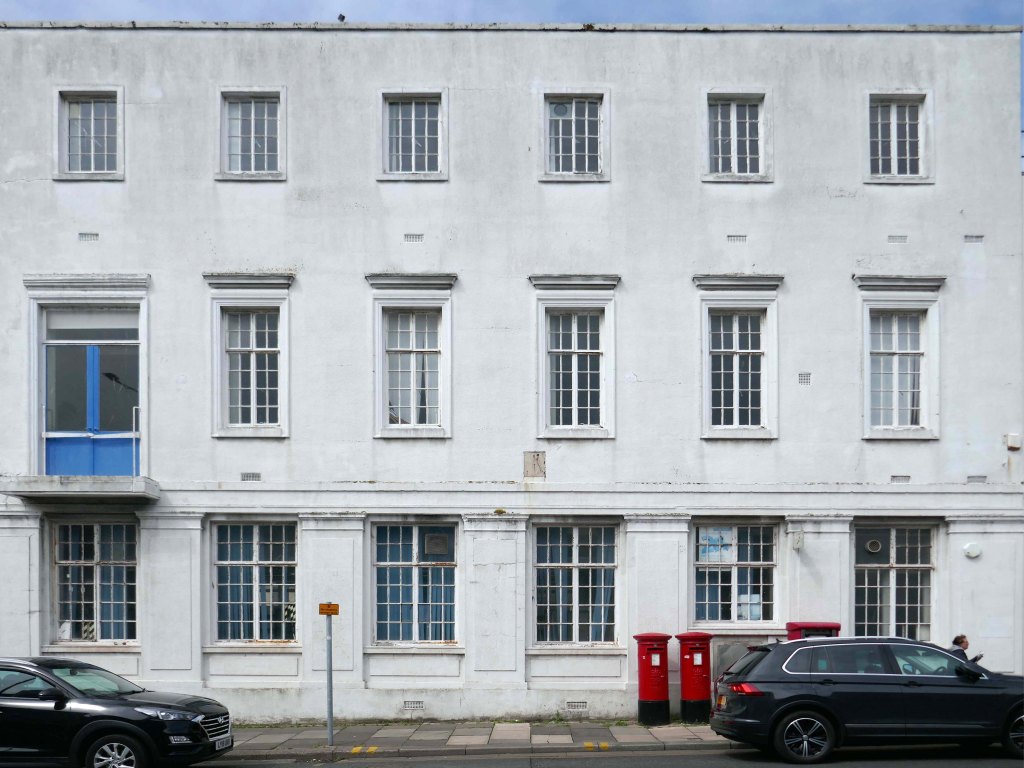

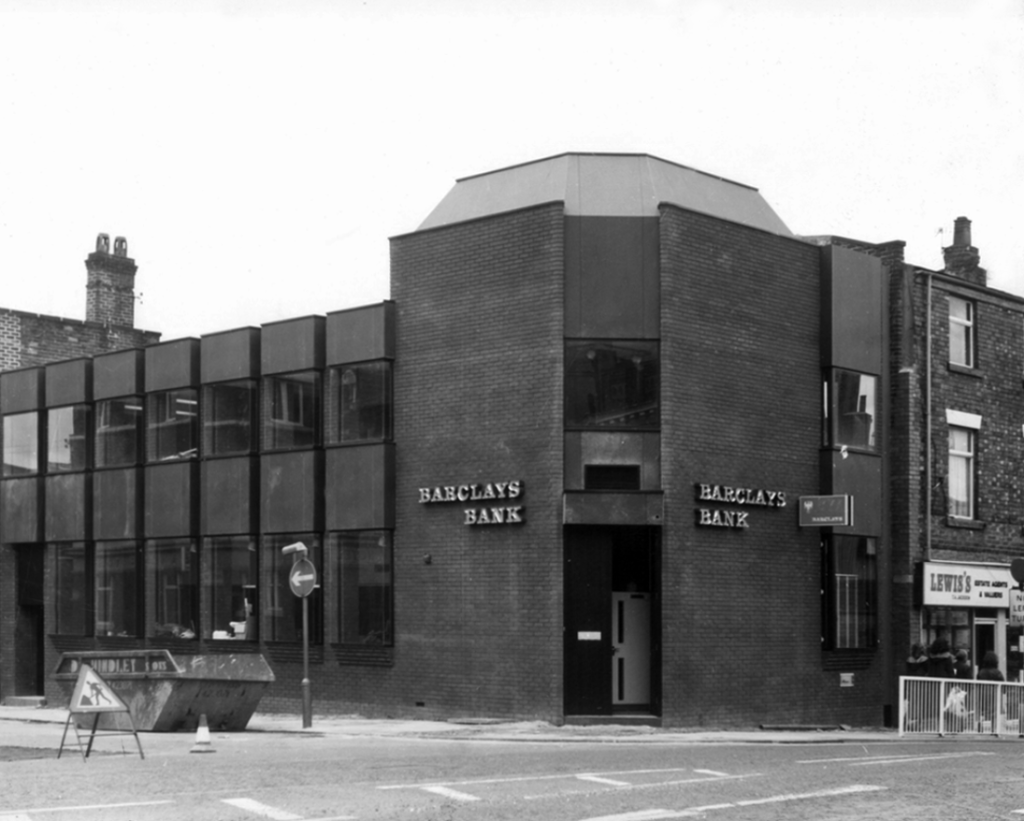
Across the way this former Barclays Bank with its 70s extension, originally a branch of the Kendal Bank, Bank of Liverpool and also Martins.
The building of 1900 is Grade II listed.
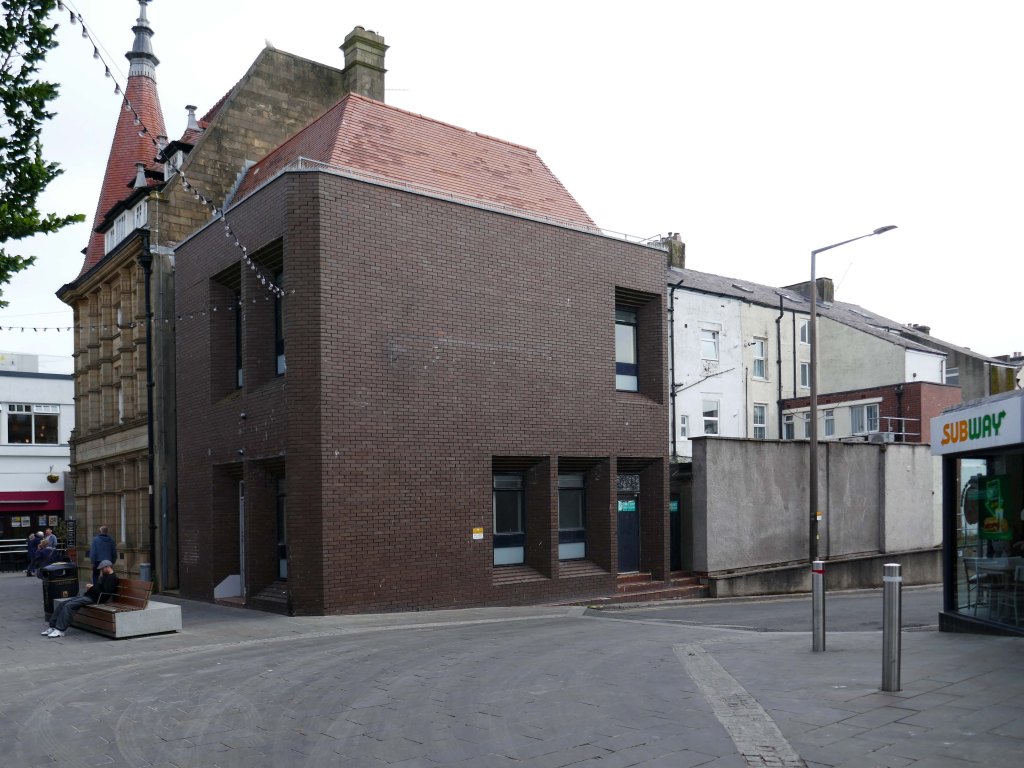

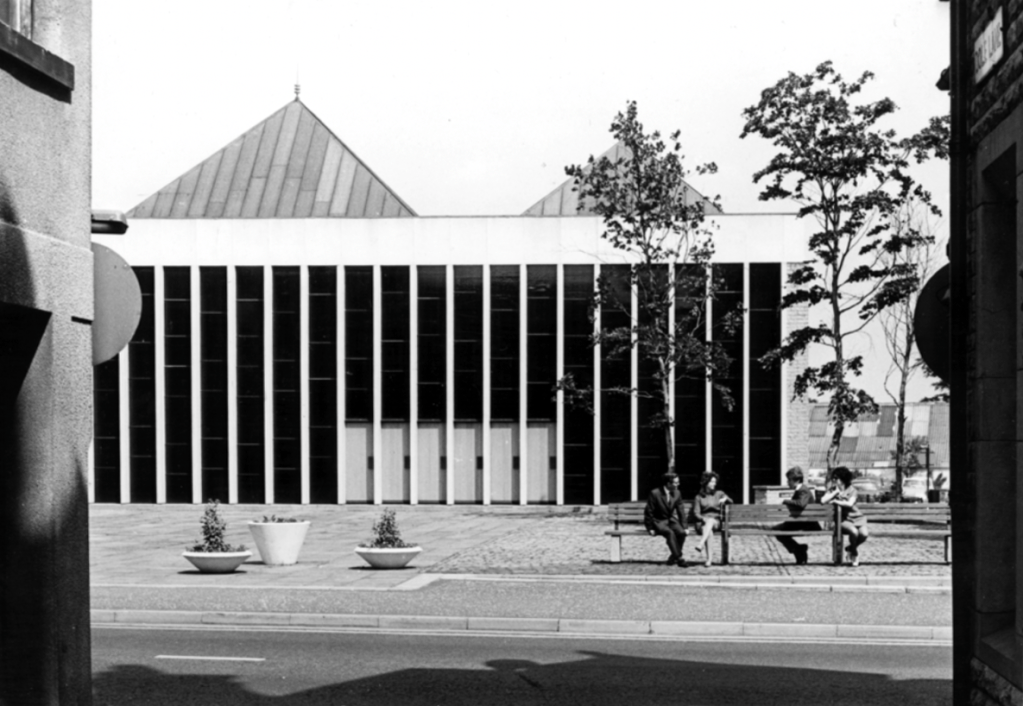
Onwards along Central Drive to the Library.
The work of County Architect Roger Booth and his team, opened in 1967.

With thanks to the Library Staff.
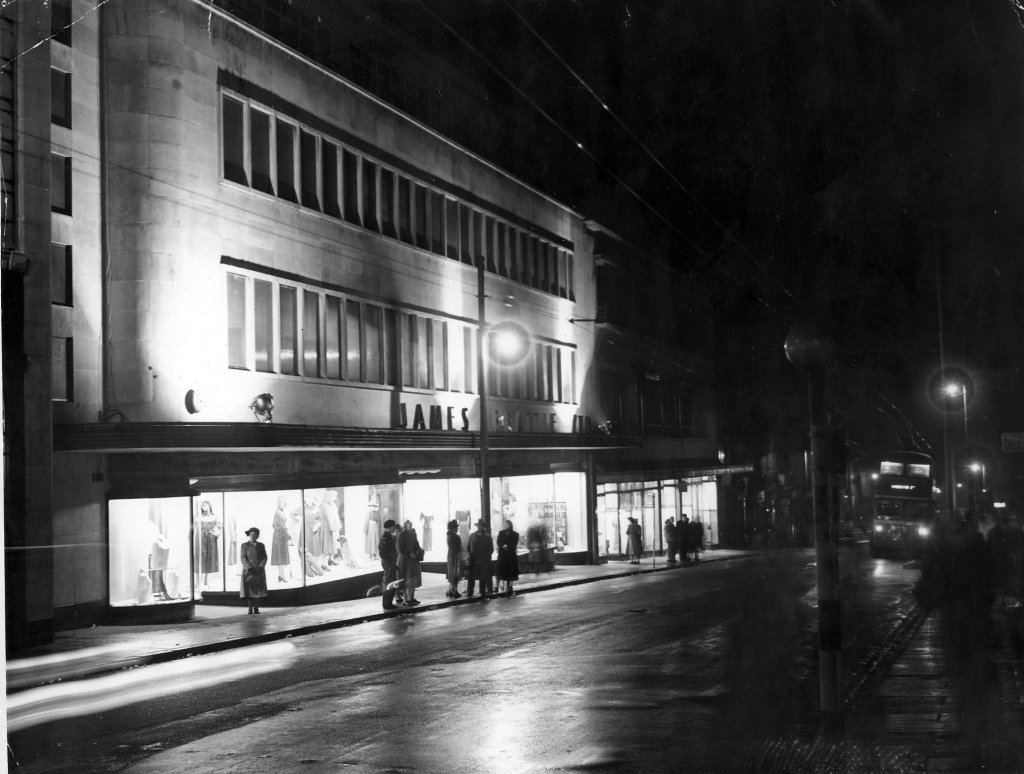
Seen here in its original form, before the alterations were made.

Image – Red Rose Collections


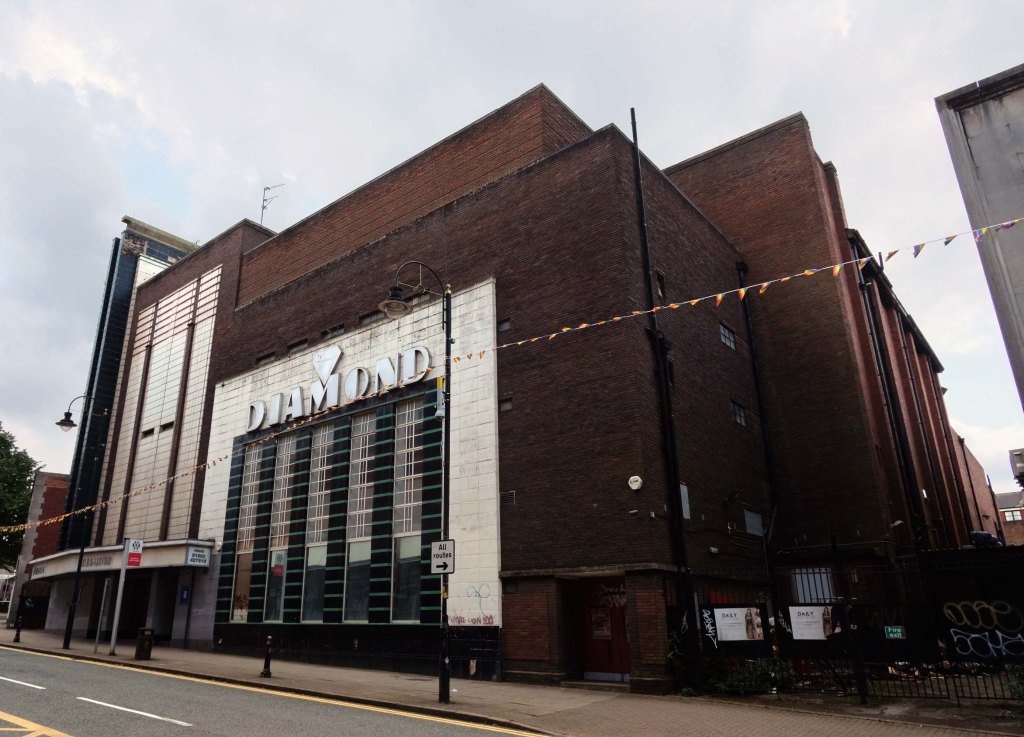
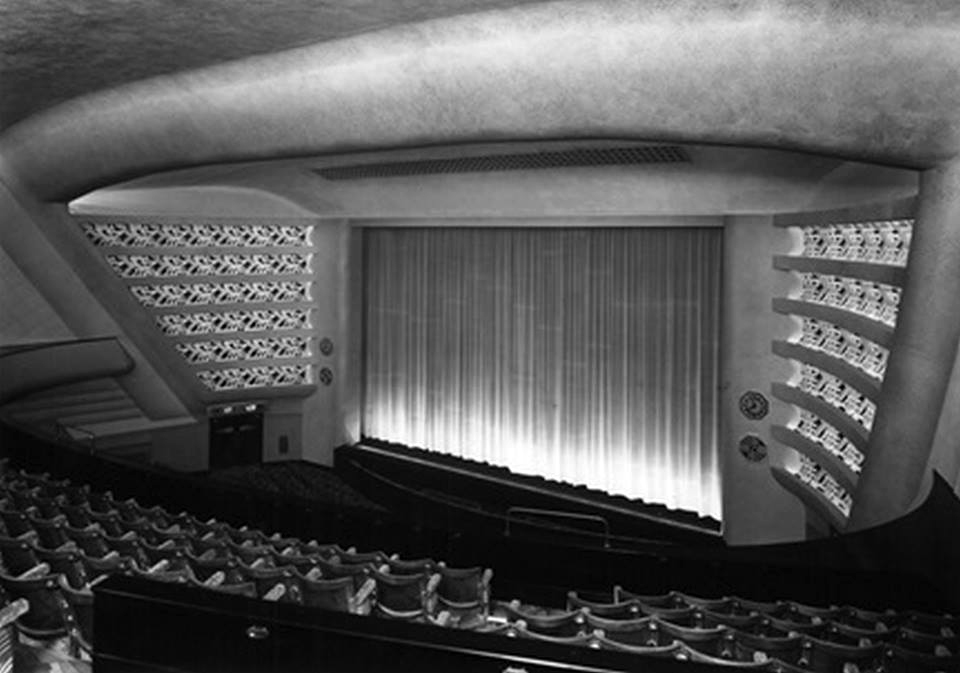
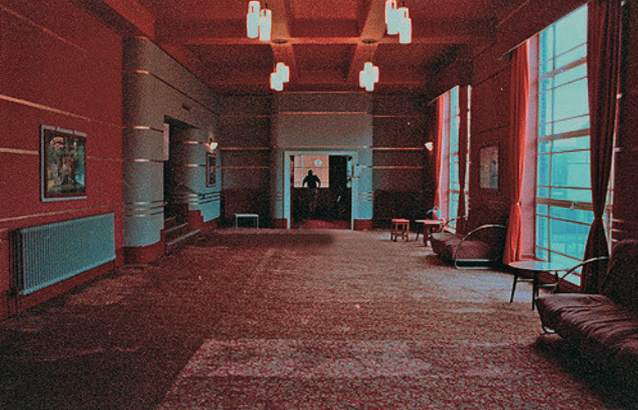
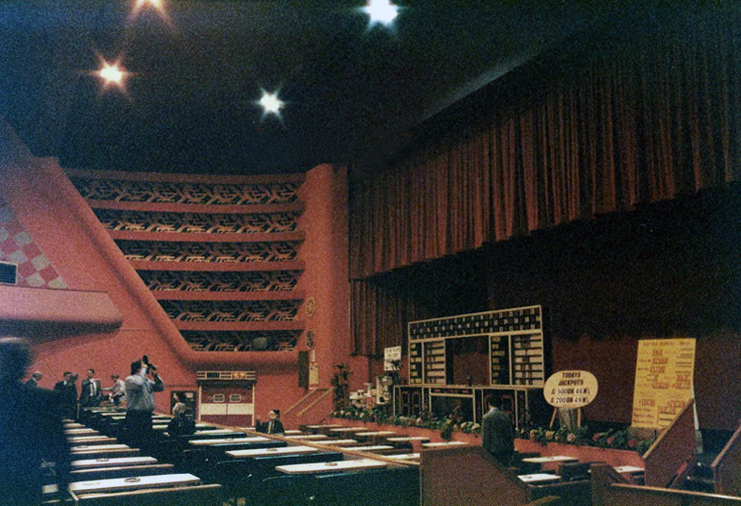
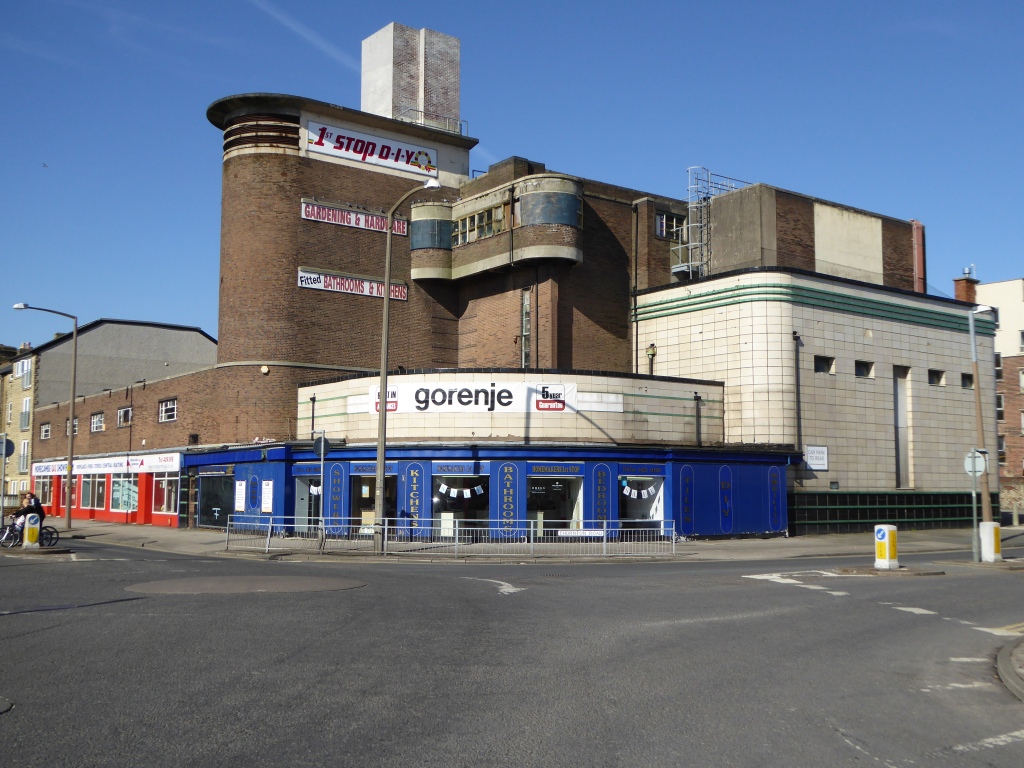
Off down to the former Odeon Cinema 1937 architects – W Calder Robson and Harry W Weedon
Like many of the original Odeon Theatres built by Oscar Deutsch, the site chosen was a little out of the main town centre – where land prices were cheaper, and the Odeon Morecambe is a good example of this. It is located at the corner of Euston Road and Thornton Road in this Lancashire seaside town. The Odeon was opened on 2nd September 1937 with Sandy Powell in “It’s a Grand Old World”. It had seating provided for 1,084 in the stalls and 476 in the circle.
Taken over by the Classic Cinemas chain in December 1967, it was re-named Classic Cinema, and was closed on 28th February 1976 with Kenneth Williams in “Carry On Behind”.
The stunning Moderne style exterior much of which including the projectionists walkway is now much deteriorated.


Next to the Police Station another Roger Booth building – recently seen on the small screen in The Bay.


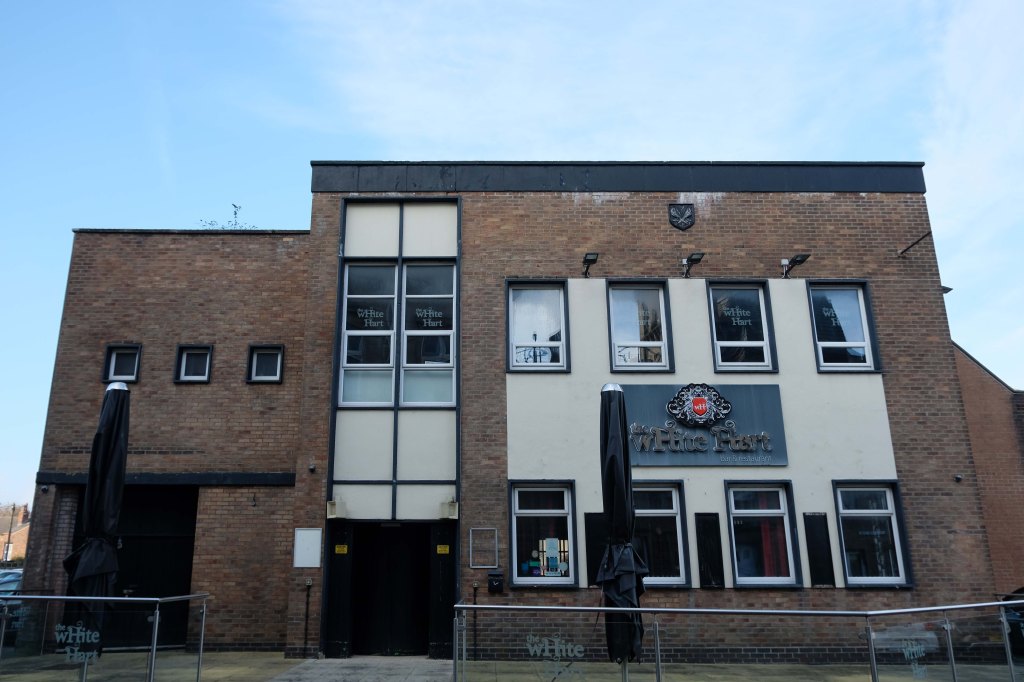
Backtracking to take in the Crescent Café entrance.

Which became Hart’s Restaurant now trading as the Black Thai.

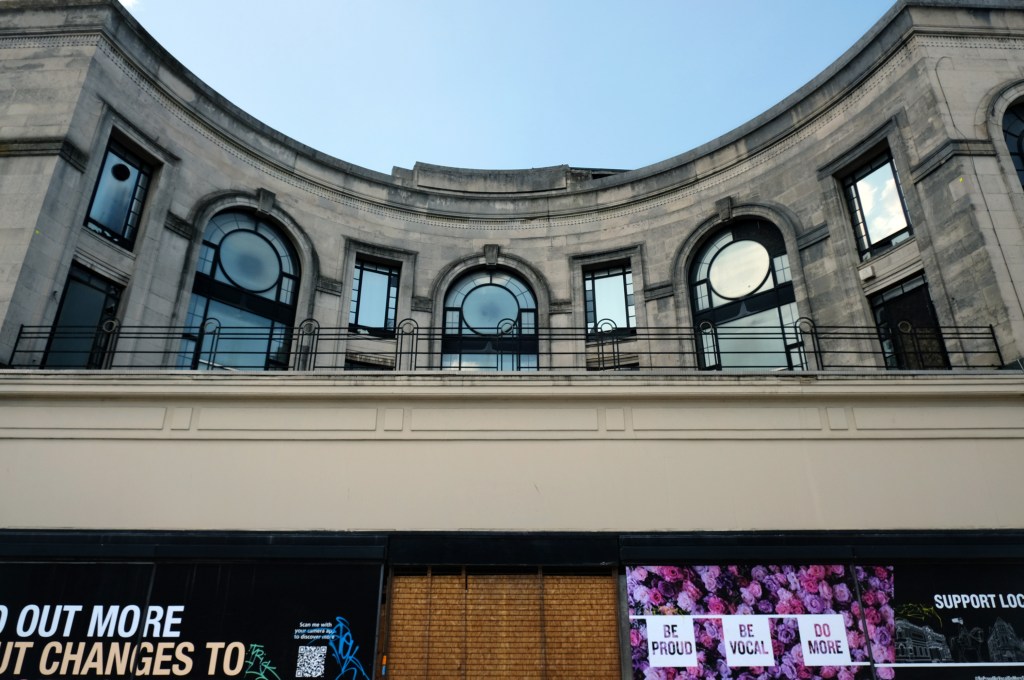
Into the town centre to look at the former Centenary House Co-op 1927.

Bought by the city council as part of the West-End Masterplan, the intention is to refurbish the building’s upper floors to provide affordable housing and accommodation for local arts businesses, retaining the Co-op late shop that occupies one-half of the ground floor.



Let’s take a look along the front – where we find a former Woolworths.
Along with other stores from the same period.


Alongside sits the former Littlewoods.
By 1939 there were 24 stores. A number of these were purpose-built for Littlewoods to designs by J S Quilter & Son. John Salmon Quilter – 1841-1907 was, in fact, long dead, but his architectural practice had been continued by his son Cecil Molyneux Quilter – 1879-1951. Quilter specialised in commercial architecture, notably public houses. He designed a new Blackpool store for Littlewoods, on the corner of Church Street and Corporation Street, which was faced in Empire stone. He also designed a store in Chester, and may have been responsible for the one in Morecambe. This faience-clad art deco building is the best surviving example of a pre-war Littlewoods store – indeed, it may be the best surviving Littlewoods of all time – even preserving diamond L motifs on the entrance lobby floors. These clearly copied Woolworth’s diamond W.


Next to Brucianni’s, a gem of a coastal café and ice cream parlour – Grade II listed.



Finally to the Midland Hotel 1932-3 by Oliver Hill
Concrete and rendered brickwork, painted white. Curved plan, with convex side facing west towards the sea. Three storeys. Windows are steel-framed casements with rendered surrounds. Above each storey are projecting horizontal bands. The entrance front has a rounded left-hand corner, and a convex central staircase projection rising above roof level. This projection has a tall window of steel casements above the doorway, divided into three by mullions, both of which are capped by sea horses, painted red, which were carved by Eric Gill. Projecting at the right is a single-storey cafe of circular plan, now known as the Ravilious Restaurant. The west side has a single-storey projecting sun lounge, which is an addition, its windows replaced in PVC-coated steel. Between the solid centre and ends of the facade the 1st and 2nd floors have their walls recessed to form balconies.
Interior: above the cantilevered circular open-well staircase is a ceiling panel carved in low relief by Eric Gill and painted by Denis Tegetmeier. They were also responsible for the pictorial map of north-west England in what was originally the children’s room at the south end of the building. Also in this room is Eric Gill’s Portland stone panel, originally in the lounge, carved in low relief with a representation of Odysseus and Nausicaa. It was moved to its present position when internal walls were demolished during the 1970s. The cafe walls were originally painted with frescoes by Eric Ravilious, representing morning and evening in an idyllic seascape setting. These deteriorated rapidly because the plaster and paint used were incompatible and were obliterated within 2 years of completion, but were repainted in the late 1980s using photographic evidence.

Eric Gill


Tirzah Garwood and Eric Ravilious

Sadly we are no longer able to see the long gone Super Swimming Stadium.
Architect: Kenneth MB Cross and Cecil Sutton

The Super Swimming Stadium at Morecambe, Lancashire, was one of the grandest of the 1930s modernist seaside lidos. This massive structure measuring 396ft. by 110ft. was said to be the largest outdoor pool in Europe when it opened in 1936, accommodating some 1200 bathers and 3000 spectators. Unusually for an inter-war lido, it was designed not in-house by a Borough Engineer but by two architects, Kenneth MB Cross and Cecil Sutton, who styled it to harmonise with the Streamline Moderne of Oliver Hill’s adjacent Midland Hotel.
The stadium was closed down in 1975 on grounds of structural problems and demolished just a year later.