Having photographed the arterial roads of Manchester in 2014, I have resolved to return to the task in 2024.
Some things seem to have changed, some things seem to have stayed the same.
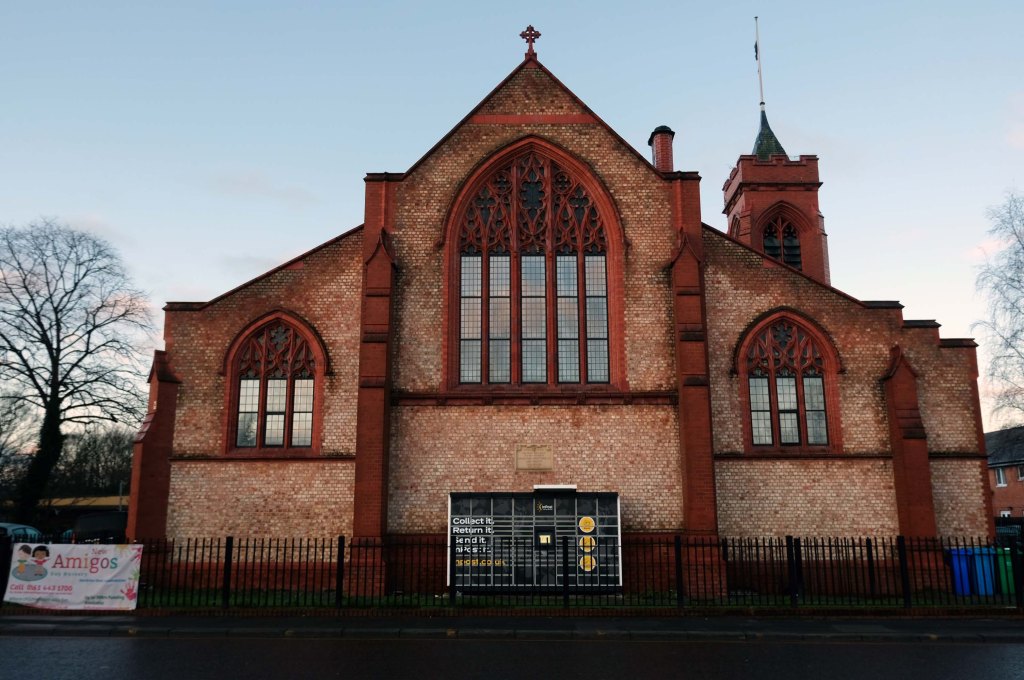
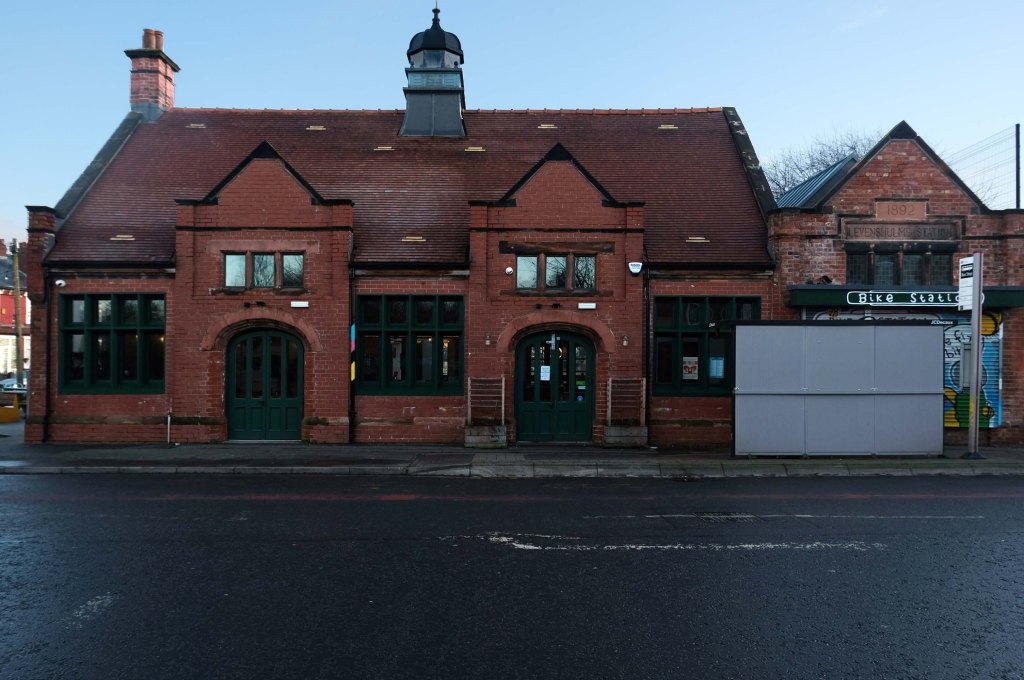
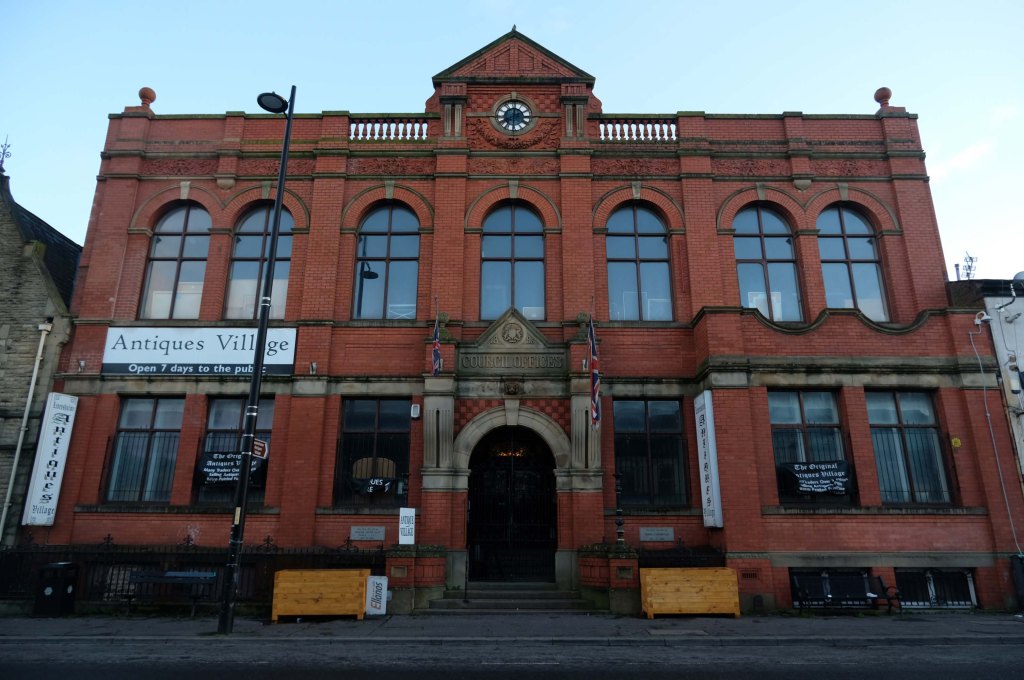
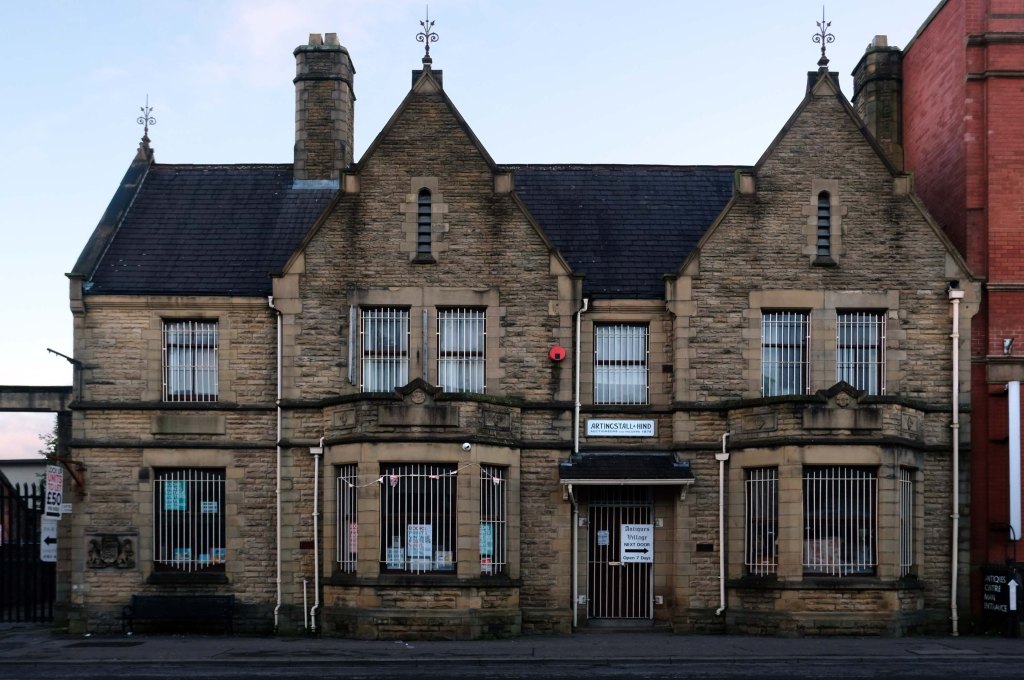
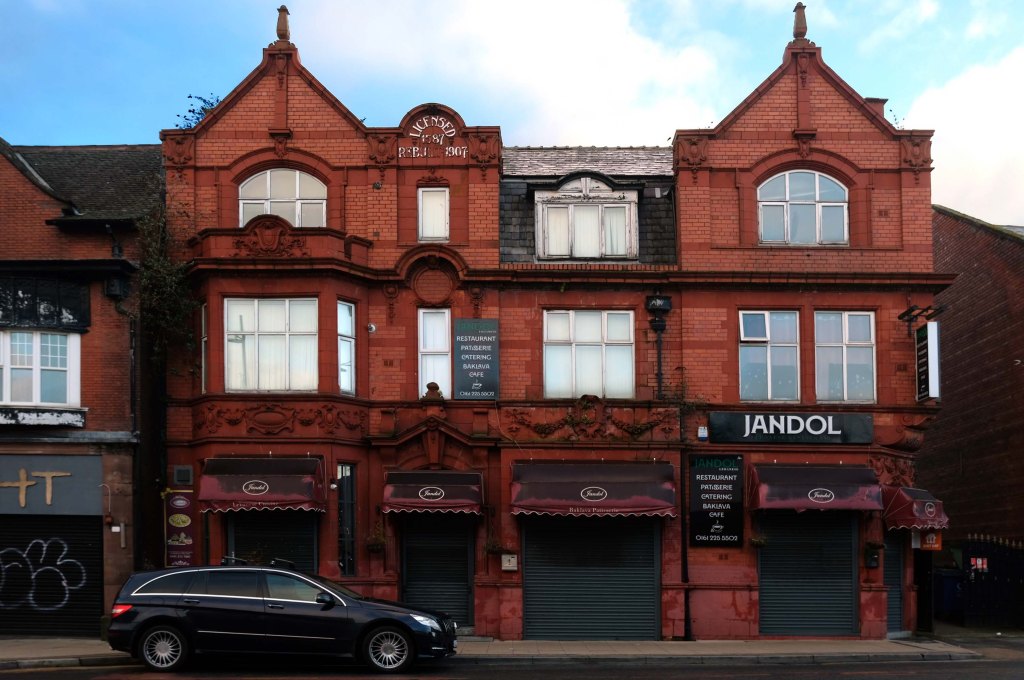
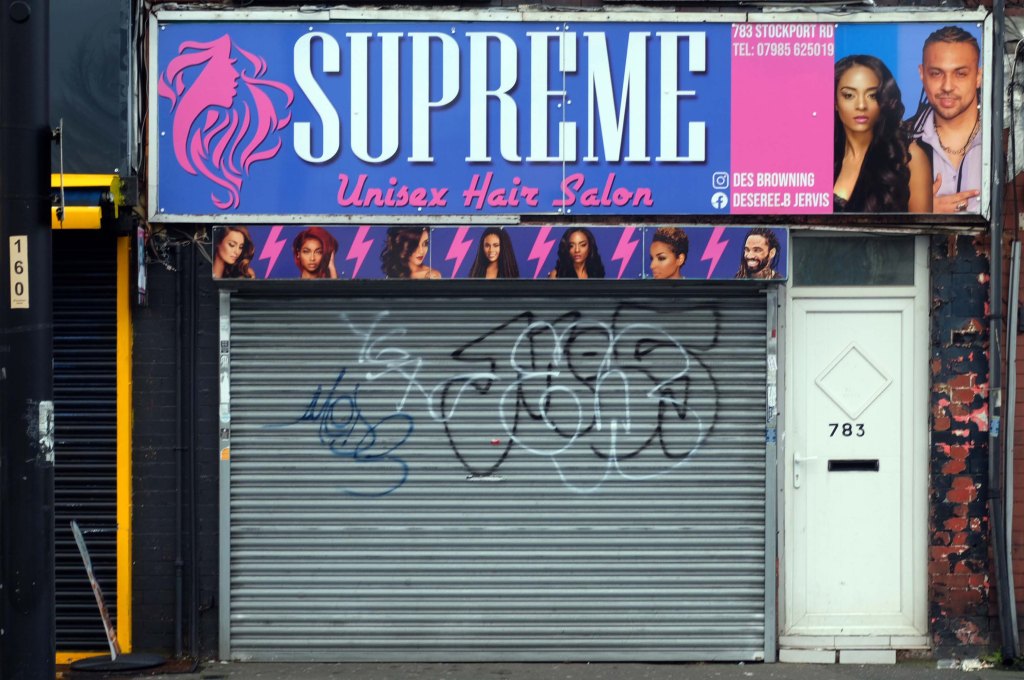
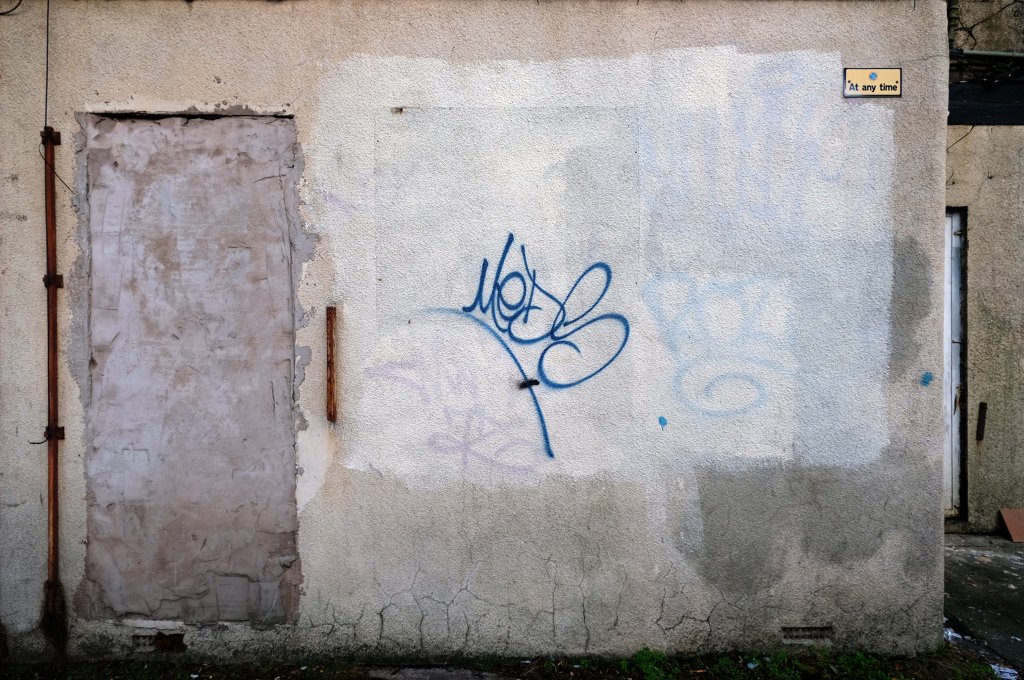
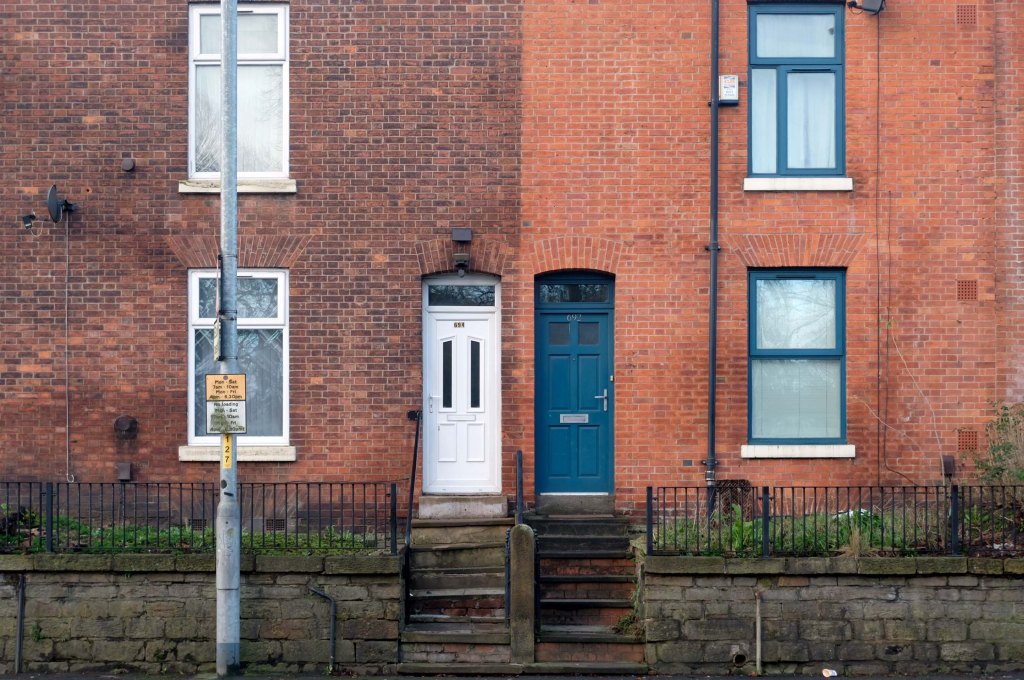
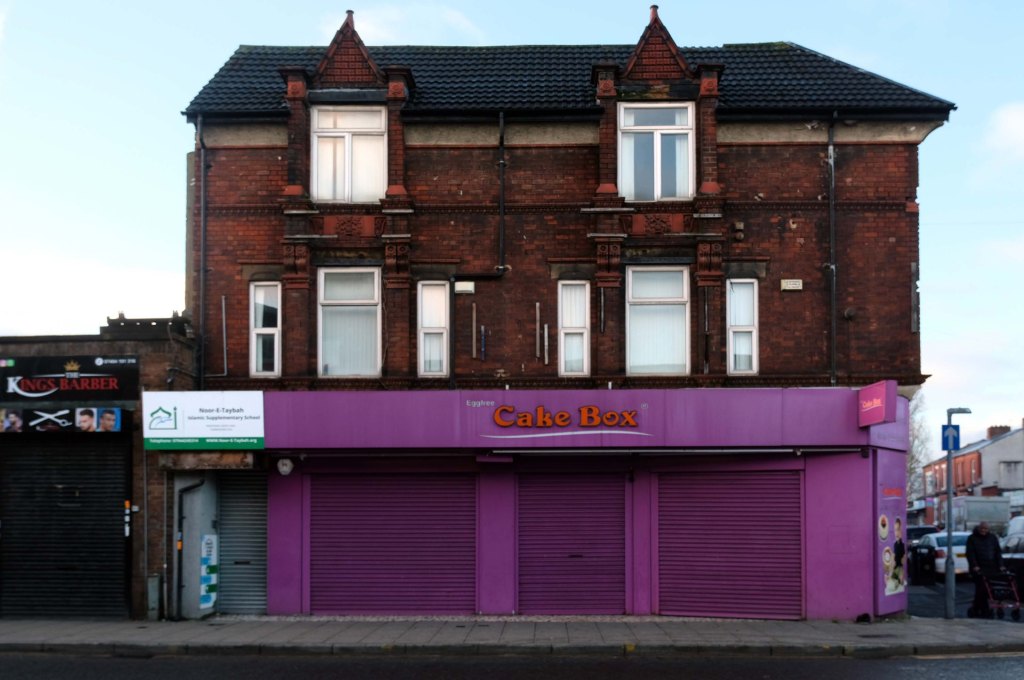
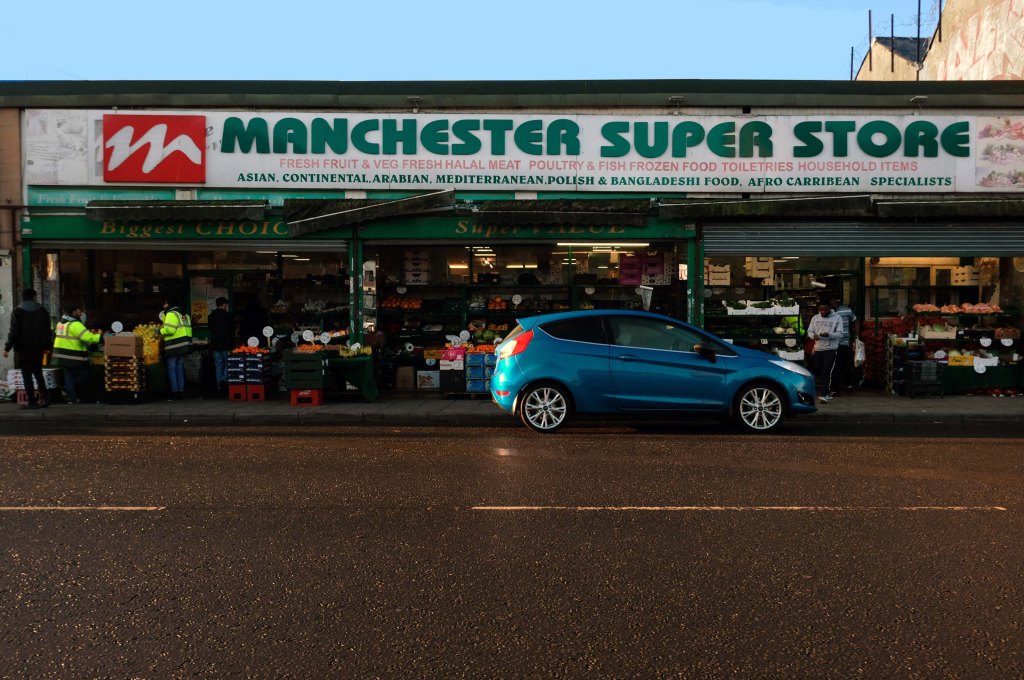
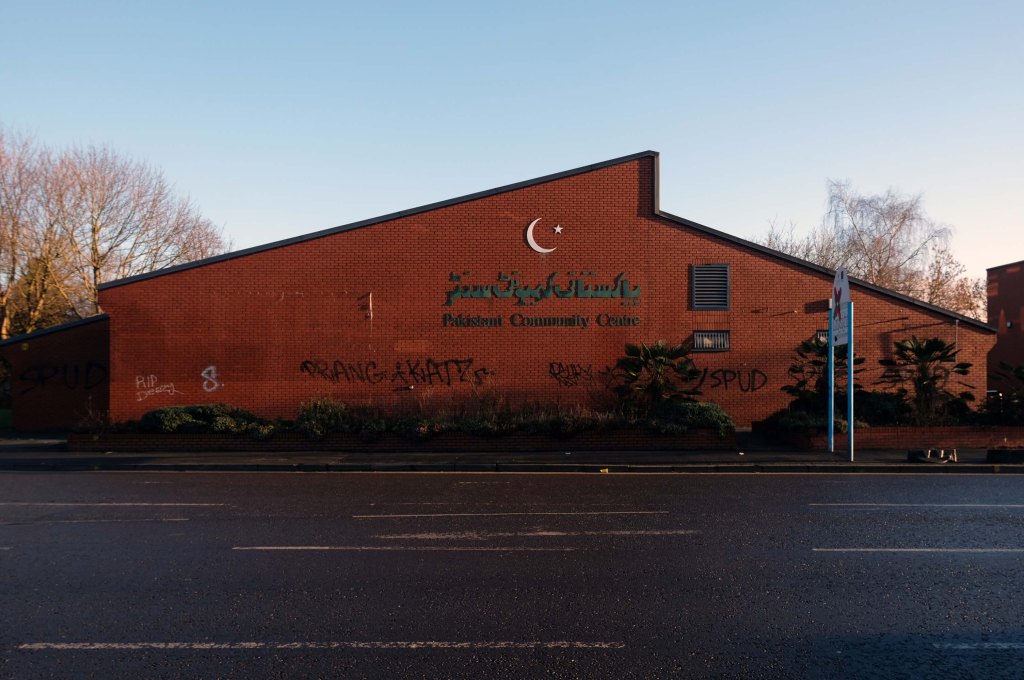
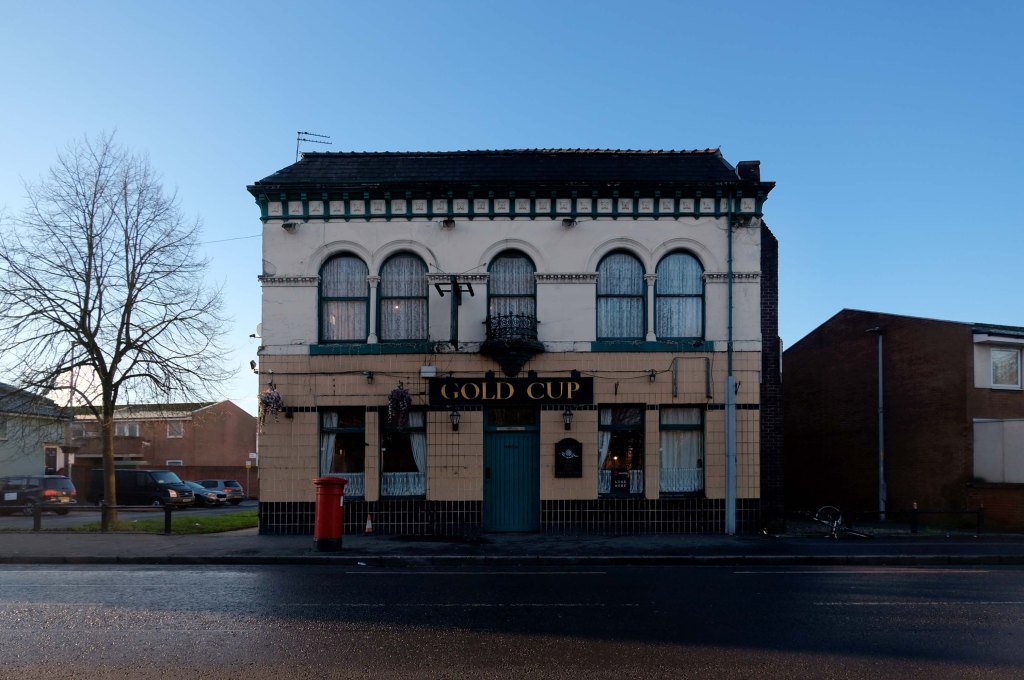
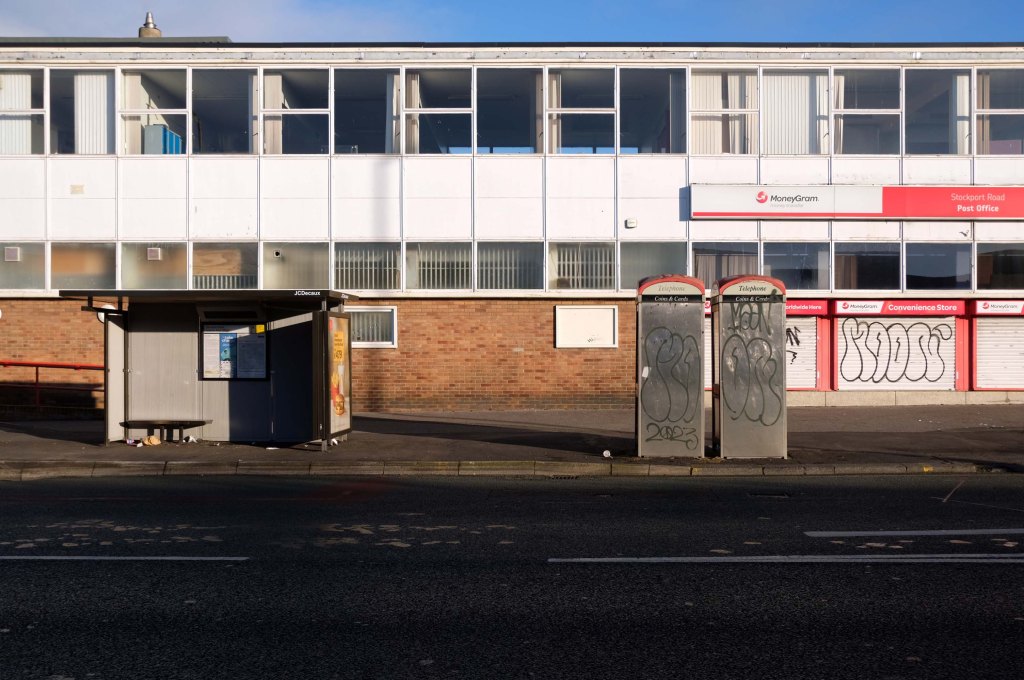










































Having photographed the arterial roads of Manchester in 2014, I have resolved to return to the task in 2024.
Some things seem to have changed, some things seem to have stayed the same.









































Well it seems that I had already cycled from Hull to Scarborough, so it must be time to head for Redcar.
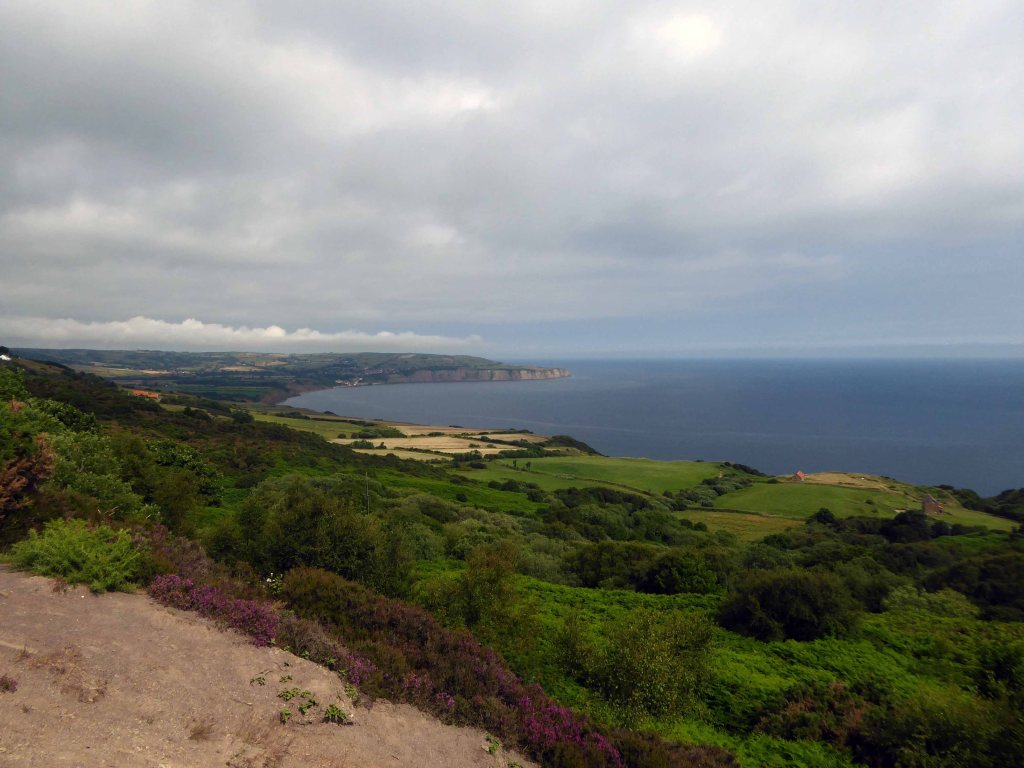
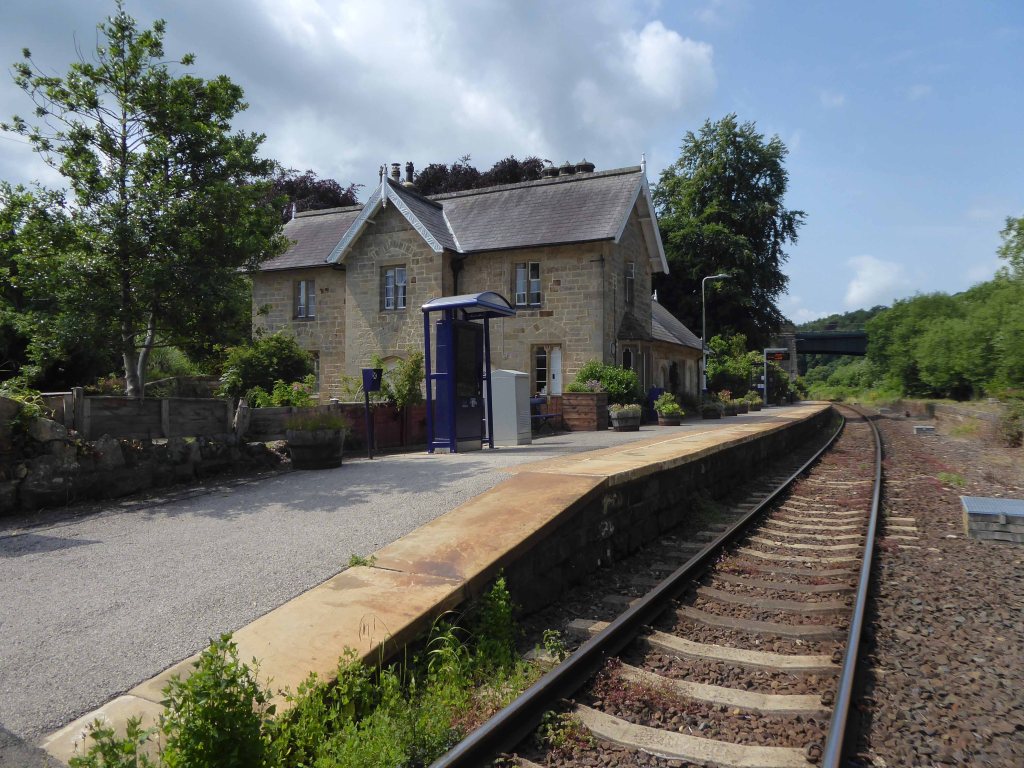
Leaving Scarborough by the Cinder Track under the expert guidance of Mr Ben Vickers.
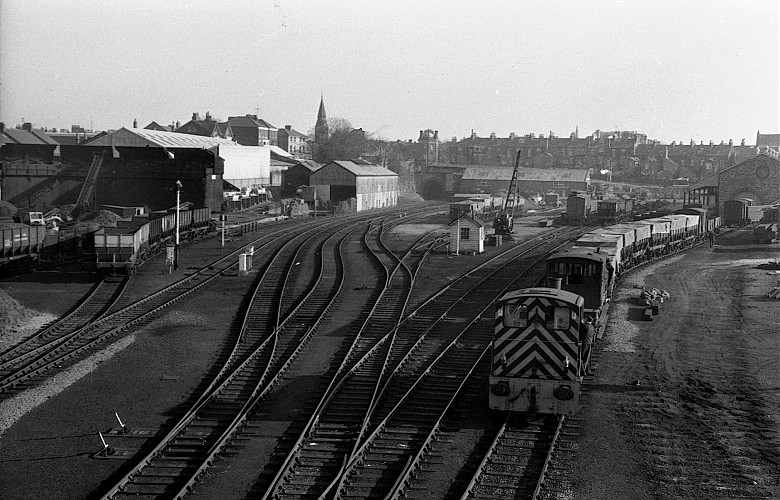

This was the site of the Gallows Close Goods Yard.
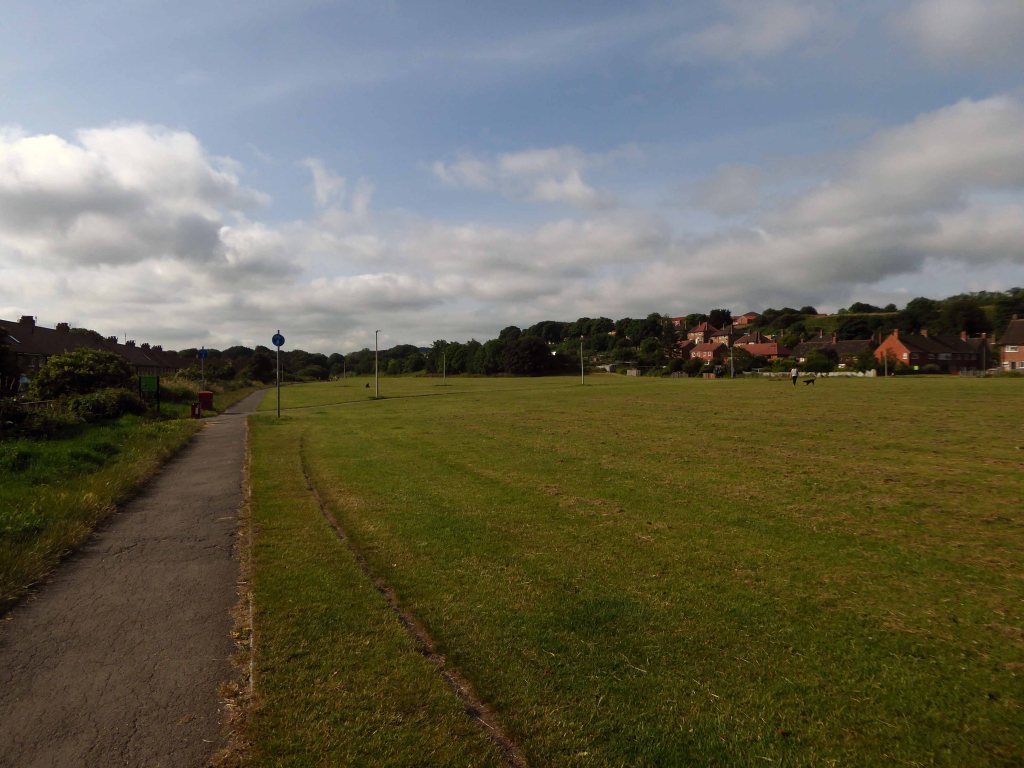

Formerly the Scarbough to Whitby Railway – the line opened in 1885 and closed in 1965 as part of the Beeching Axe.


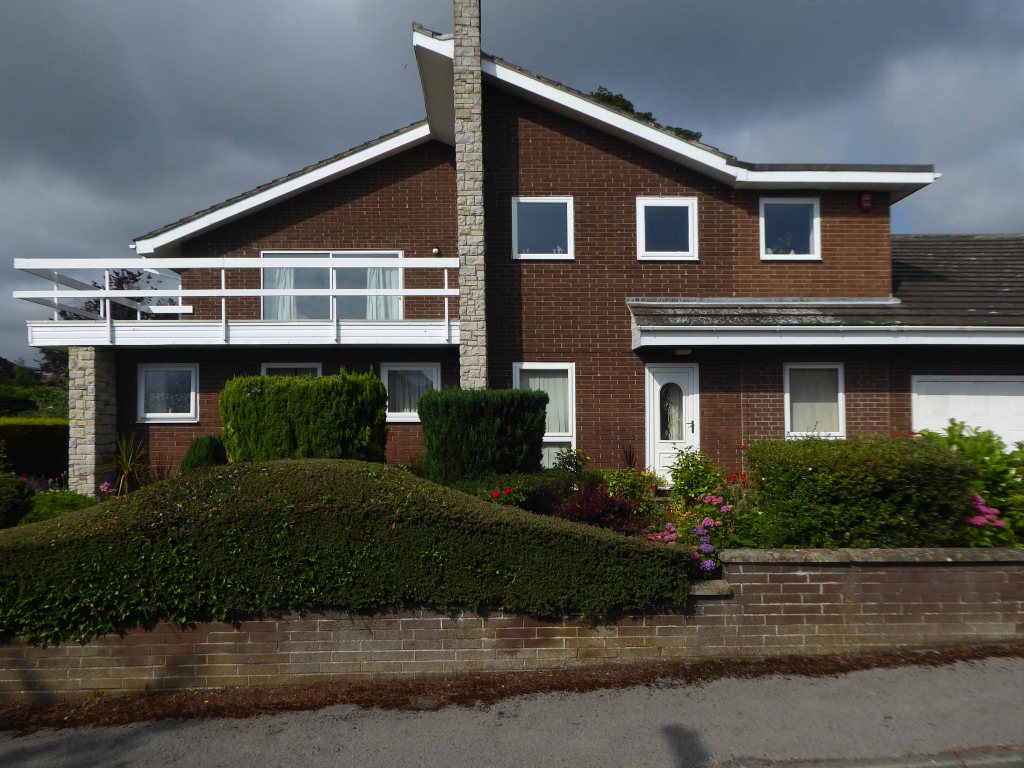
Yet again I chance upon a delightful post-war home.
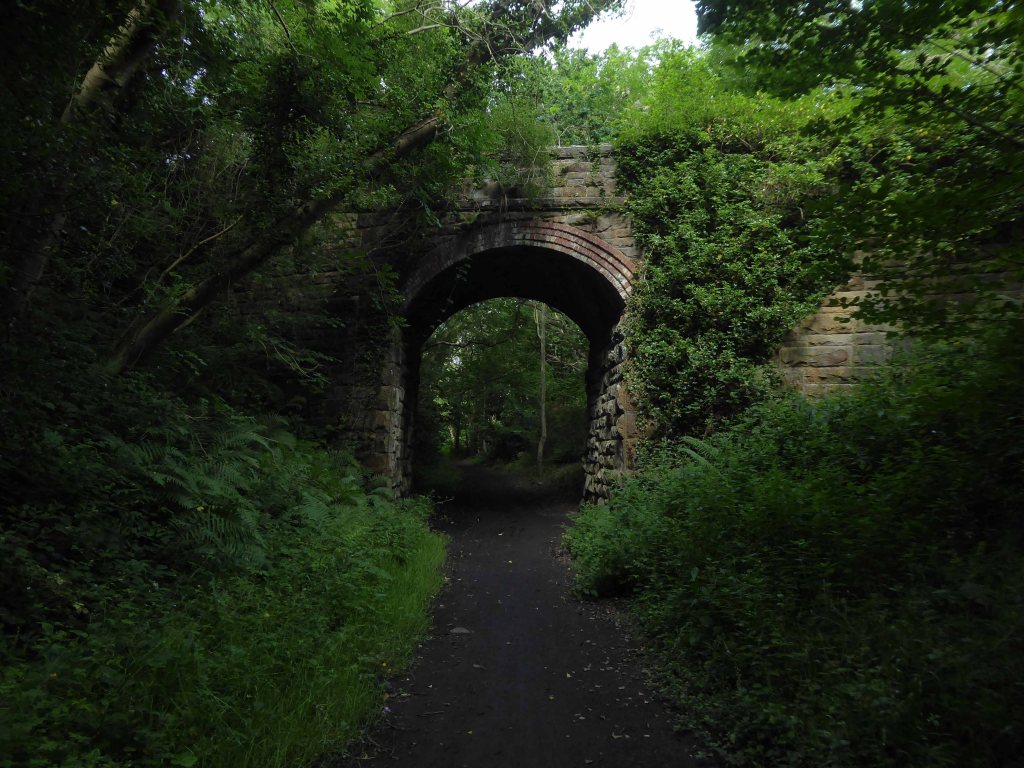
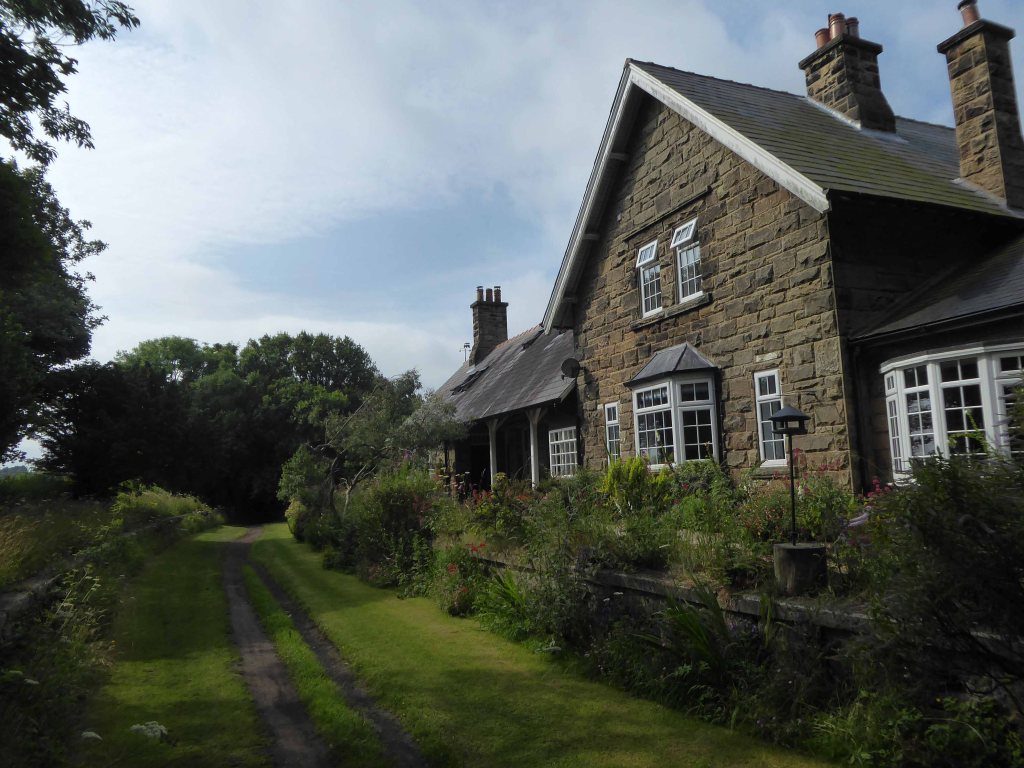





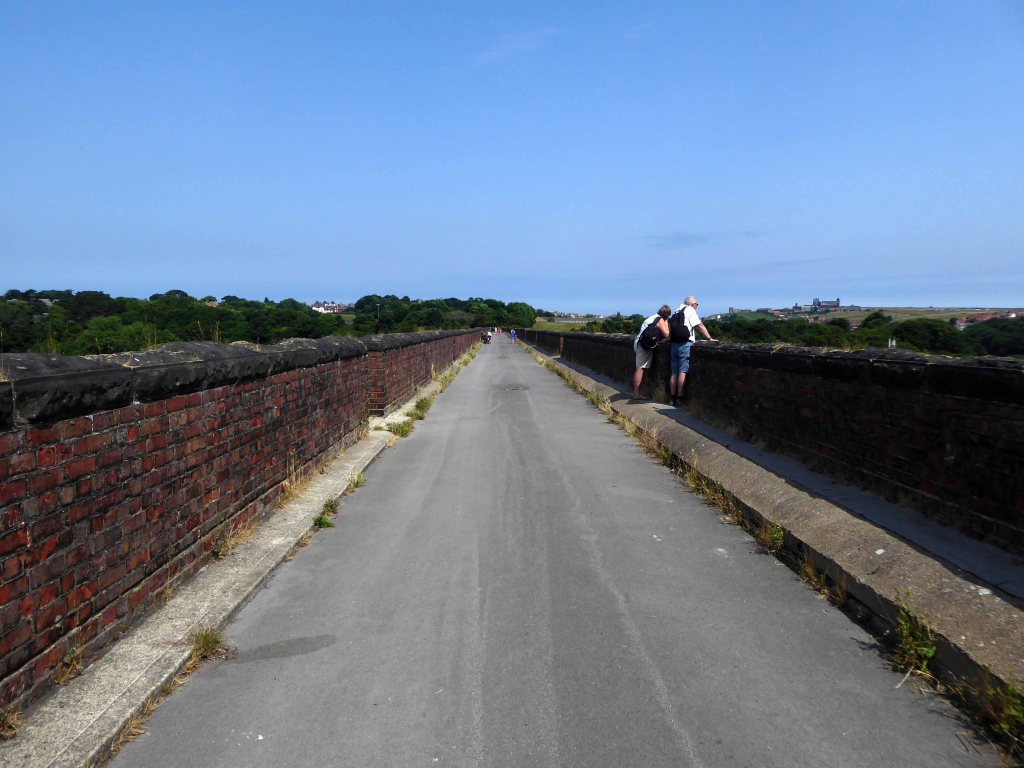
I parted company with the track dropping down to the Esk Valley from the Larpool Viaduct.
Construction began in October 1882 and was complete by October 1884.
Two men fell from the piers during construction, but recovered.

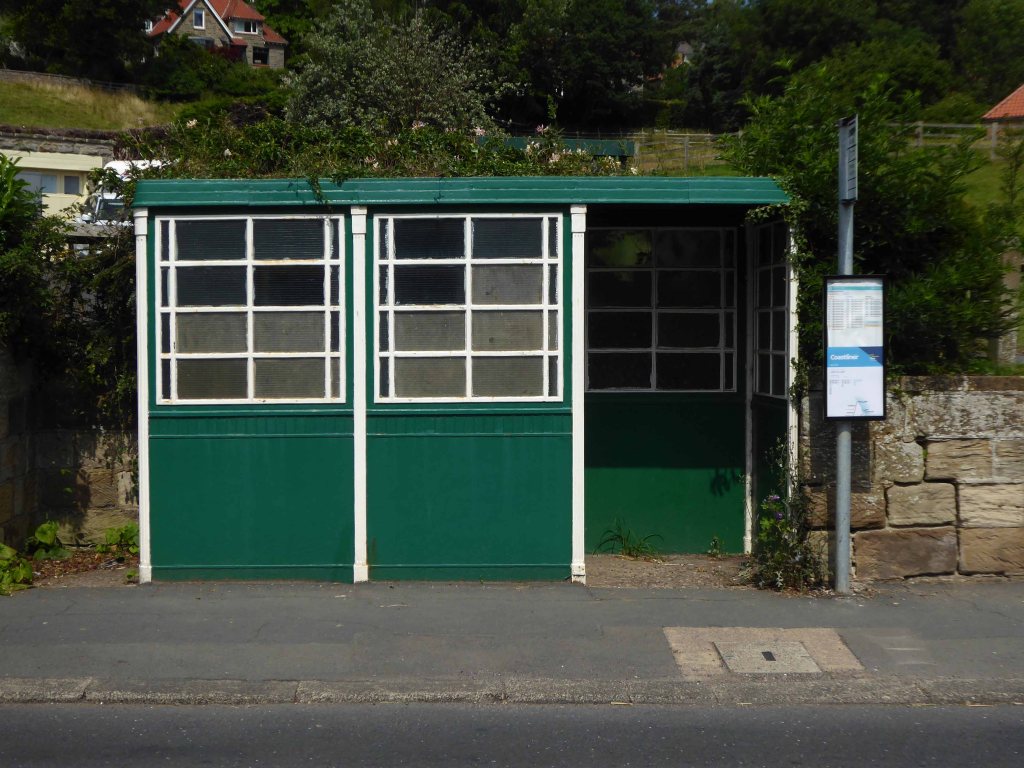
I found myself in Ruswarp, home to this enchanting bus shelter.

I bombed along the main road to Sleights.

There then followed a hesitant ascent, descent, ascent along a badly signed bridleway, fearing that I had climbed the hill in error I retraced, then retraced.
A difficult push ensued, a precipitous path, rough and untended, rising ever higher and higher.


Finally arriving at Aislaby, more than somewhat exhausted – the village is mentioned in the Domesday Book as Asuluesbi.
Pausing to catch my breath I took the wildly undulating road to Egton – along the way I was alerted to the presence of a tea stop by two touring cyclists from Nottingham.
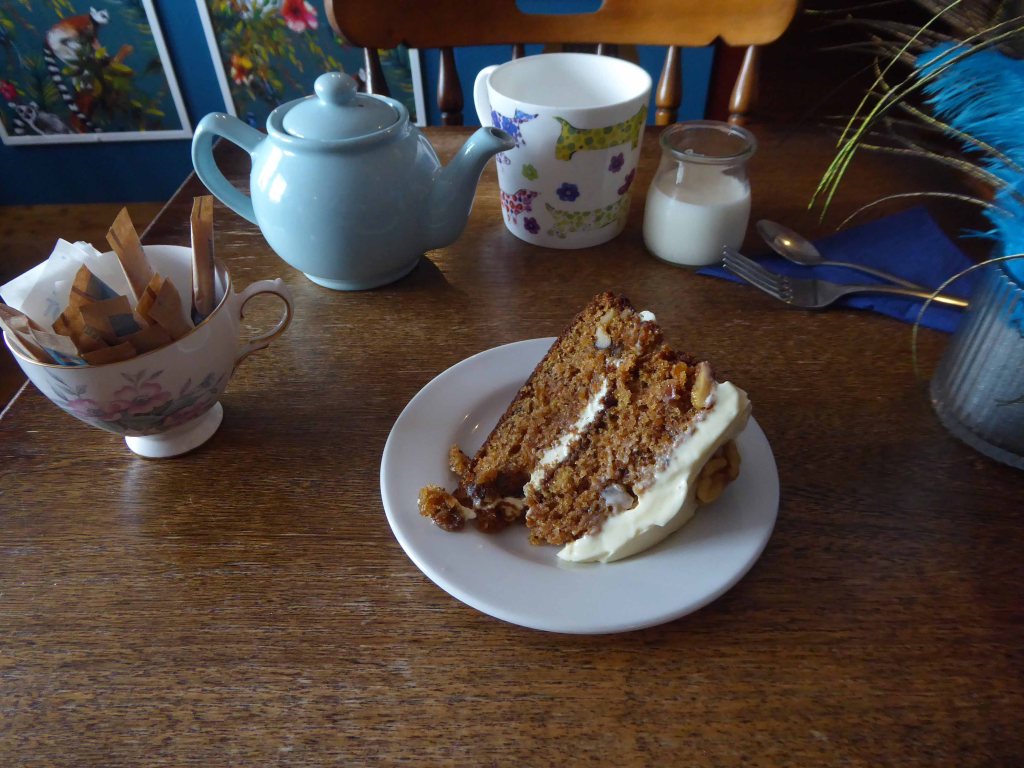

A welcome wet and a hunk of home made carrot cake.
Brewmeister Maria was good enough to suggest route through Castleton Moor and over the tops to Saltburn.
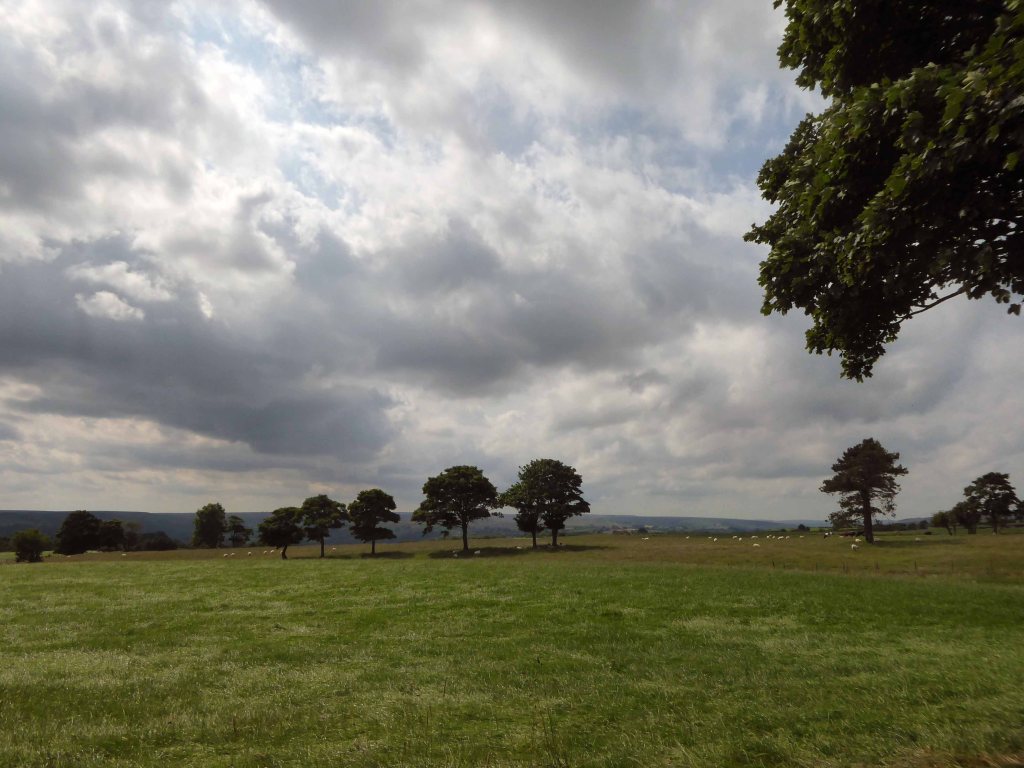
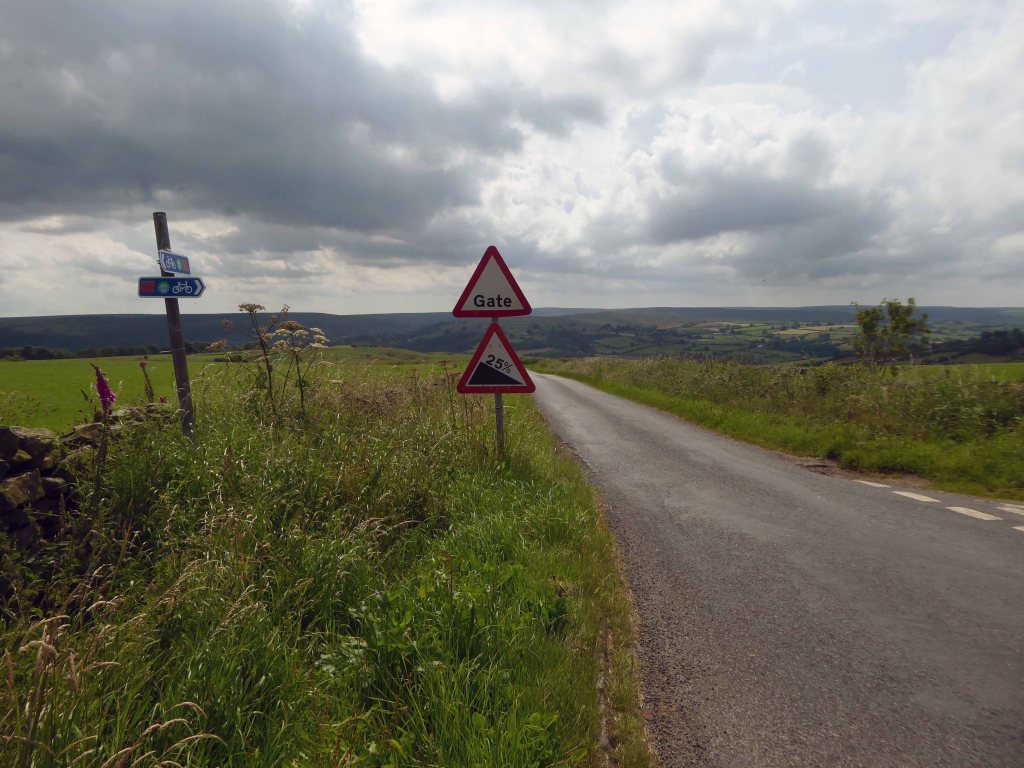


It was too hot a day for a detour to Fryup.
The curious name Fryup probably derives from the Old English reconstruction Frige-hop: Frige was an Anglo-Saxon goddess equated with the Old Norse Frigg; hop denoted a small valley.
An old woman at Fryup was well known locally for keeping the Mark’s e’en watch – 24 April, as she lived alongside a corpse road known as Old Hell Road.
The practice involved a village seer holding vigil between 11pm and 1am to watch for the wraiths of those who would die in the following 12 months.

Castleton Moor ghost.

In the village I was given further directions by two elderly gents, who had been engaged in a discussion concerning their long term mapping of acid rain levels in the area.
One was wearing a Marshall Jefferson t-shirt.

I climbed Langburn Bank onto the flatish open moorland.
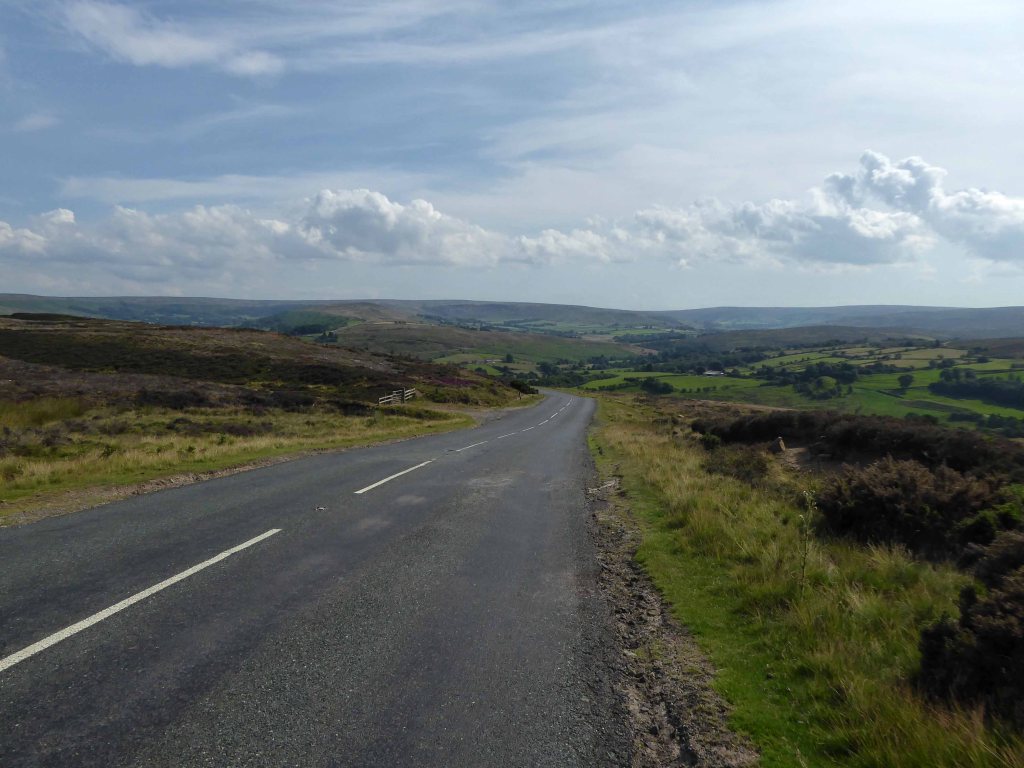

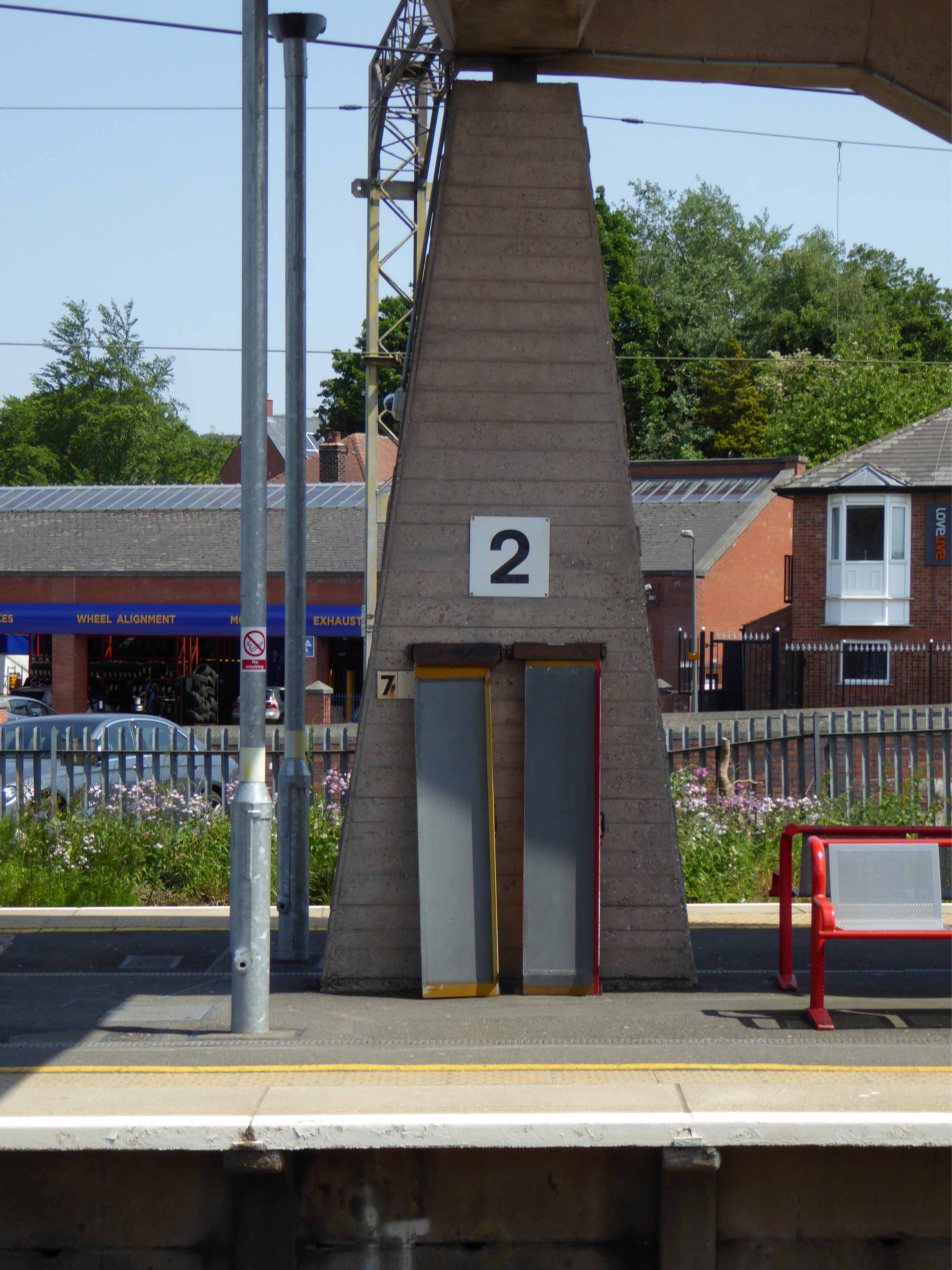
Taking a brief break to snap this concrete shelter.
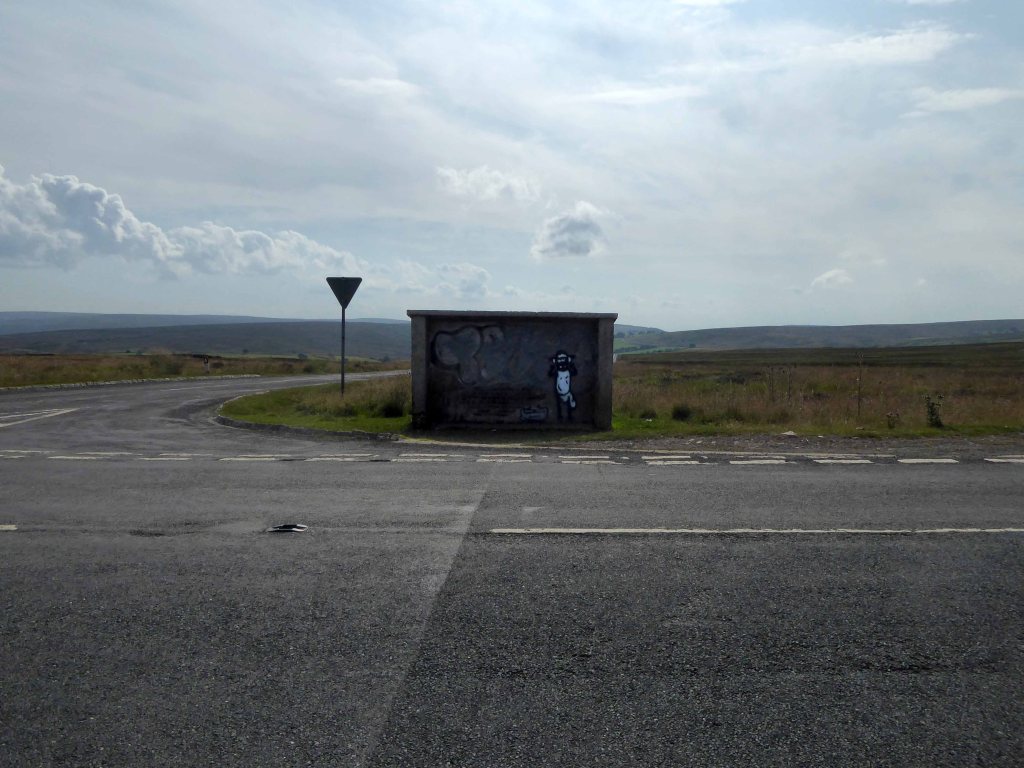

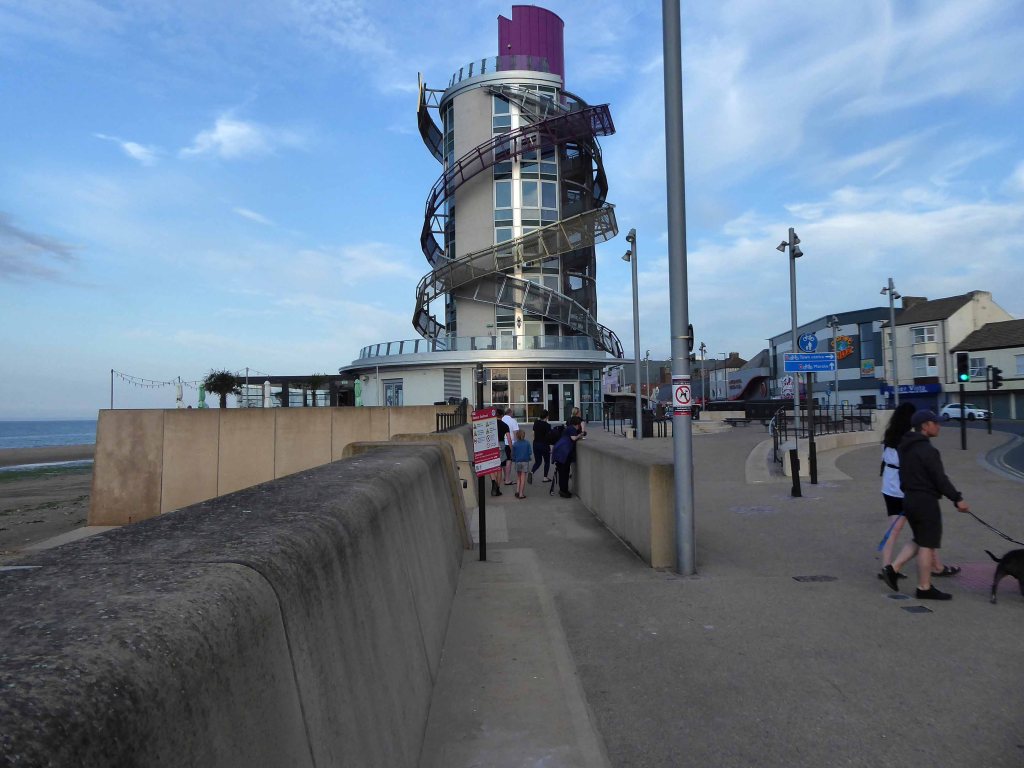
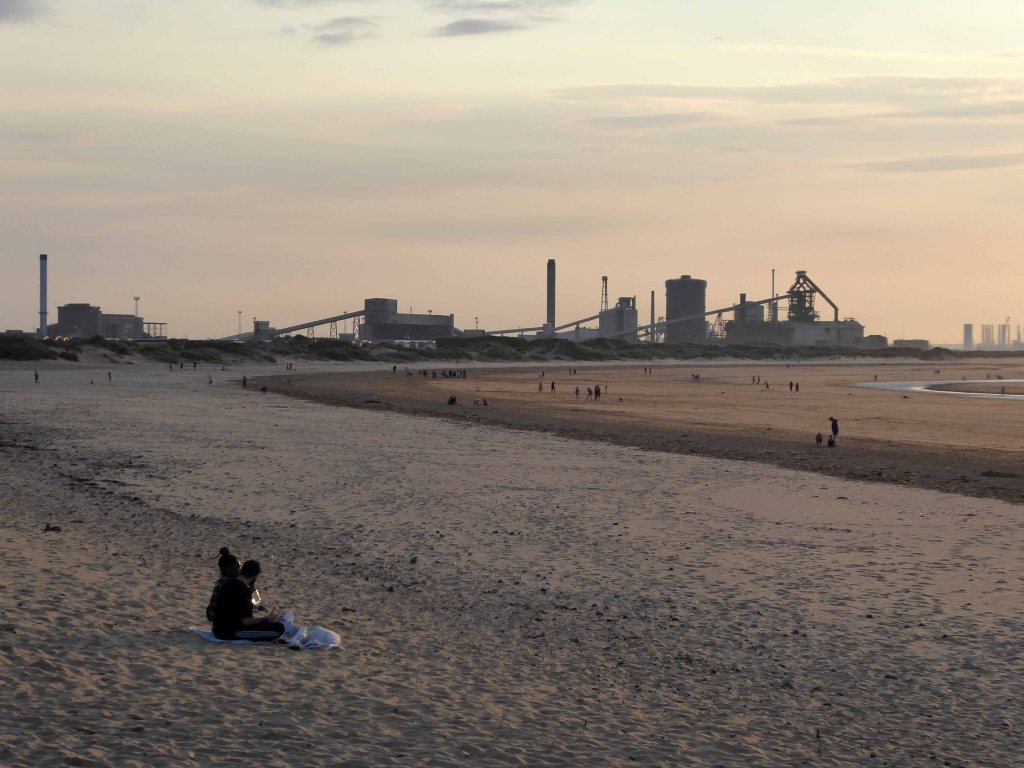
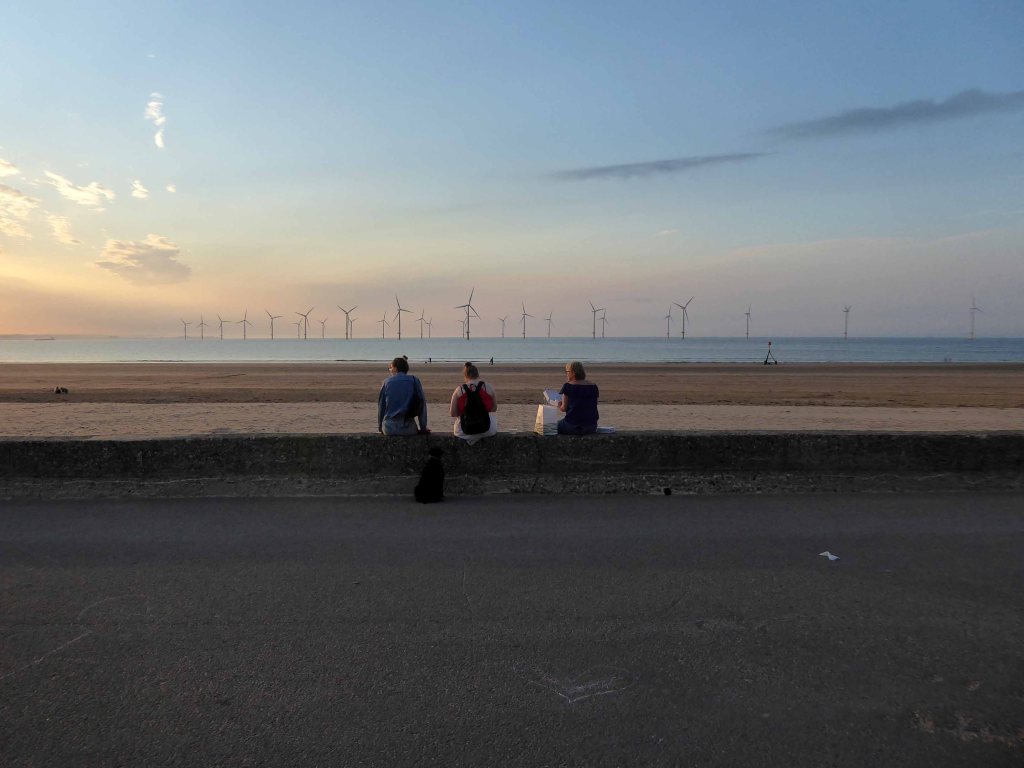
There then followed a hair stirring series of hairpin descents to the coast at Saltburn.
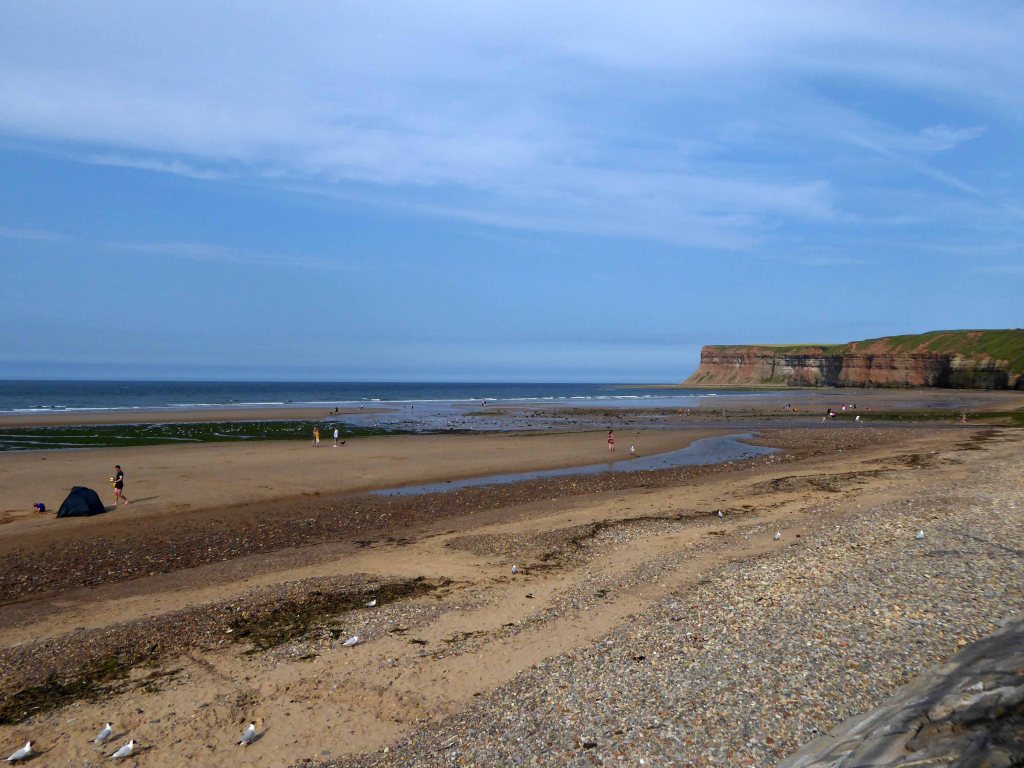

Followed by an off road route to Redcar.
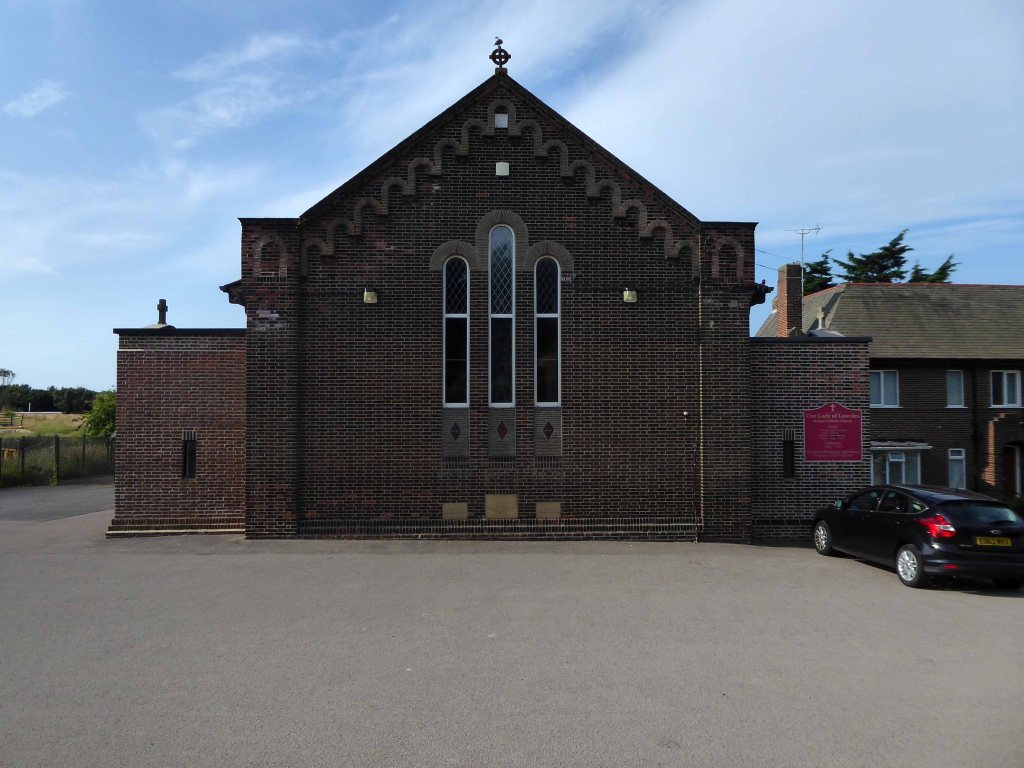
Our Lady of Lourdes – Architect: Kitching & Archibald 1928
Built in 1928, this church was designed with some care and is an attractive, if fairly modest, Lombard Romanesque-style essay in brick. The use of a semi-circular apse, narrow brickwork and use of tile for decorative effect give it a pleasing appearance, typical of restrained but elegant work between the wars.

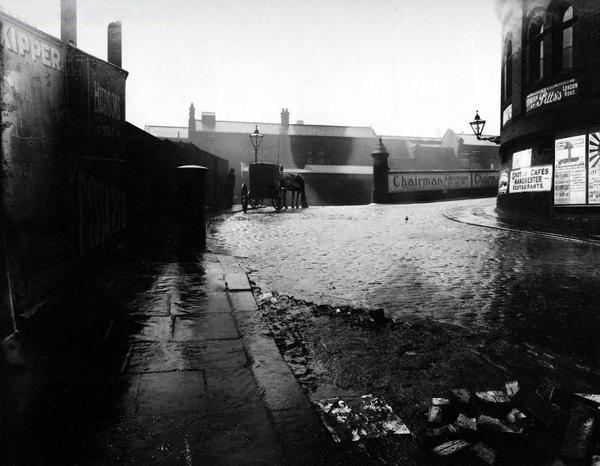
I arrived and took a look around, first time in town, here’s what I found.
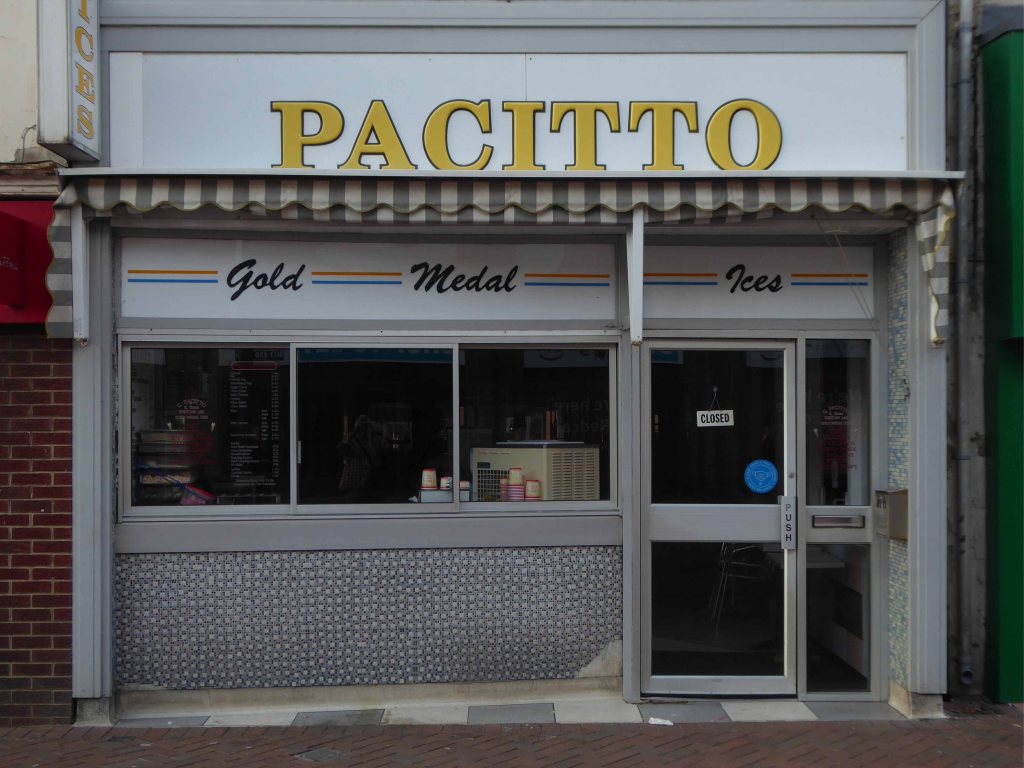
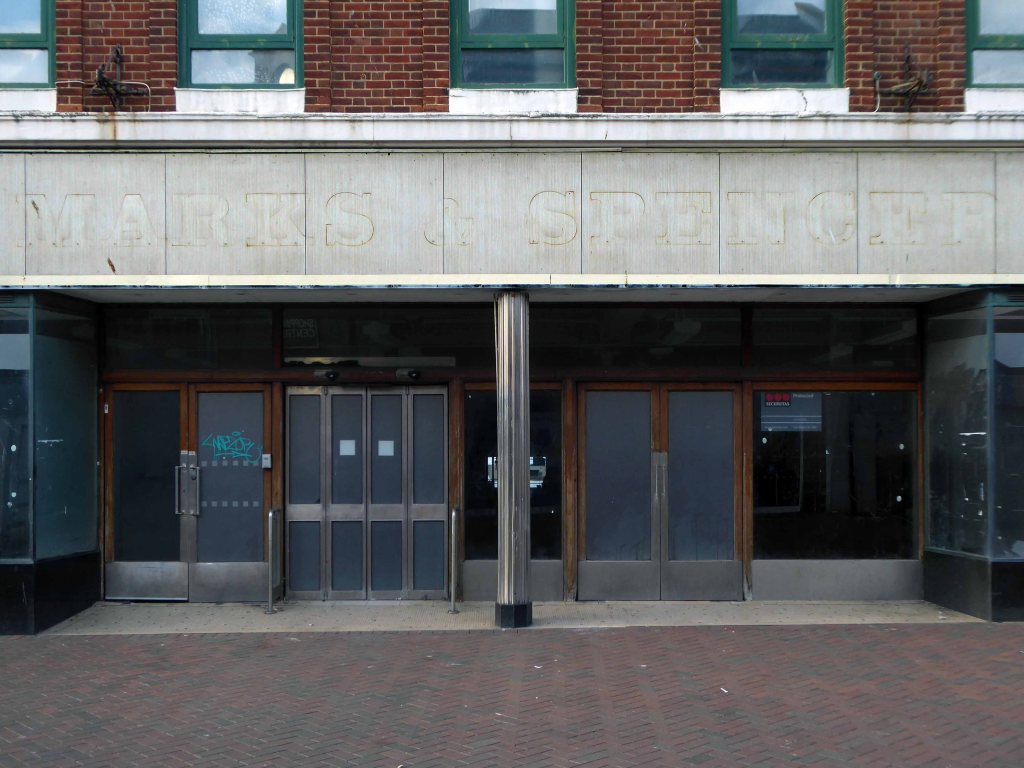
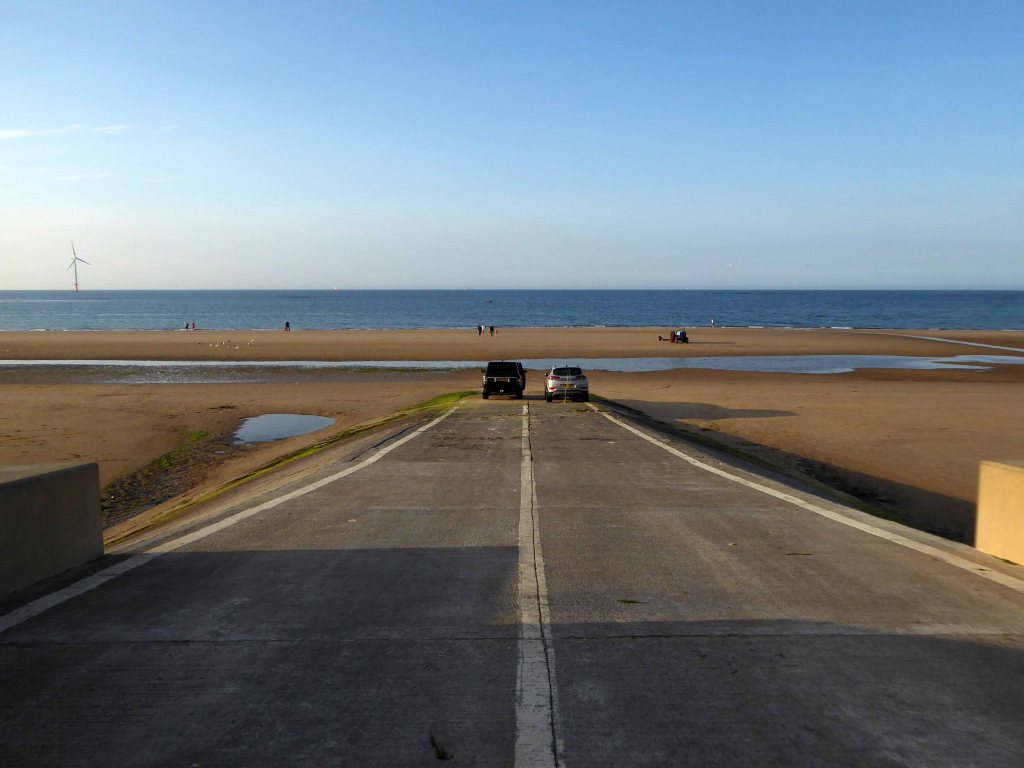
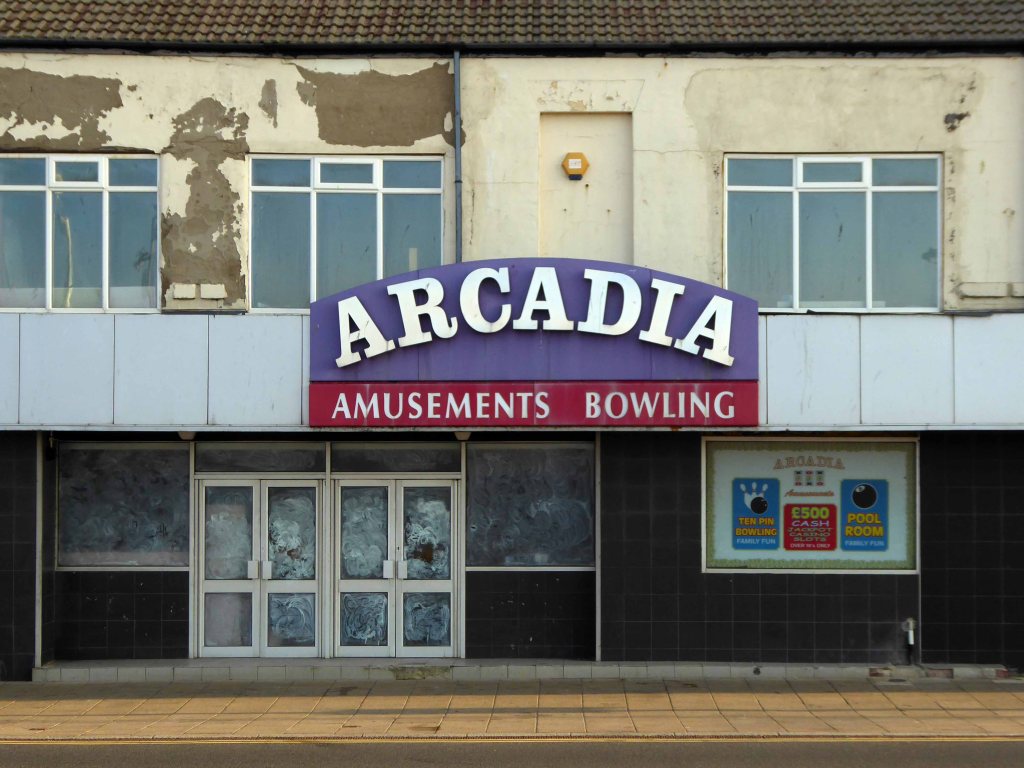
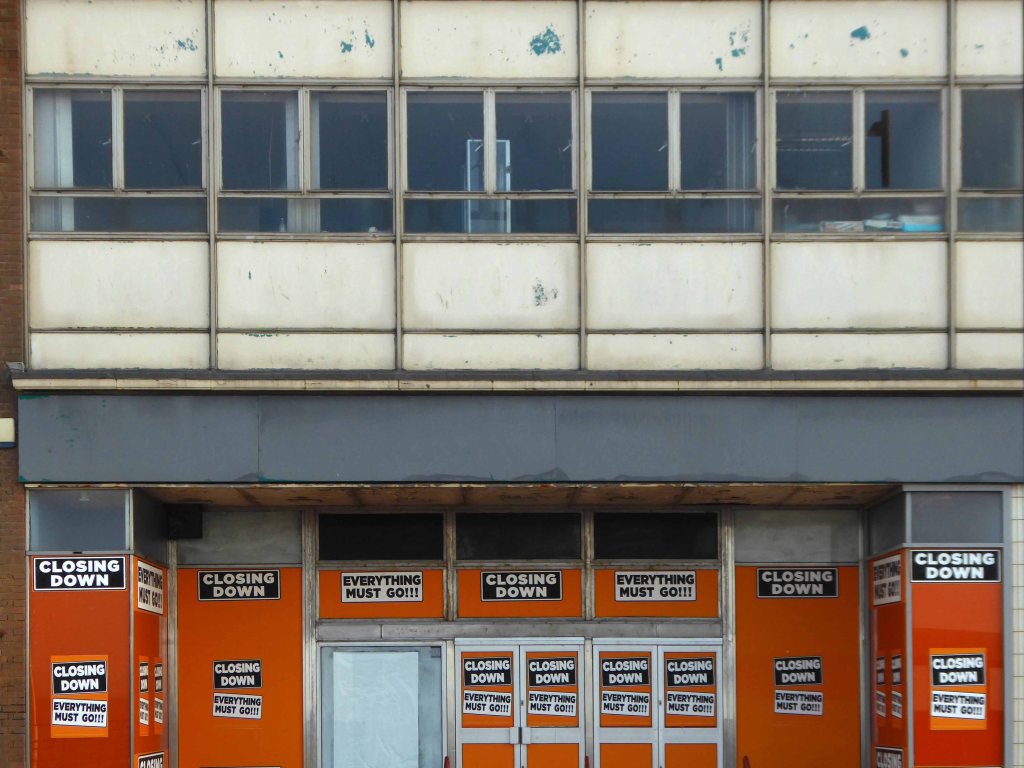












Another long day – I went to sleep.

Where the Victorians modelled their stations on cathedrals, temples and palaces.
Modern Man models his on shopping centre and office blocks.
Richards and MacKenzie – The Railway Station
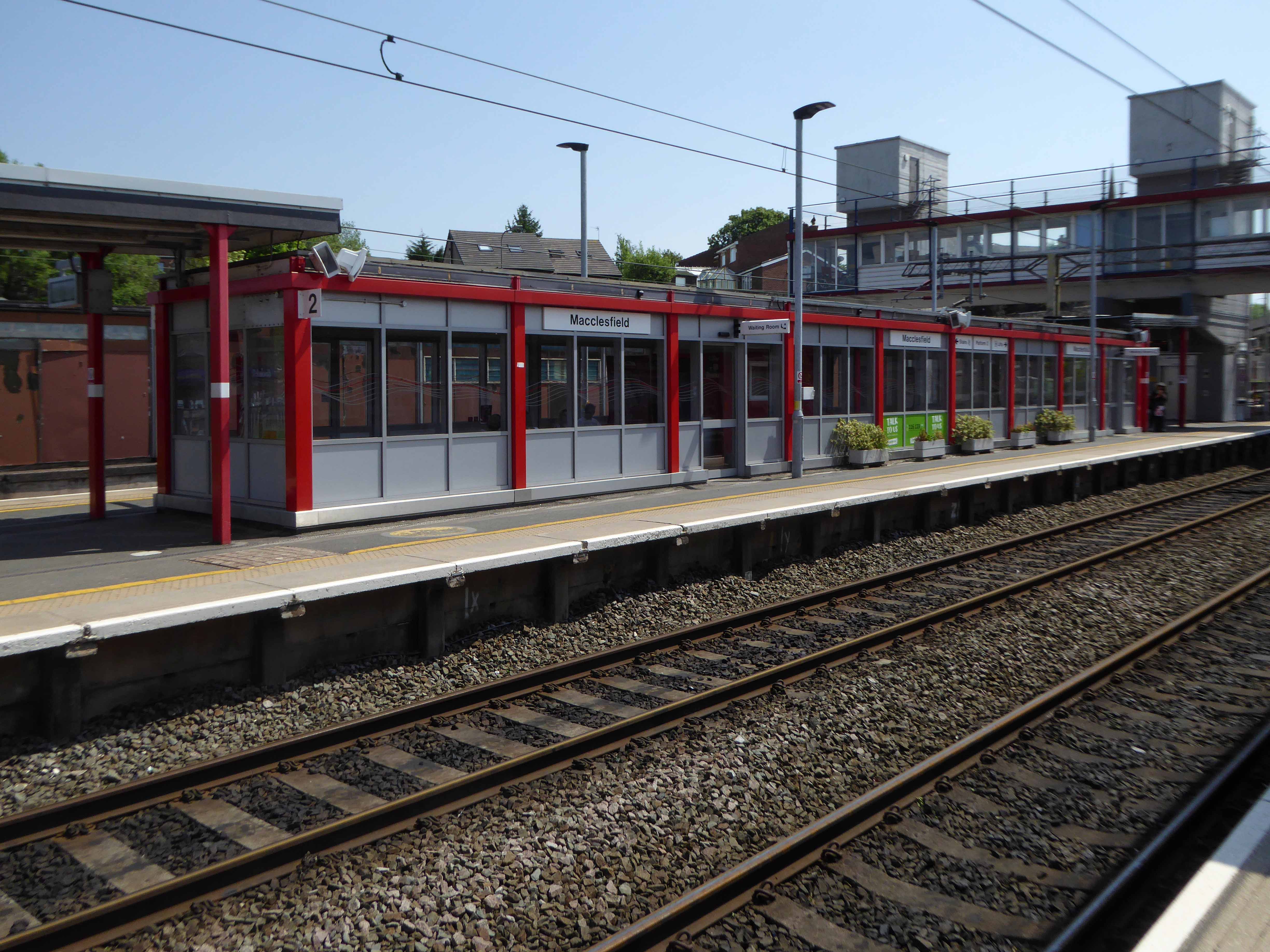
Though it seems to me that Macclesfield Station, in its earlier and current states, refuses to dovetail neatly into either of these sloppy binary paradigms.

The former – single storey buildings, fitting unostentatiously into the topographic and practical constraints of the site. A neat, tightly packed rhythm of brick arches with a compact and bijou porch welcoming the expectant traveller.

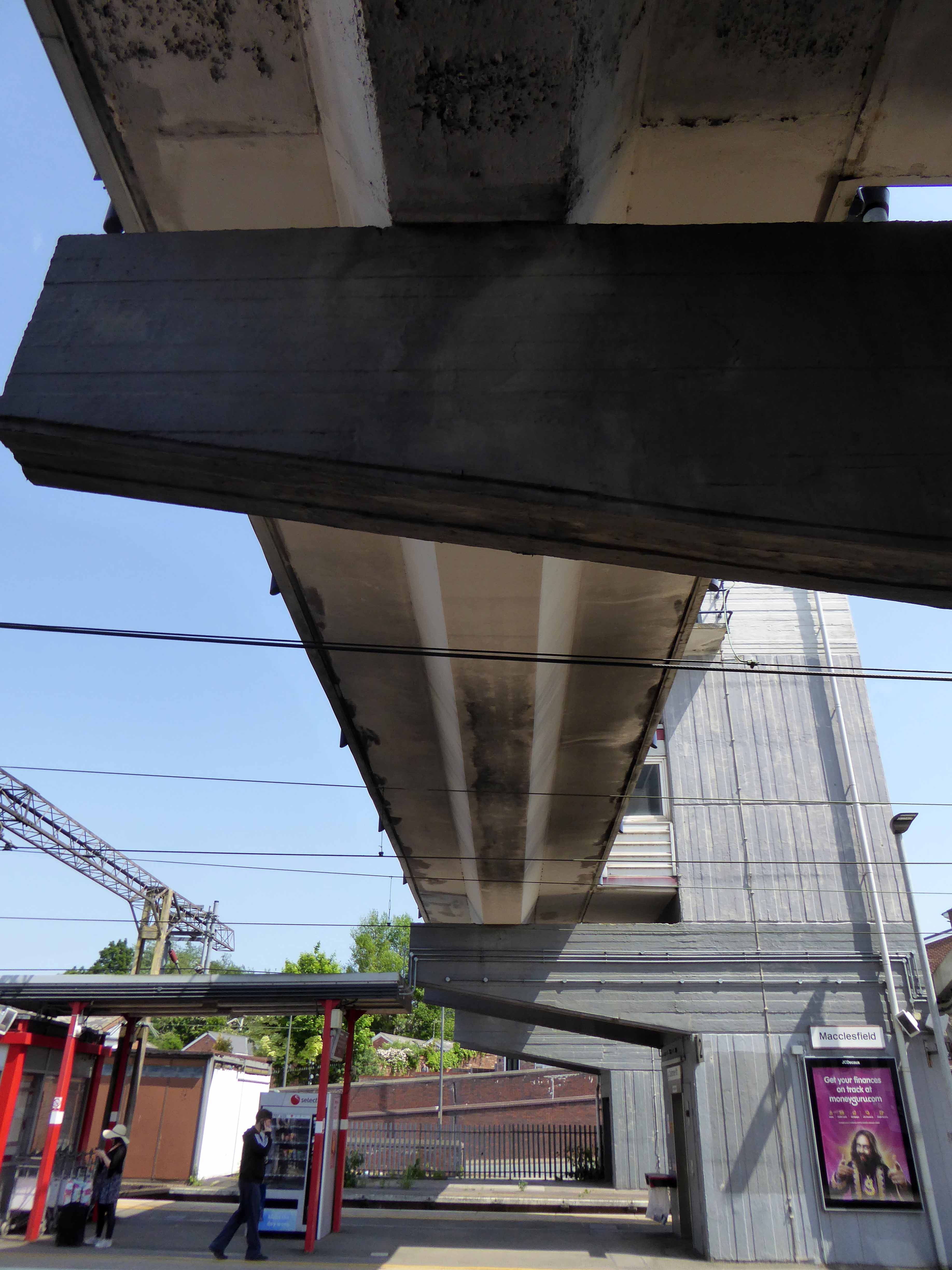
The latter a functionalist block, fully utilitarian crossings with lift access columns, embodying a particularly industrial demeanour.
From the golden age of steam to the moribund years of diesel, Macclesfield sits comfortably somewhere, betwixt and between ugly duckling and fully fledged swan.
Nestled in the lea of the East Cheshire Highlands, offering practical everyday transport solutions to the beleaguered commuter.
No frills, no thrills.
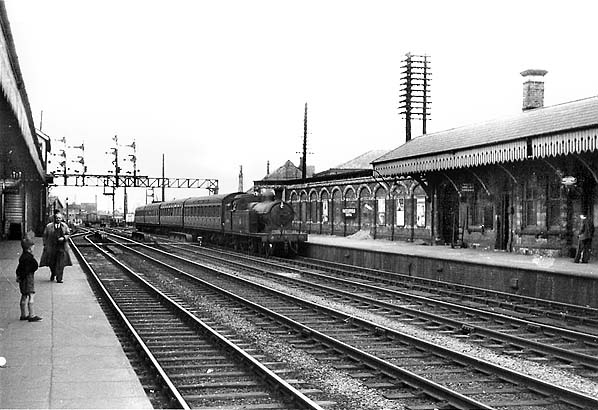


The London and North Western Railway opened the line between Manchester and Macclesfield on 19 June 1849 – Macclesfield Central was born. Later it would become a key station on the Stafford branch of the West Coast Main Line, remodelled in 1960 and rebranded as the much snappier Macclesfield Station.
Which it proudly announces topically and typographically to the world.

Welcome to Macclesfield a town that is clearly going places, and so are you.
The station won the Best Kept Station in Cheshire Award for 2007, but was reported in summer 2011 to be distinctly shabby, with peeling paintwork.
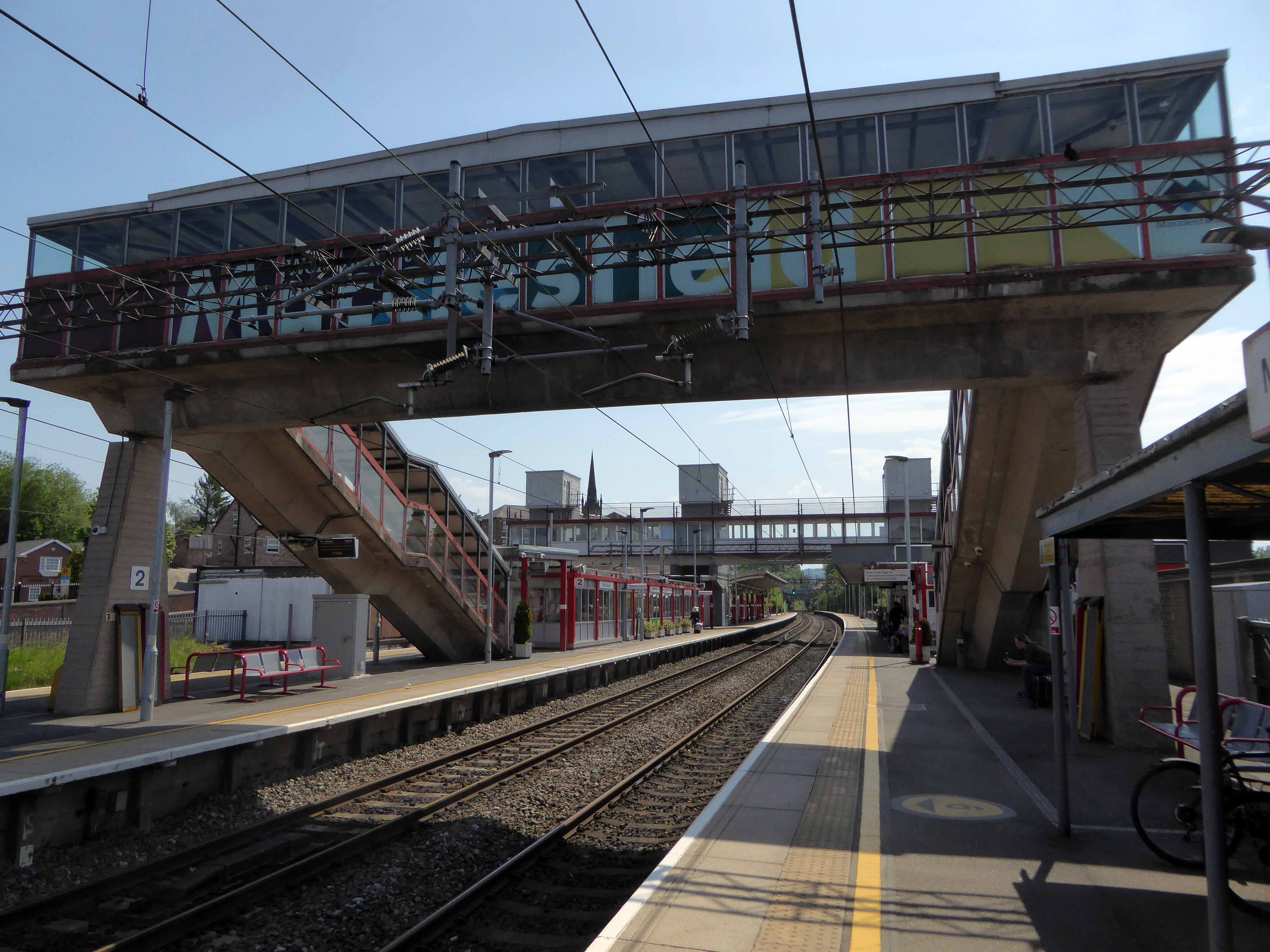
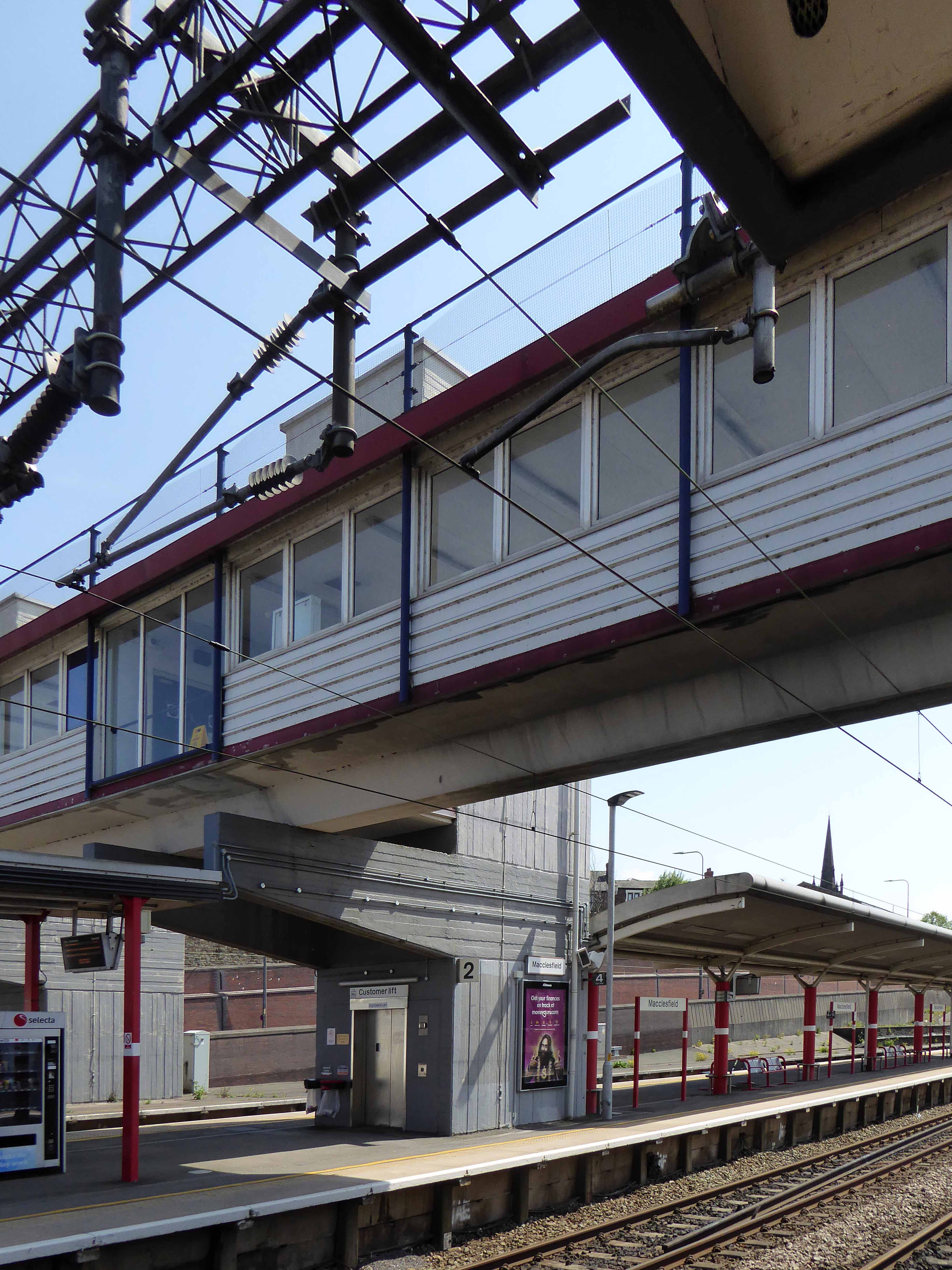
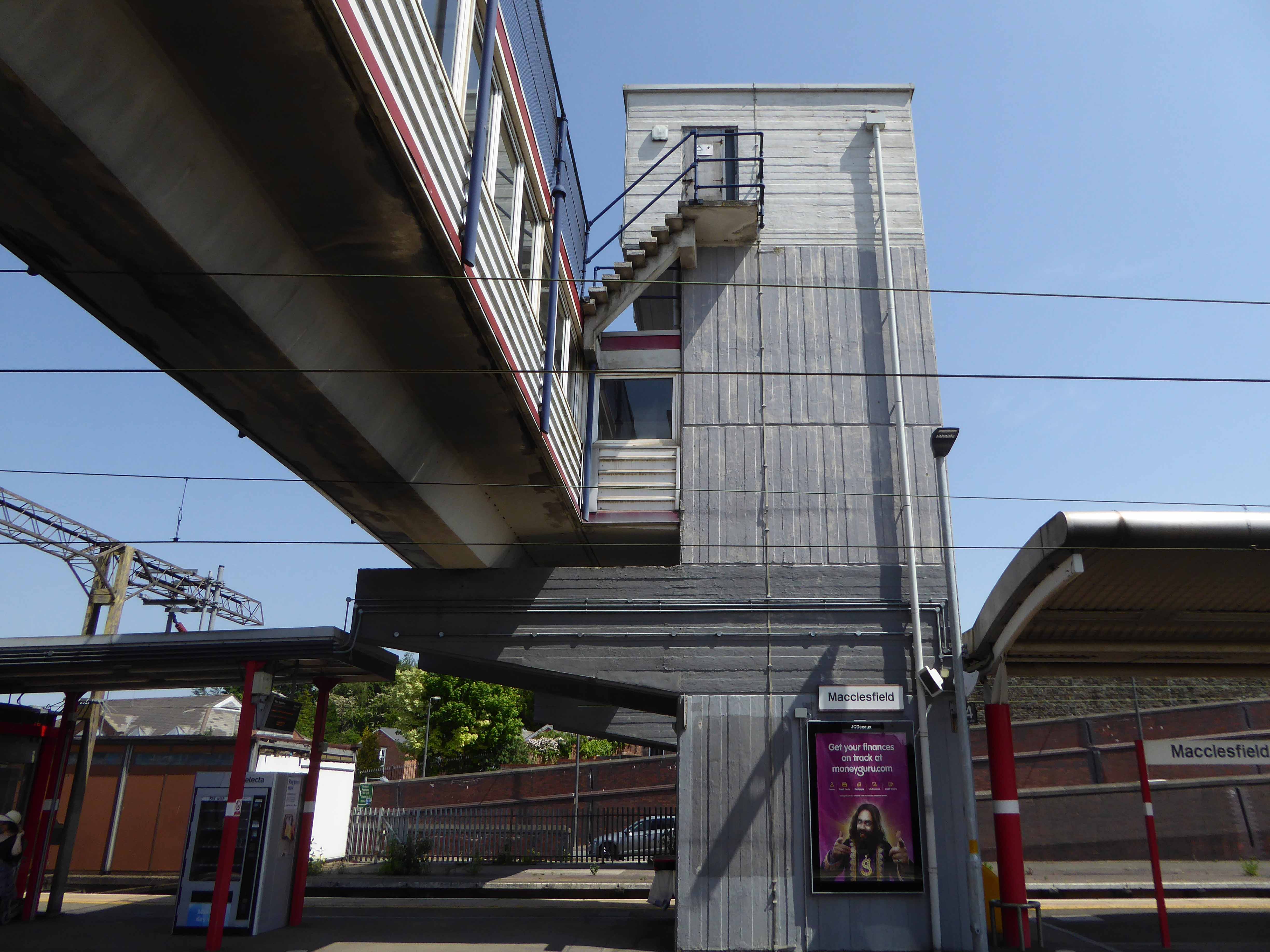
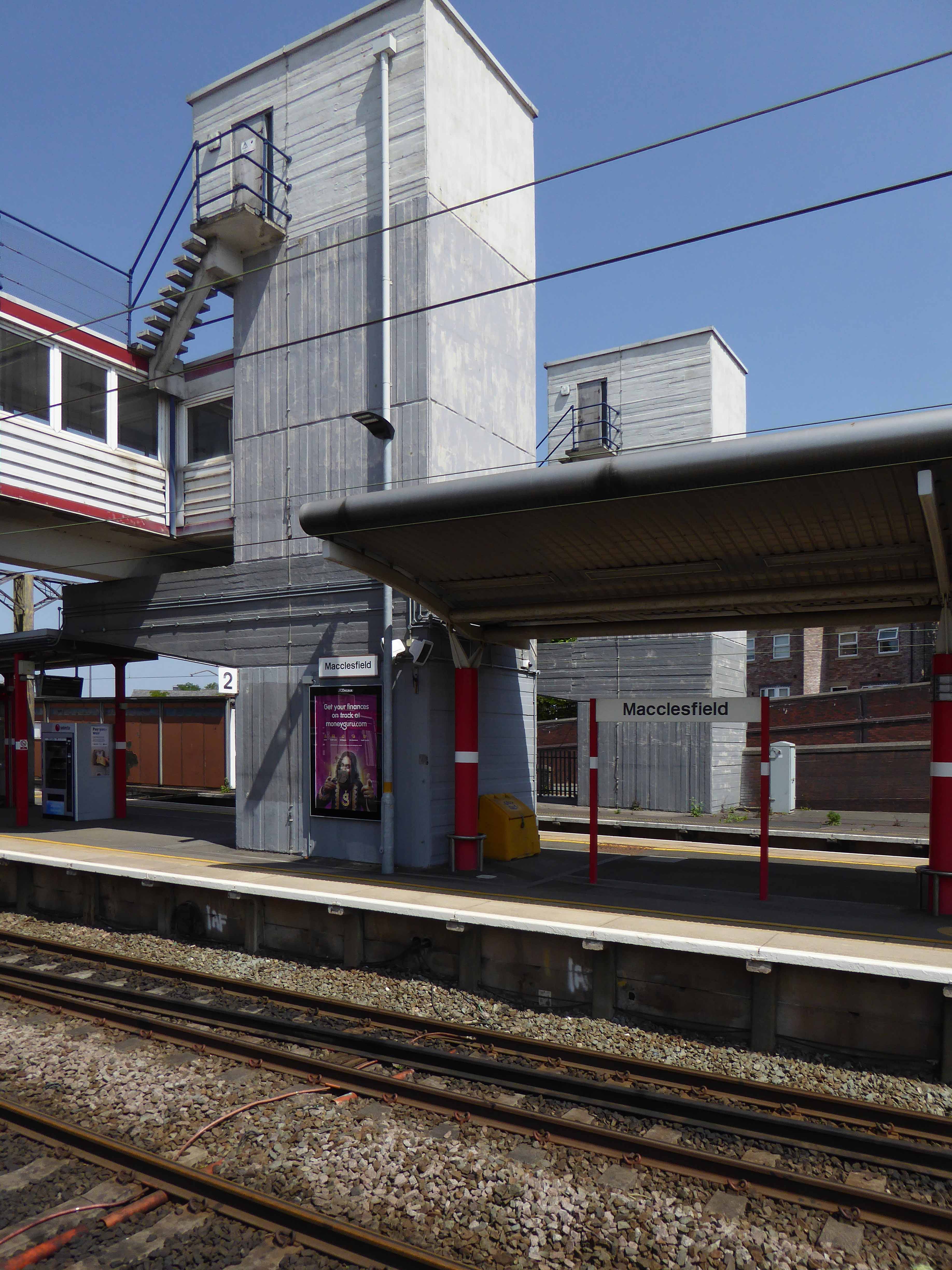
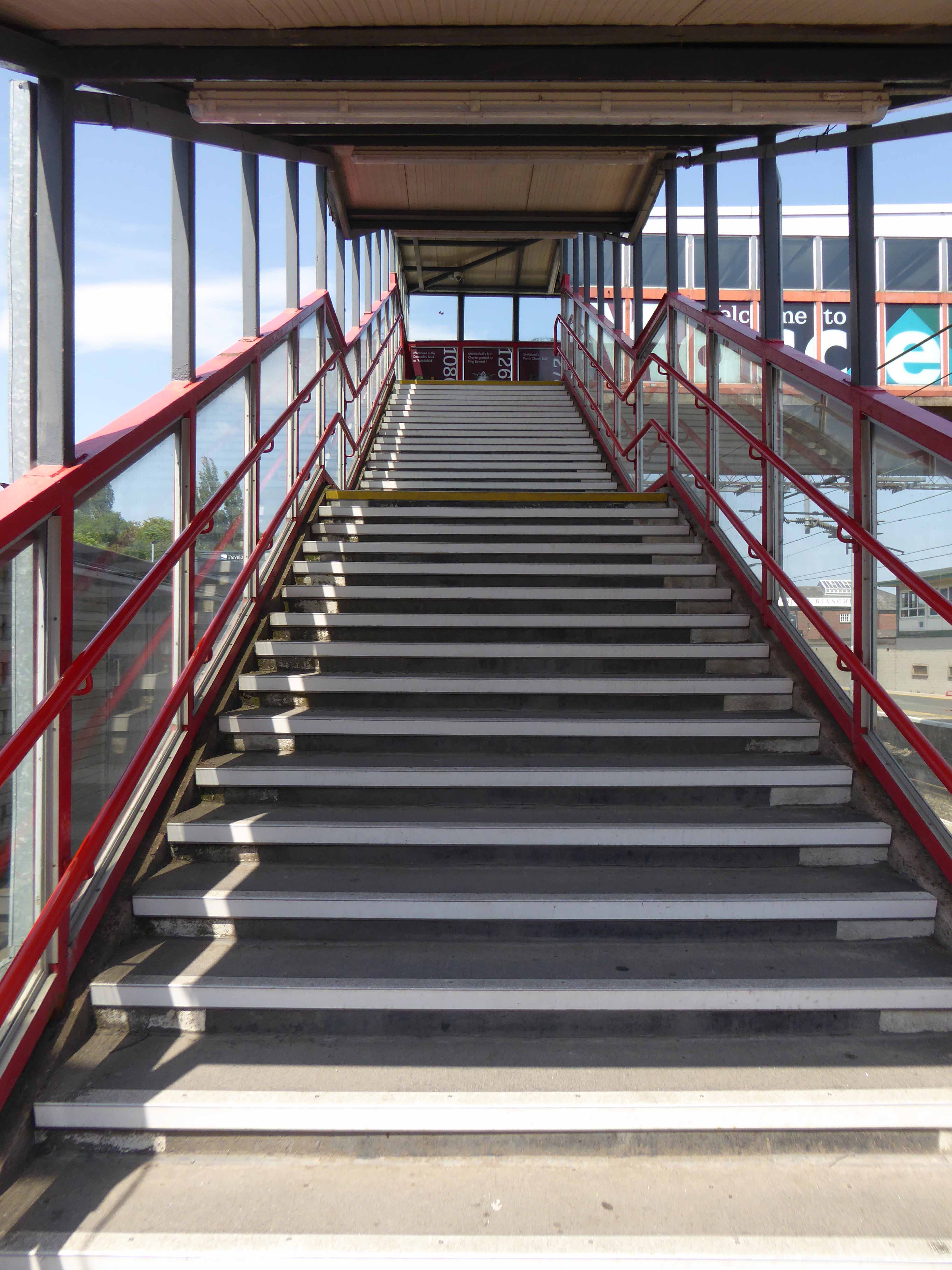
And yet there is something in the constituent Platonic steel, glass and concrete forms that never ceases to amuse and amaze me, this is Brutalism on a human and provincial scale.
The raw concrete softened with three or four shades of grey, as a concession to the delicate suburban sensibilities of this once silk-fuelled town.
Take a trip with me – join the Cheshire train set.















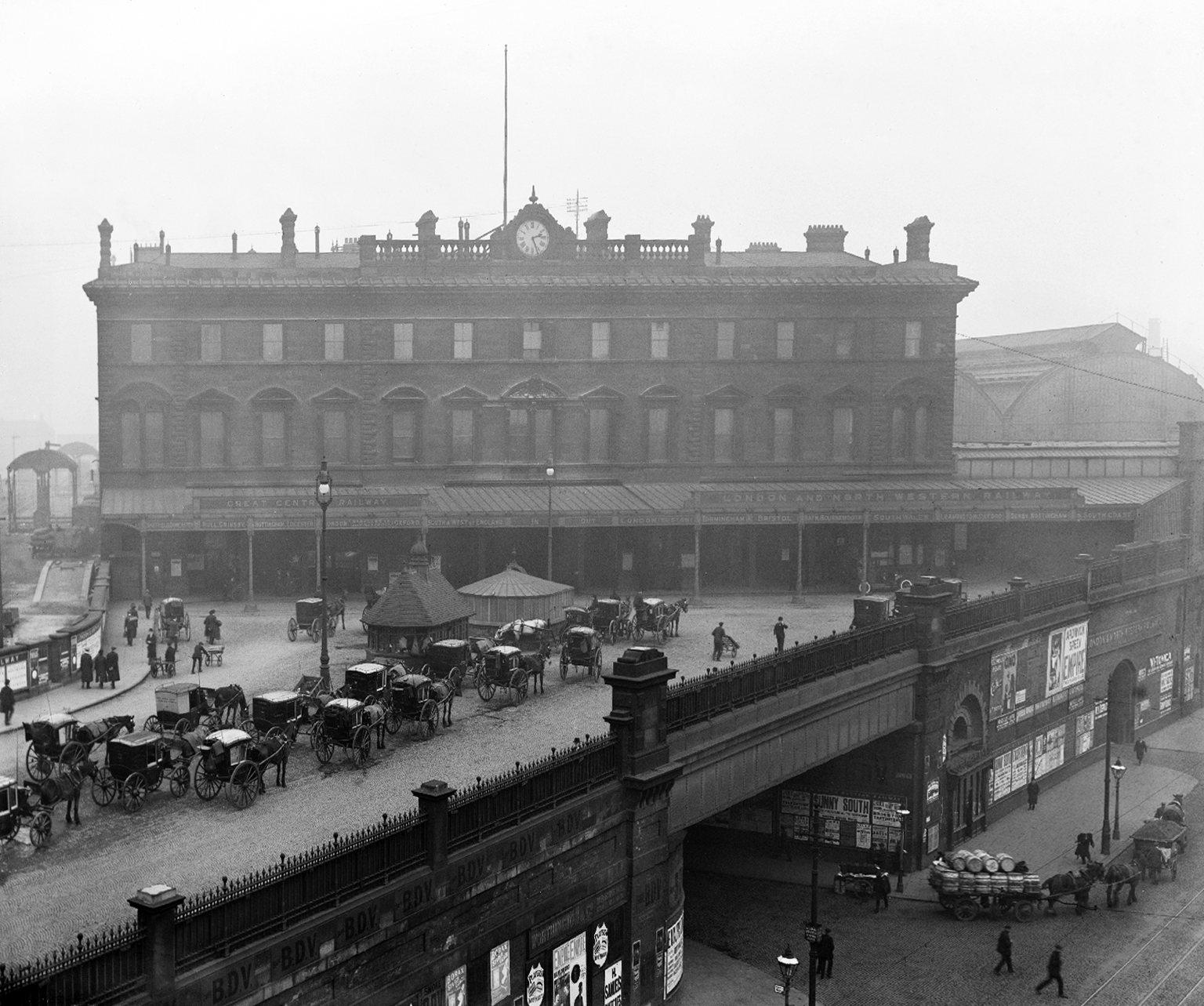
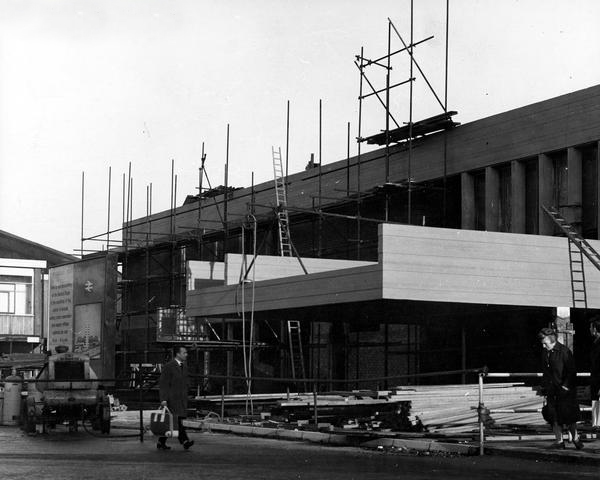
The station was originally built as Store Street Station by the Manchester and Birmingham Railway in 1842, before being renamed London Road Station in 1847. It was shared by the Sheffield, Ashton-under-Lyne & Manchester Railway and it has been rebuilt and added to a number of times, with two news spans added to the train shed roof in 1881 and island platforms added linking to Manchester Oxford Road in 1882 (replacing two old Manchester, South Junction and Altrincham Railway platforms which were built next to the station).

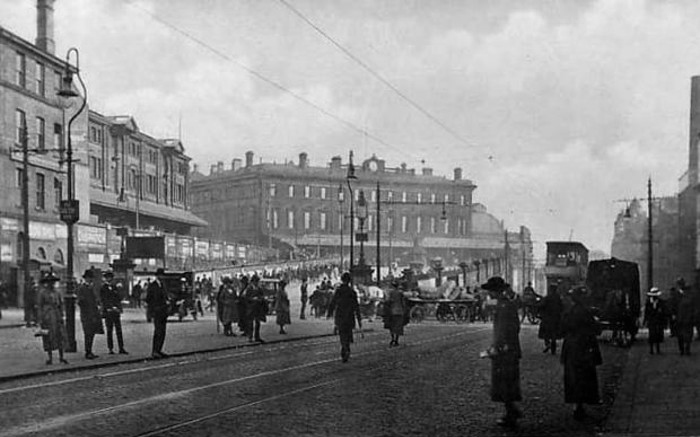
An imposing classical façade with a substantial cast iron and glass train shed, the approach sloping up to the frontage, as of necessity the line entered the city on a raised trackbed.

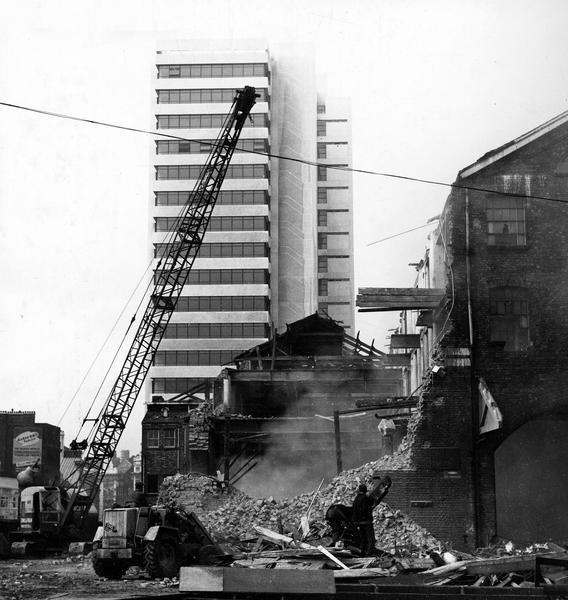
Initially the approach was lined with railway warehousing, subsequently demolished to make way for the redevelopments of the 1960s.

Detailed plans are made to reshape the station concourse and entrance.


Dreams are turned into reality, as near as makes no difference.
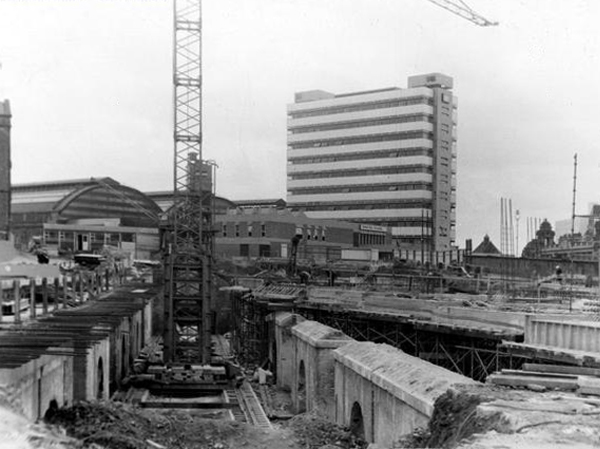
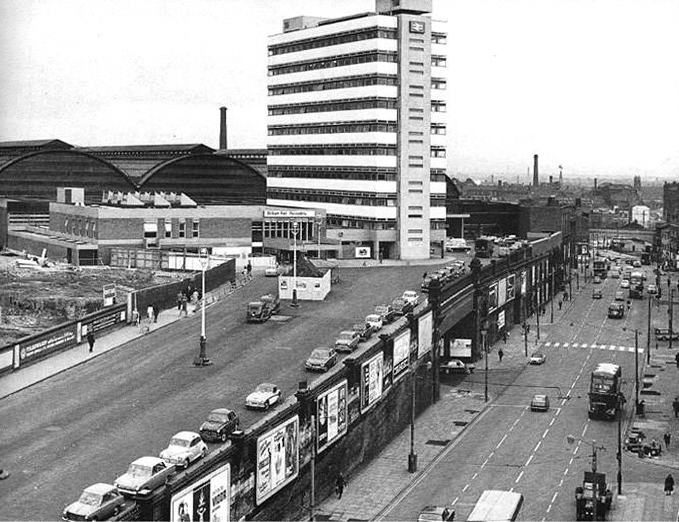



The newly electrified lines opening up the city to a world of high speed intercity travel.

The Krays it seems were deemed to be unwelcome visitors, everyone else came and went, met with equanimity and a bright new modernist vista.
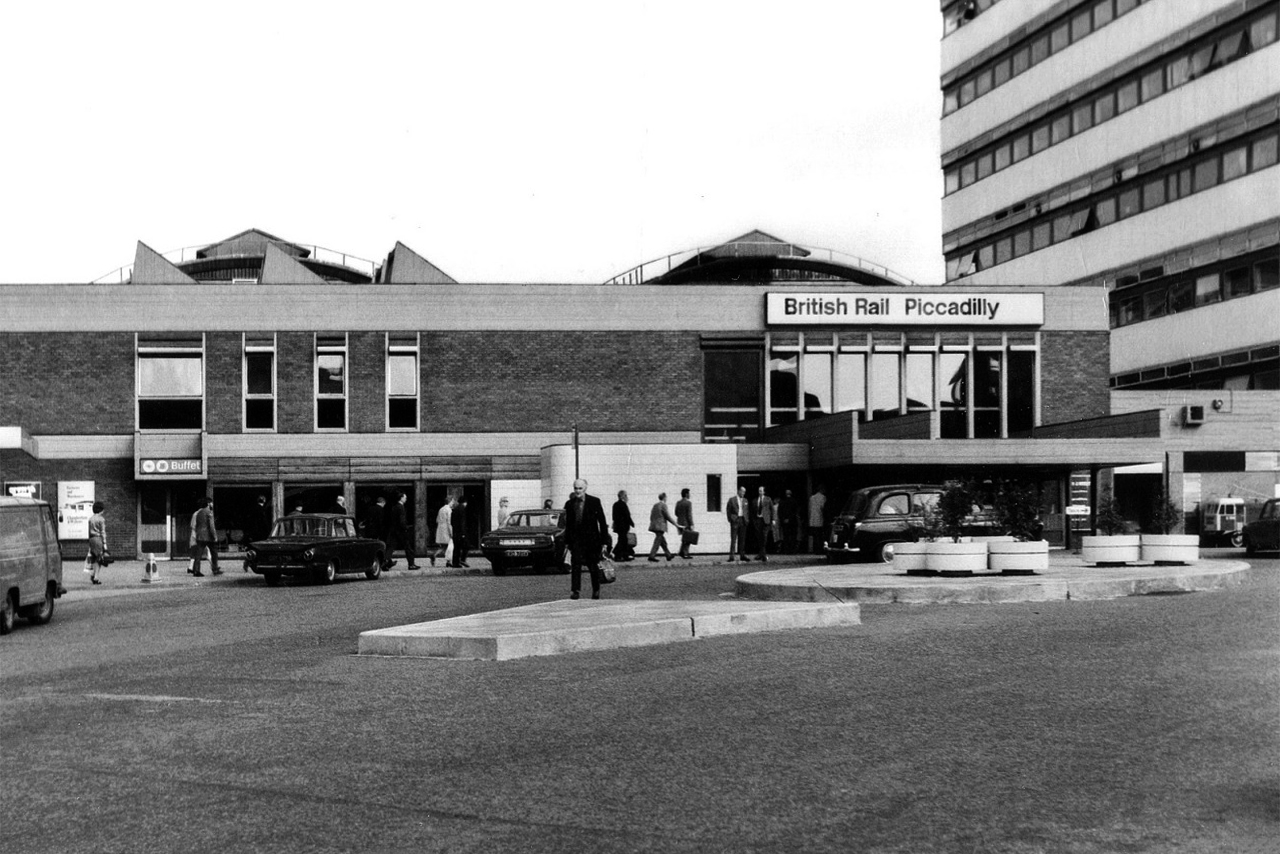

The brand new shiny buffet replaces the archaic dining rooms, as Brylcreemed, bow tied and moustachioed waiters are consigned to the scrapheap of history.
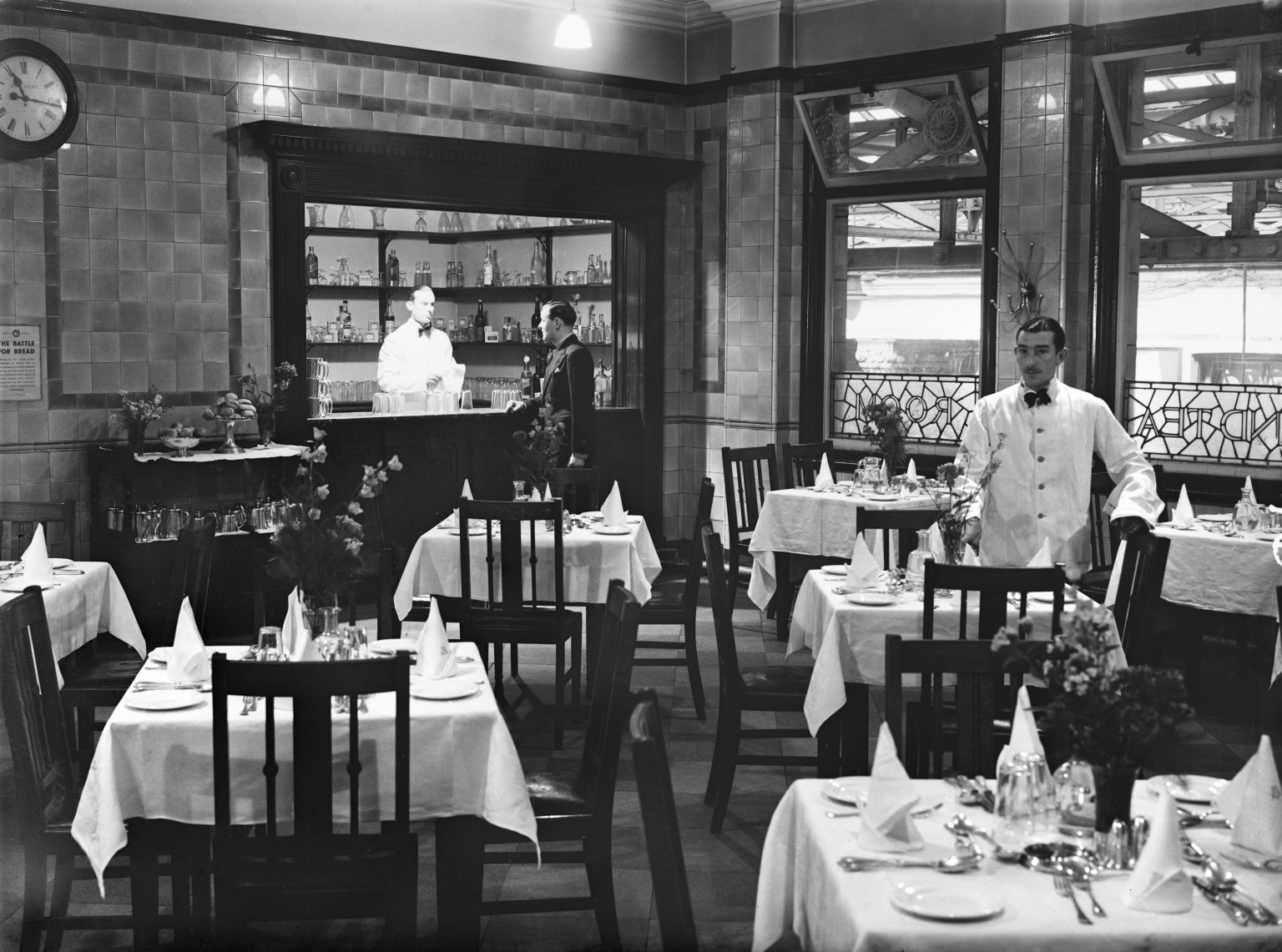

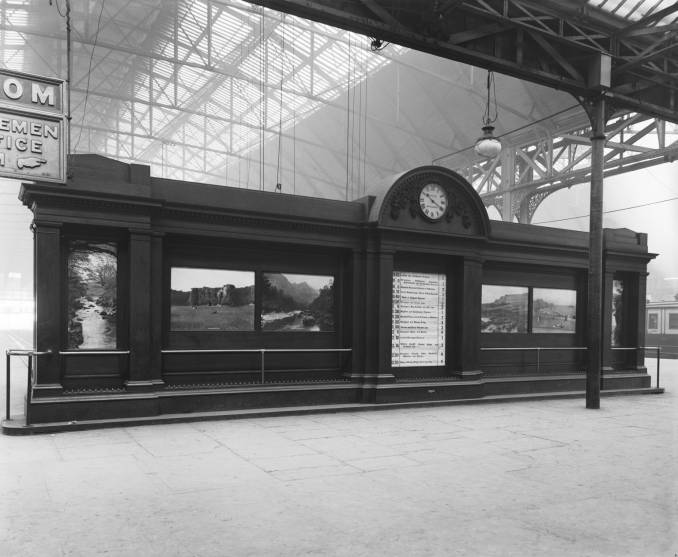
Likewise the gloomy destination boards – out with the old!

And in with the new.
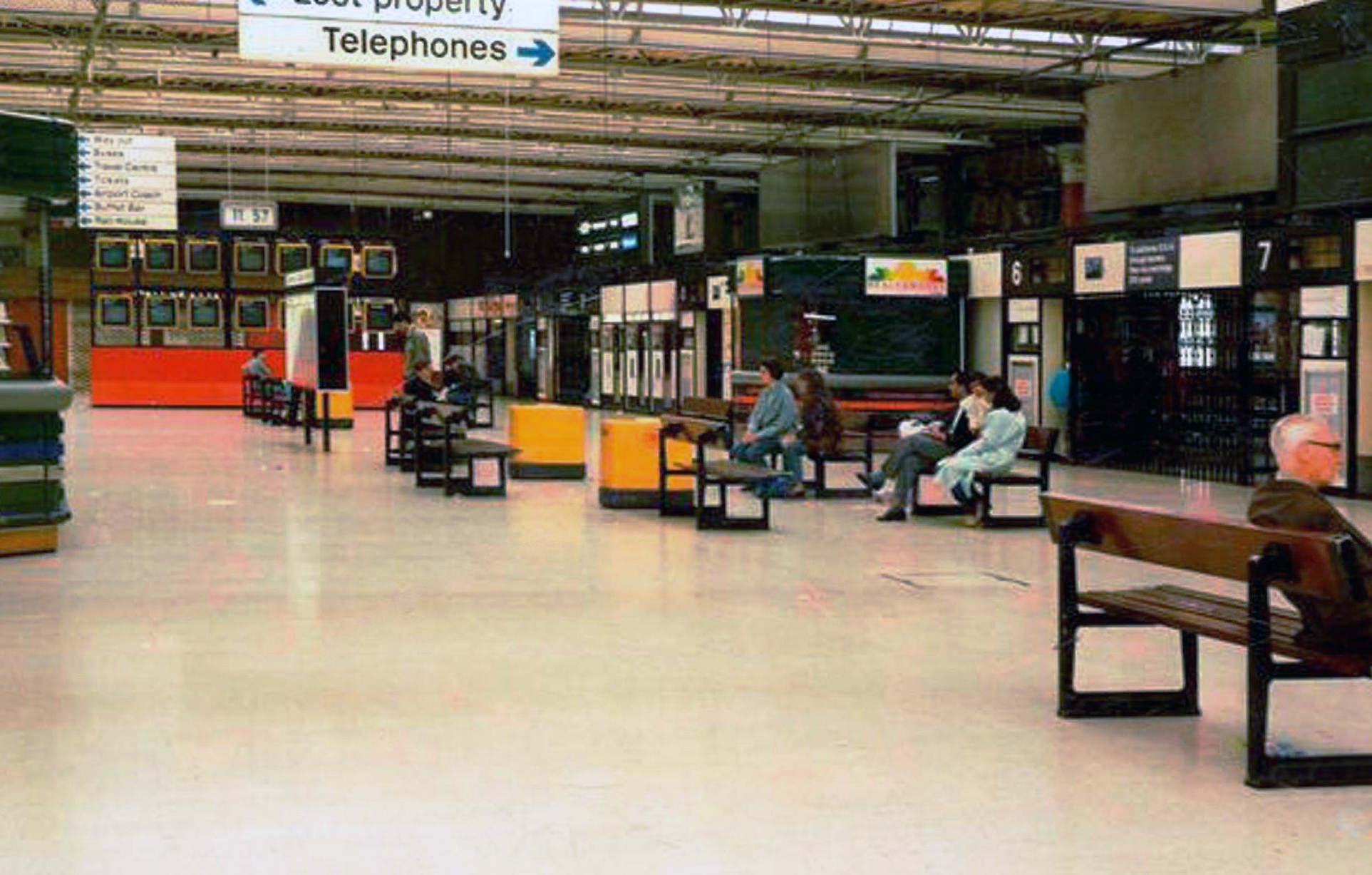


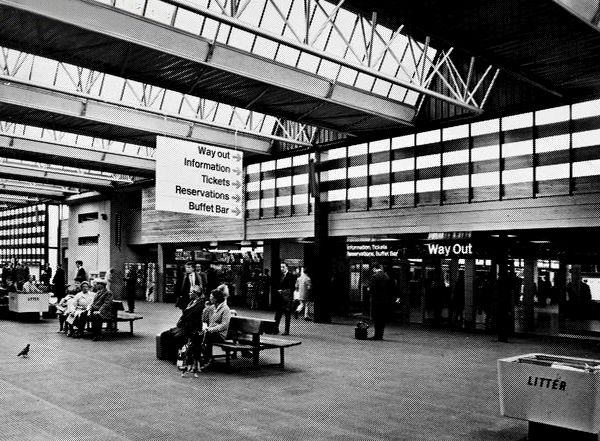
We have a fully integrated modern interior to deal with the modern passengers’ every need – including crystal clear signage, seating and bins.
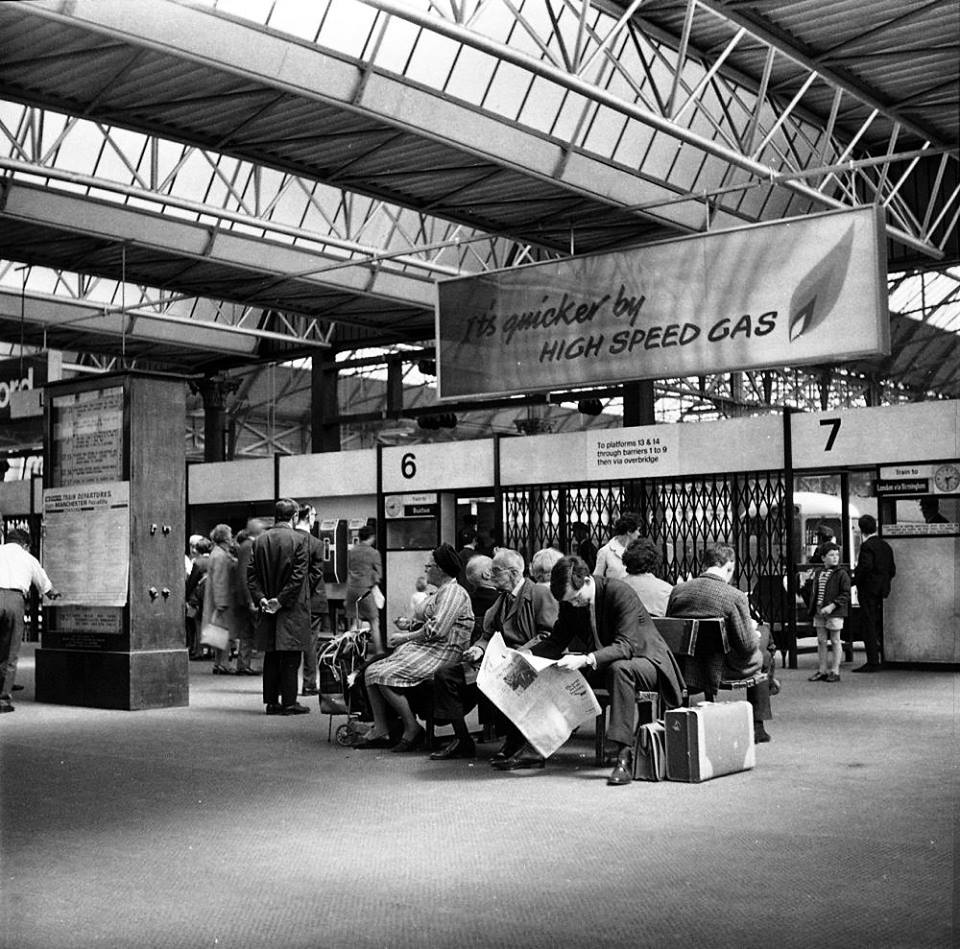






Stars of screen and stage are guided through with consummate ease, Margot Fonteyn and Rudolf Nureyev in his brand new baby seal skin coat arrive in 1968 to dance Swan Lake at the Palace.

Esteemed footballer Eusebio on his travels during the 1966 World Cup.
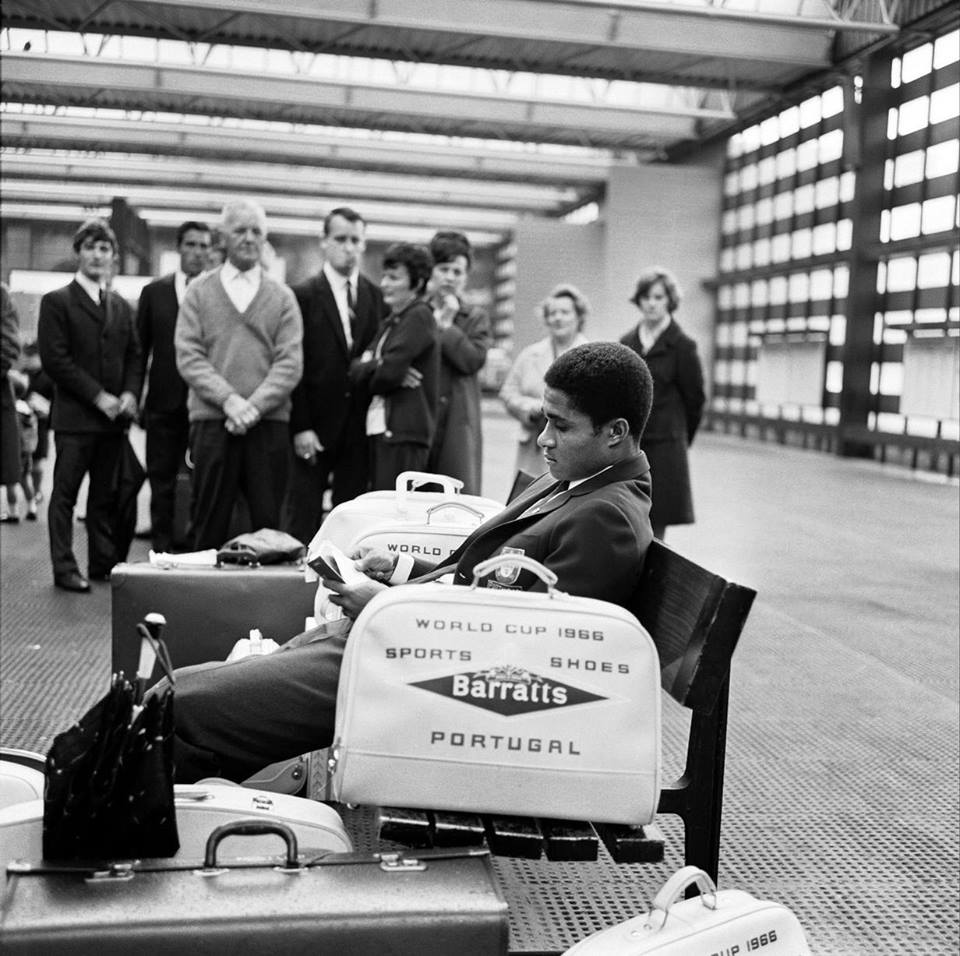

In 1969 Gateway House arrives, Richard Sieffert & Partners wavy hello and goodbye to Manchester’s premier railway station.
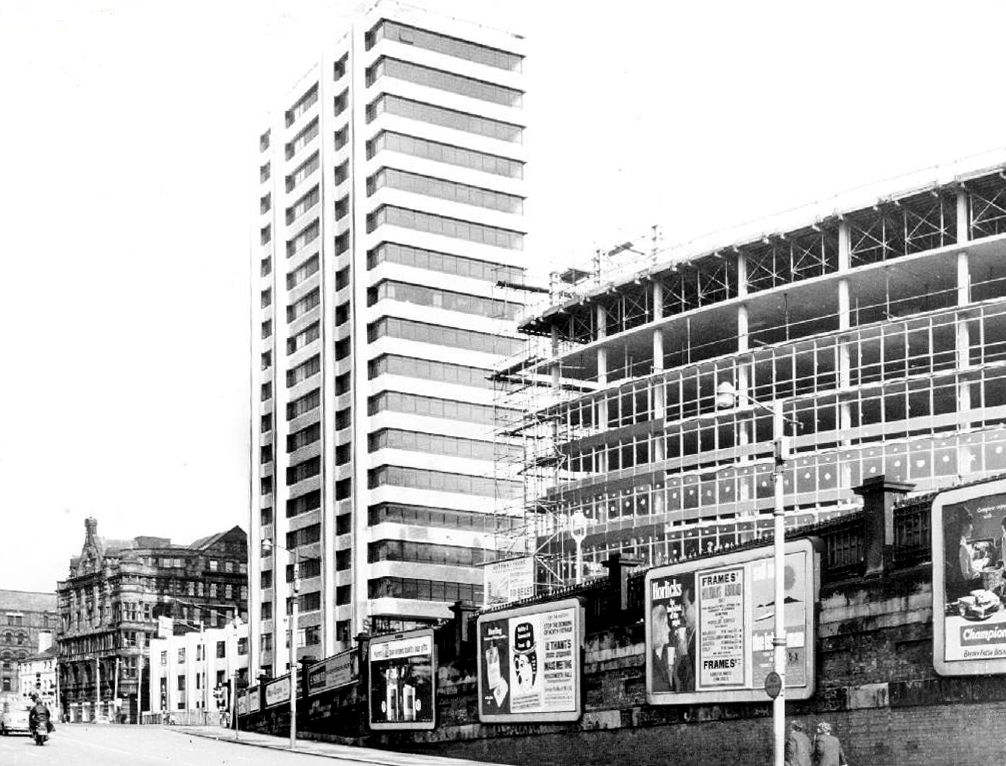

Piccadilly has now seen several revamps, the concourse an exercise in contemporary cluttered retail/airport chic, a 125mph Pendolino journey away from the carefully considered internal order of yesteryear.
Who knows what the future holds?
HS2 to name but one – sit back let the train take the strain.

Archival images Manchester Local Image Collection
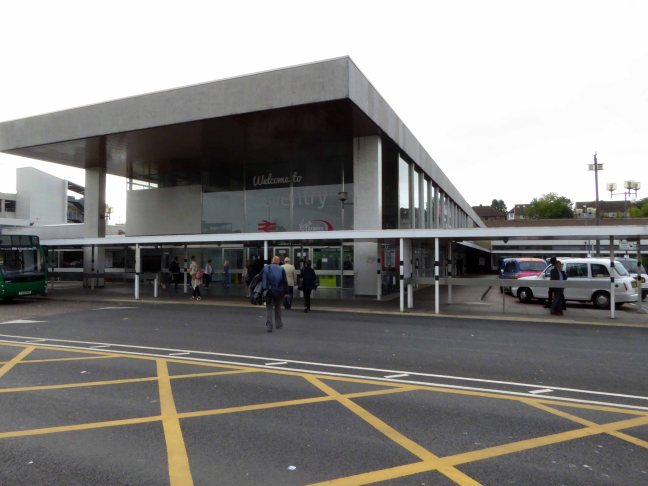

Steven Parissien, director of Compton Verney Museum in Warwickshire, says:
“Coventry is a great station. Its predecessor was pummelled to bits but it really wasn’t particularly marvellous anyway.

“The new station really came into its own. Built in the same month as the cathedral, in a way it was just as emblematic as the cathedral, though not quite so famous.
“It’s a light and airy place with a nice design. You do come out and have the ring road right in front of you which pedestrians have to guess where to go but that’s not really the fault of the station developers.”
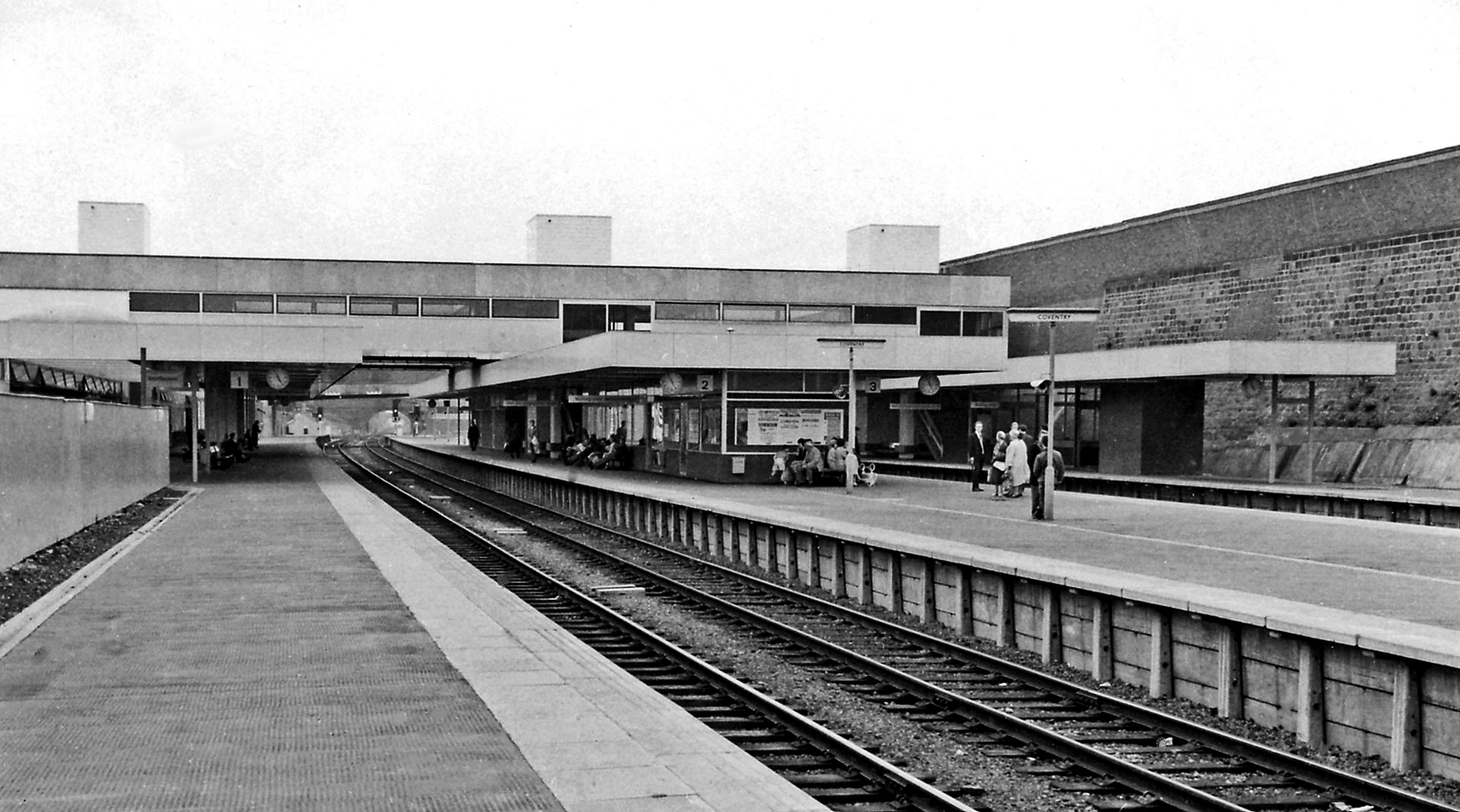



The original station was built in 1838 as part of the London and Birmingham Railway and could be entered from Warwick Road, where two flights of stairs took the passengers down to the platform. Within two years it had been replaced, with a new larger station, a few hundred feet nearer to Rugby, this time, accessed via Eaton road. In the late 19th century the Coventry tram network extended to the station at Eaton Road. The original station remained in service as the station masters offices, until the station was redeveloped in the early 1960s by the London Midland Region of British Railways.
Architects Derrick Shorten worked with John Collins, Mike Edwards and Keith Rawson.
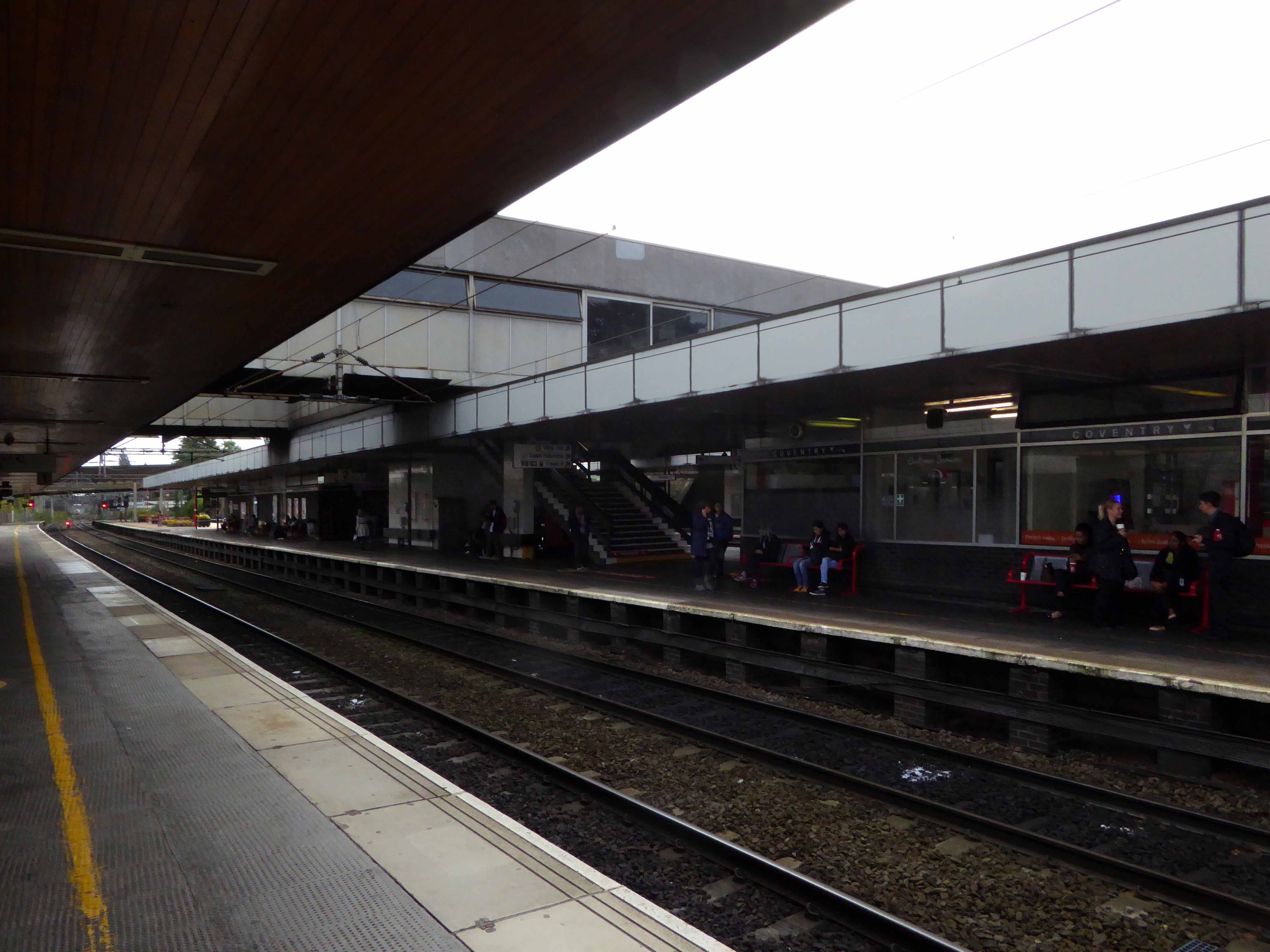
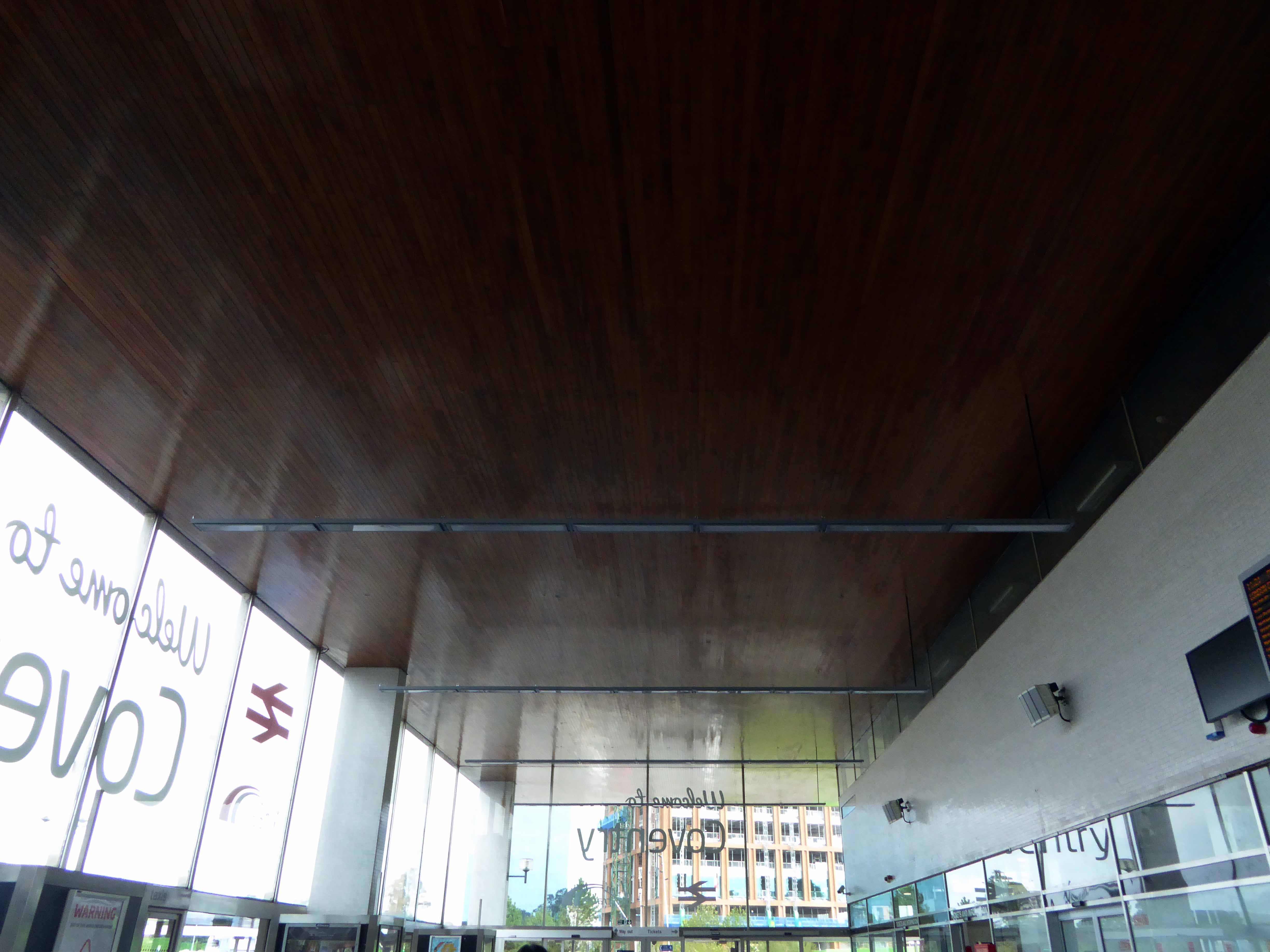
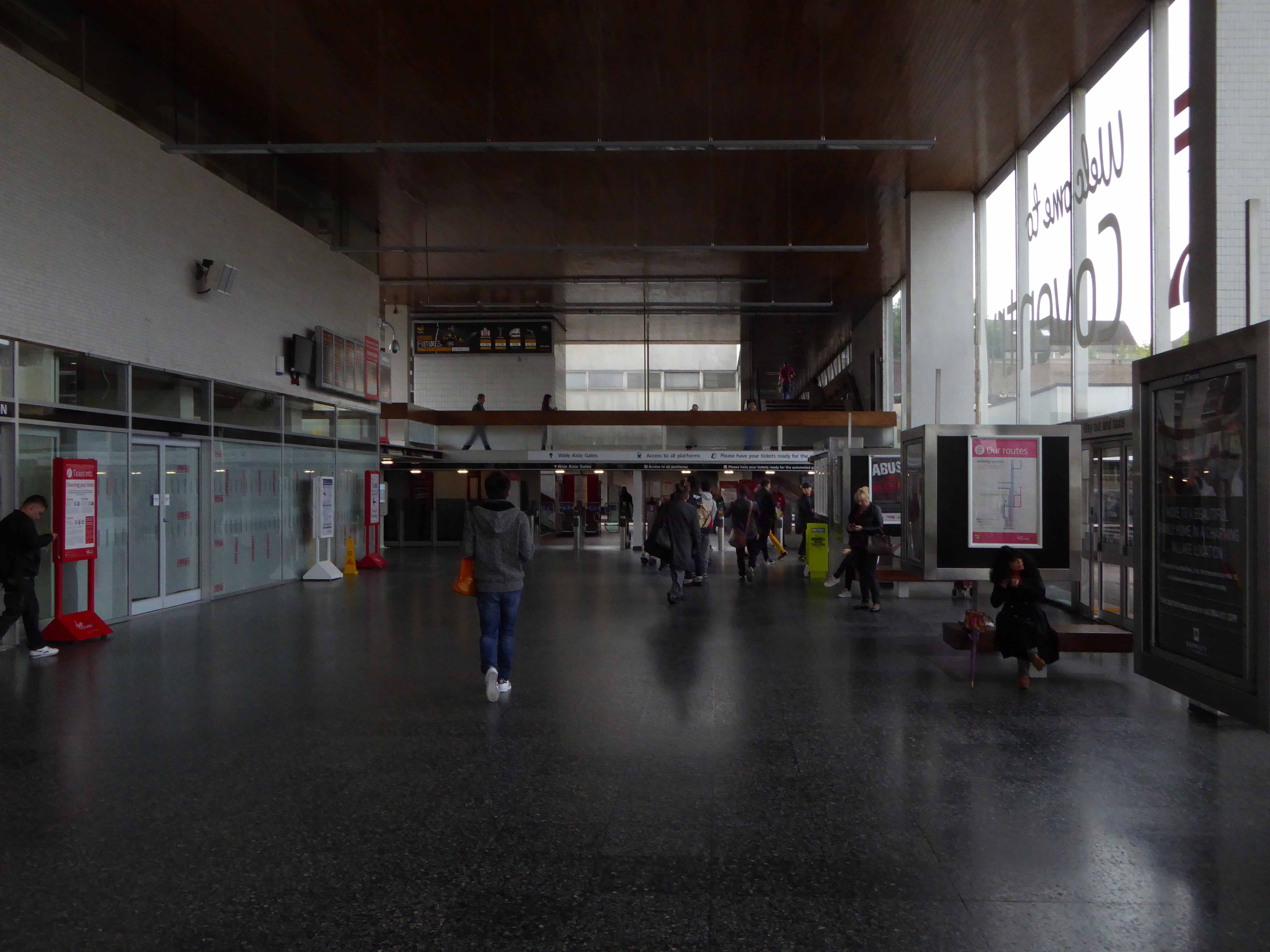
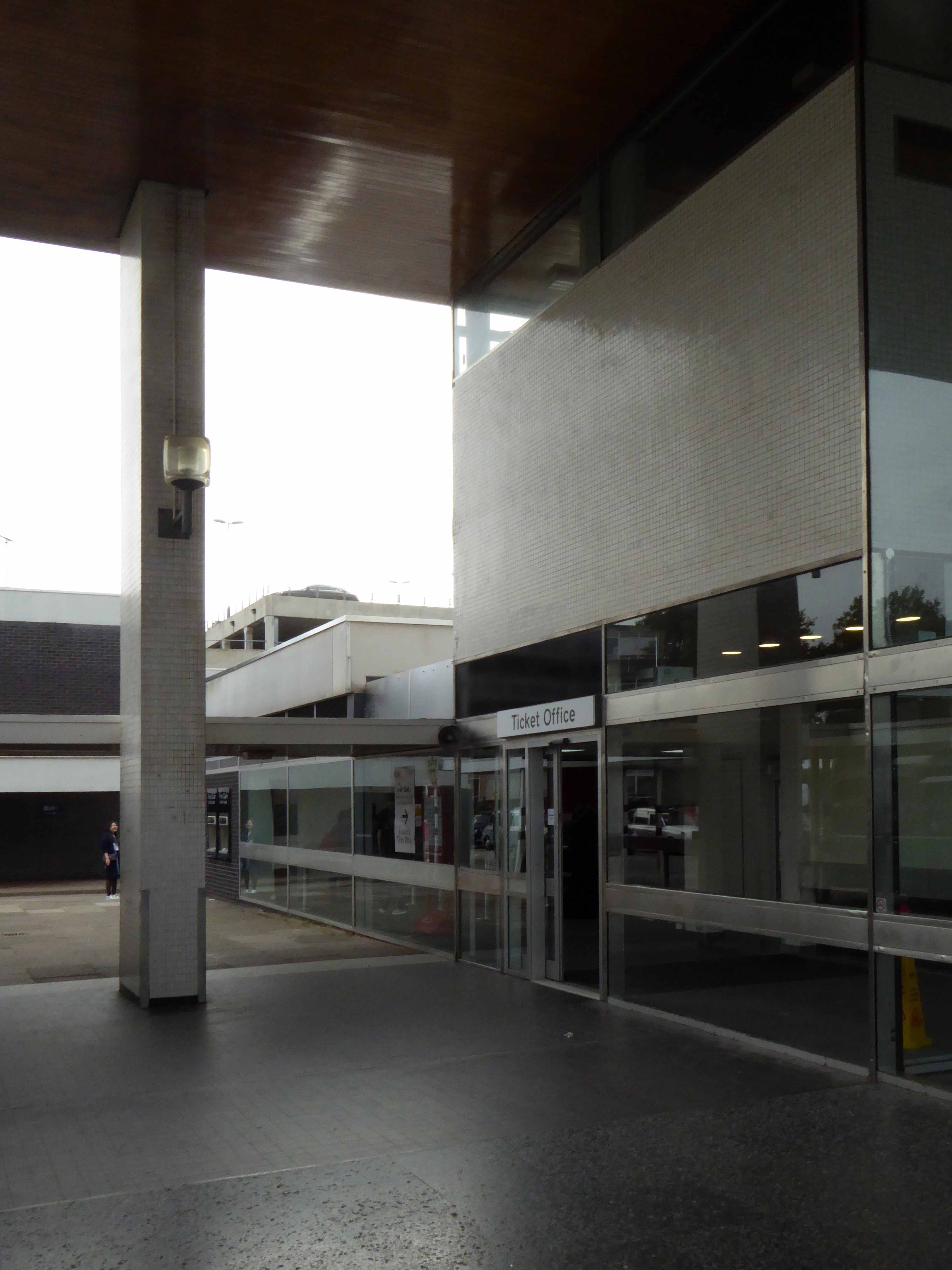
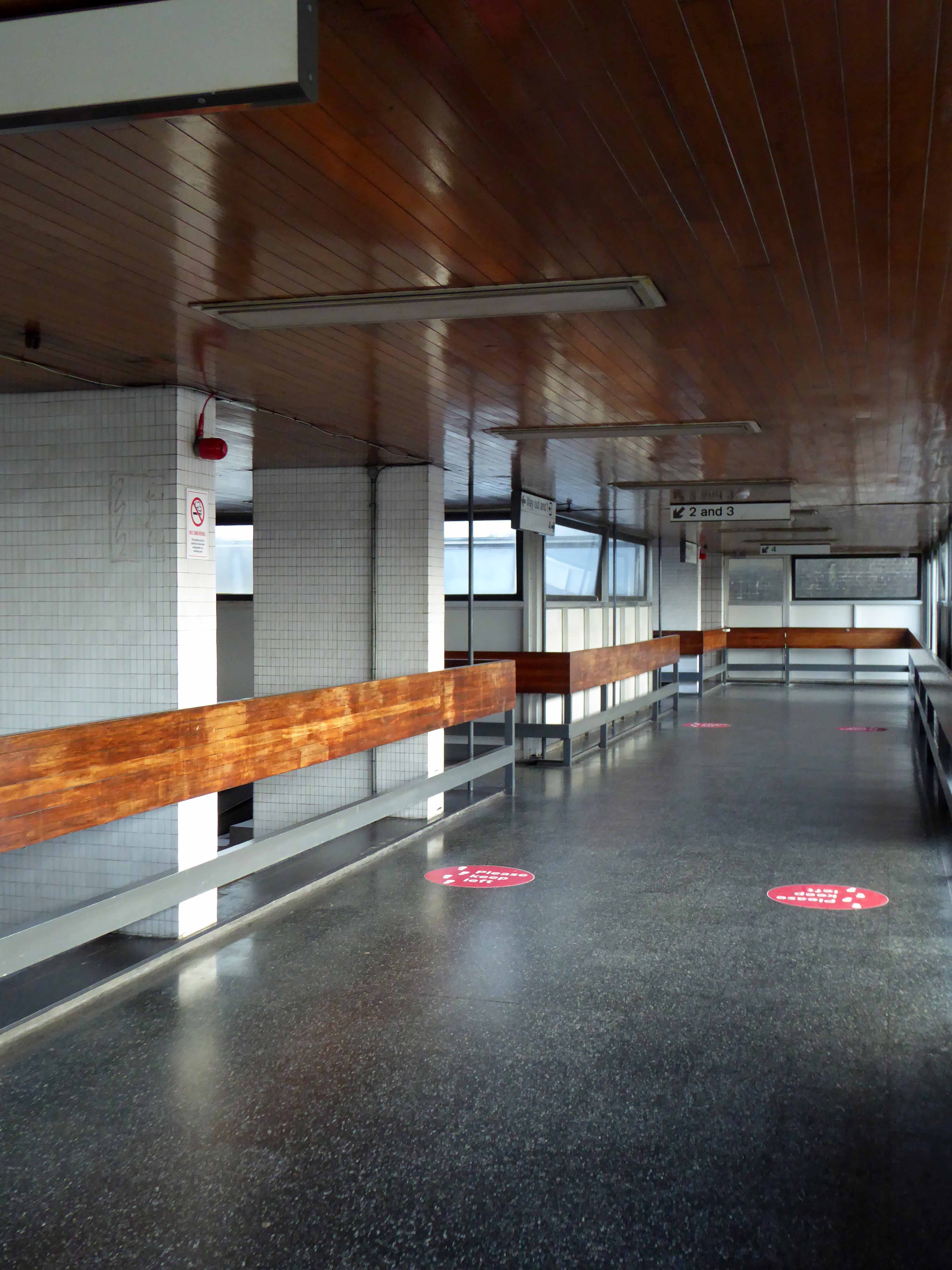
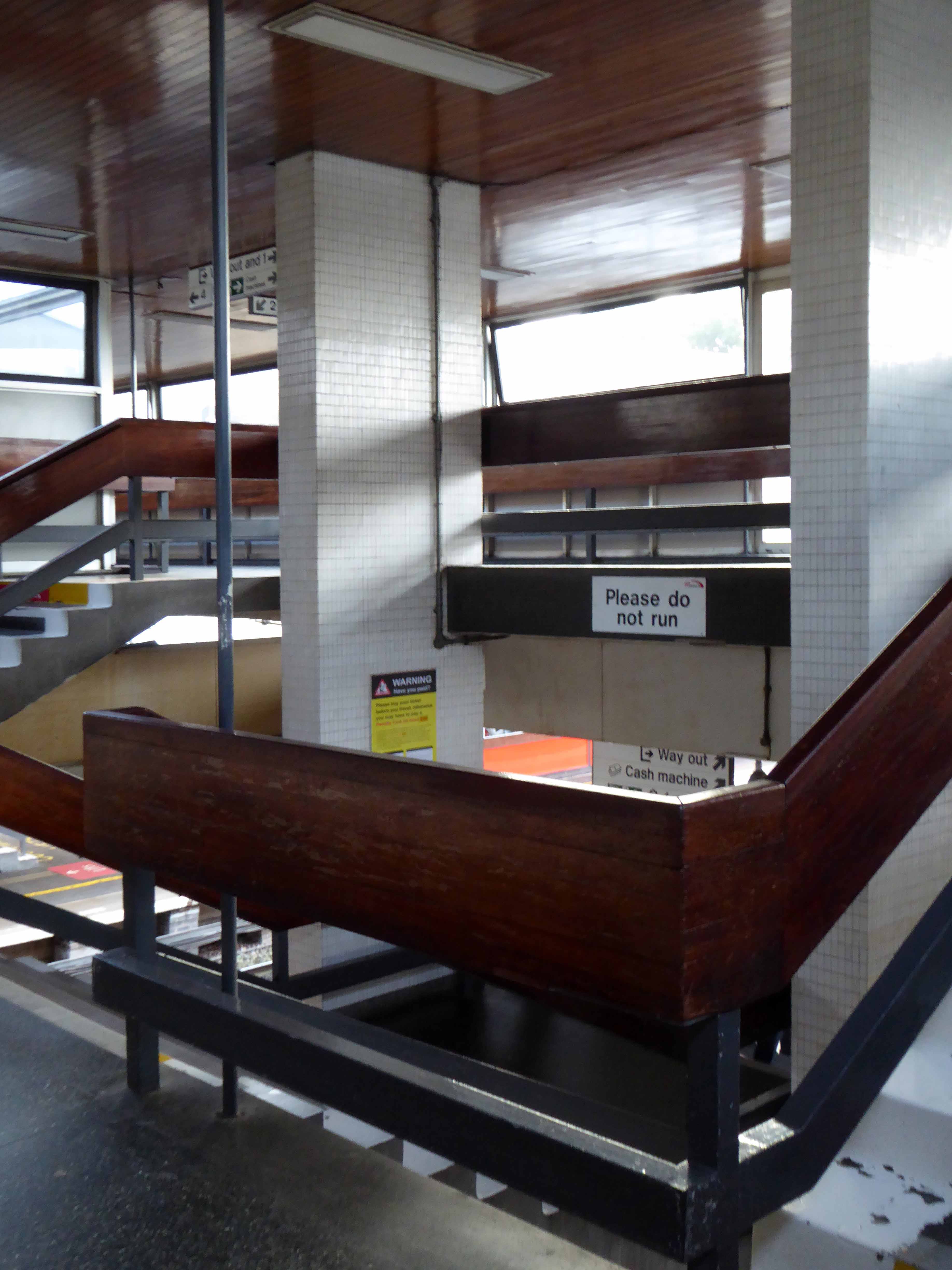
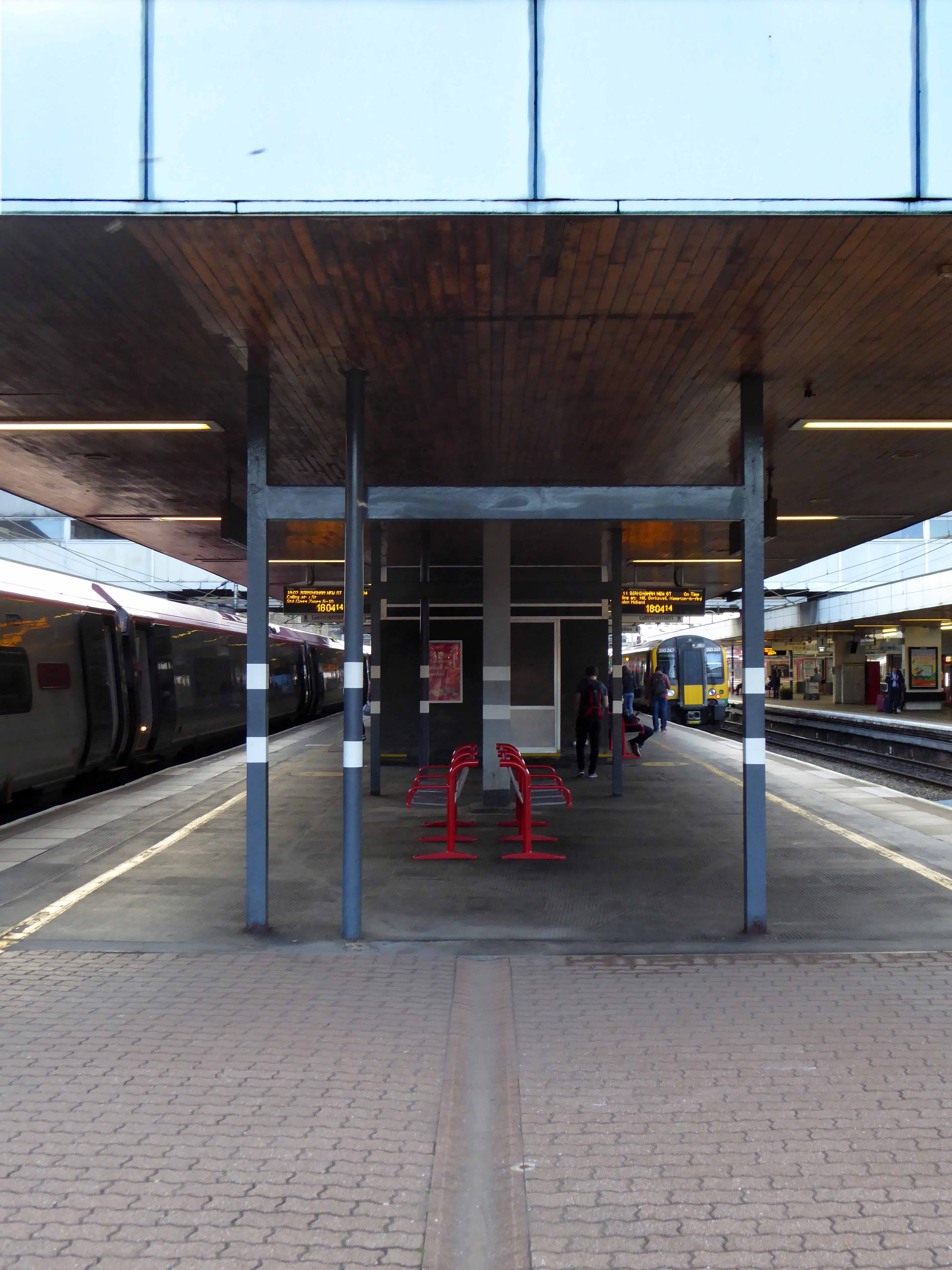
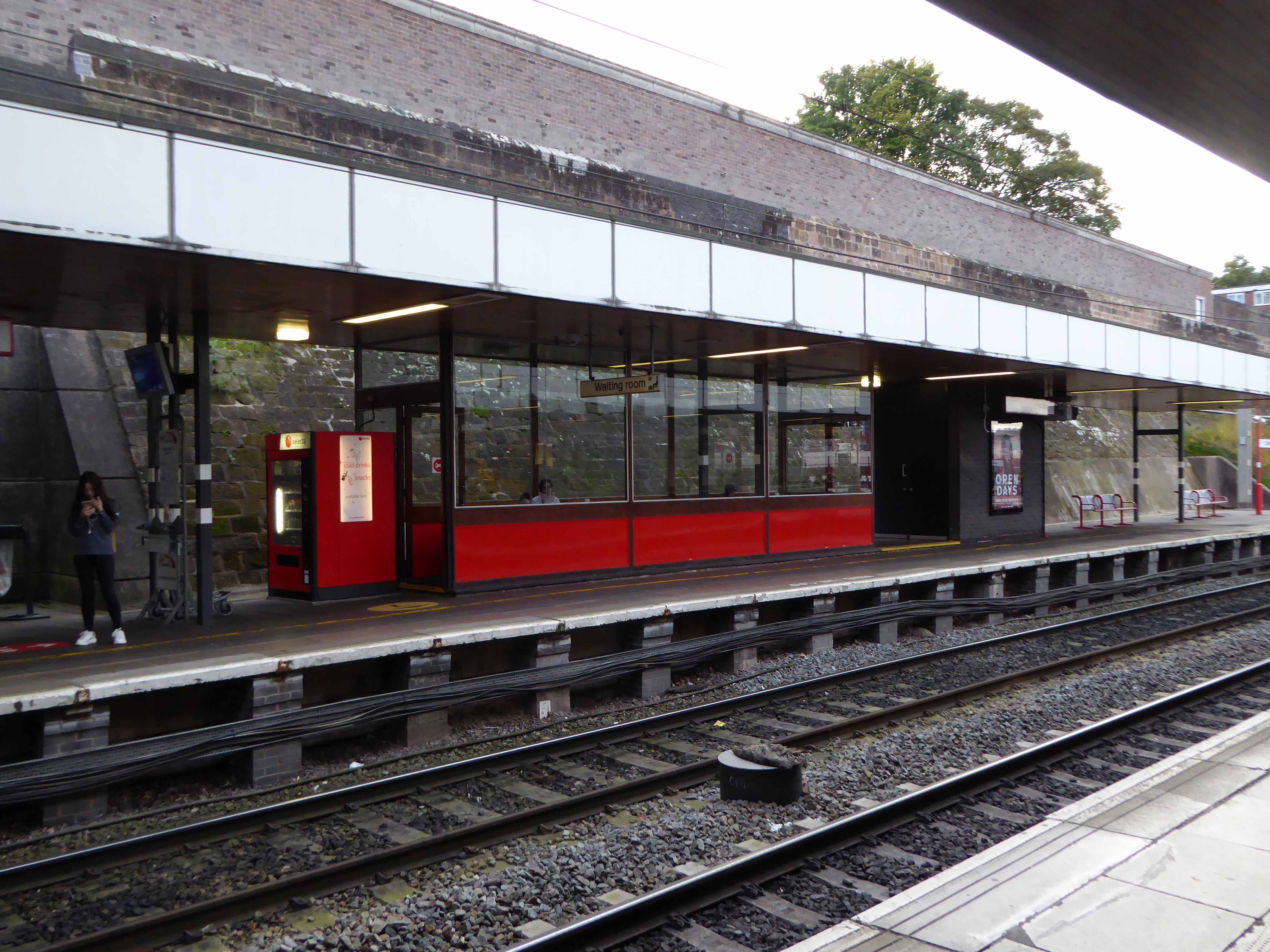
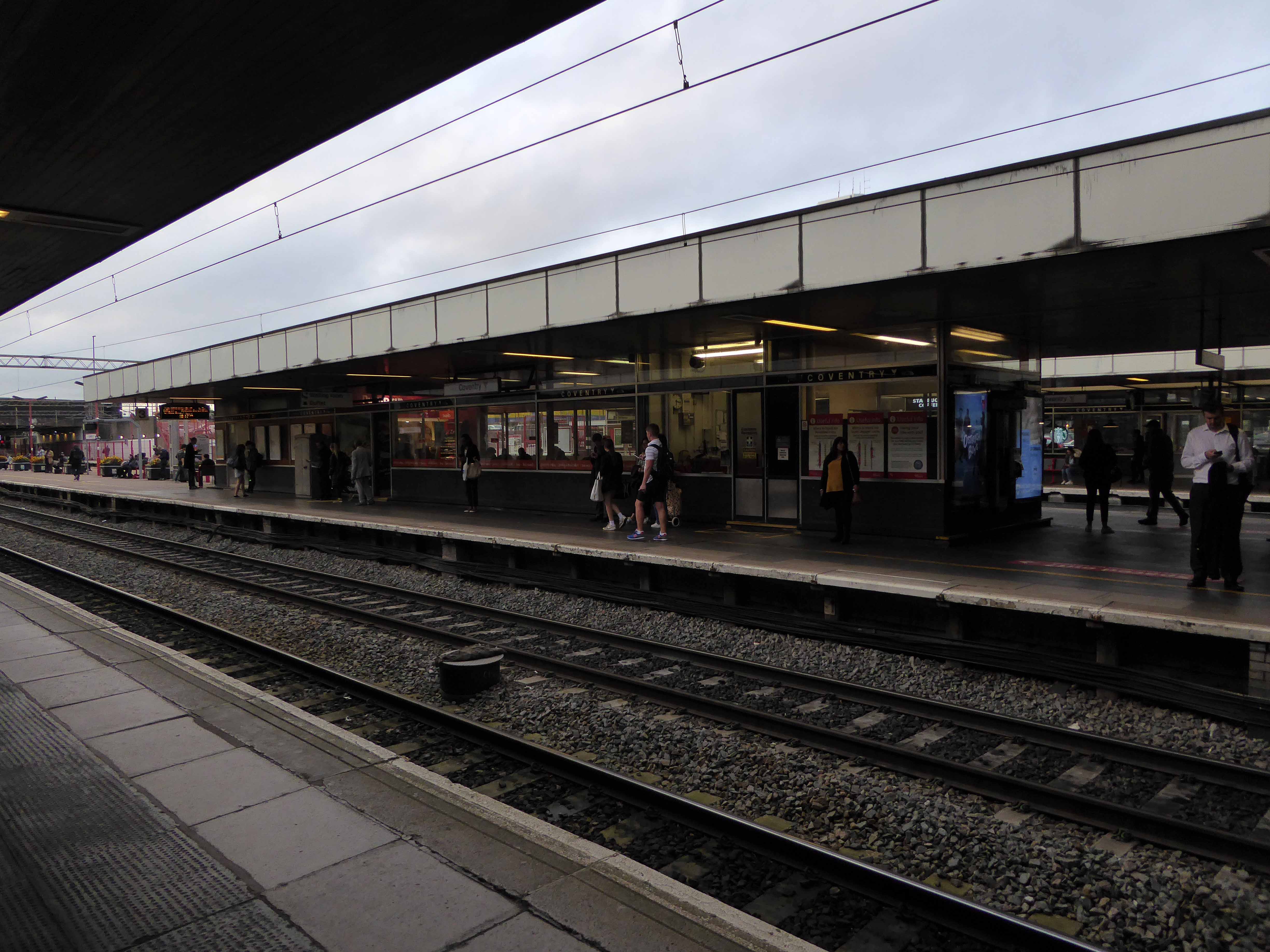
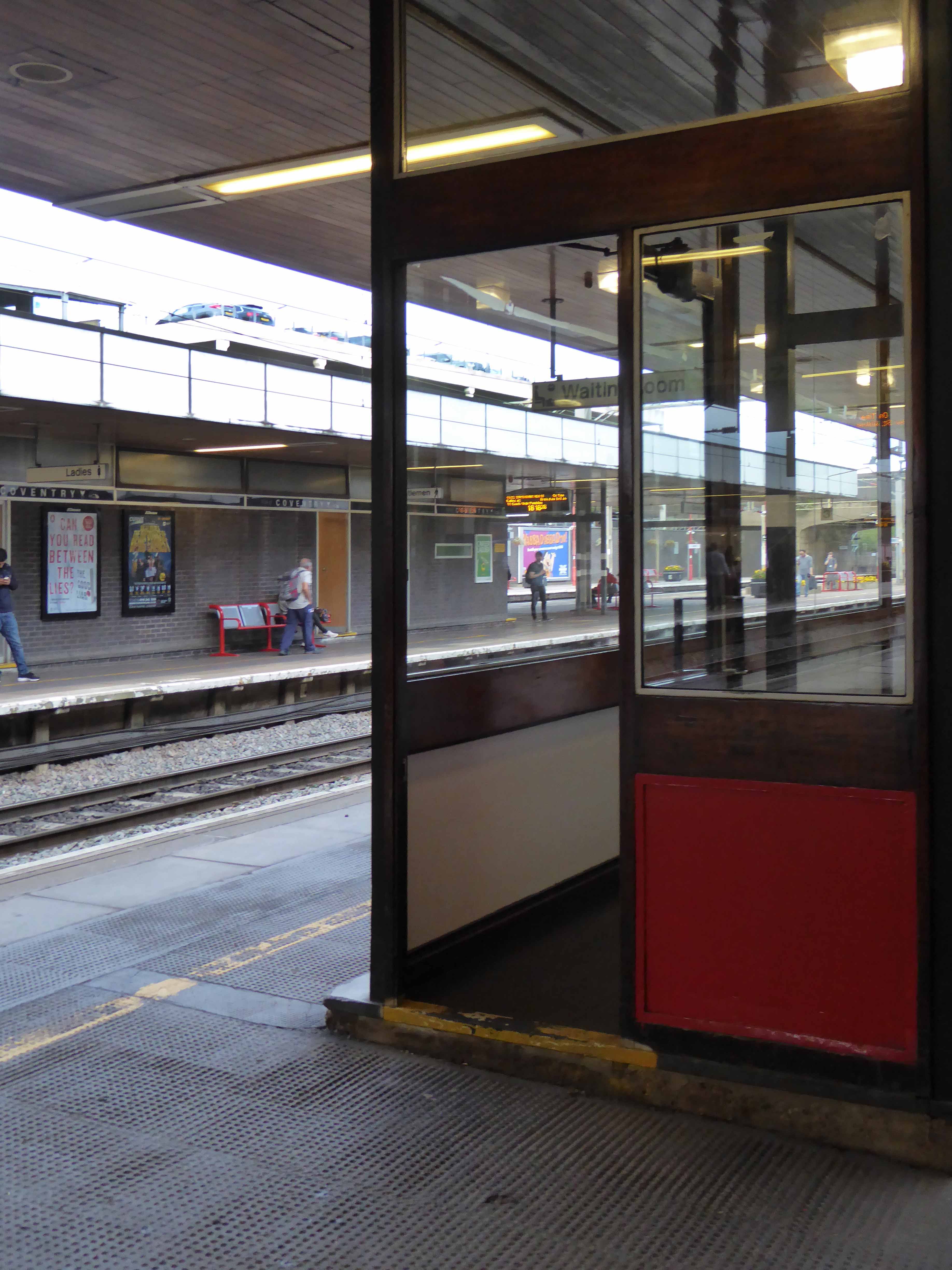
Sent to Coventry, under an imperative to explore the post-war redevelopment of a great city, I arrived by train, more than somewhat unsurprisingly at the station.
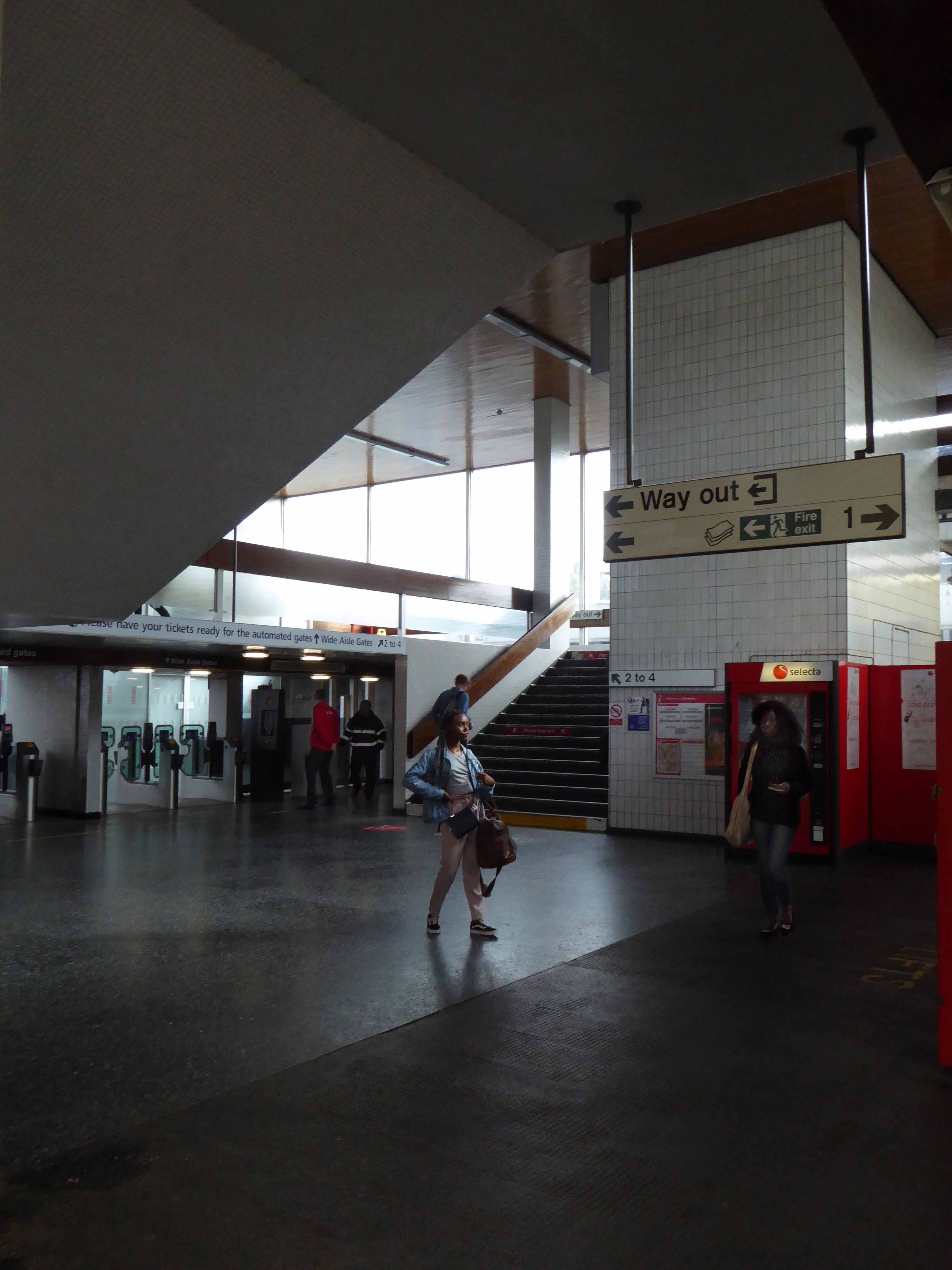
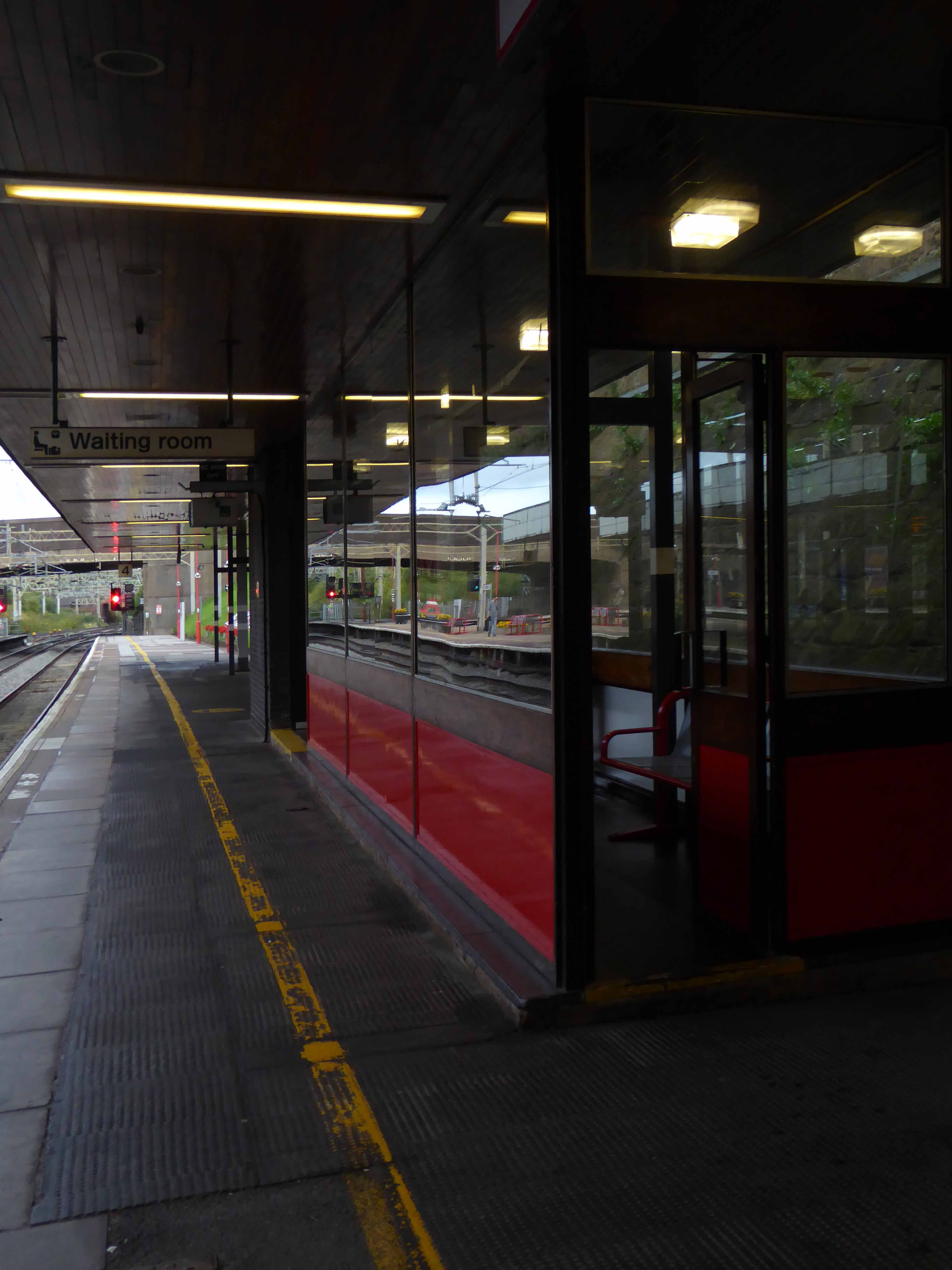
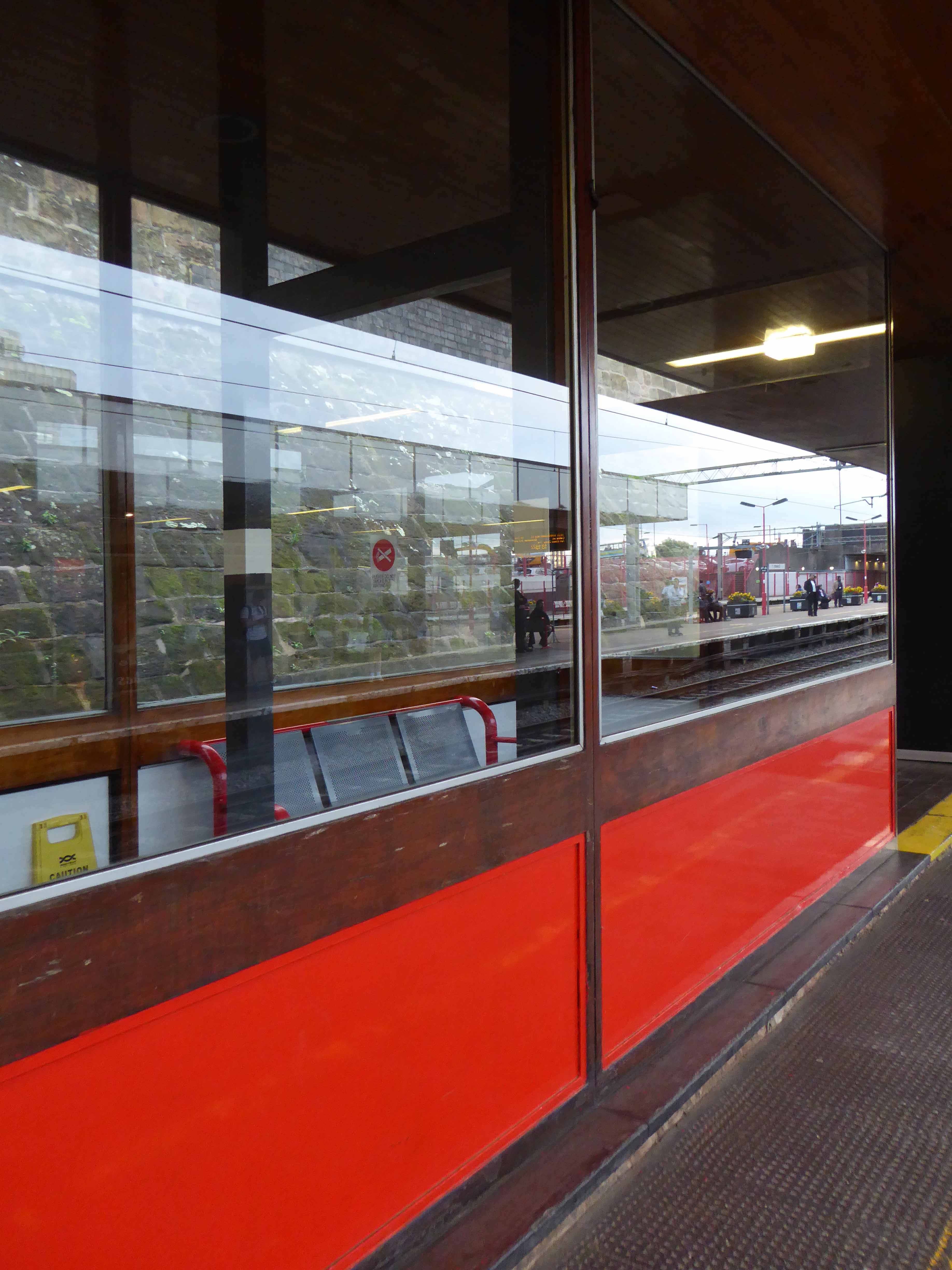
A fine building of 1962 light and airy, warm wooden ceilings, gently interlocking aluminium, glass and steel volumes, original signage and a lively feeling of calm controlled hustle and bustle.
The ideal way to start the day – take a look.
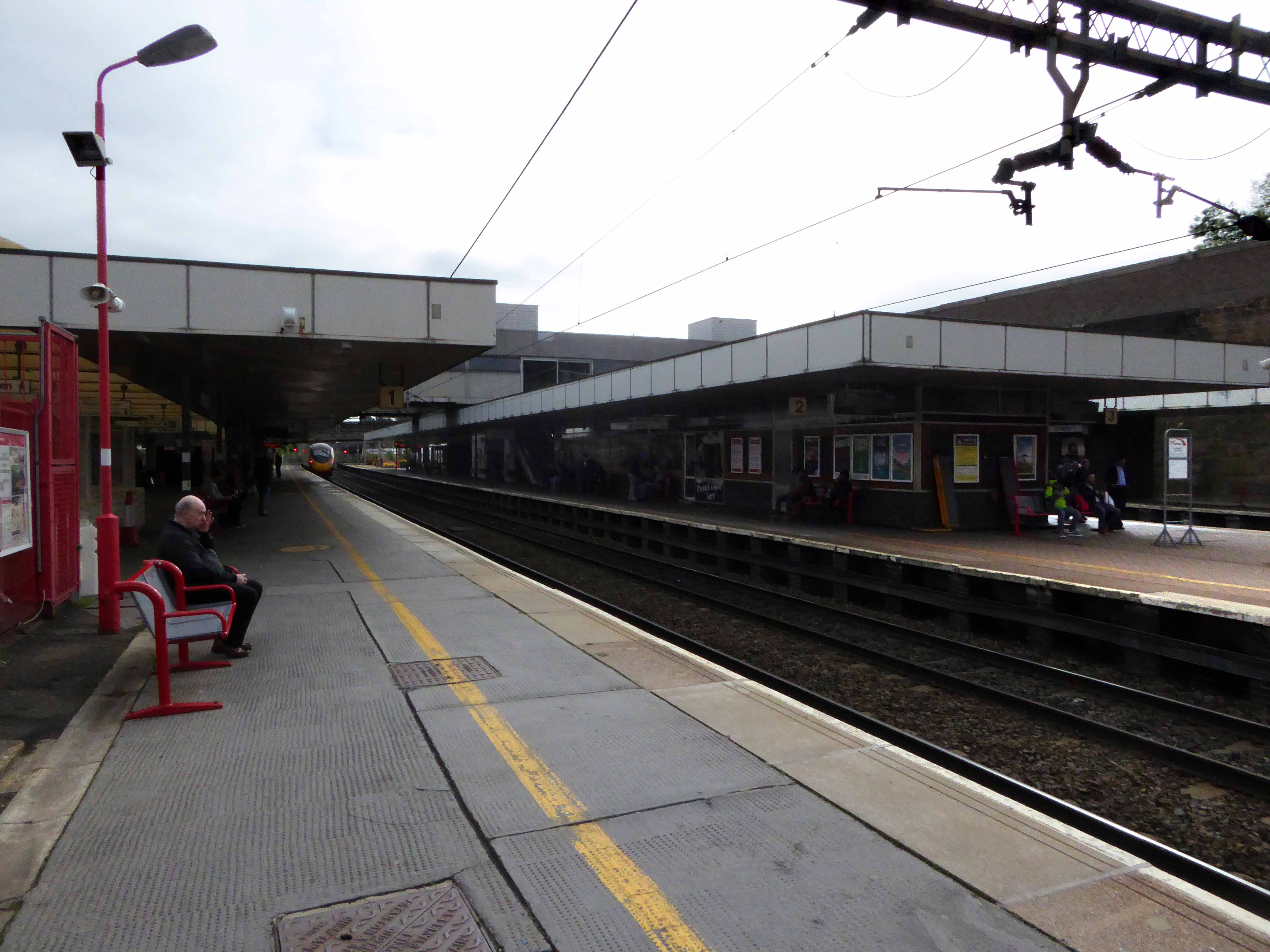
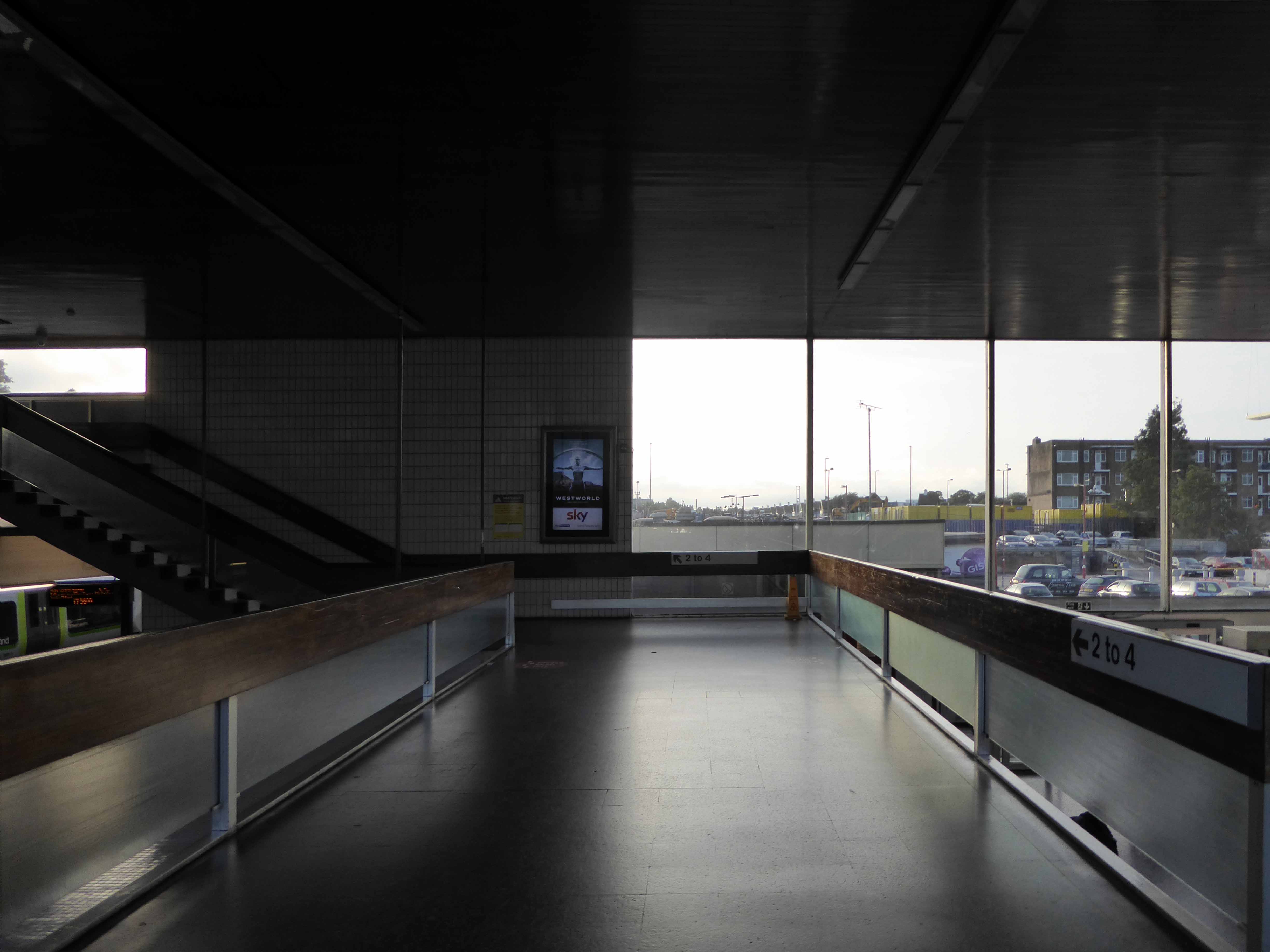
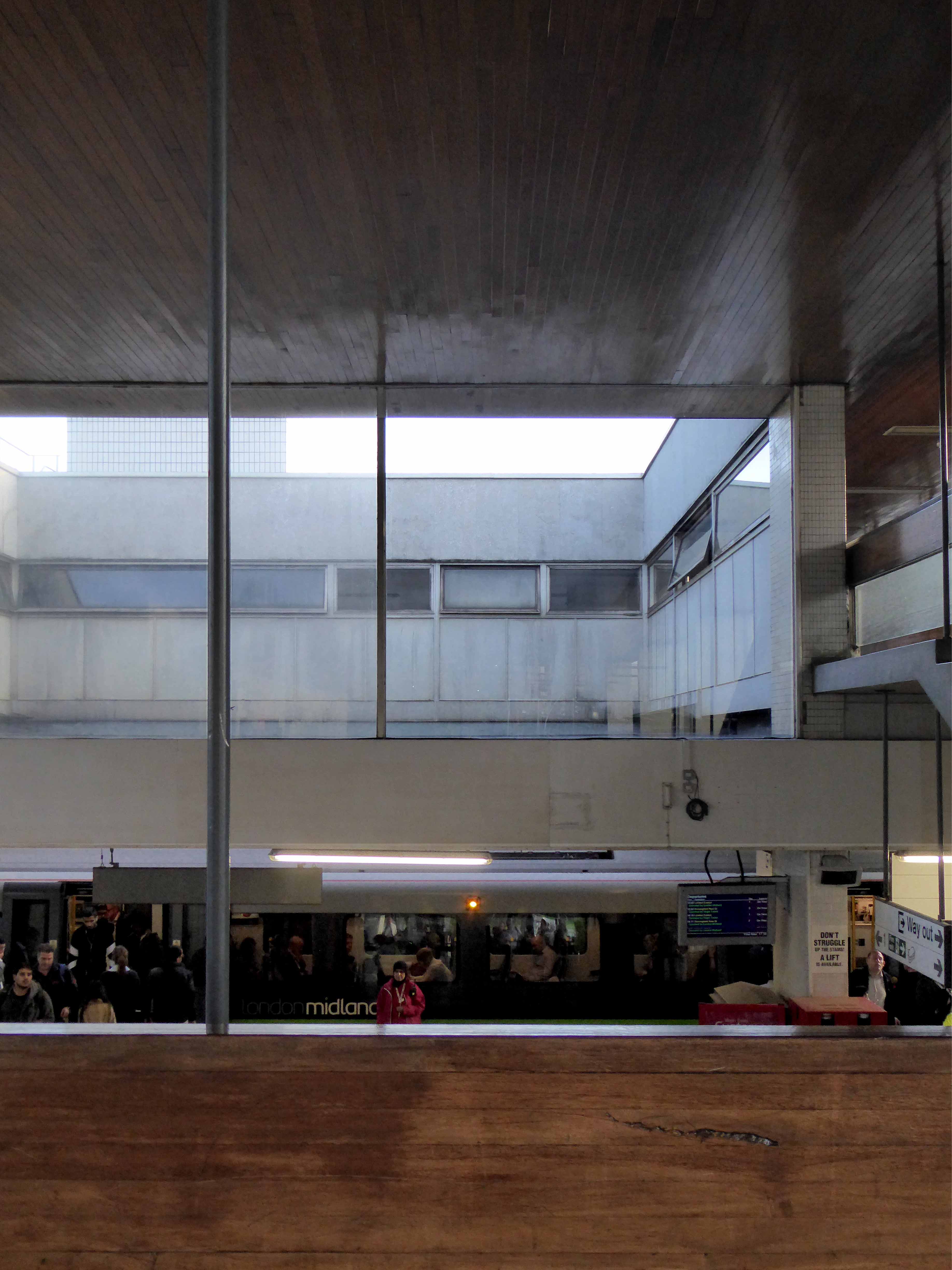
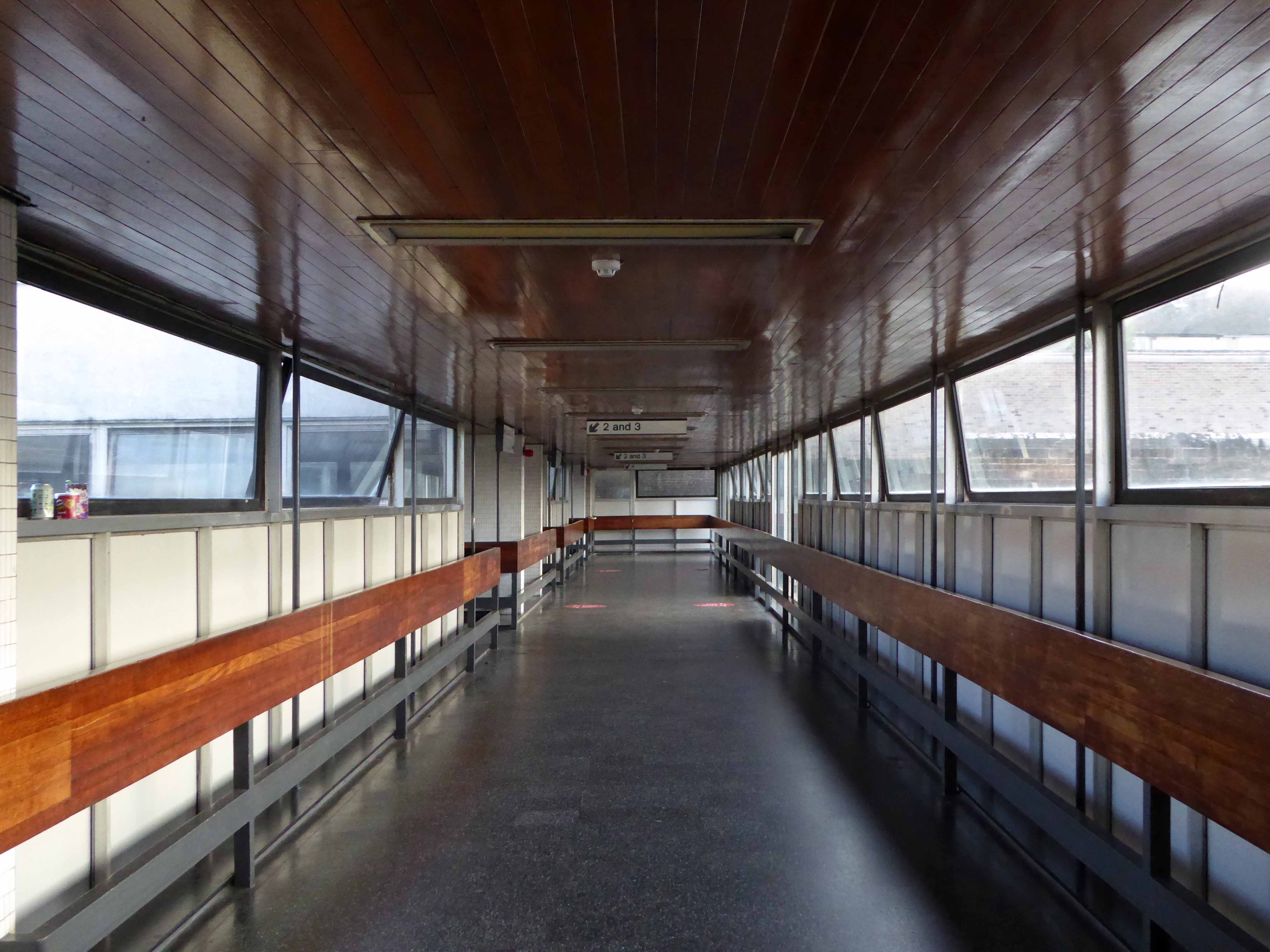




























Where are you?
Neither here nor there.
Up in the air.
Betwixt and between.
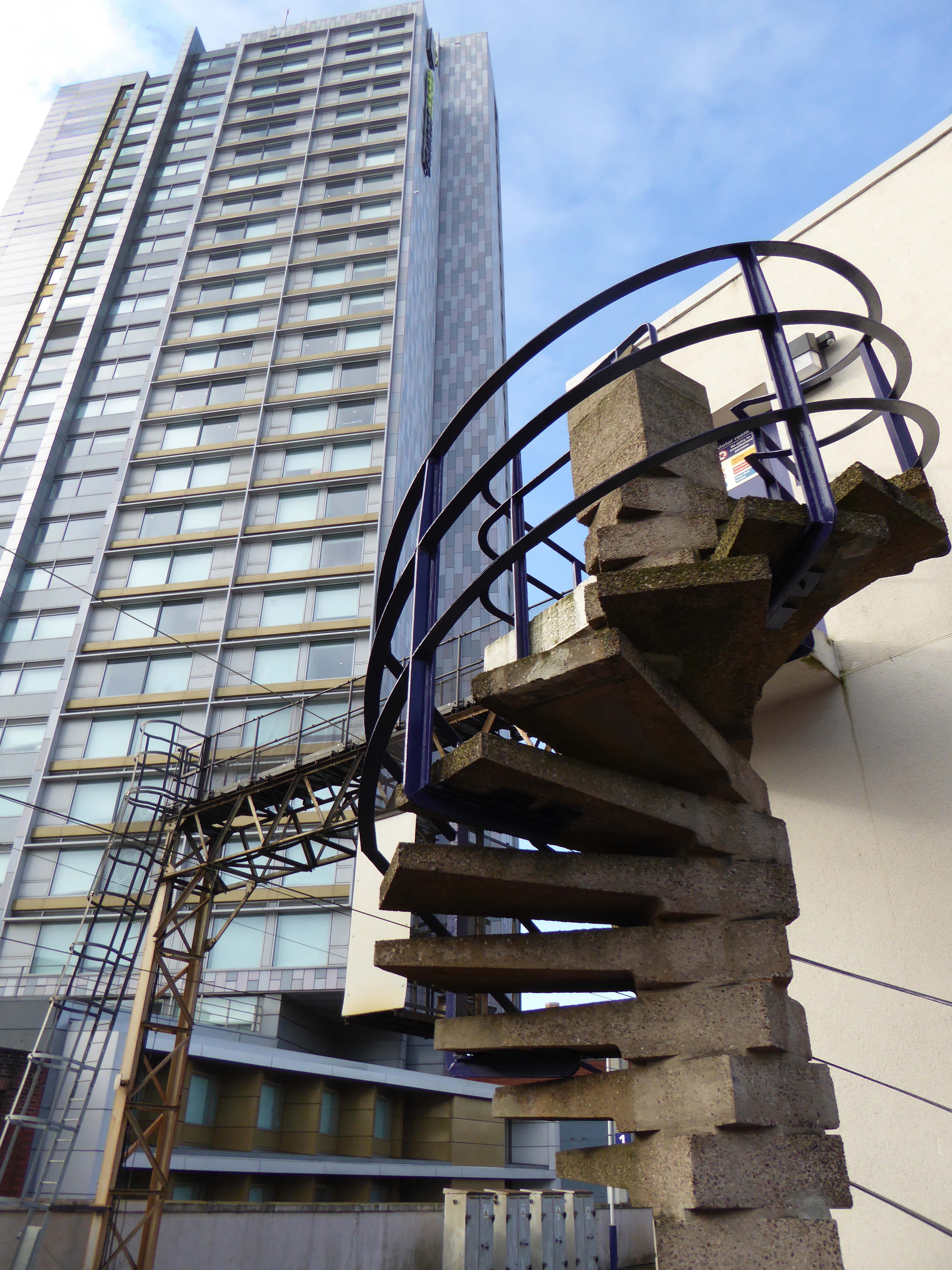
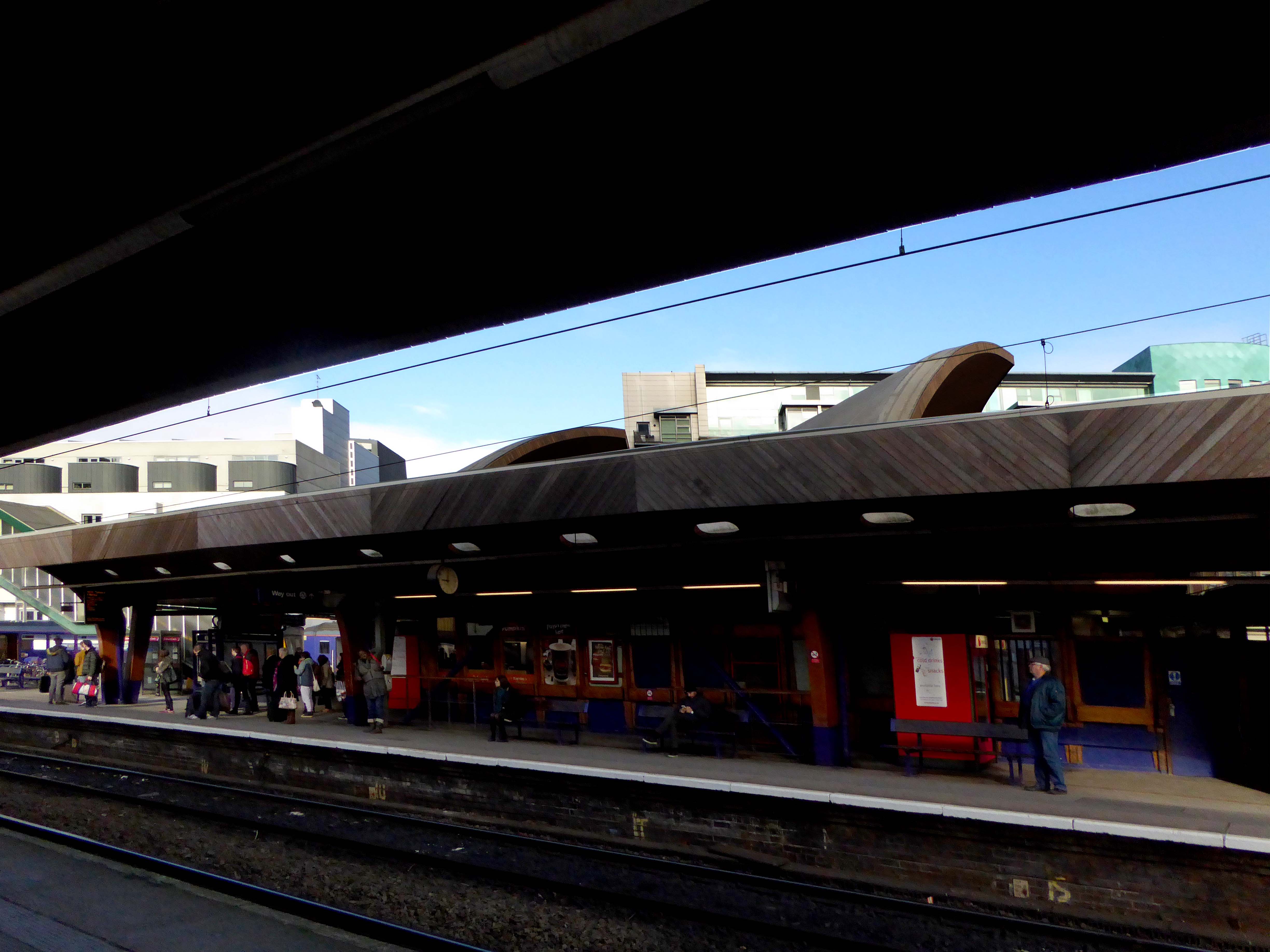
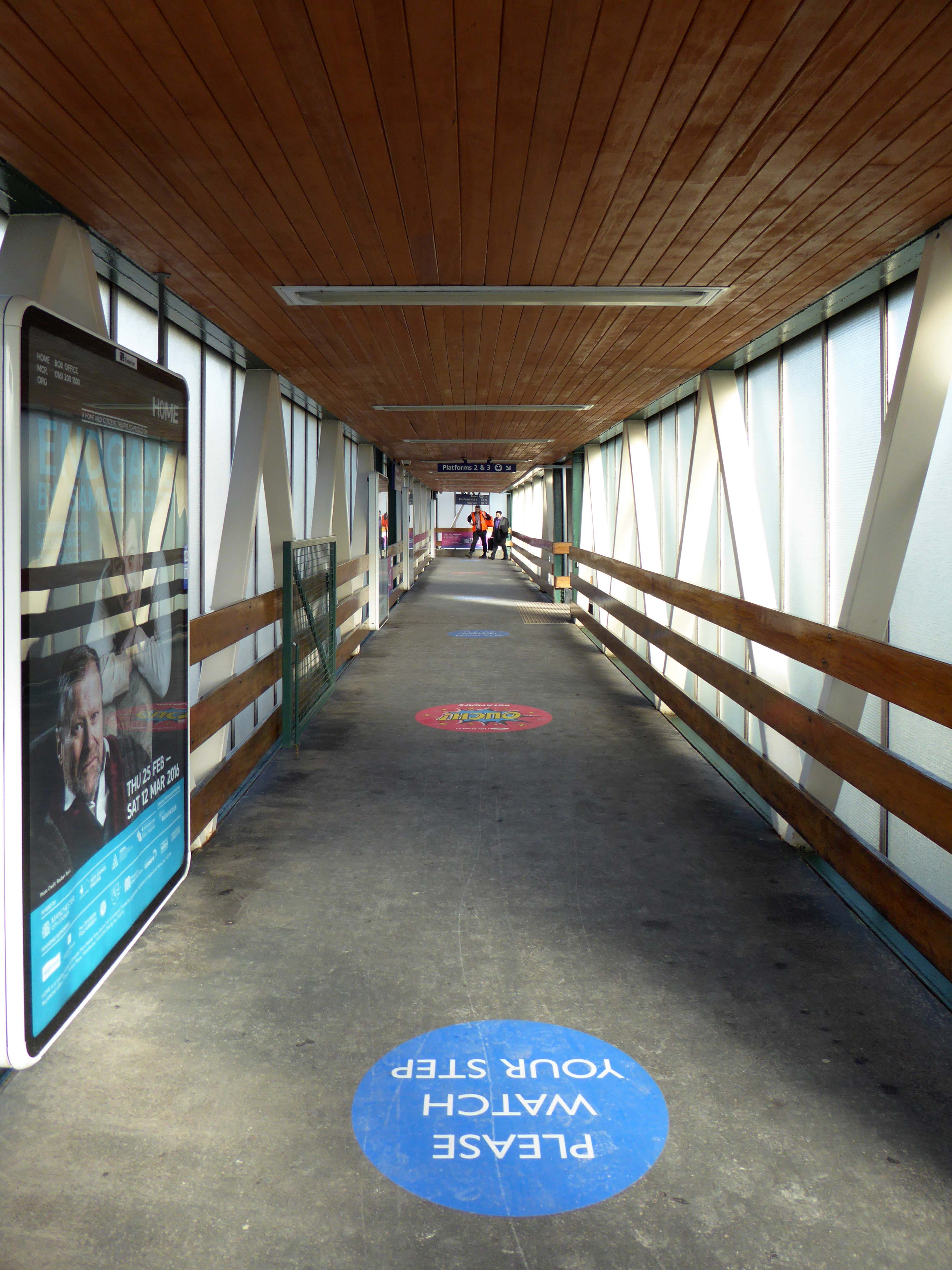
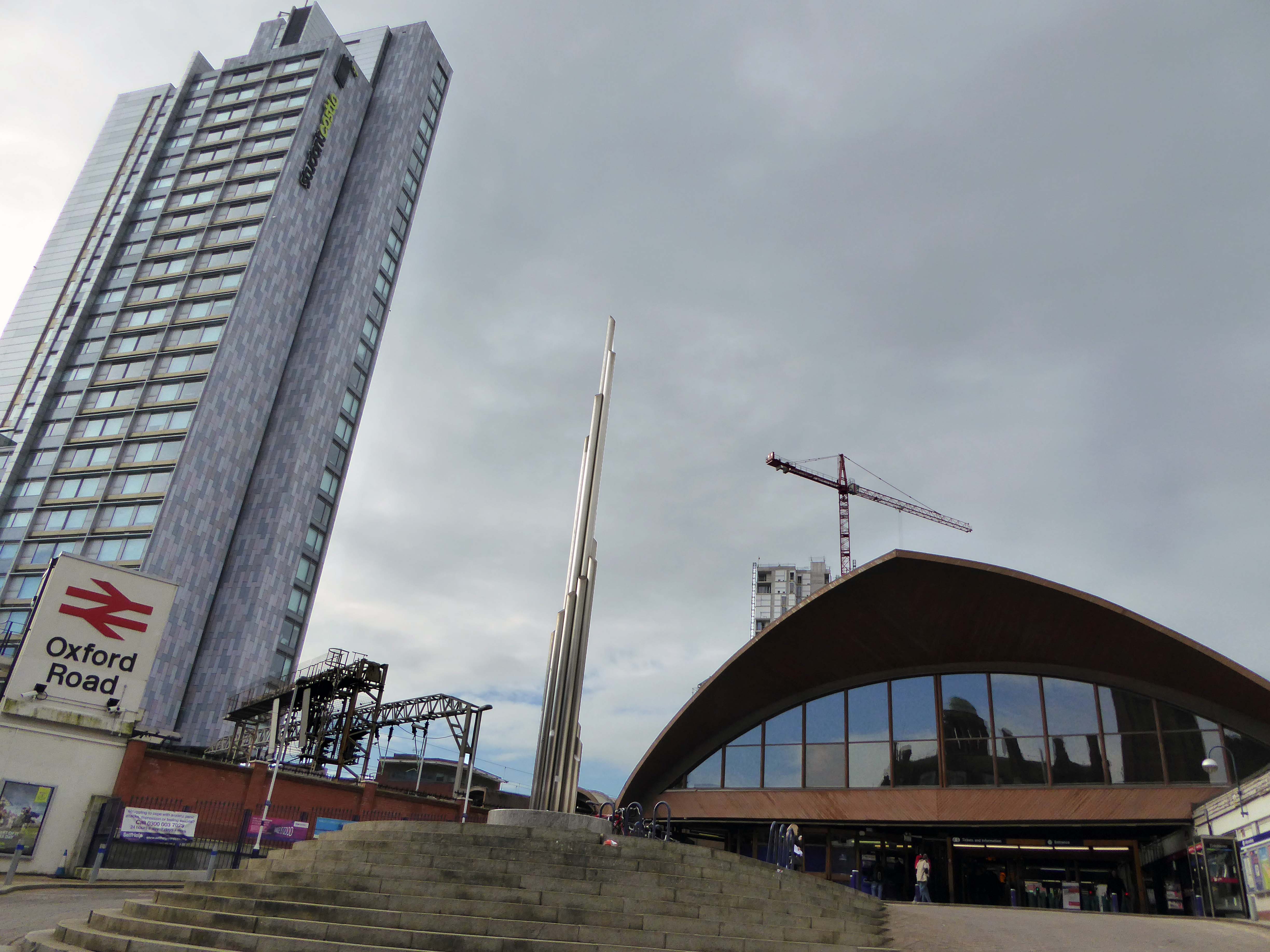
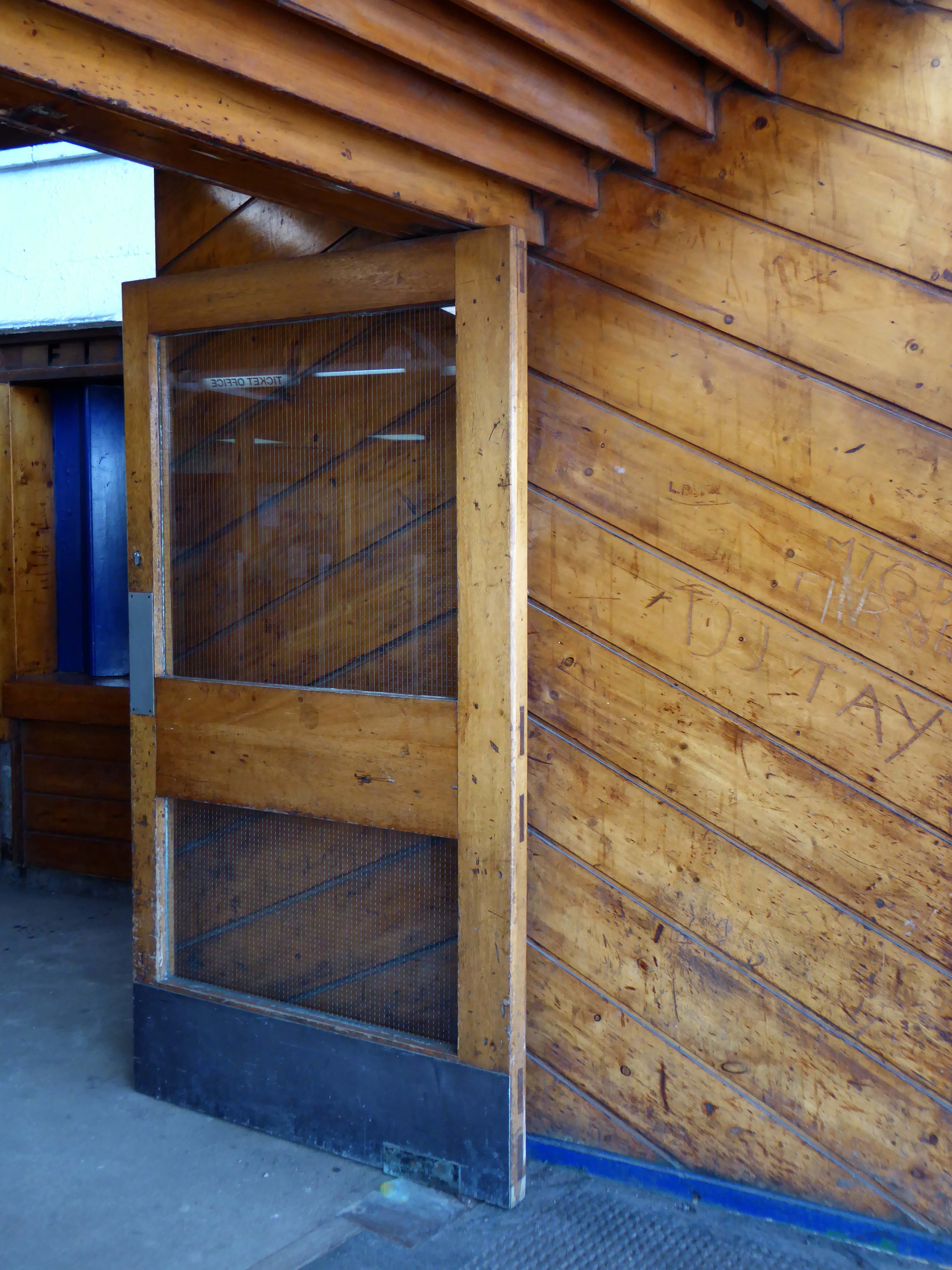
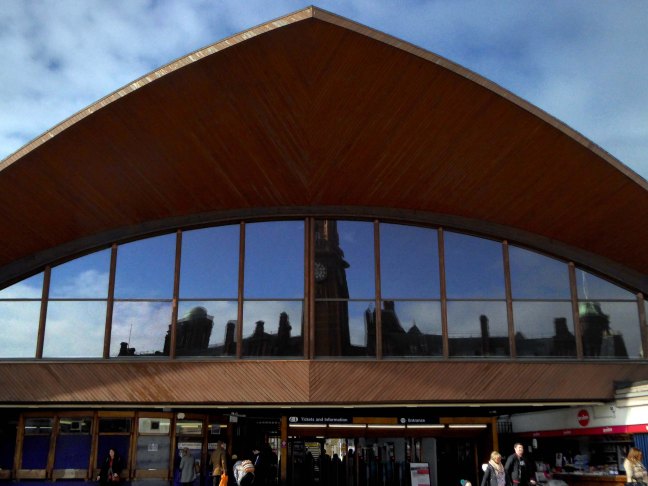
Possibly on the way to somewhere else, stranded at Oxford Road Station.
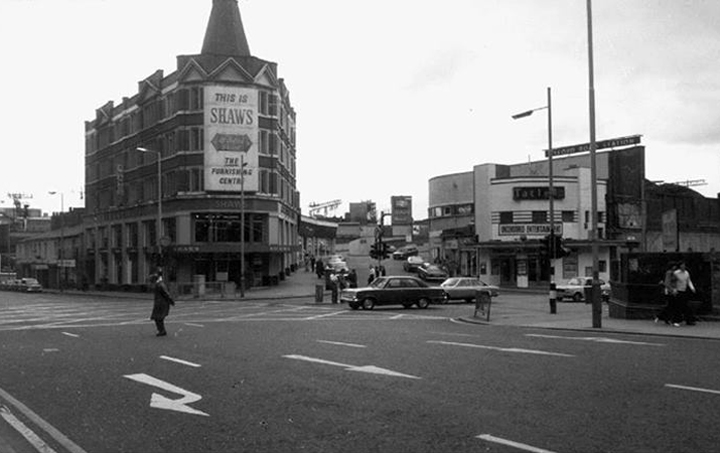
Tucked in behind Shaw’s Furniture and The Tatler Cinema.
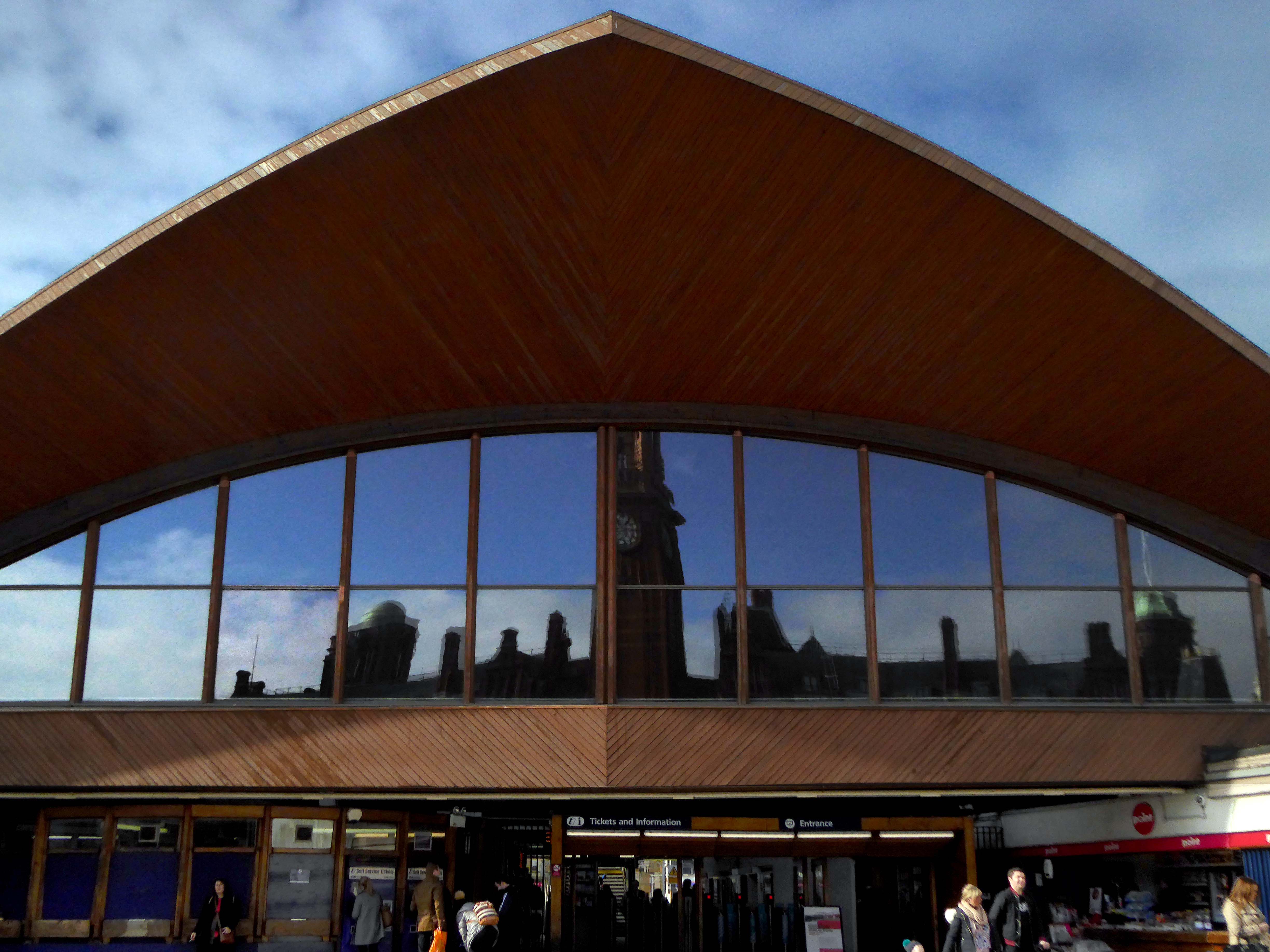
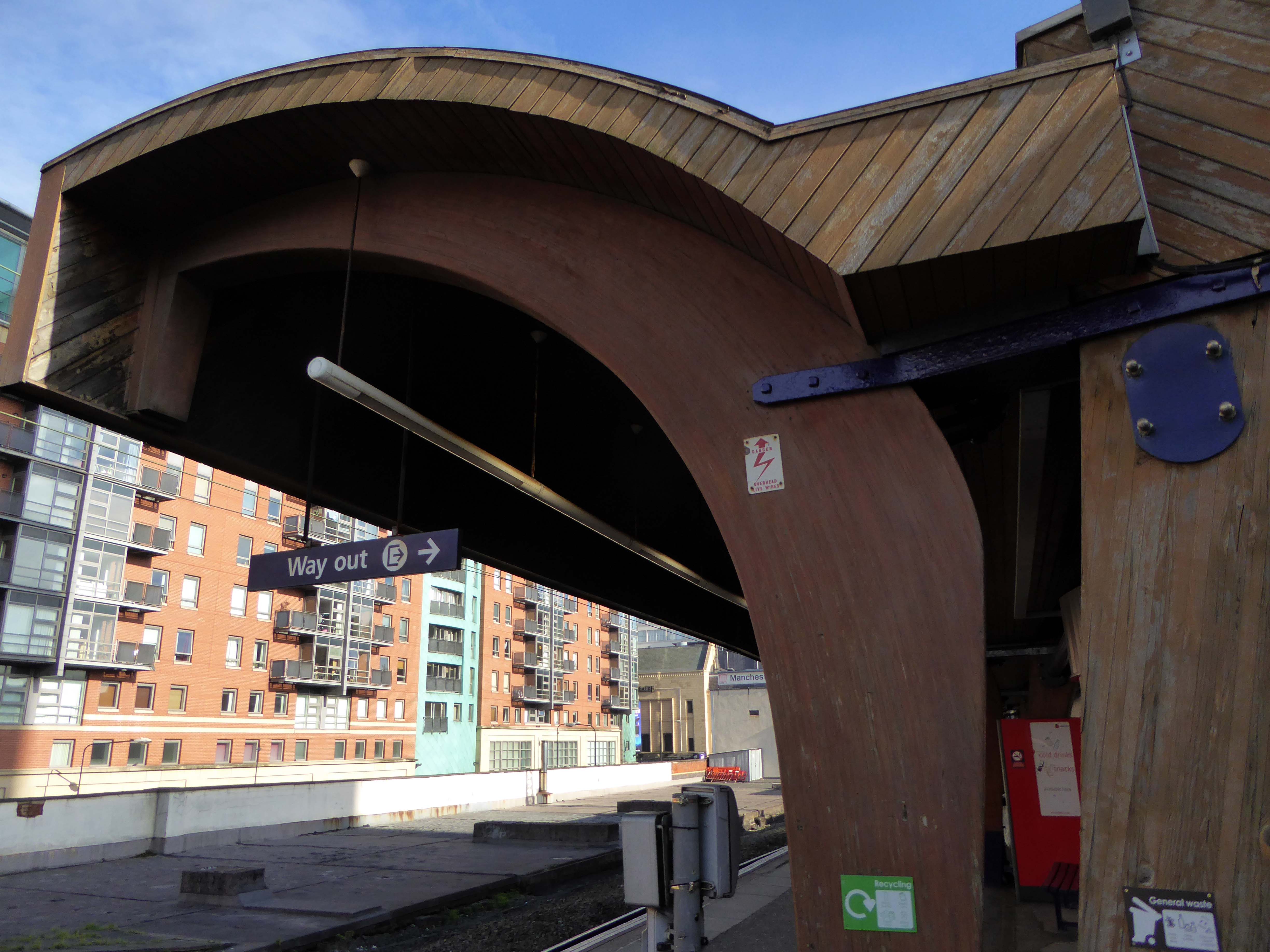
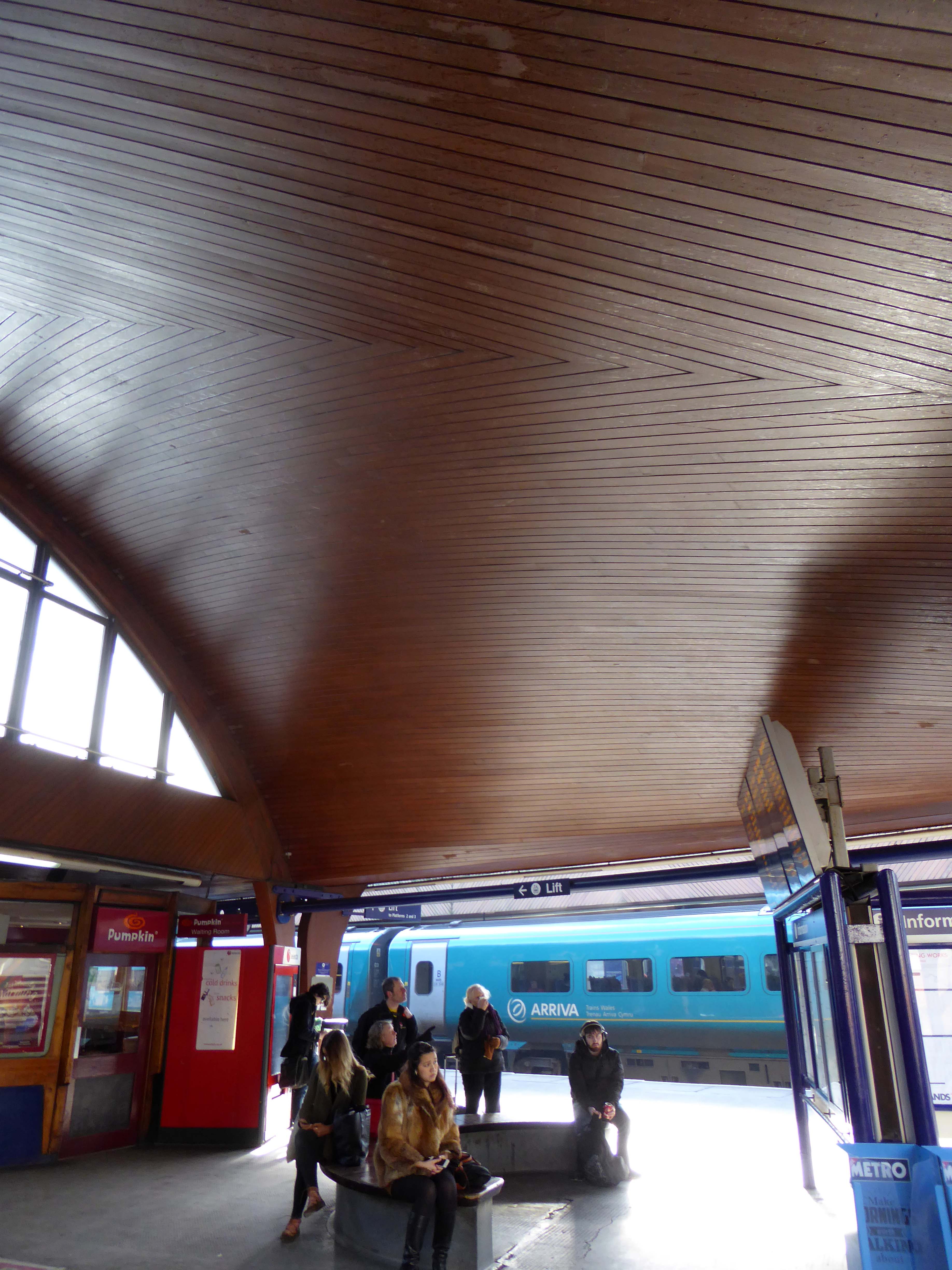
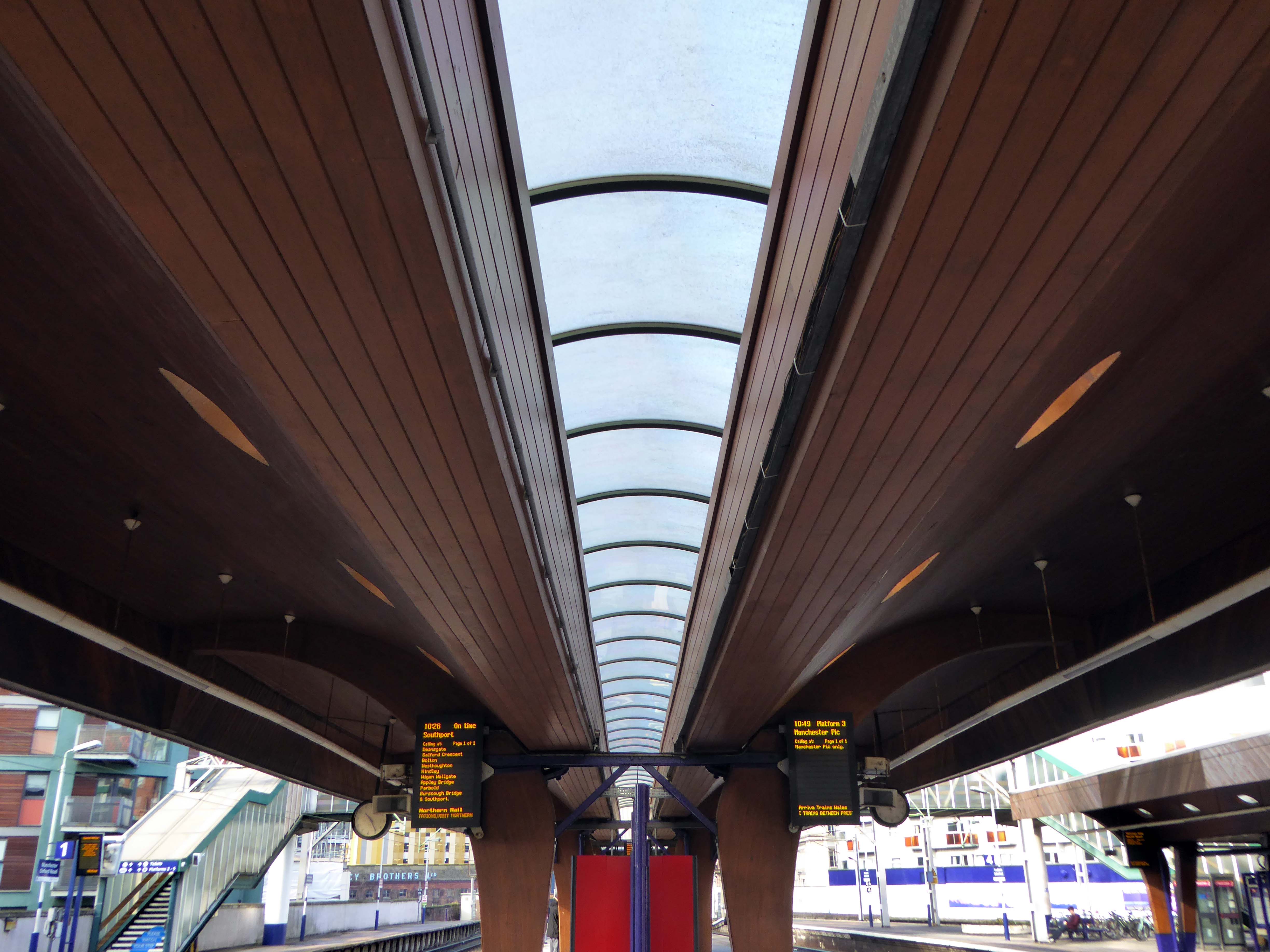
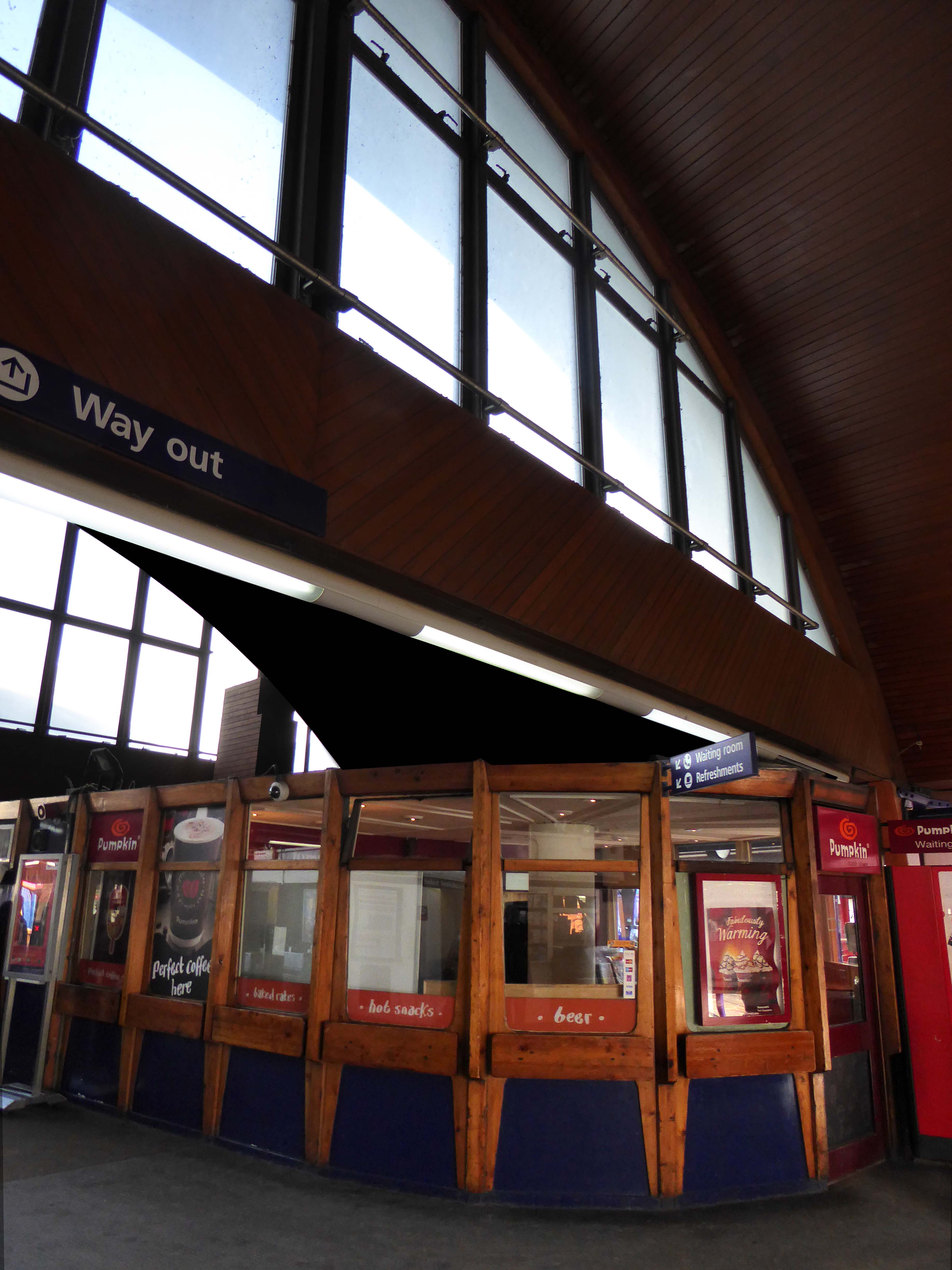
I love every curvy corner, timber frame and canopy, concrete spiral, empty kiosk and precipitous steps – I’m happy to be stranded.

It opened in 1849 and was rebuilt in 1960.
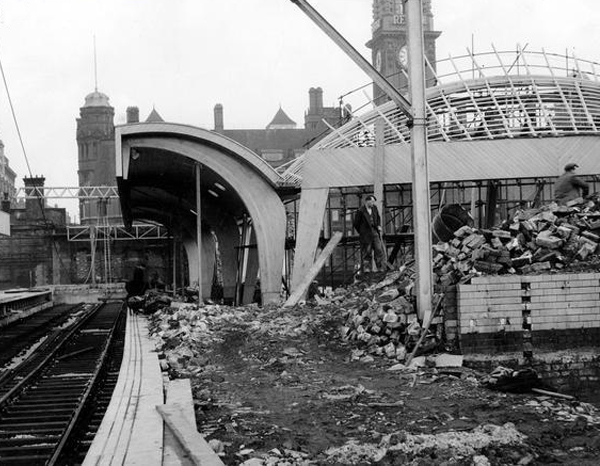


The station was opened as Oxford Road on 20 July 1849 by the Manchester, South Junction and Altrincham Railway . The station was the headquarters of the MSJAR from its opening until 1904. It had two platforms and two sidings, with temporary wooden buildings. To allow for extra trains in connection with the Manchester Art Treasures Exhibition in 1857, extra platforms and sidings were built. In 1874 the station was completely rebuilt providing two bay platforms and three through platforms. Further reconstruction took place during 1903-04. From 1931 it was served by the MSJAR’s 1500V DC electric trains between Altrincham and Manchester Piccadilly.
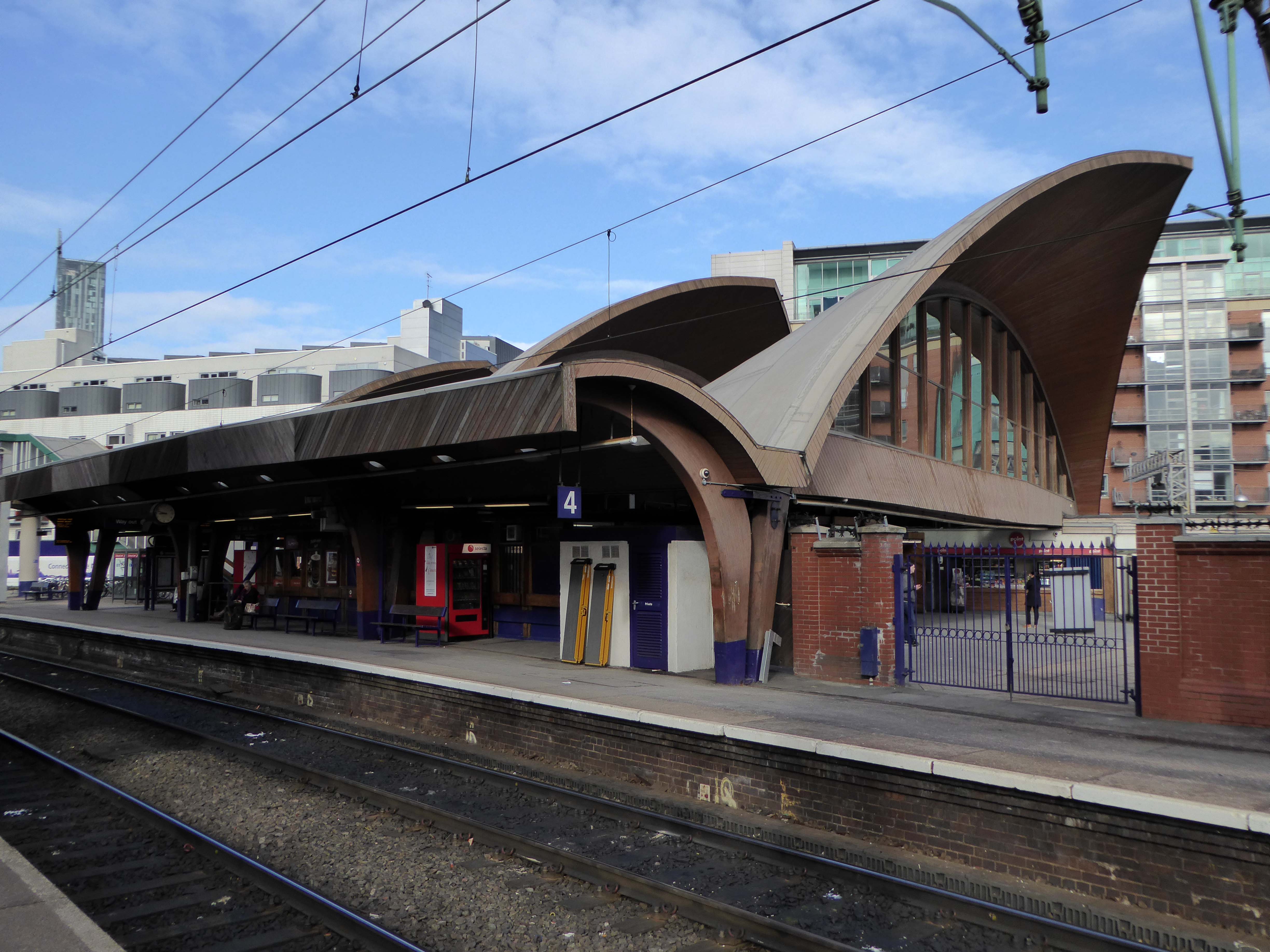
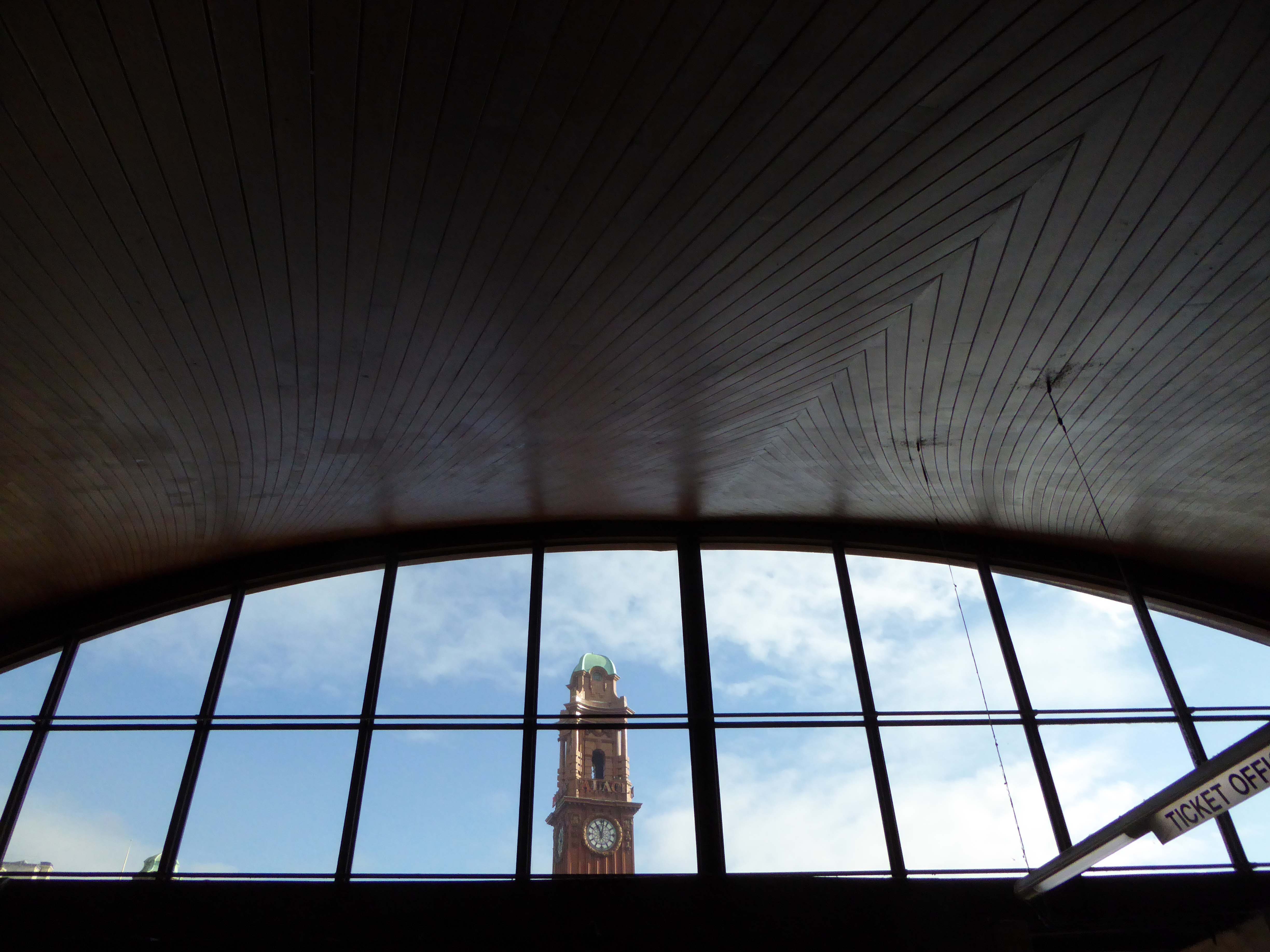
The station had become dilapidated by the 1950s, and in connection with the electrification and modernisation programme of the Manchester to London line in 1960, the old buildings were replaced by the current structure by architects W.R. Headley and Max Glendinning and structural engineer Hugh Tottenham. It was designed in a distinctive style in concrete and wood with curves bringing to mind the Sydney Opera House.
Use of the station increased from May 1988 when the Windsor Link was inaugurated between Deansgate and Salford Crescent, connecting lines to the north and south of Manchester.
The station is a grade II listed building.
One of the most interesting and innovative buildings of the period, the most ambitious example in this country of timber conoid shell roofing.
Further development awaits, widening the viaduct and lengthening platforms as part of the Northern Hub Project.
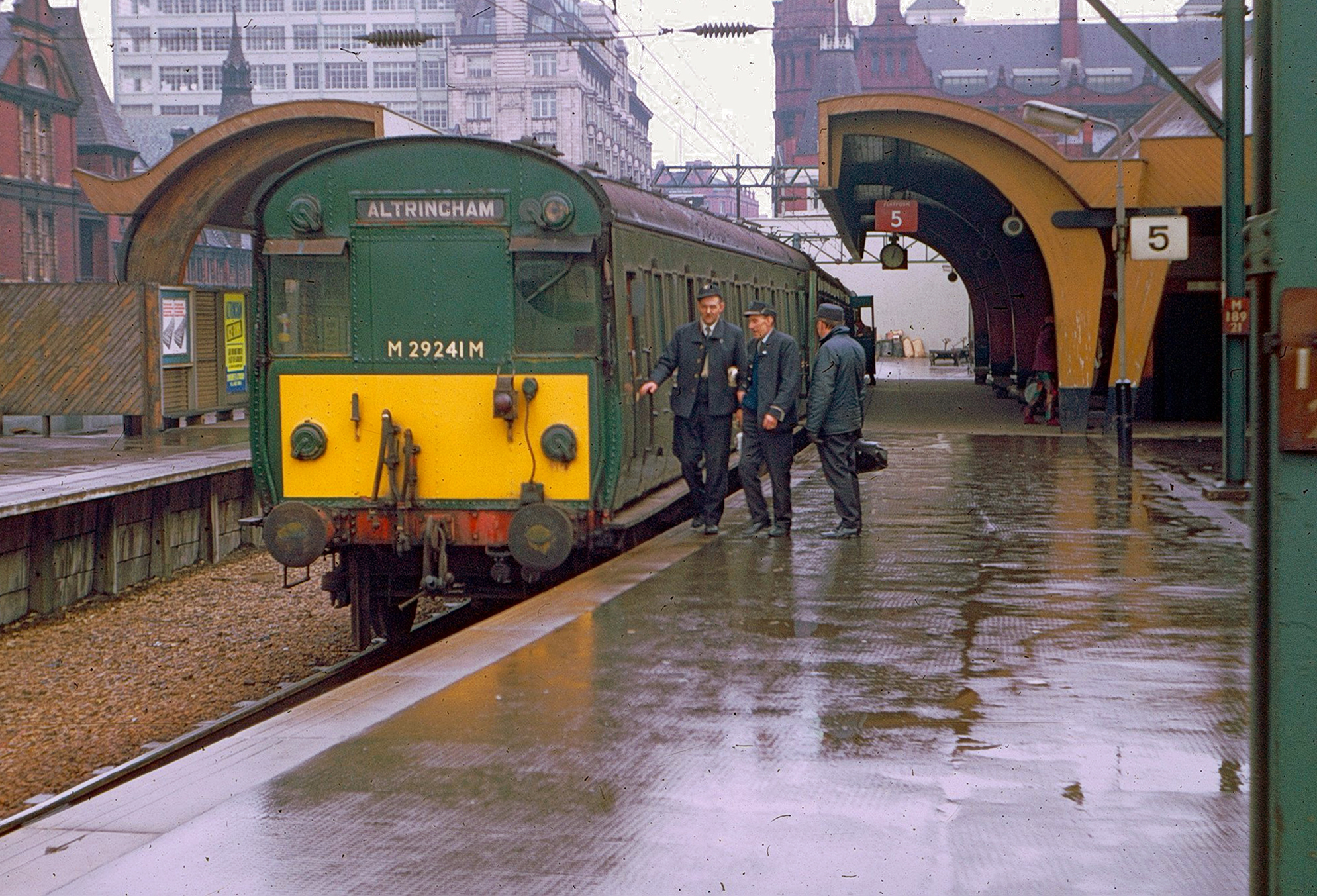

The defunct Platform 6 and lost awning to the left – Photo: 20 3 1971 Tom Burnham
Altrincham bound 931 Metro-Cammell MSJAR 1500 volt DC EMU – all withdrawn by 1971, when the line was converted to AC.





















