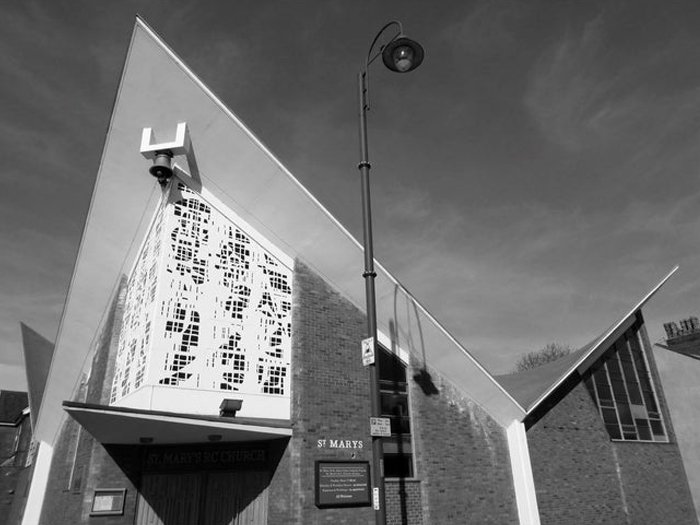
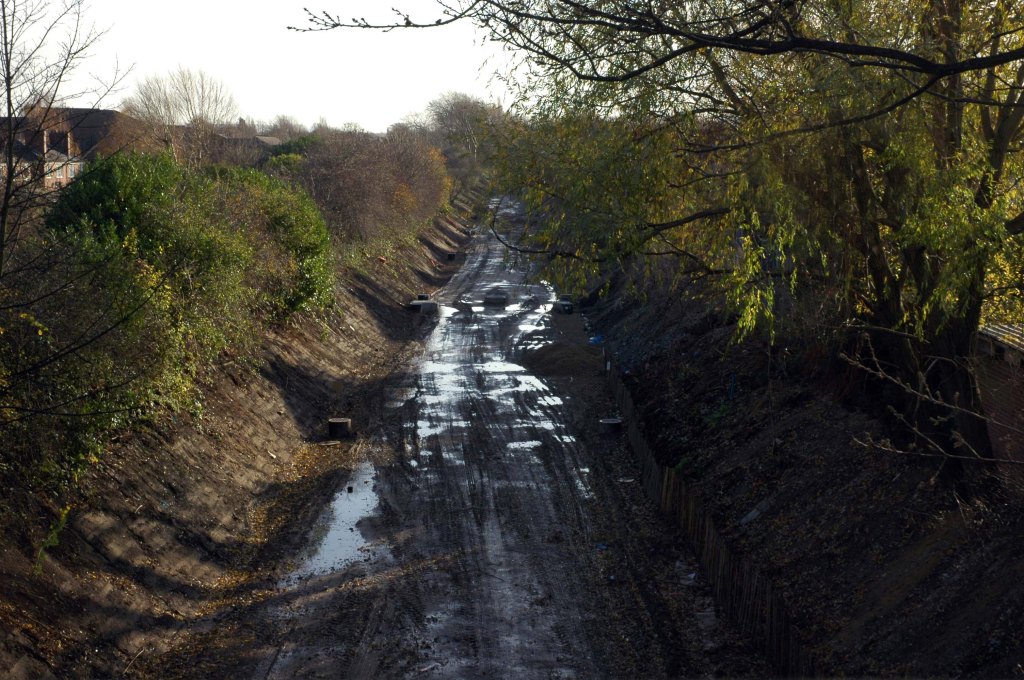
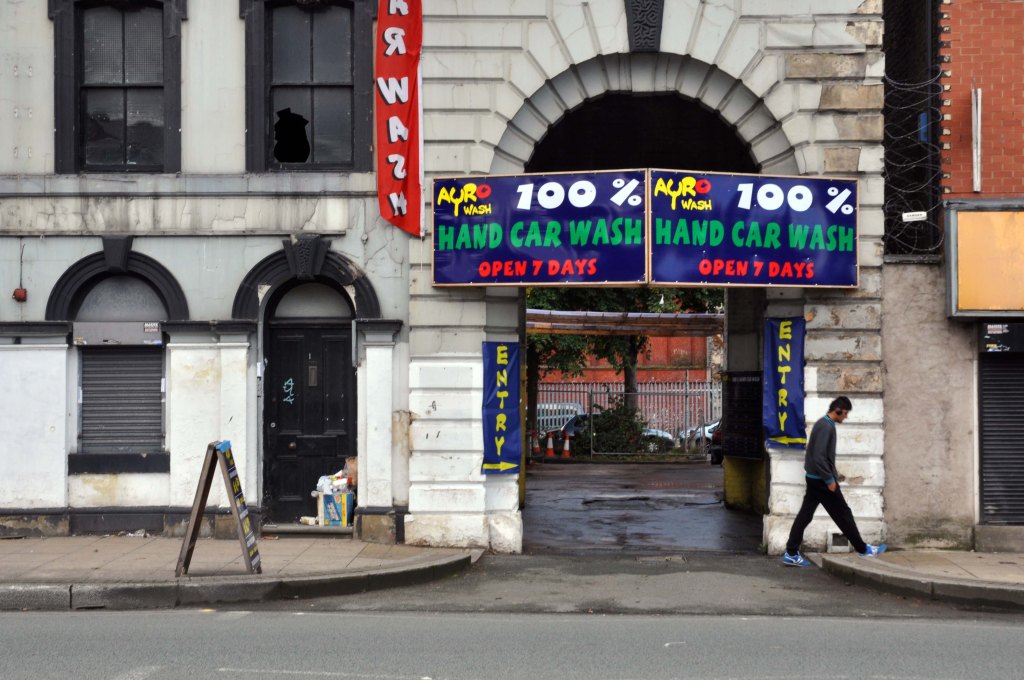
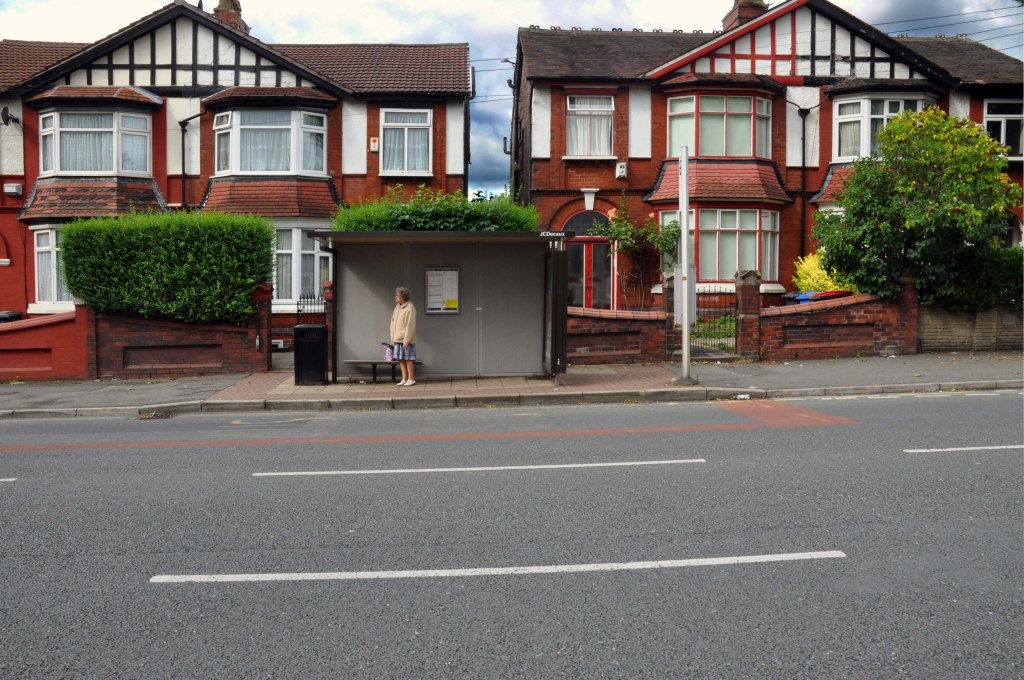
Having photographed the arterial roads of Manchester in 2014 I have resolved to return to the task in 2024.
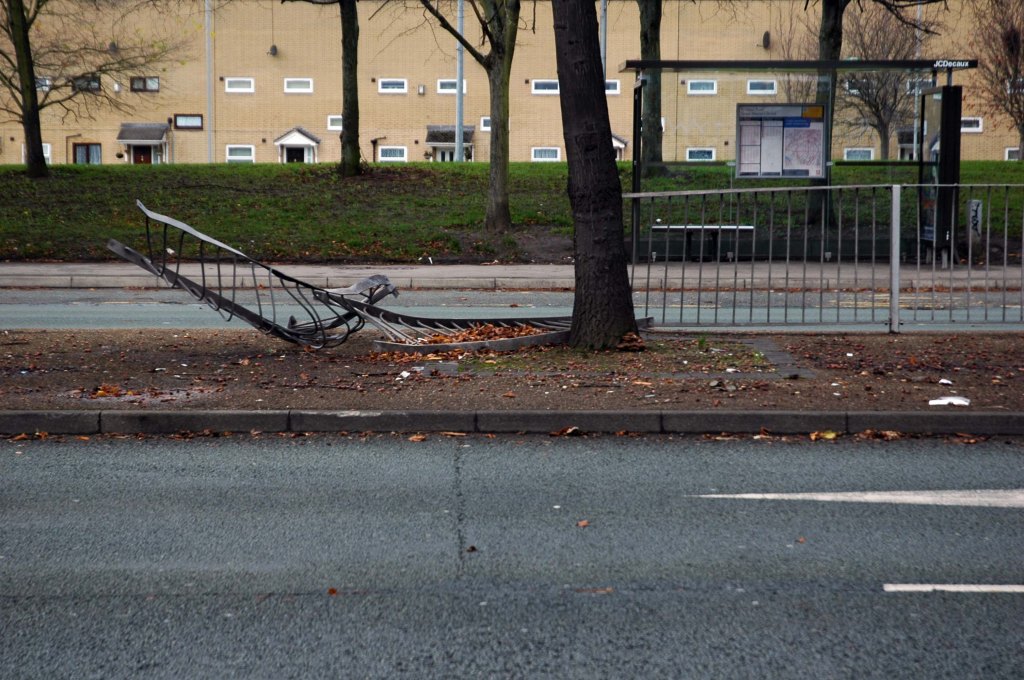
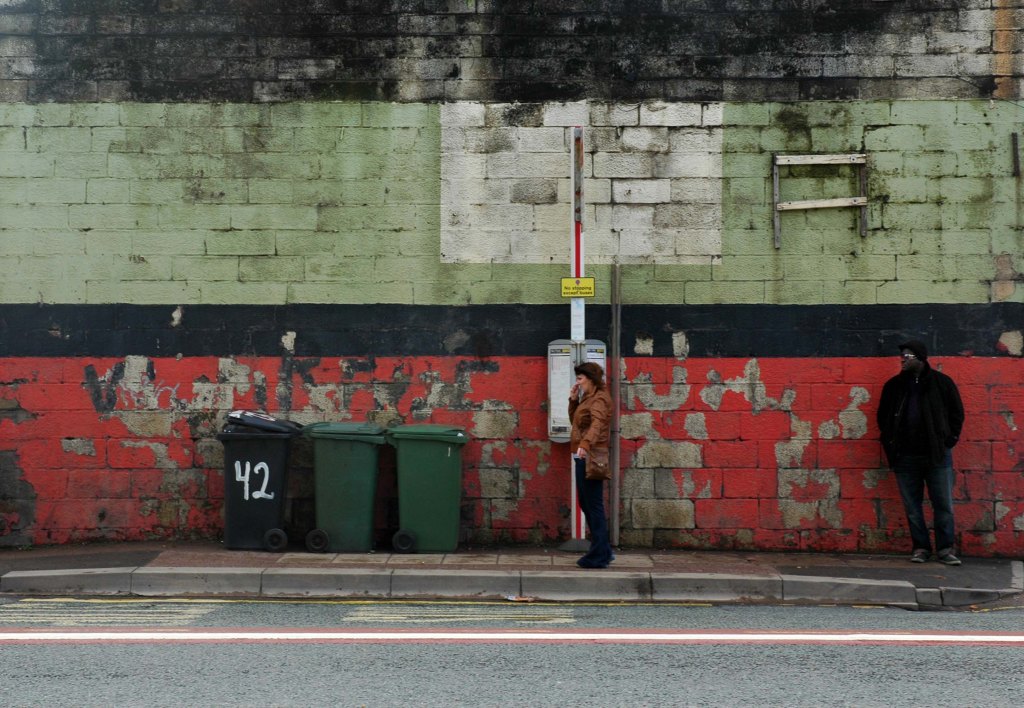
Some things seem to have changed, some things seem to have stayed the same on Ashton New Road.
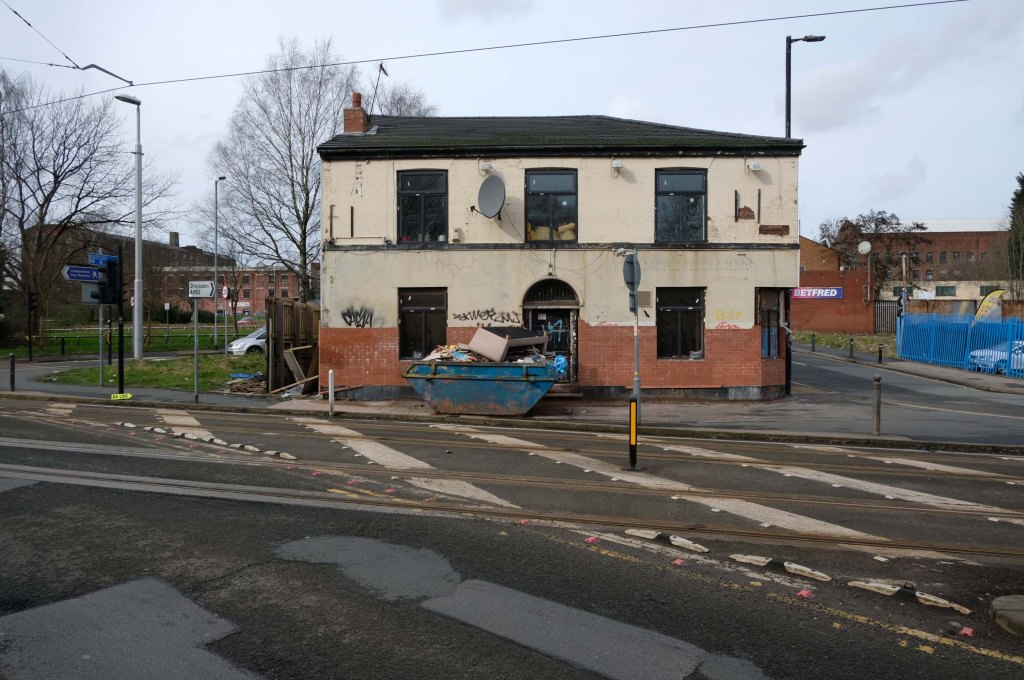
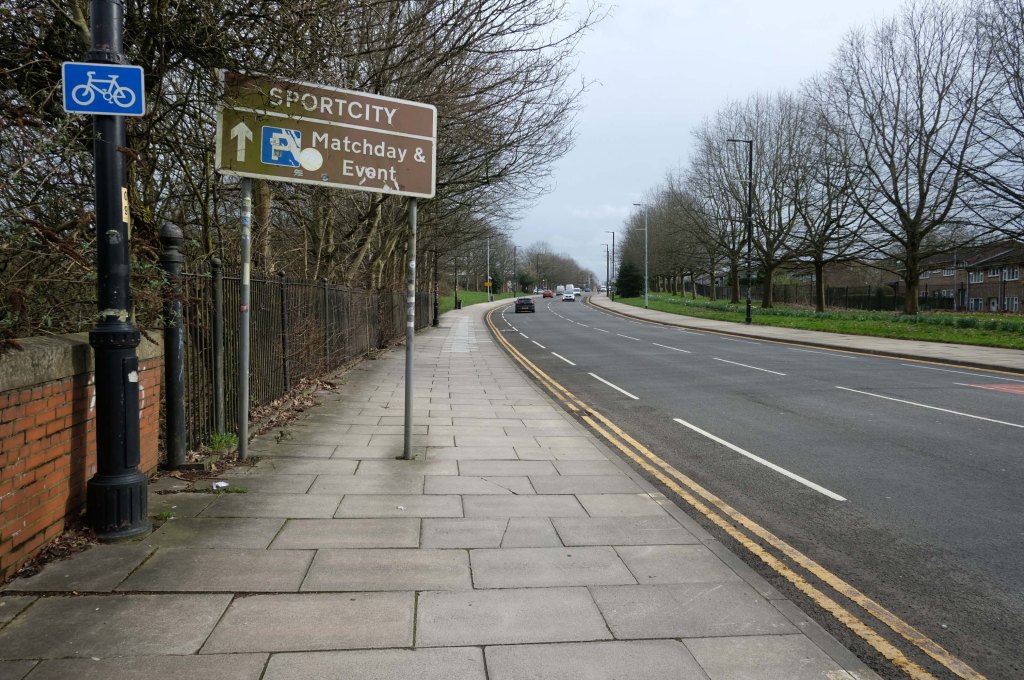
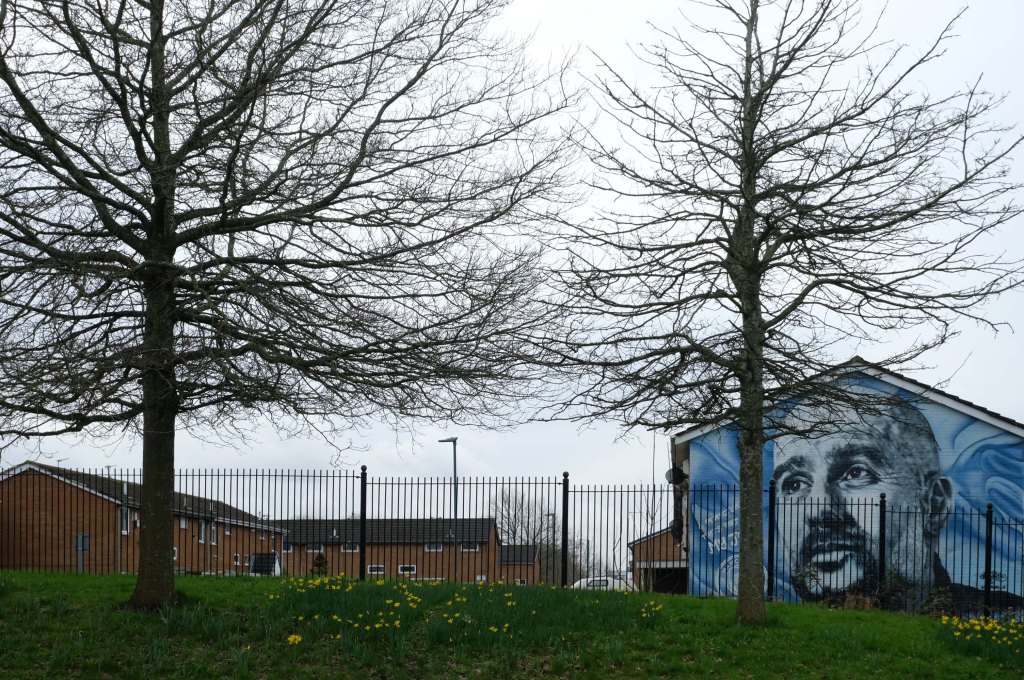
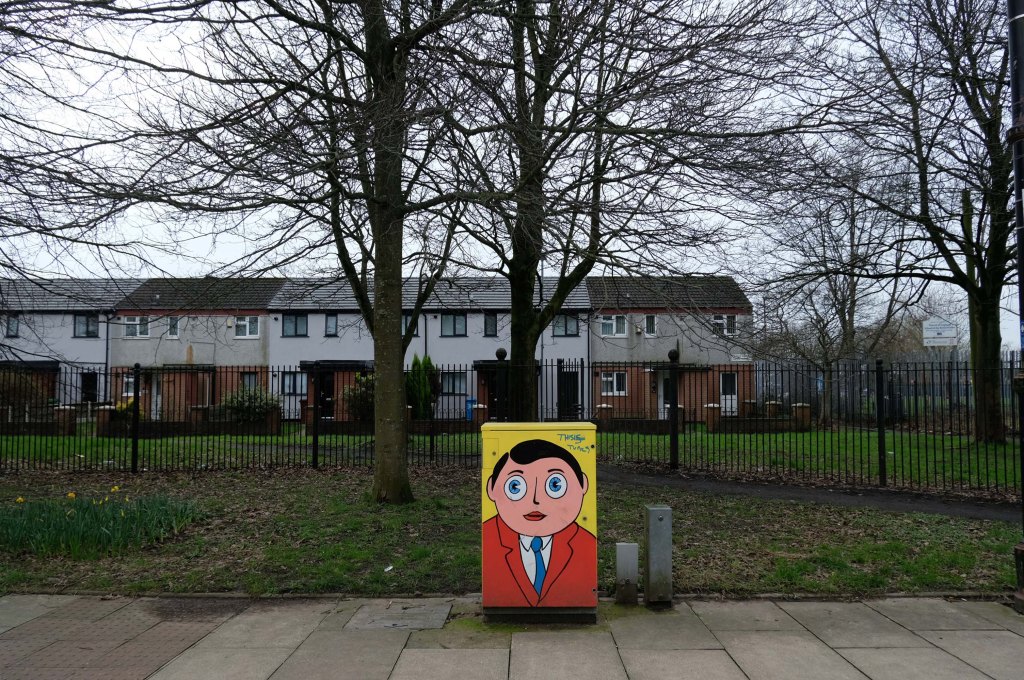
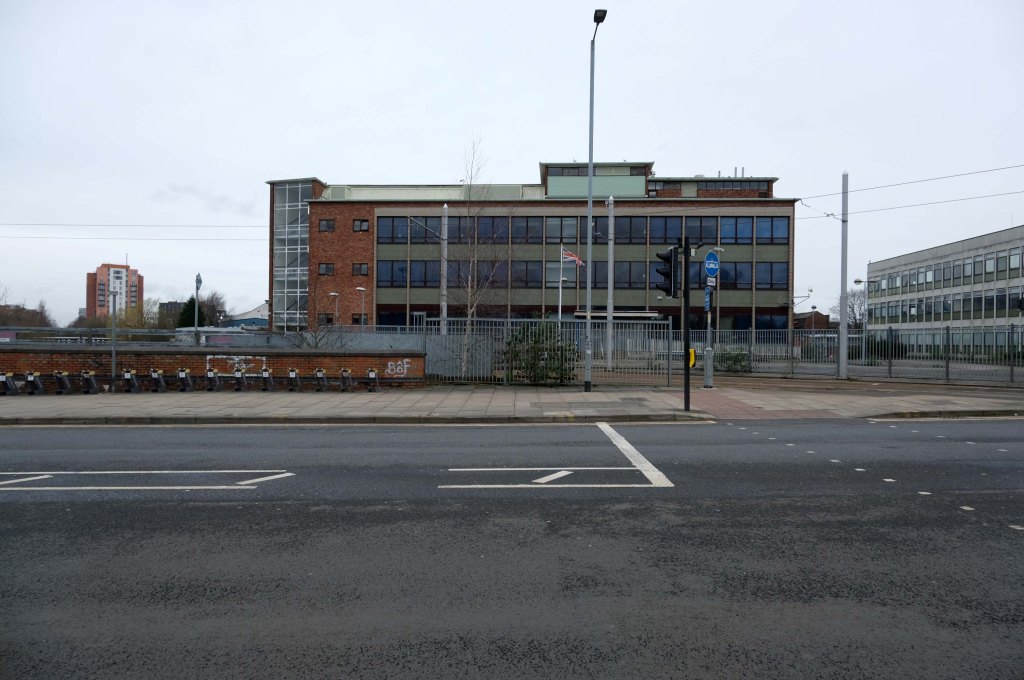
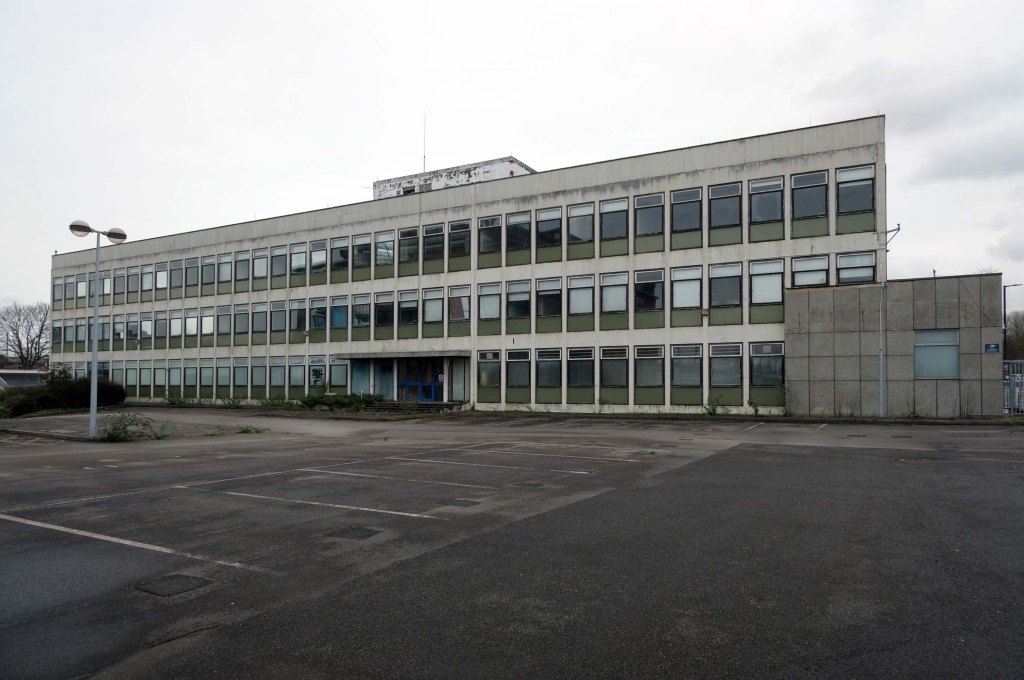
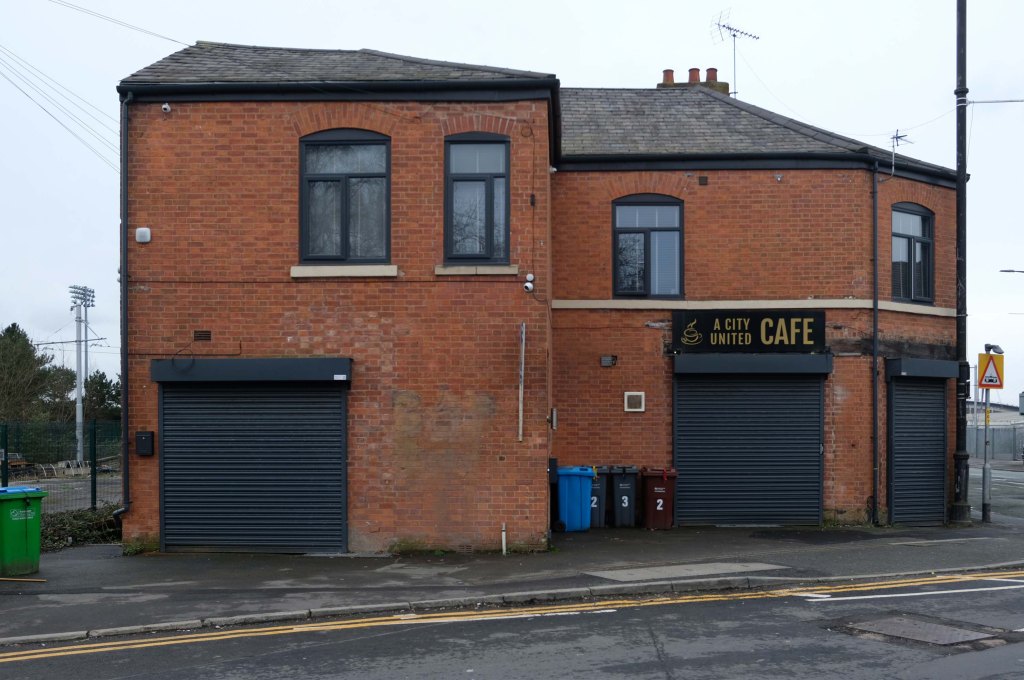
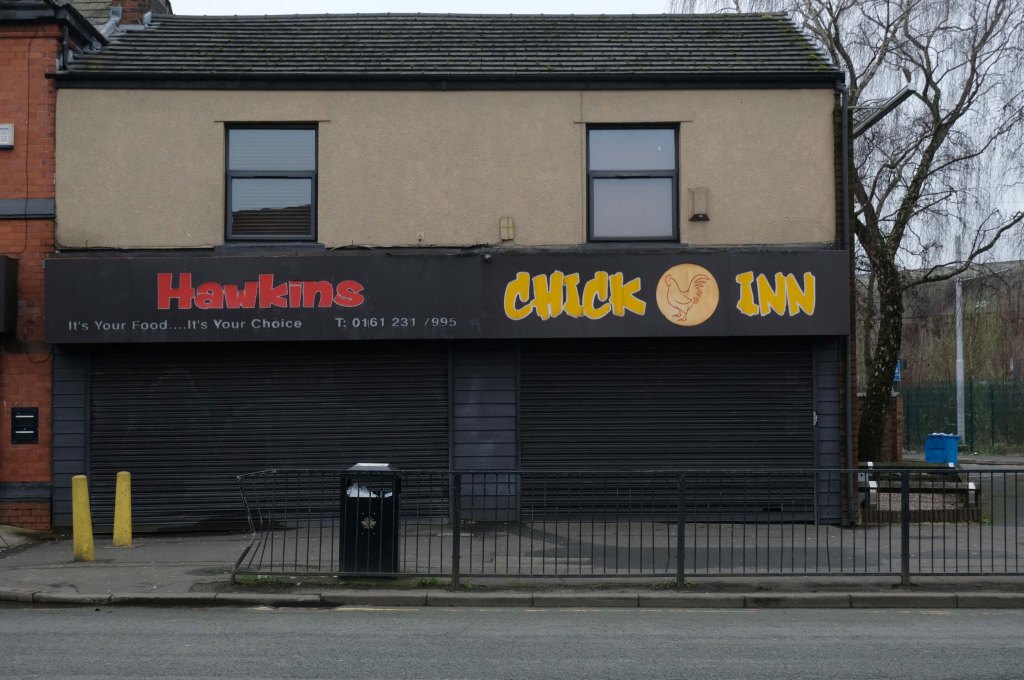
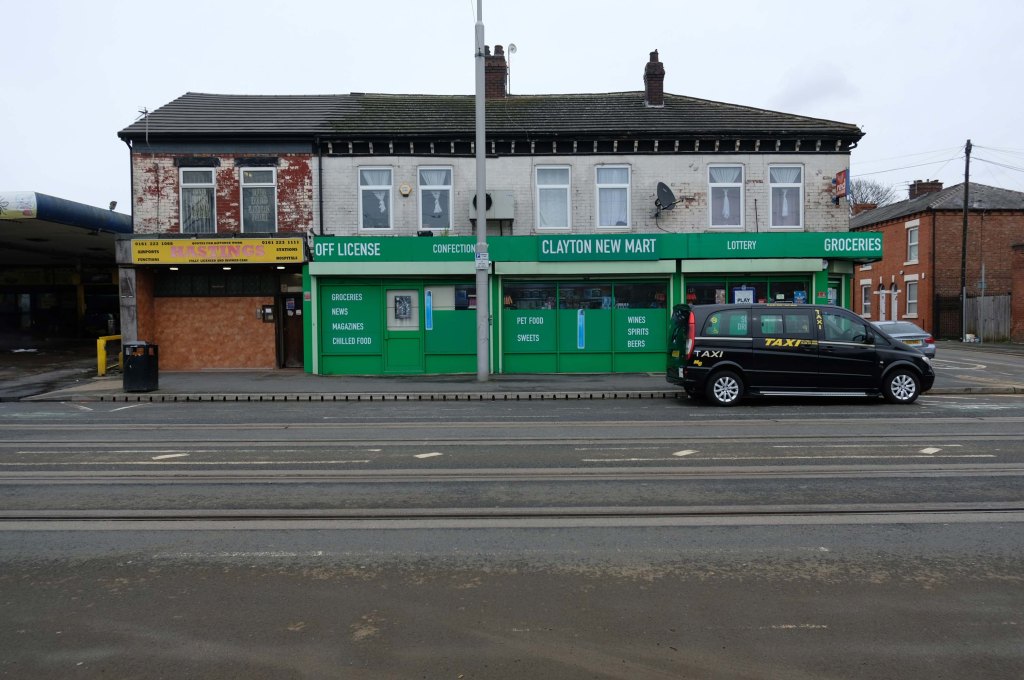
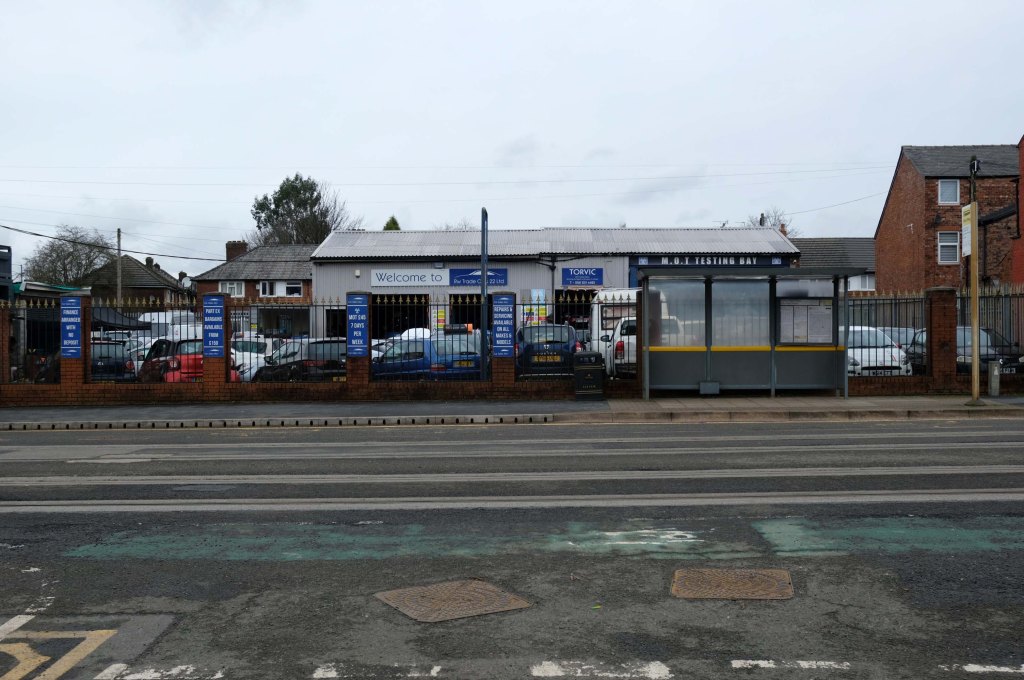
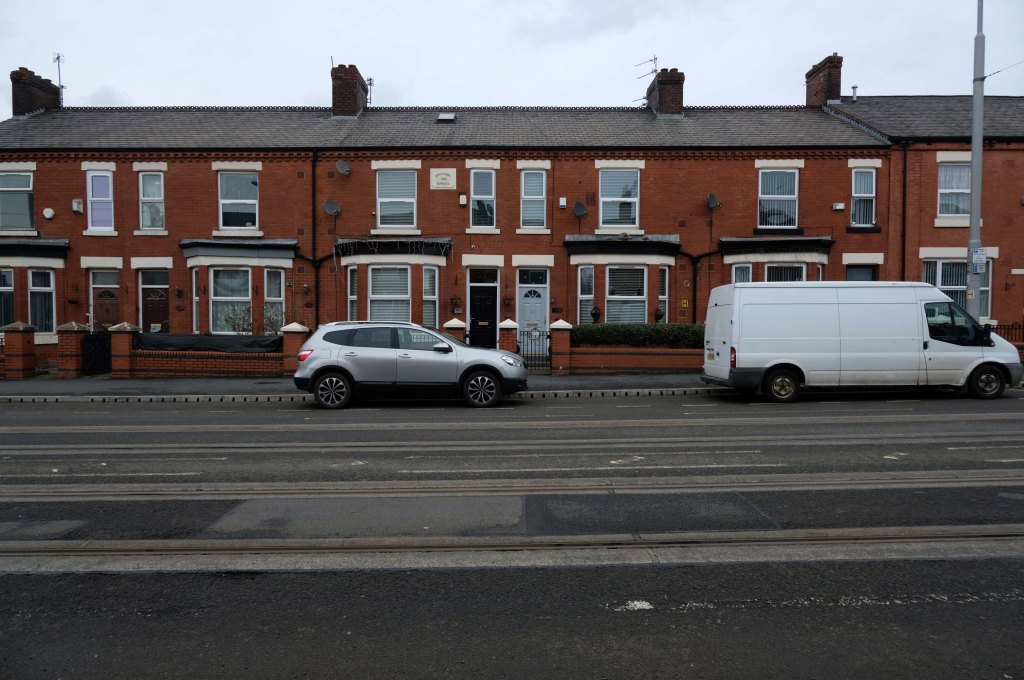
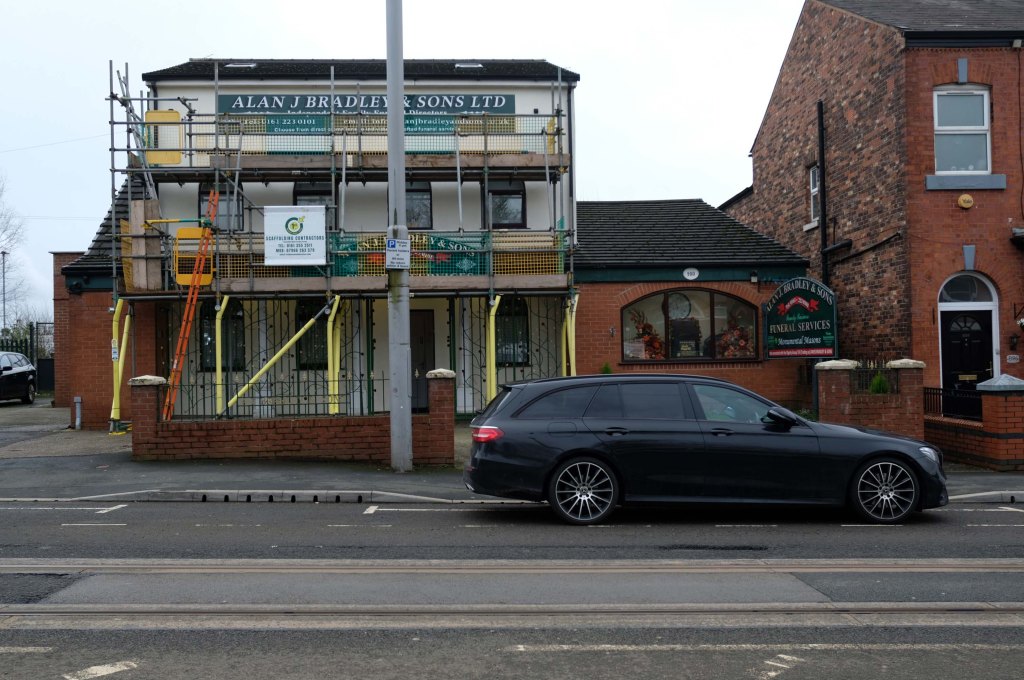
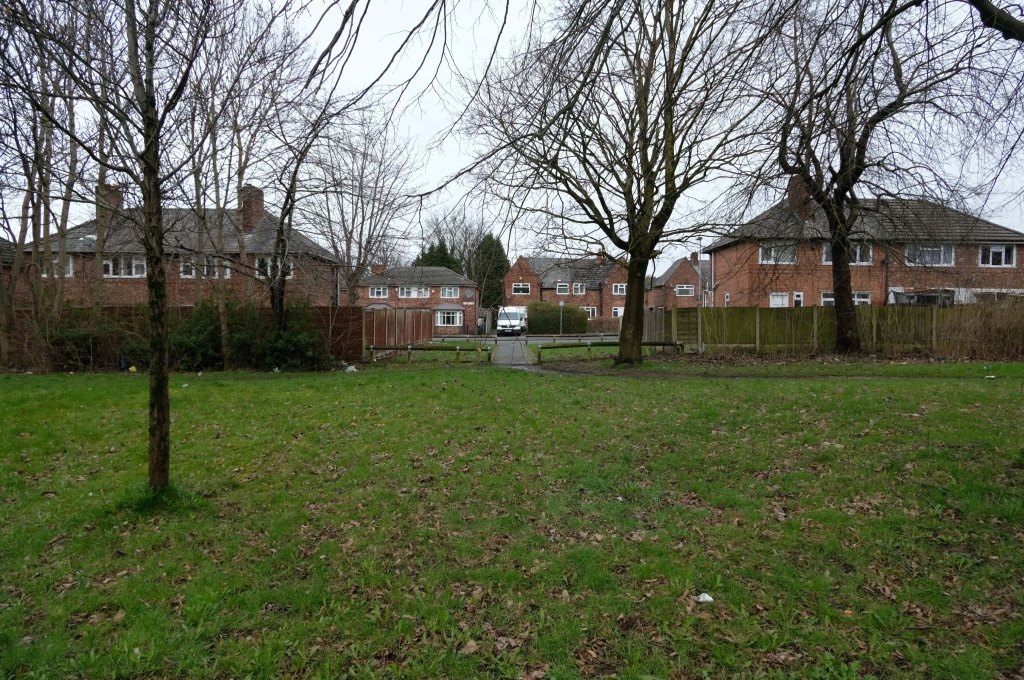
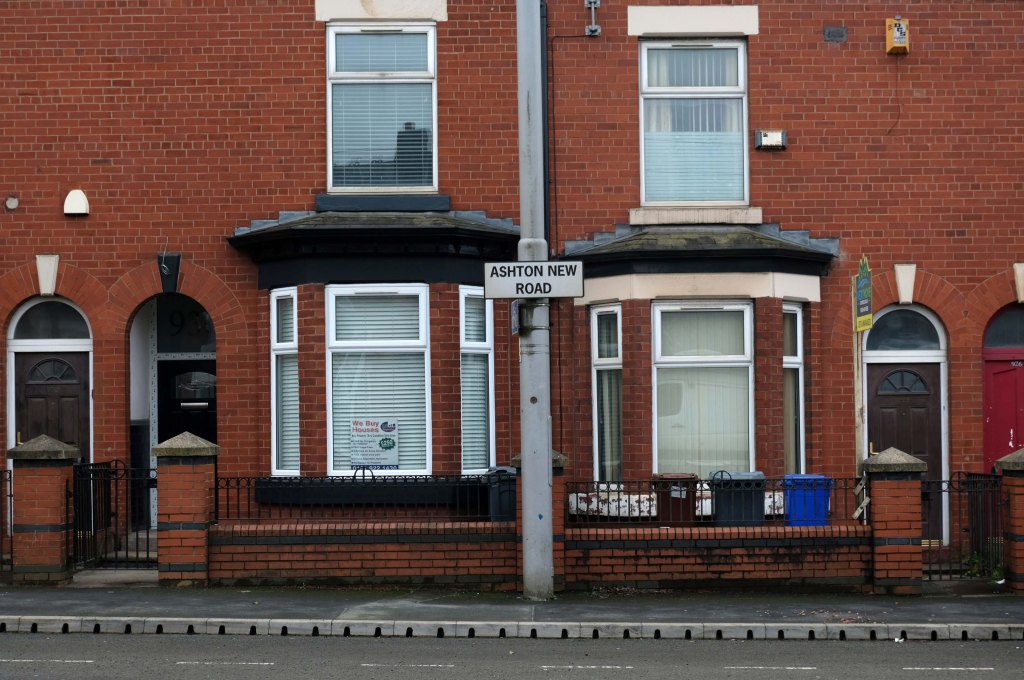
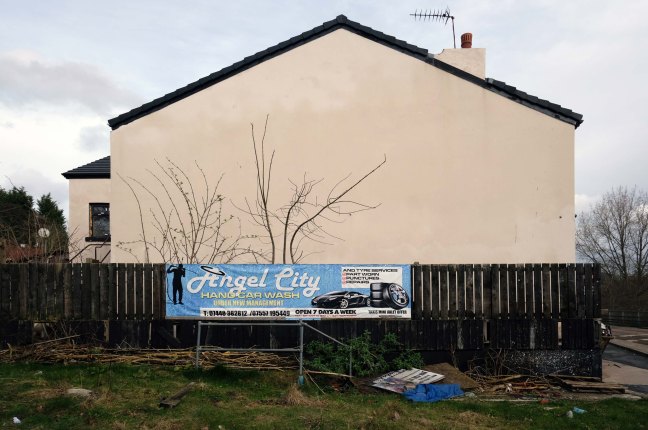












































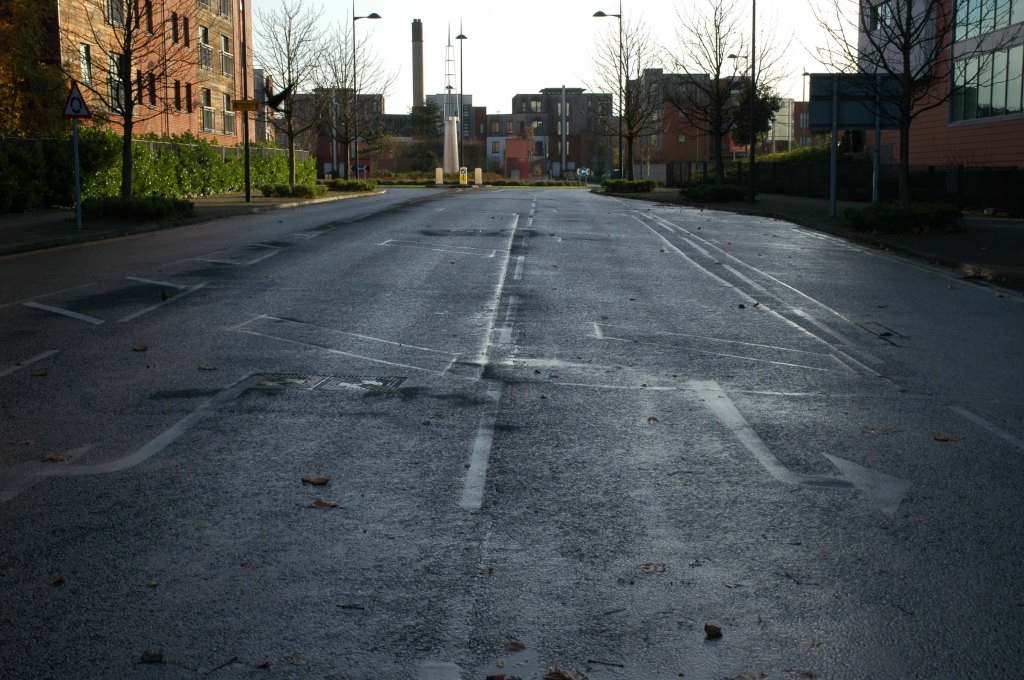
Having photographed the arterial roads of Manchester in 2014 I have resolved to return to the task in 2024.
Some things seem to have changed, some things seem to have stayed the same on Ashton New Road.











































Having photographed the arterial roads of Manchester in 2014, I have resolved to return to the task in 2024.
Some things seem to have changed, some things seem to have stayed the same.
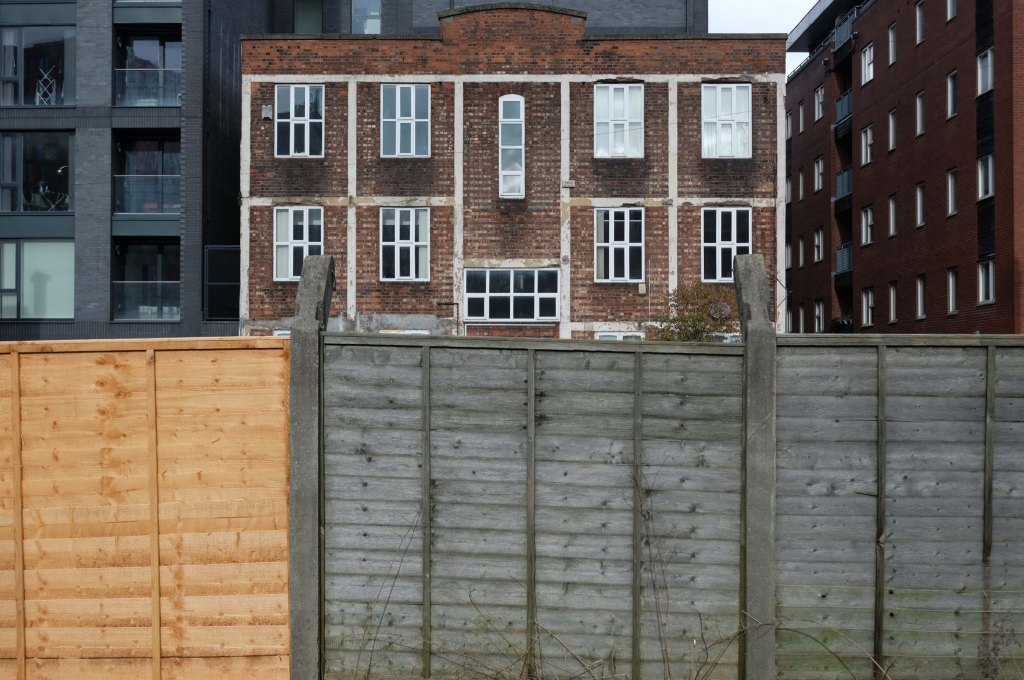
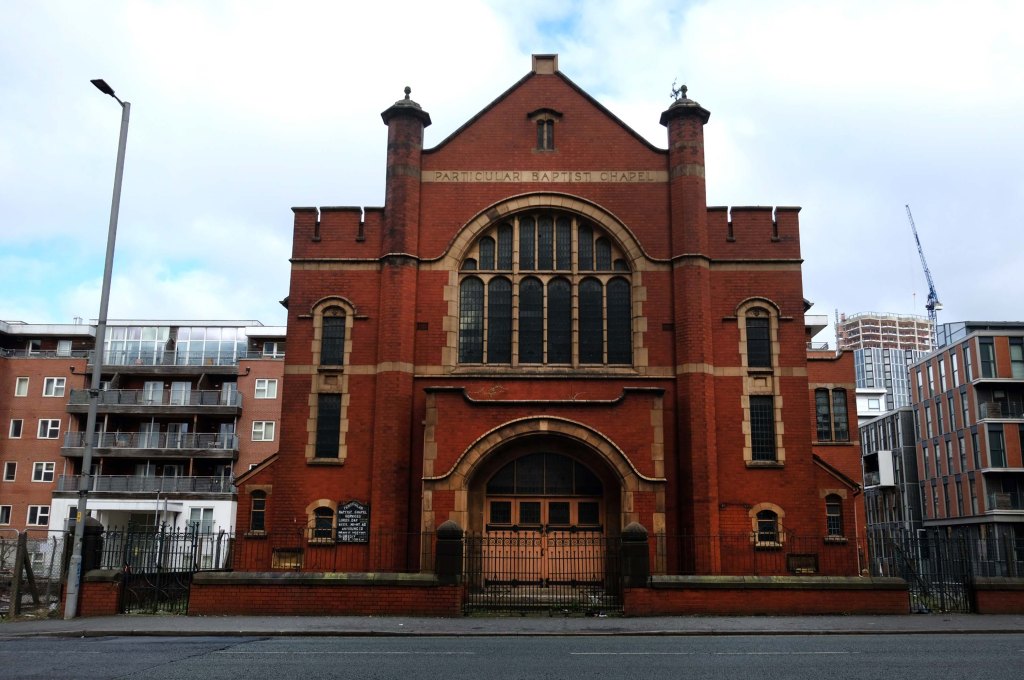
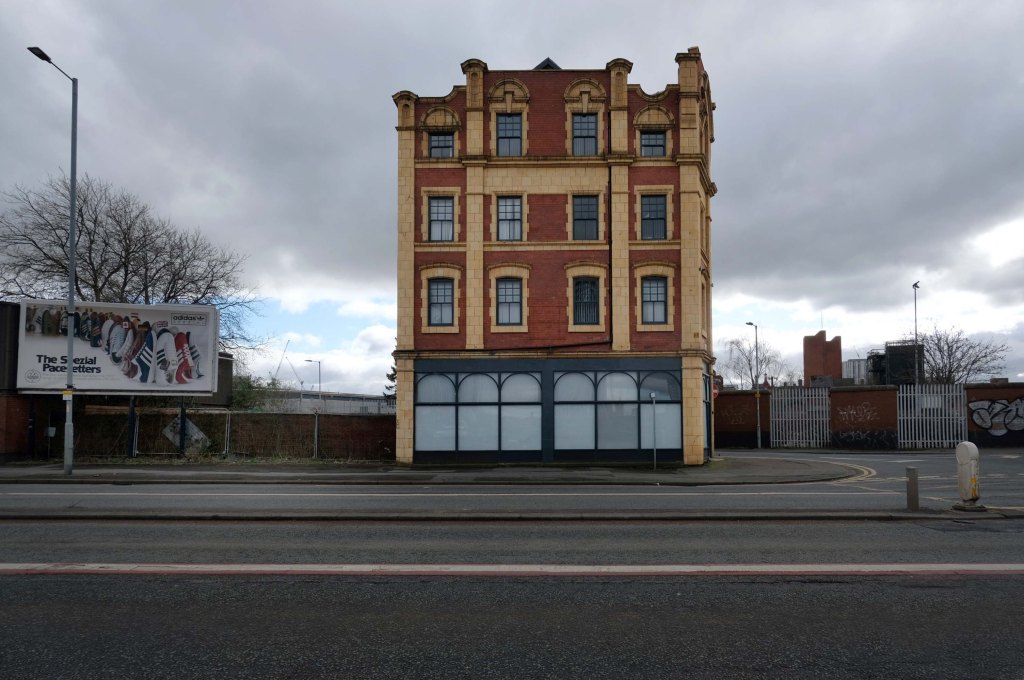
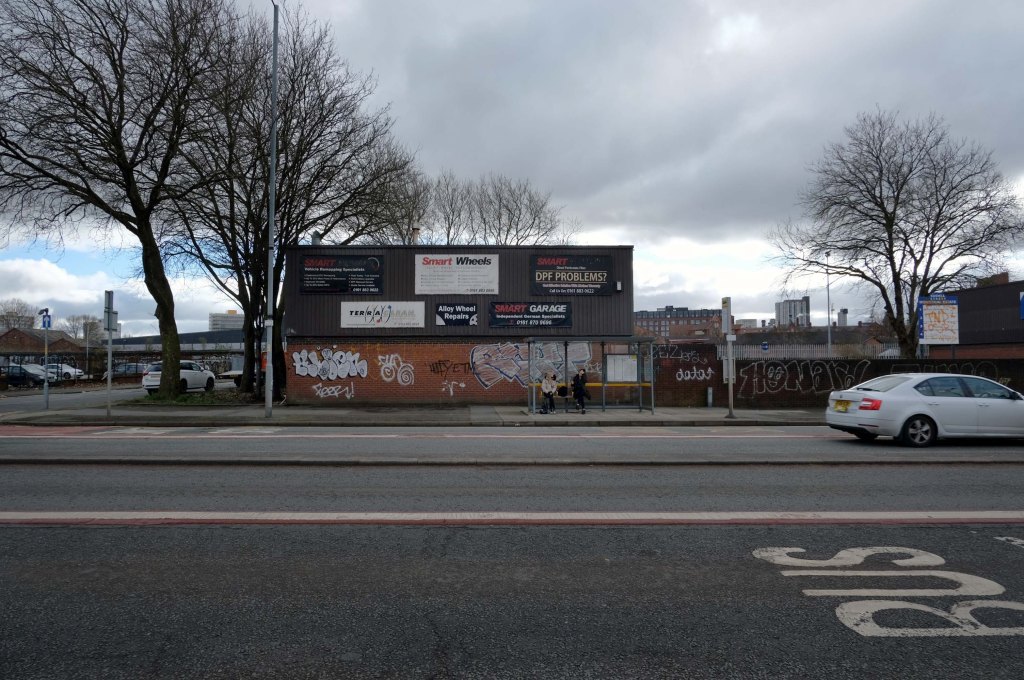
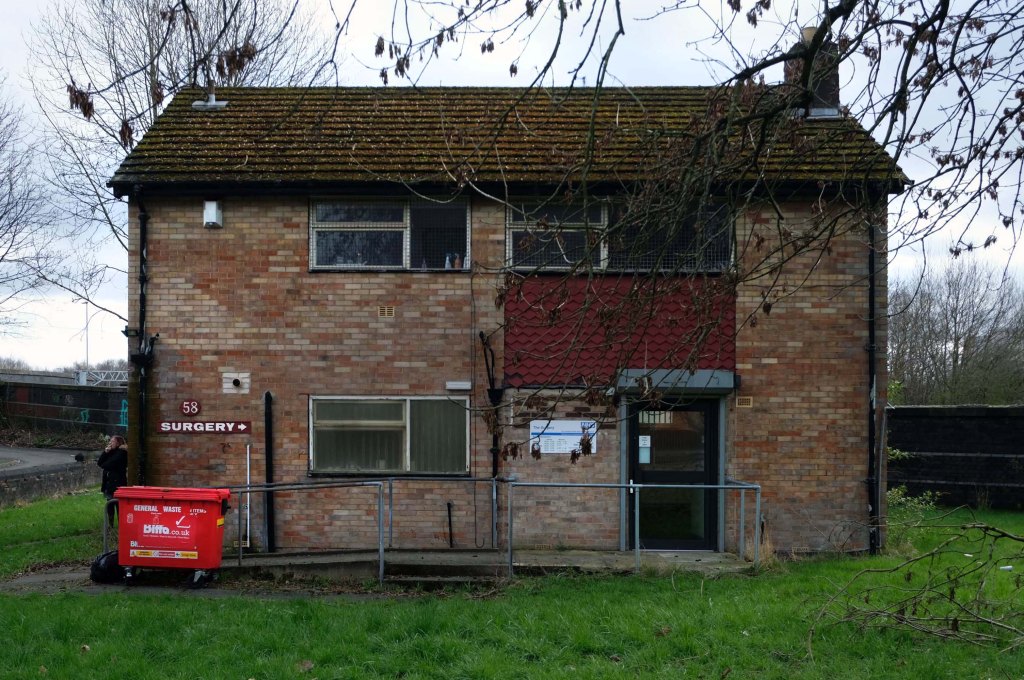
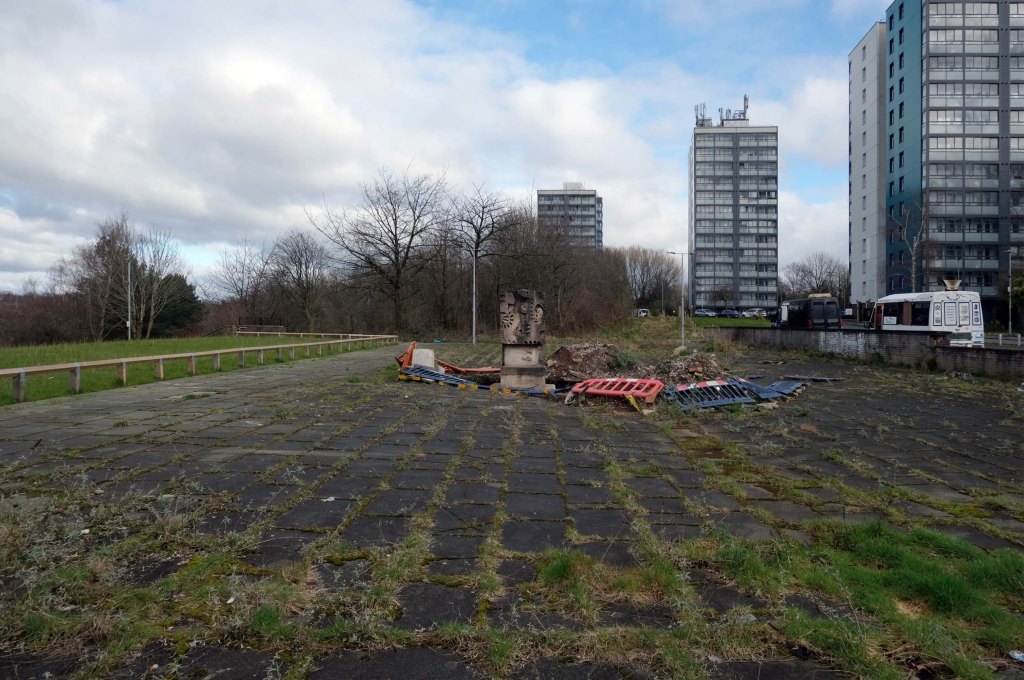
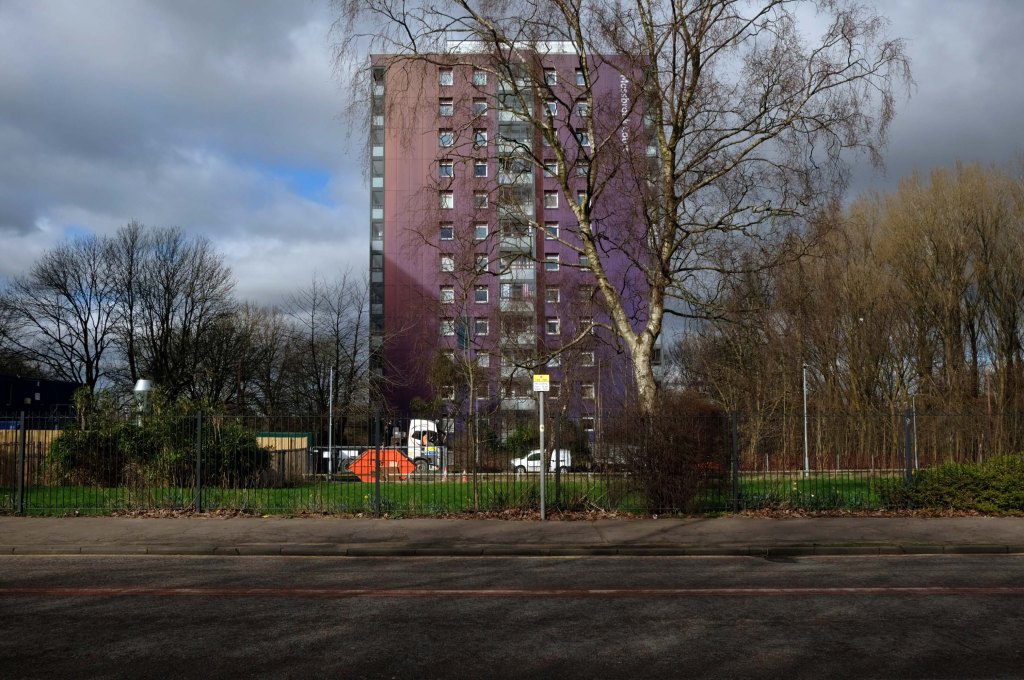
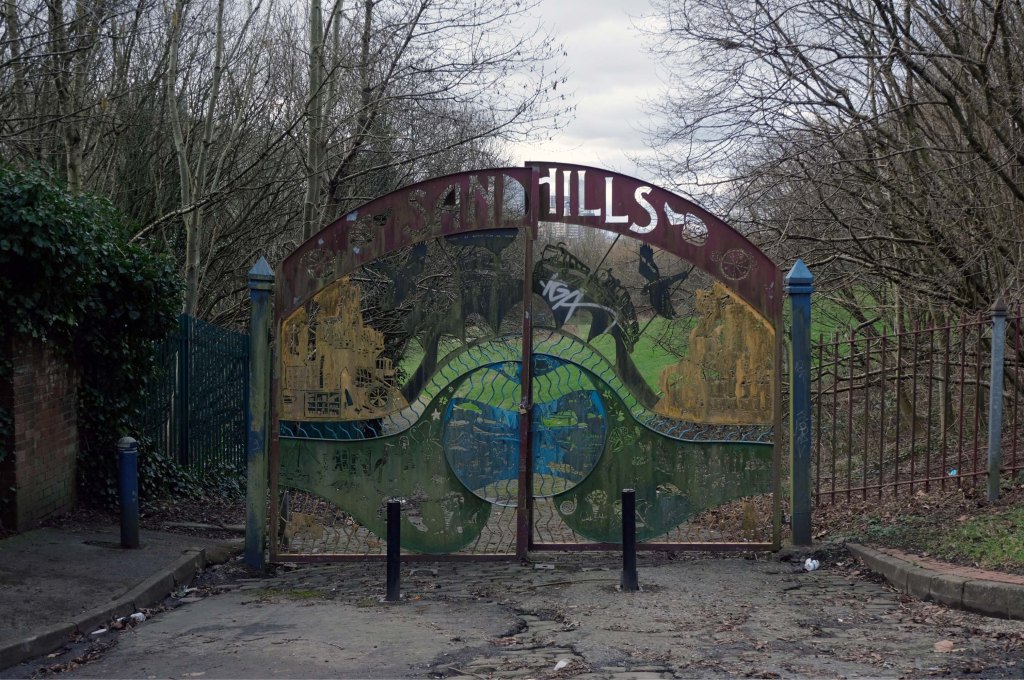
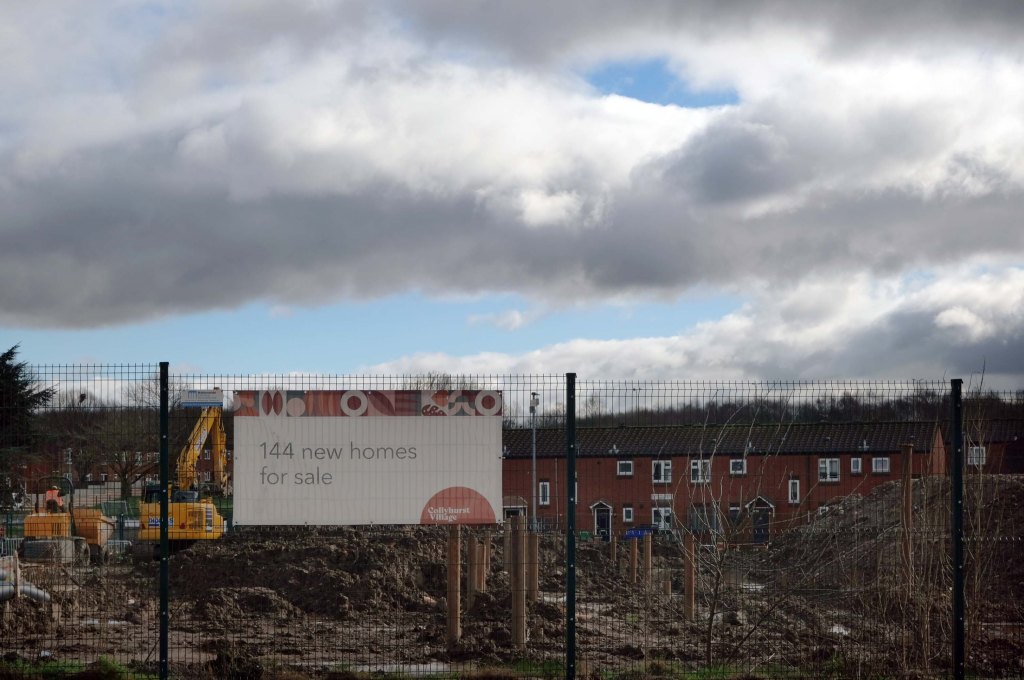
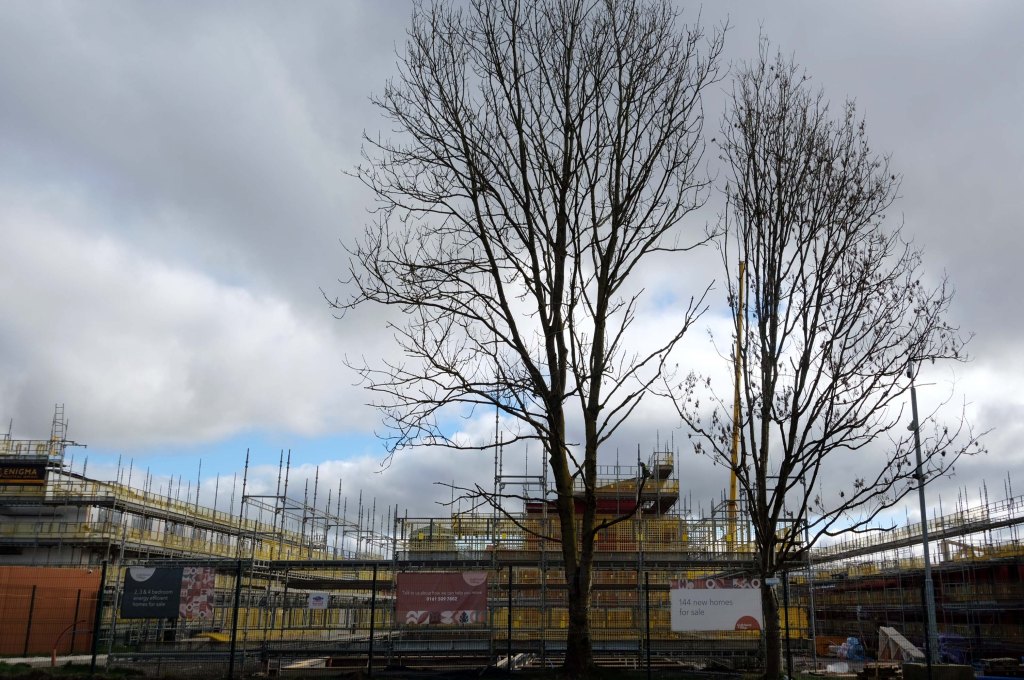
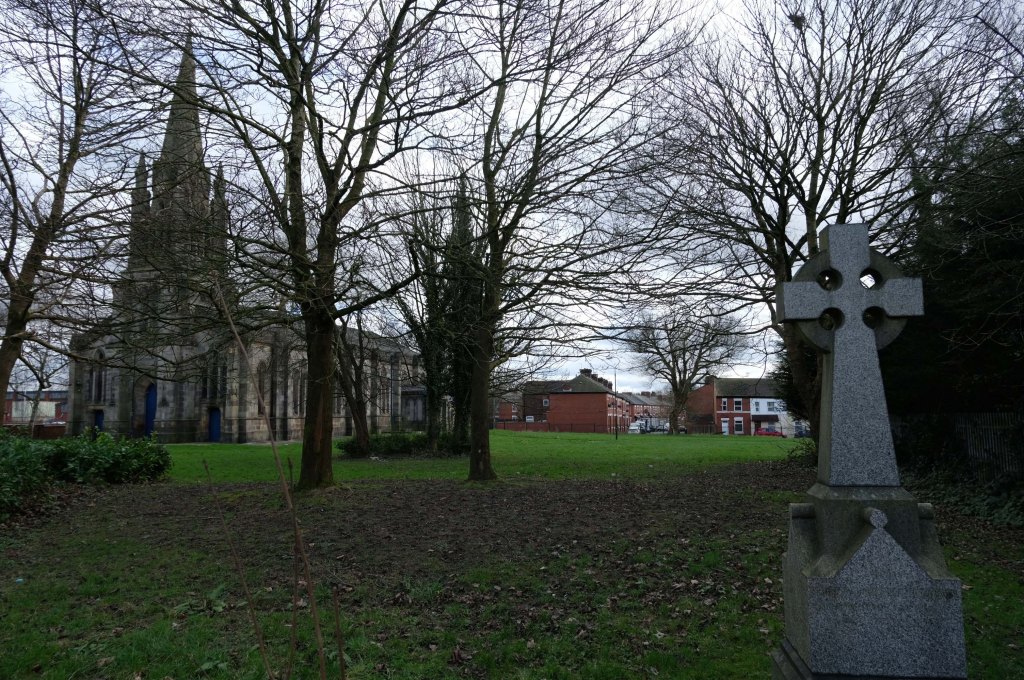
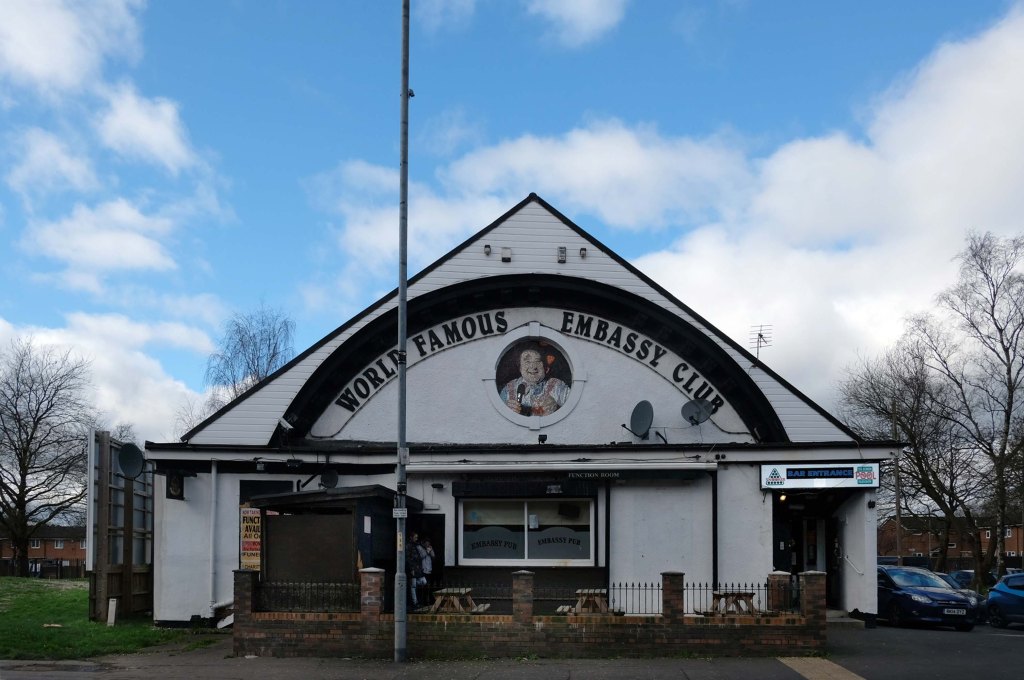
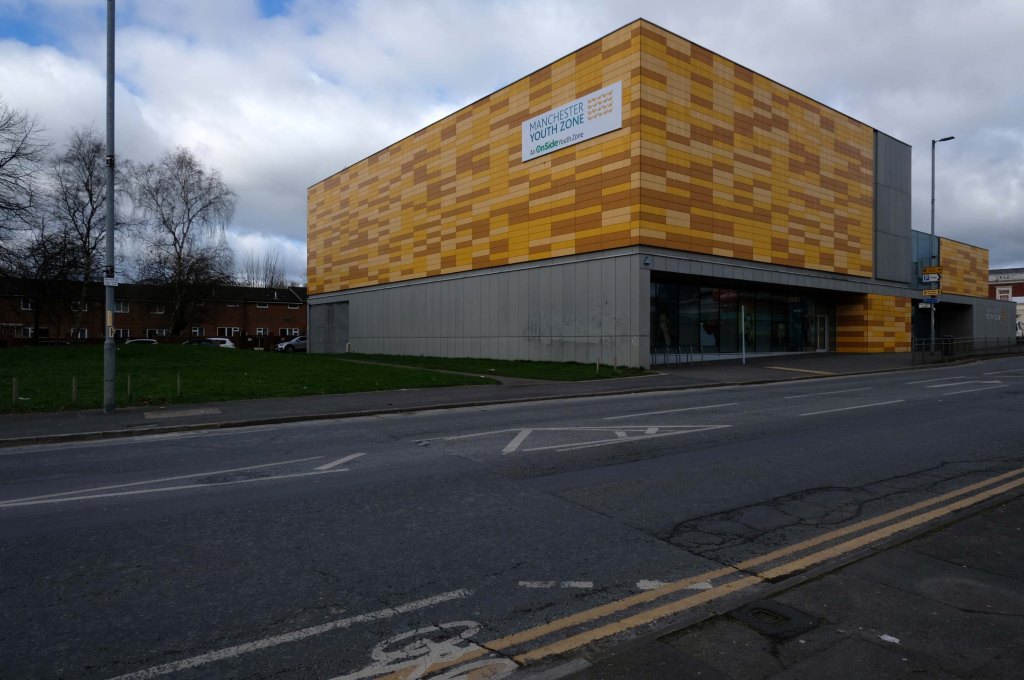
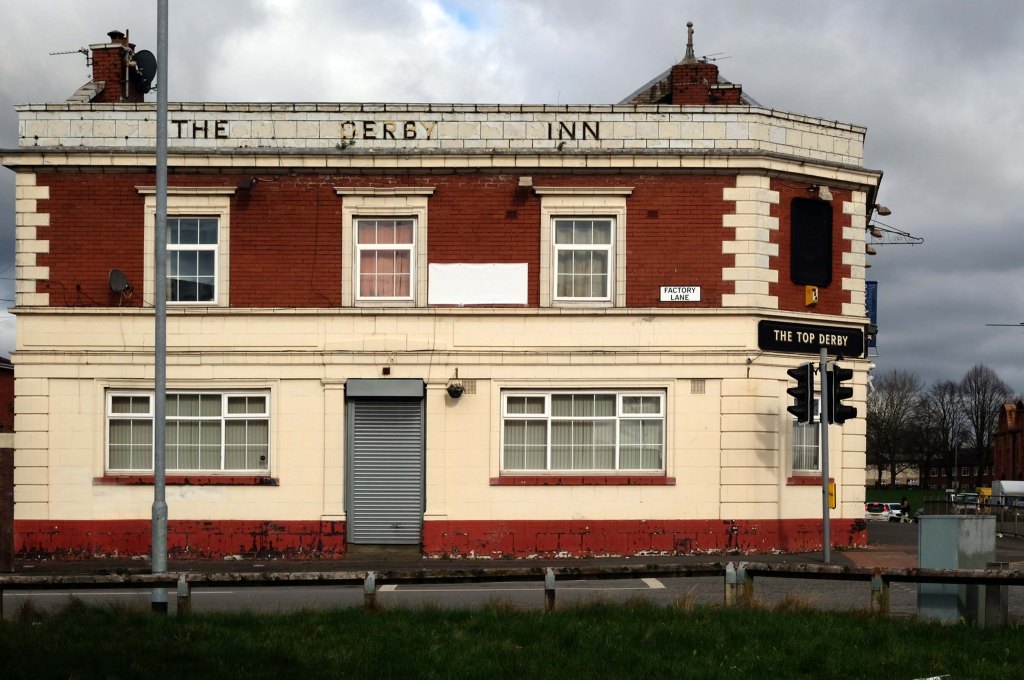
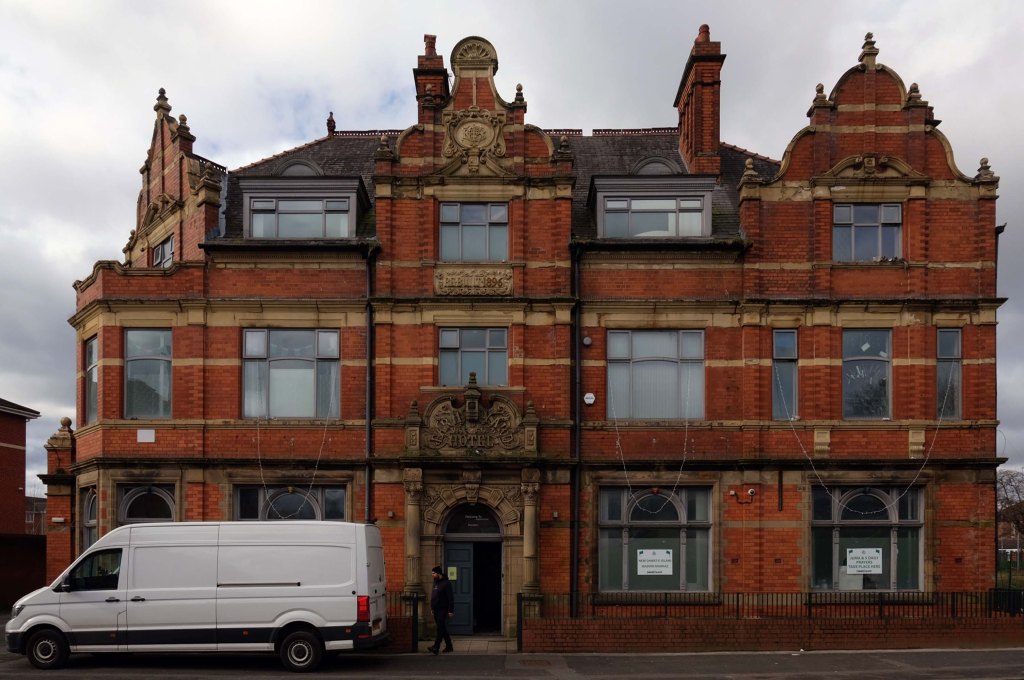
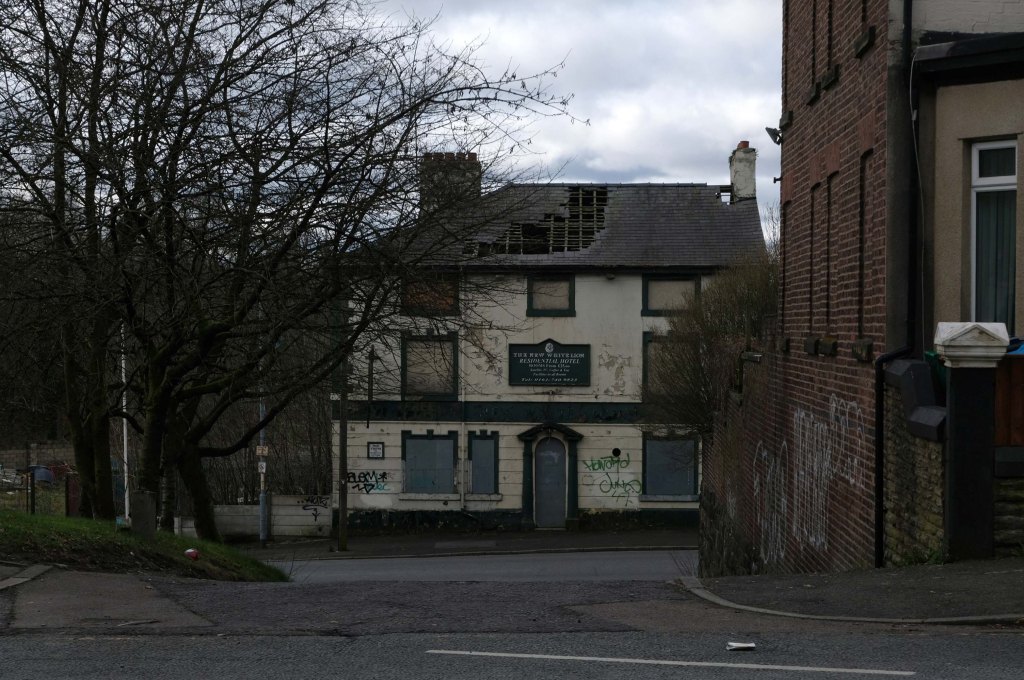




















































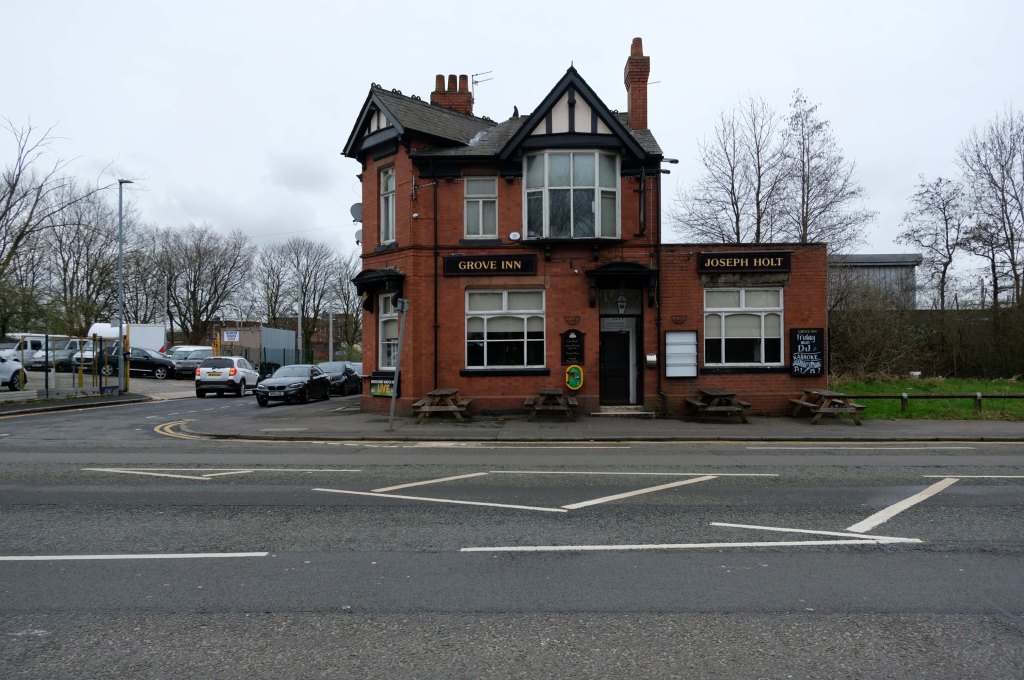
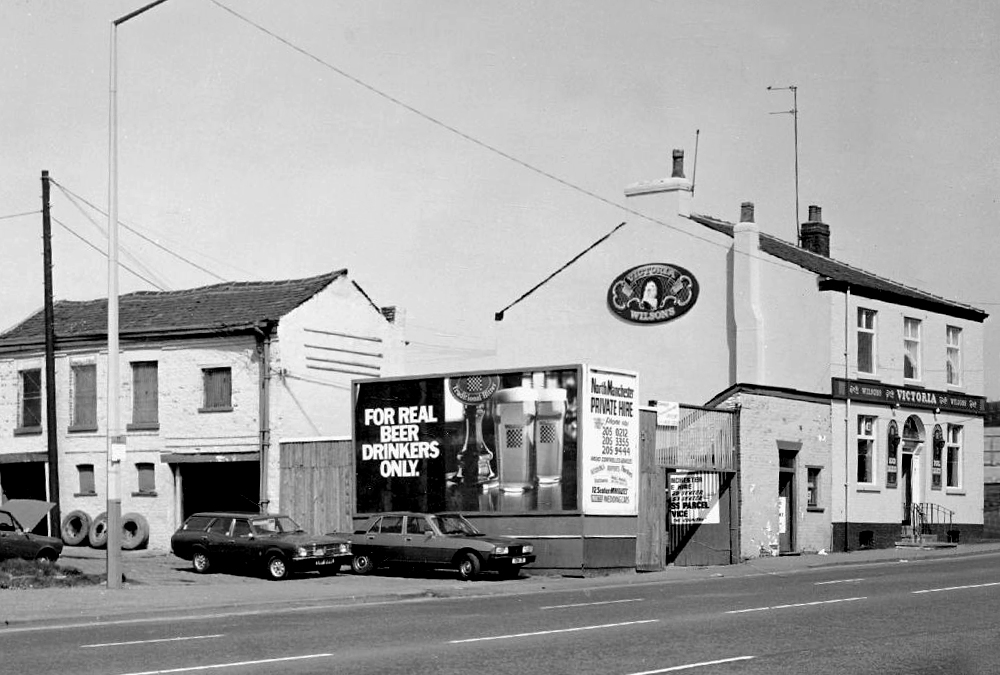
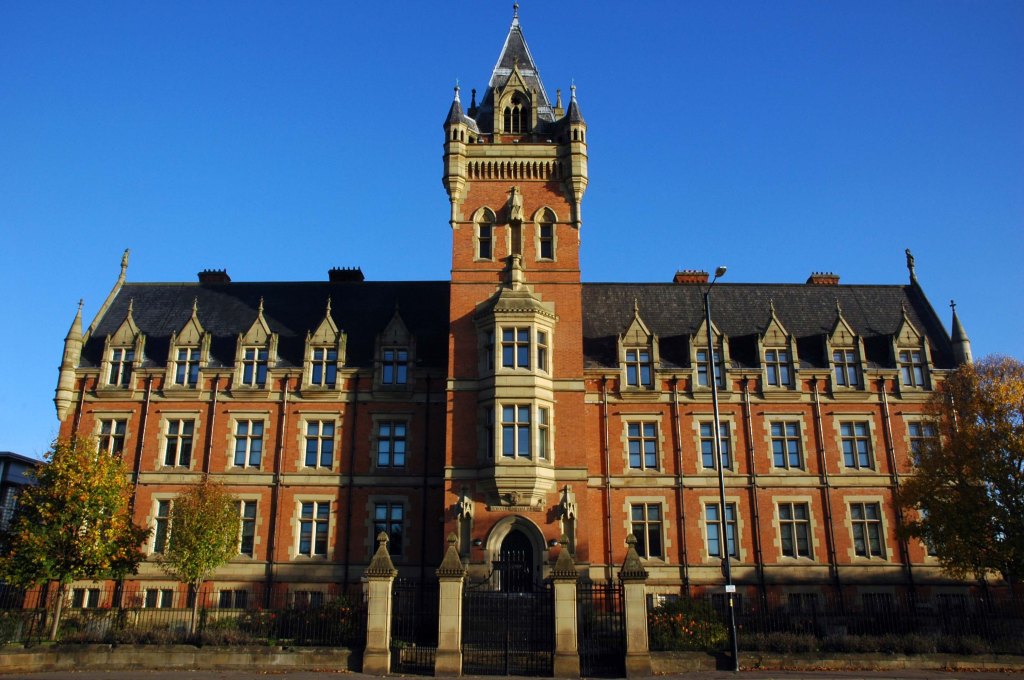
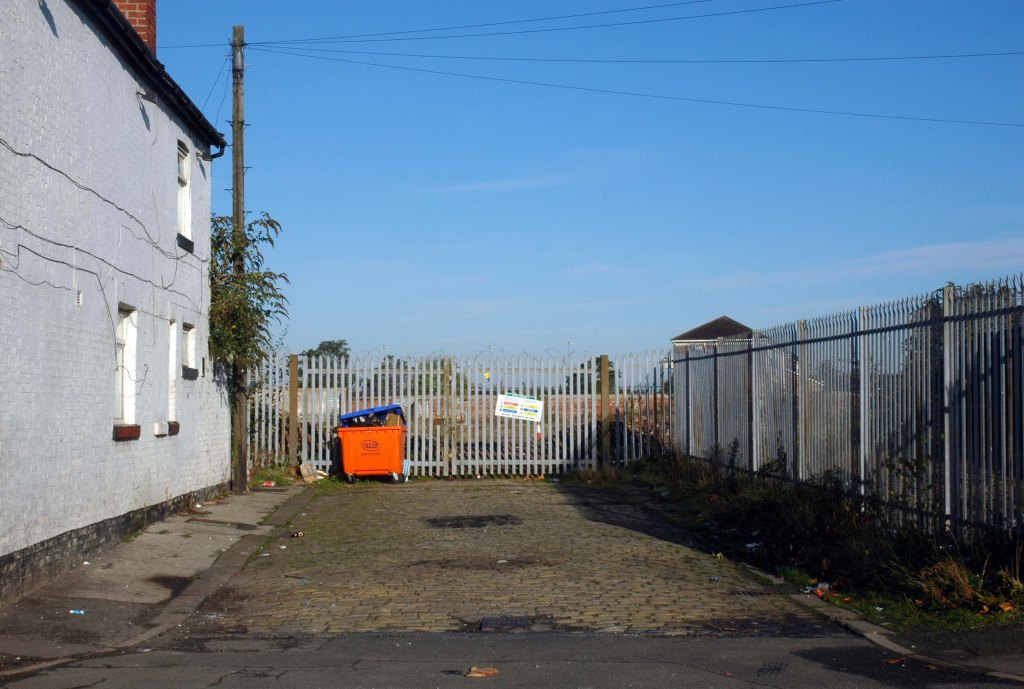
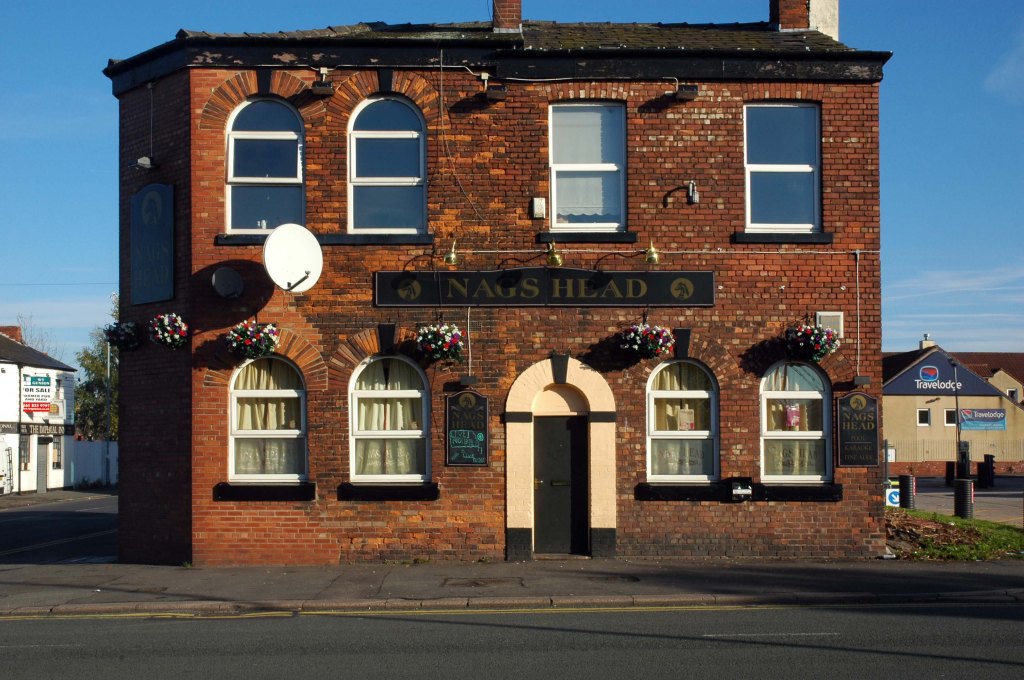
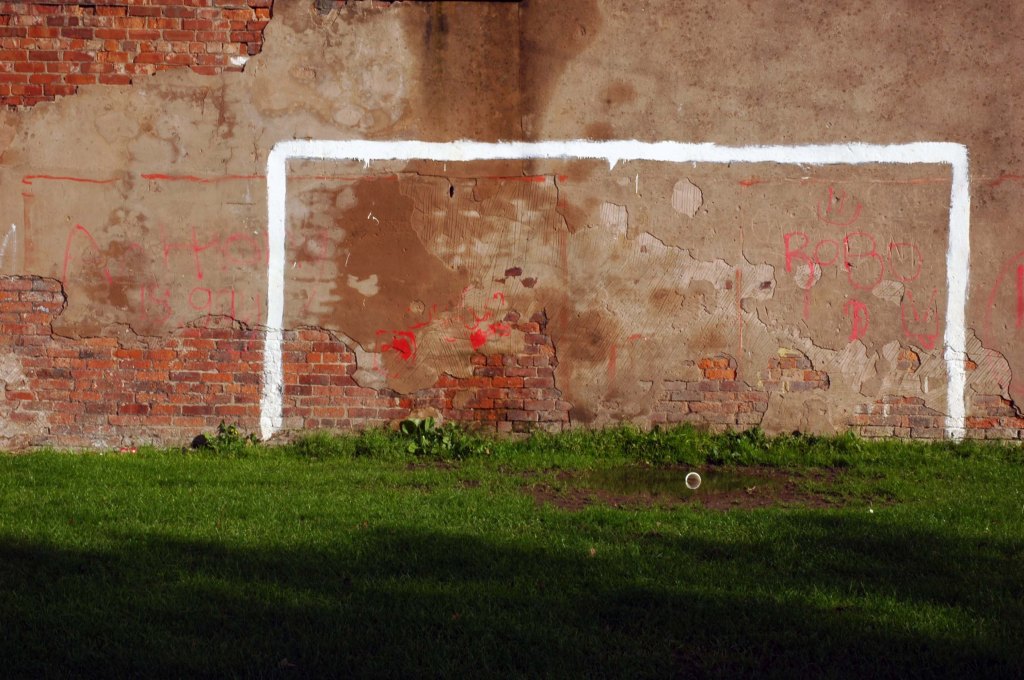
This is Oldham Road Manchester – this also Memory Lane.
Walking from the city centre to Failsworth I noted the absence of public houses, some long since demolished, some now serving other purposes – very few open selling beer.
Many of the breweries no longer trading.
Much of this the consequence of changing economic circumstances, the decline in manufacturing and subsequent serious absence in regular drinkers.
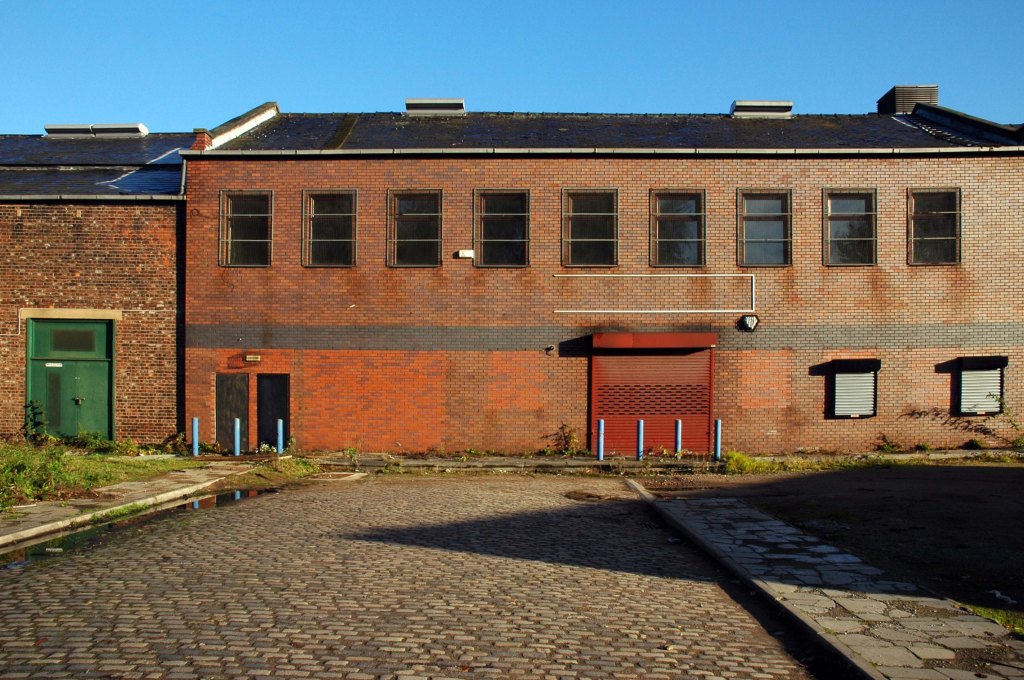
I encountered a similar situation on Hyde Road.
Where possible I have linked back to Pubs of Manchester Blogspot and the Brewery History Society.
There may well be errors and omissions which I am happy to correct – have a look let me know.
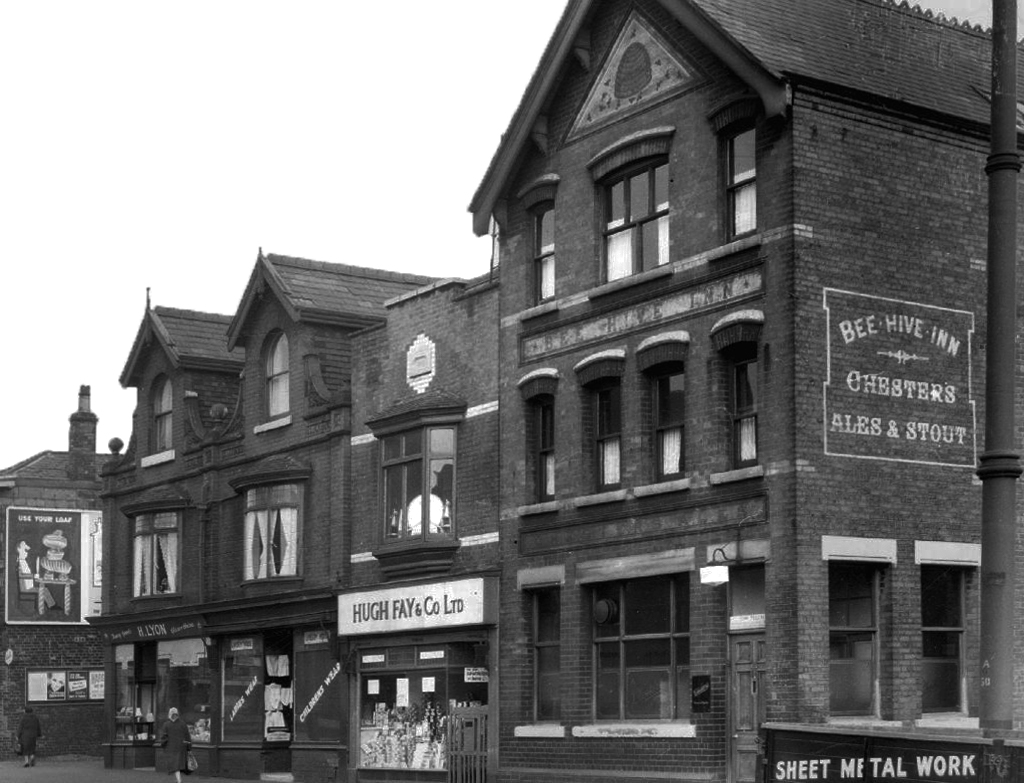
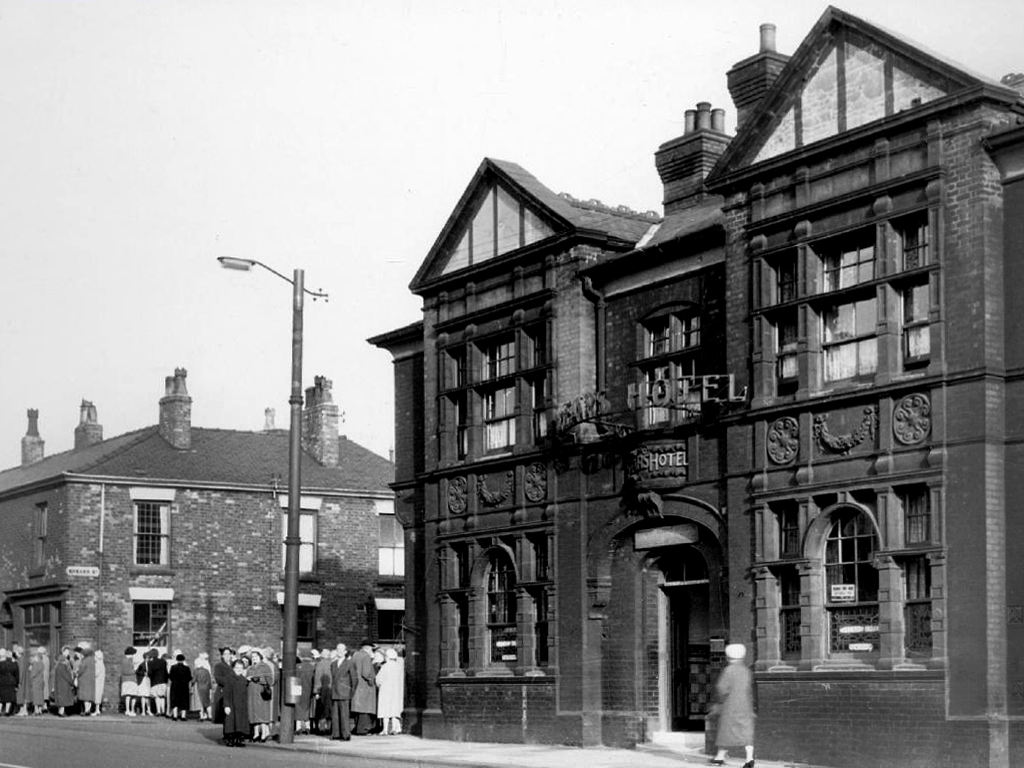
Bee Hive Inn – Chesters Brewery


Bird In Hand – latterly Ace of Diamonds on the 2nd April 2010 the Ace of Diamonds burnt down.

Birmingham Tavern – Wilsons Brewery


City Arms – Groves and Whitnalls

Cloggers Arms – Wilsons
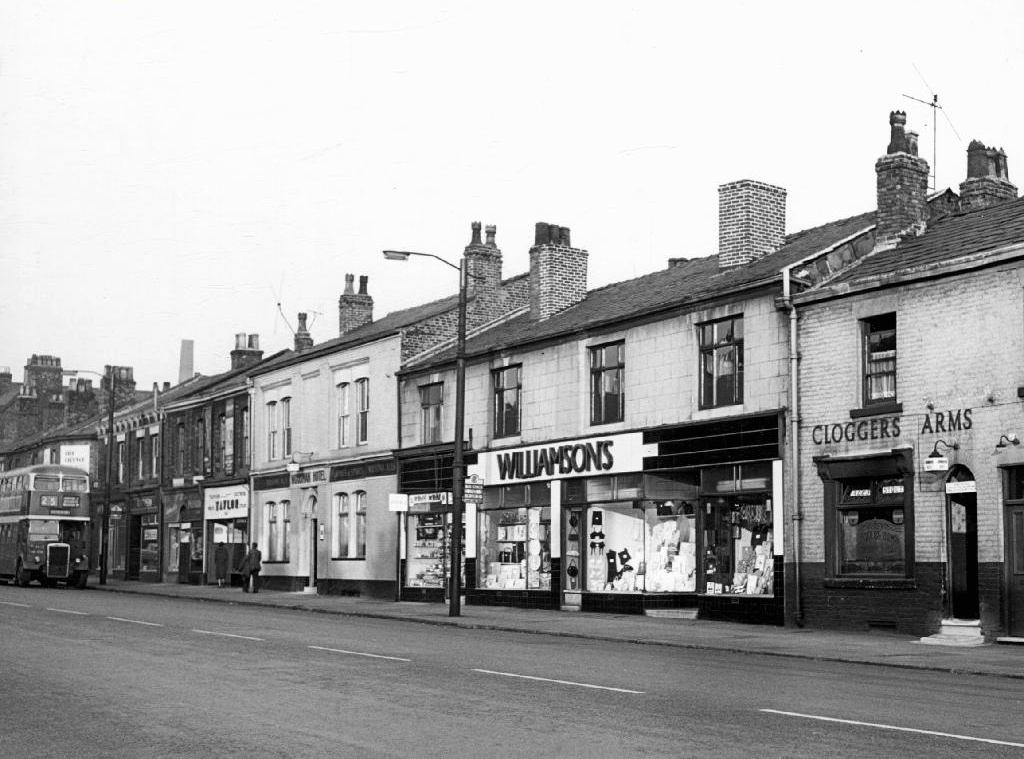


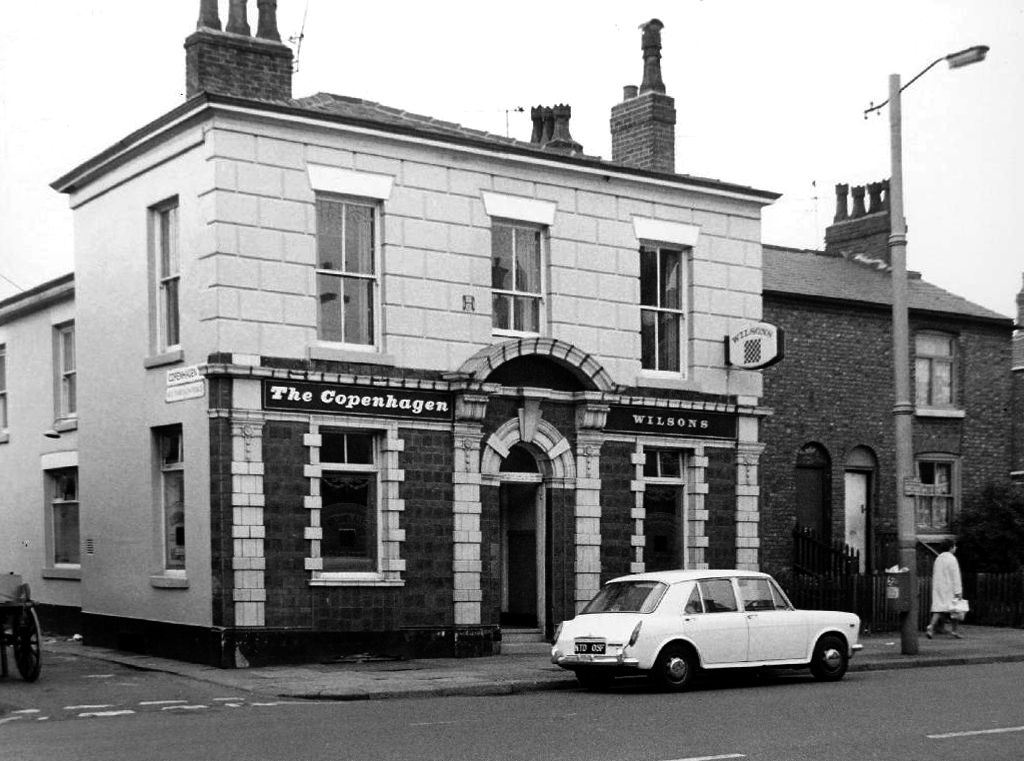
The Copenhagen – Wilsons

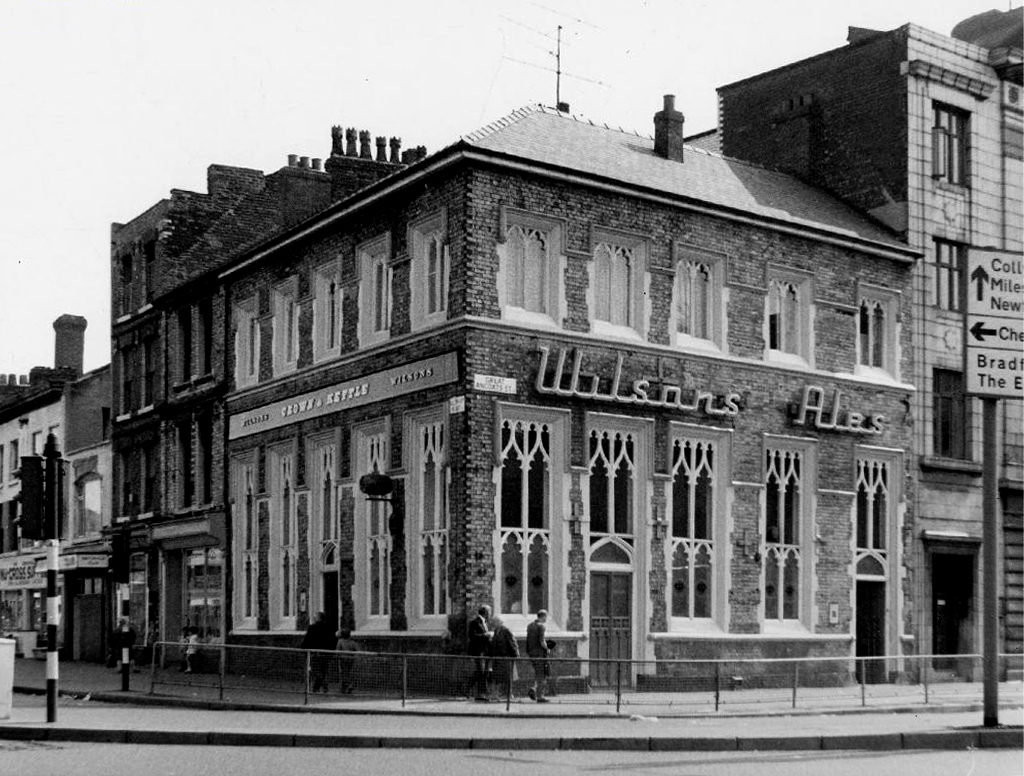
Crown & Kettle – Wilsons though now a free house.
I do remember the huge Winston Churchill relief in the Room and R100 Airship wooden panelling in the lounge. Also of note were the ornate plater work ceilings and pendulous lighting, much damaged as the pub awaited restoration.

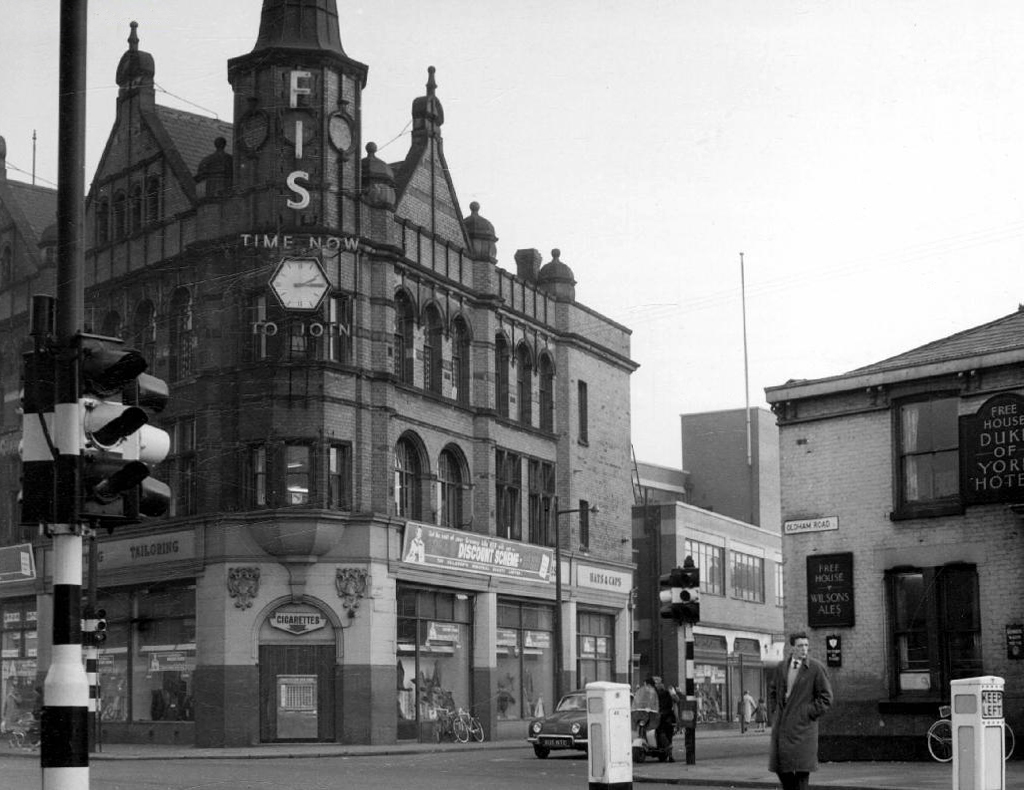
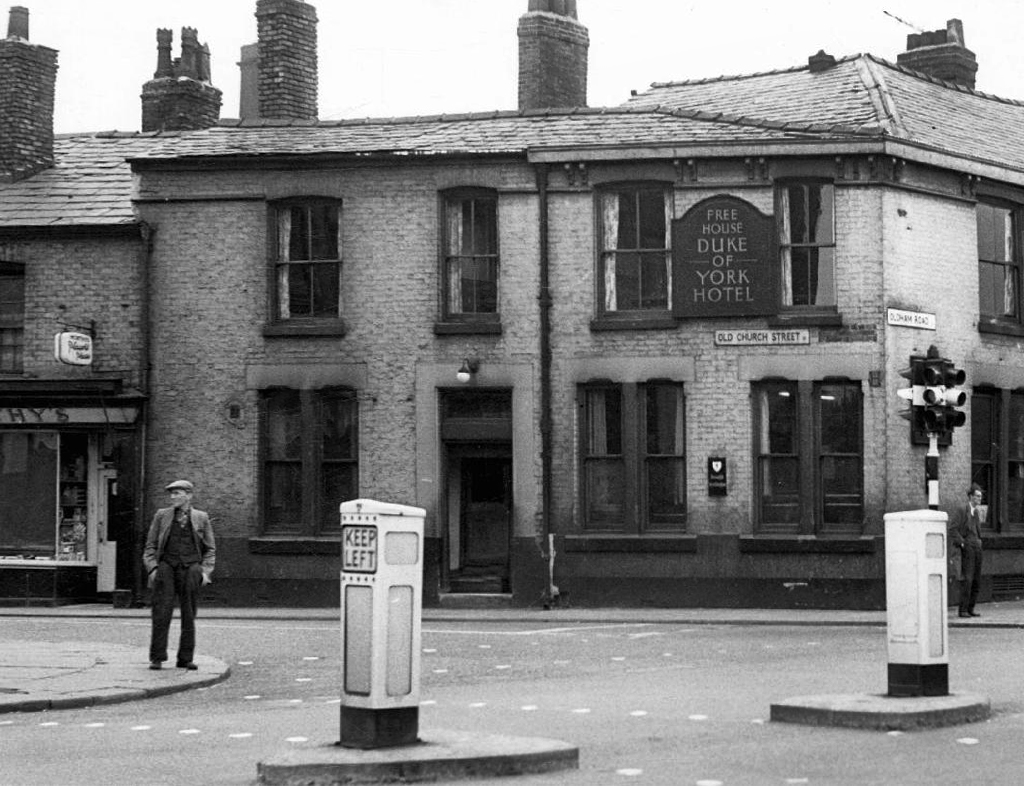
Duke of York – Wilsons Free House


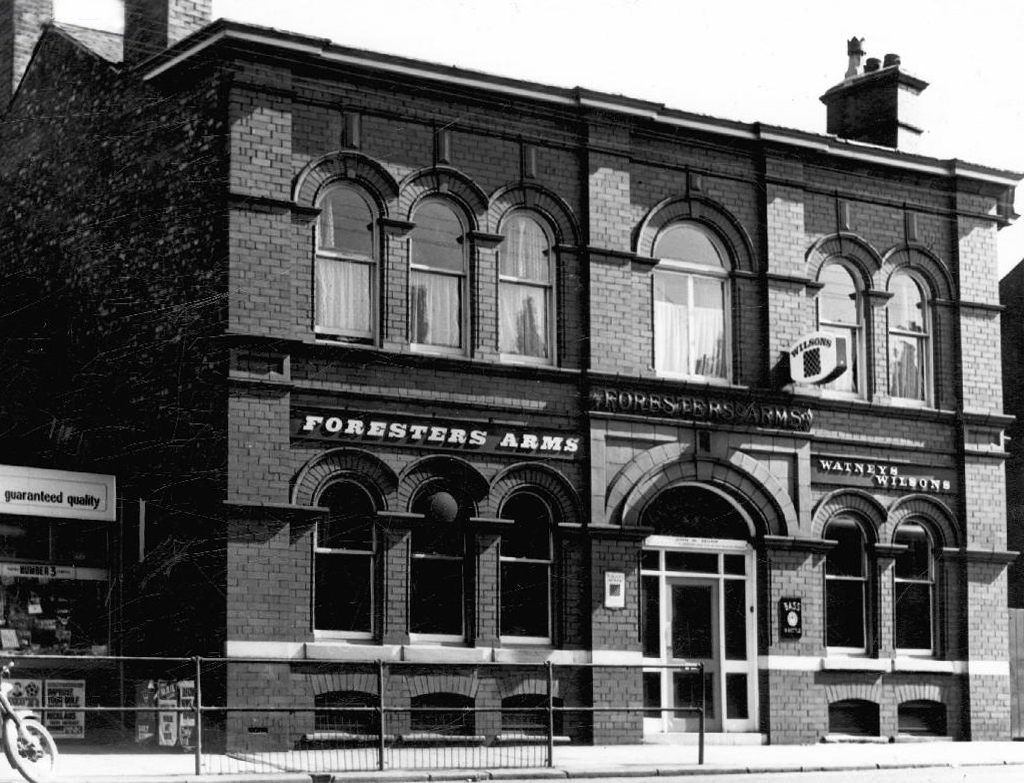
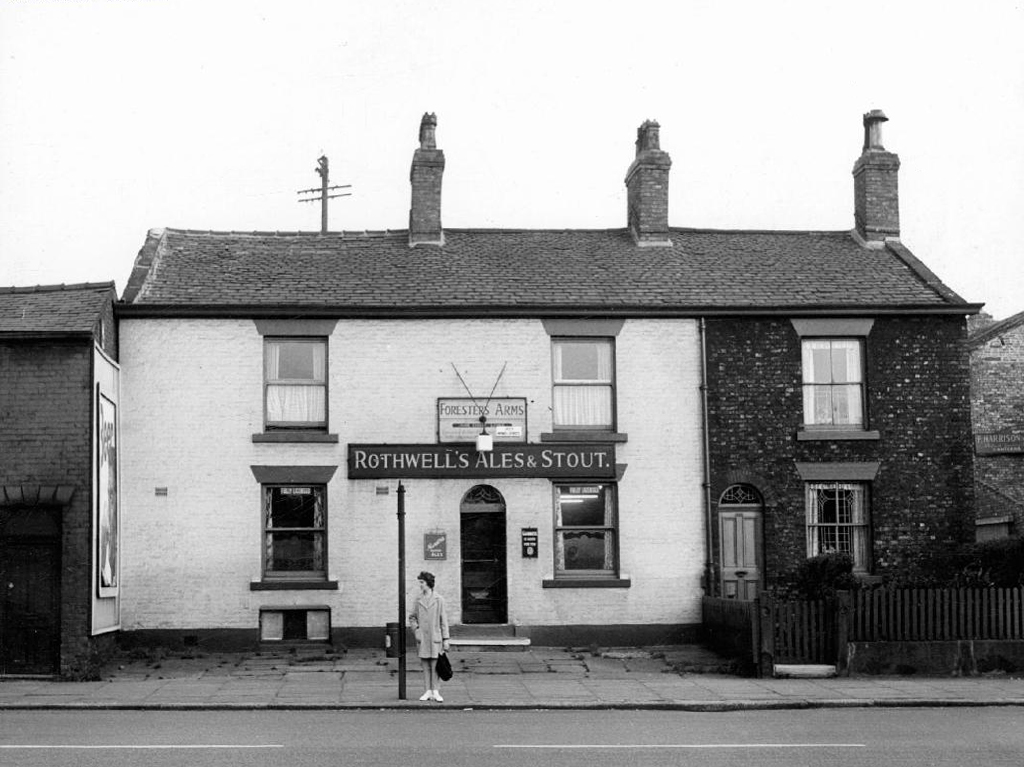
Foresters Arms – Wilsons
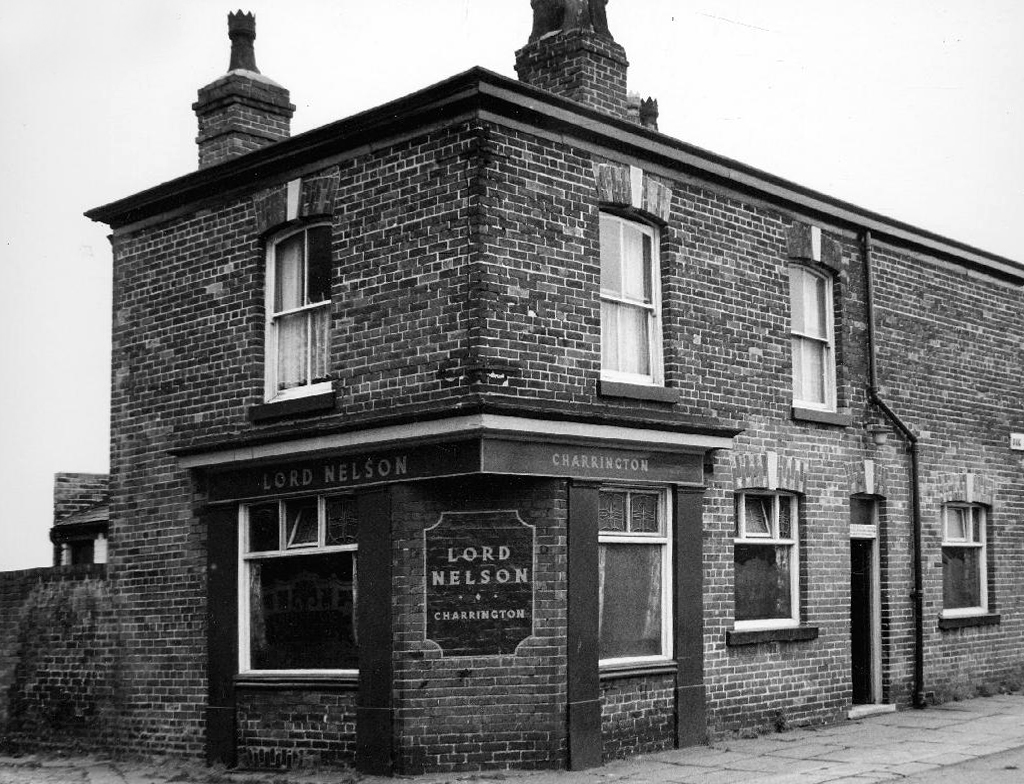
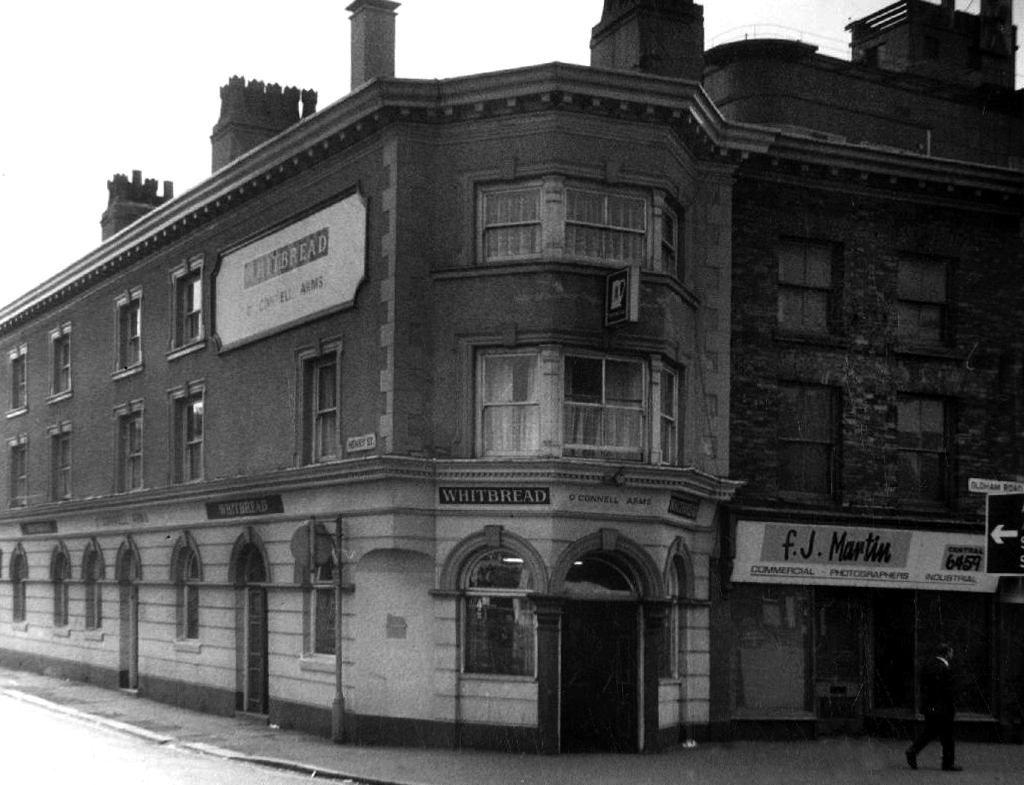





Old Pack Horse – Wilsons
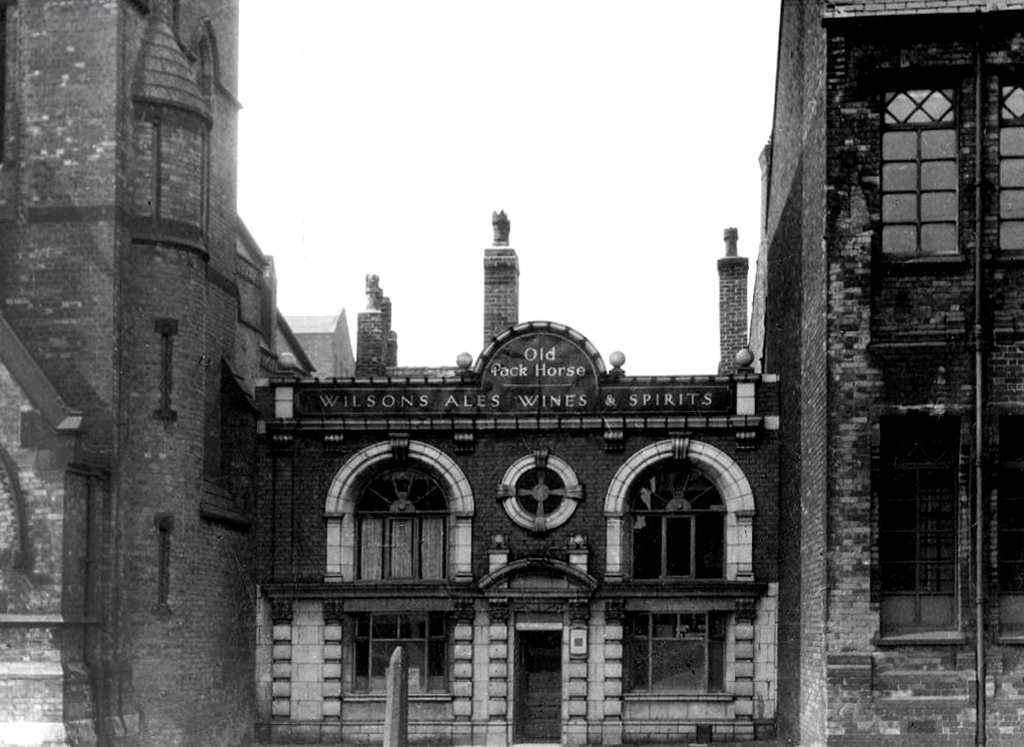
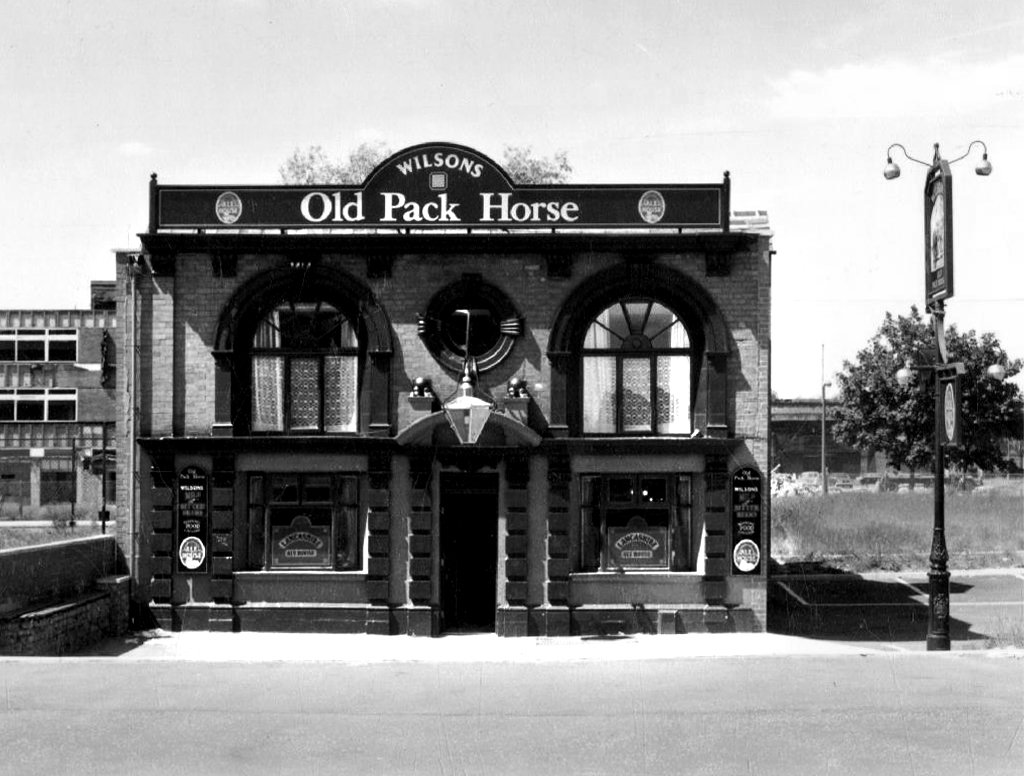
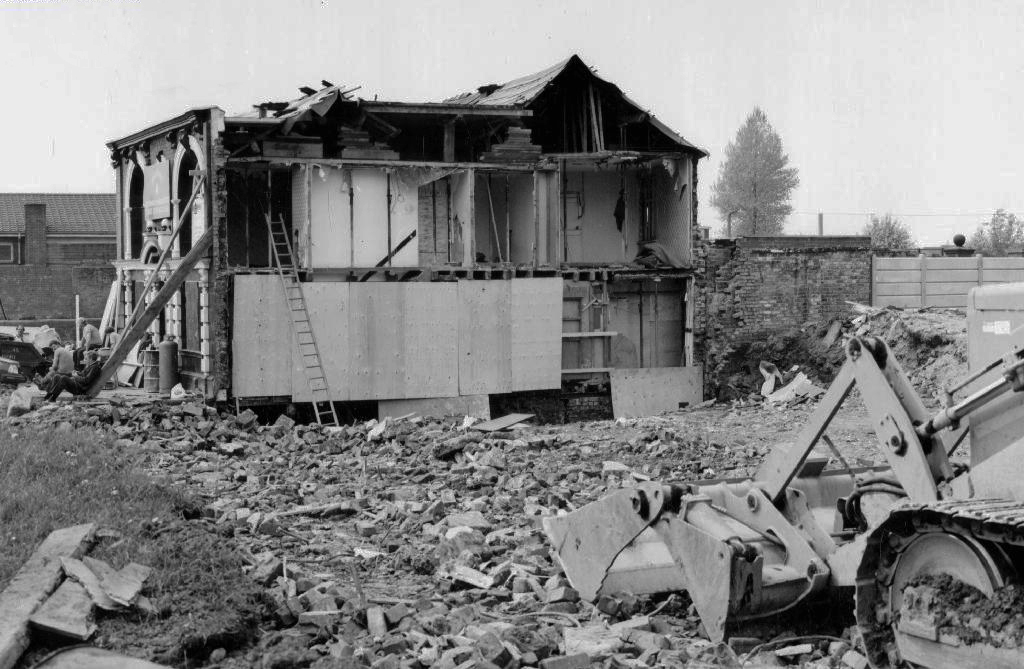







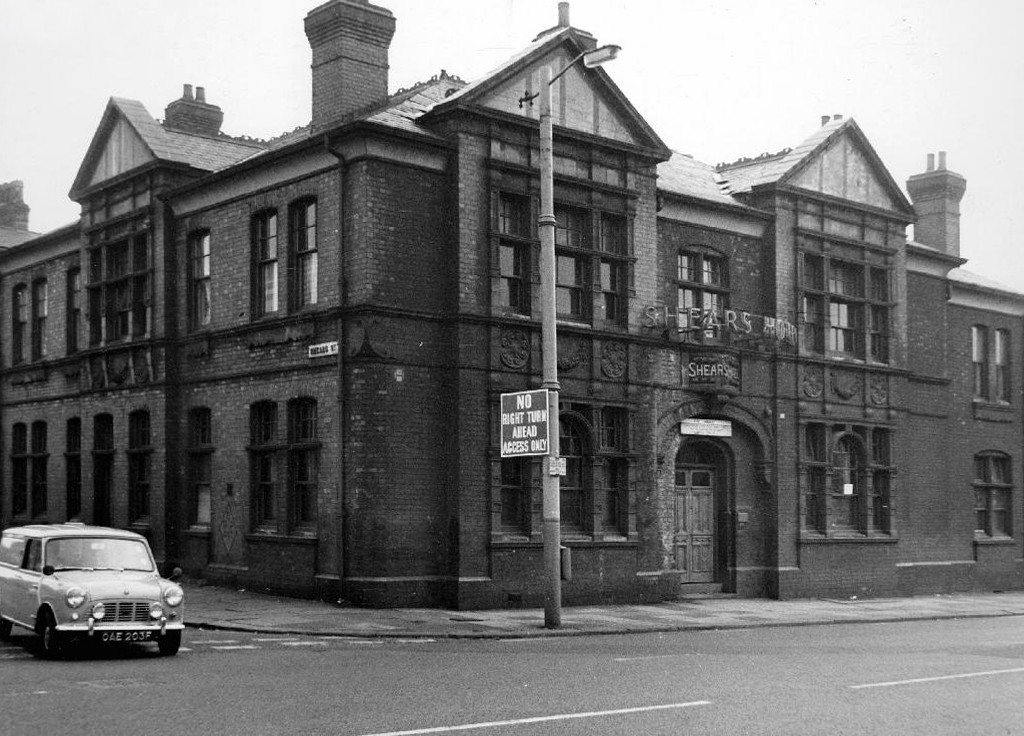
Royal Oak Hotel – Wilsons




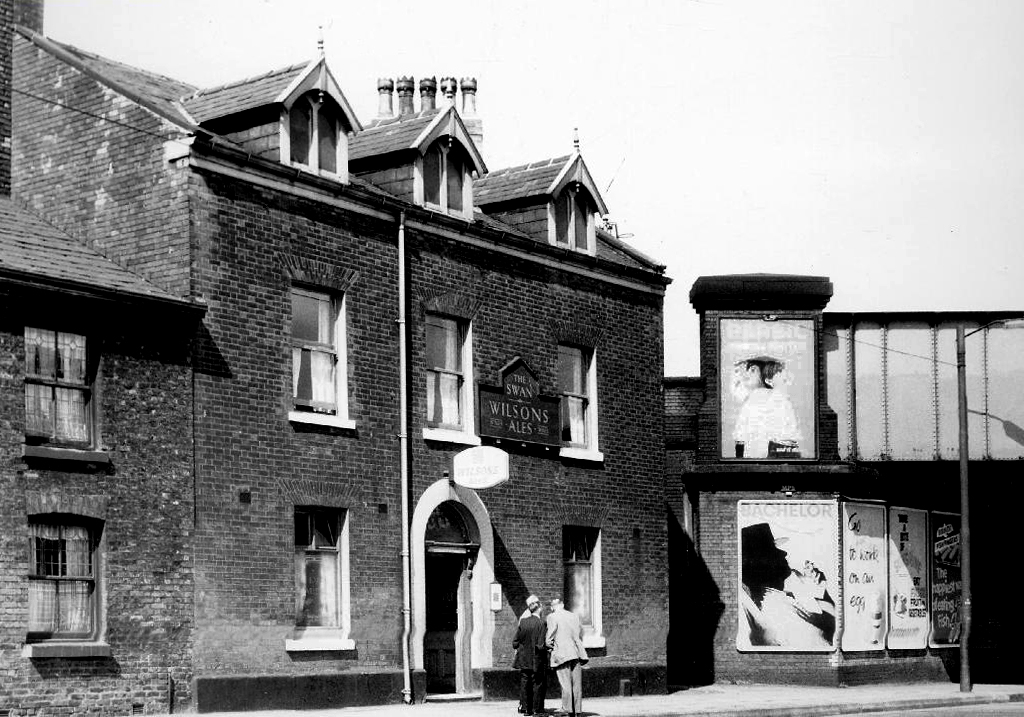
The Swan – Wilsons

Three Crowns – Wilsons
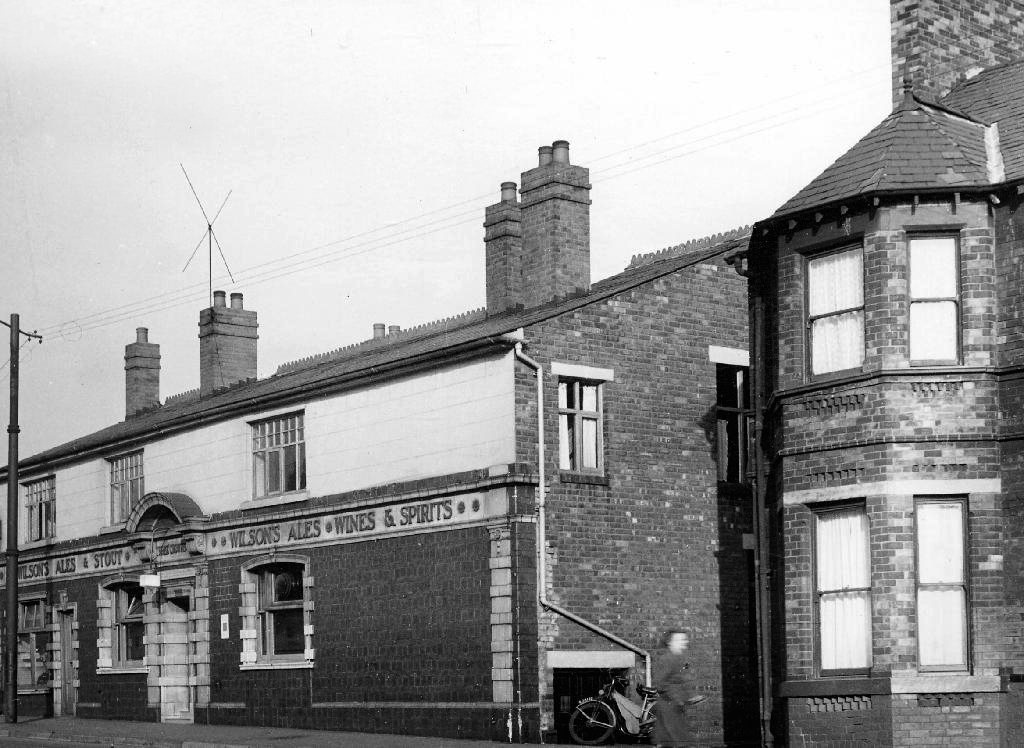

The Victoria – Wilsons
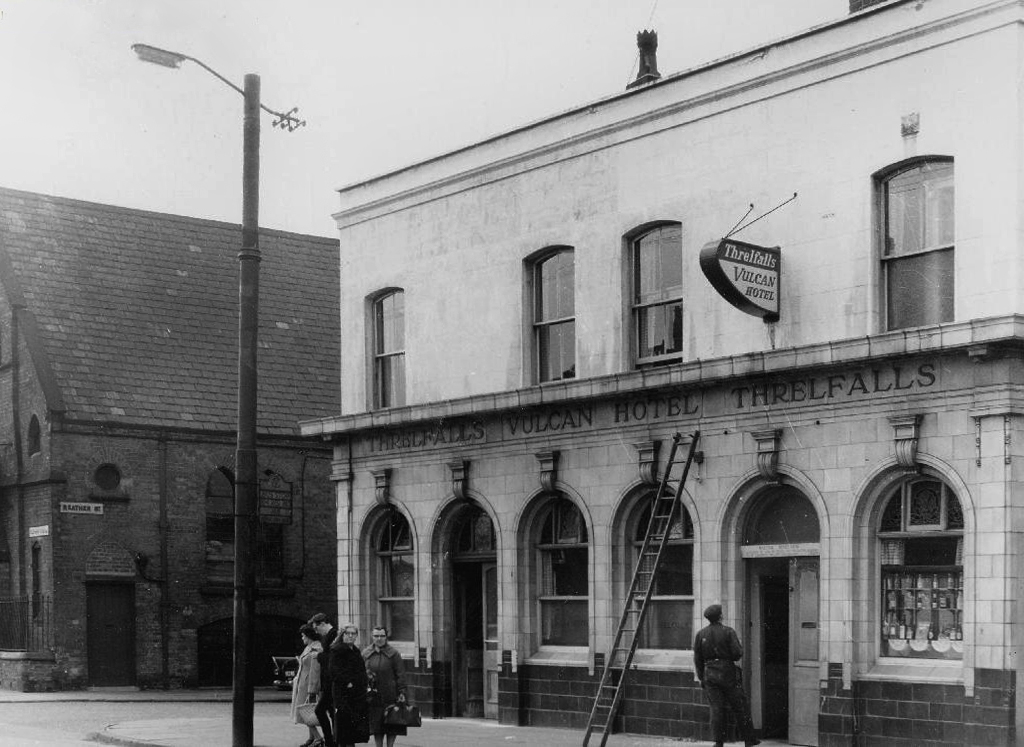



Wosons House?

Woodman Hotel – Wilsons

All photographs from the Manchester Local Image Collection.

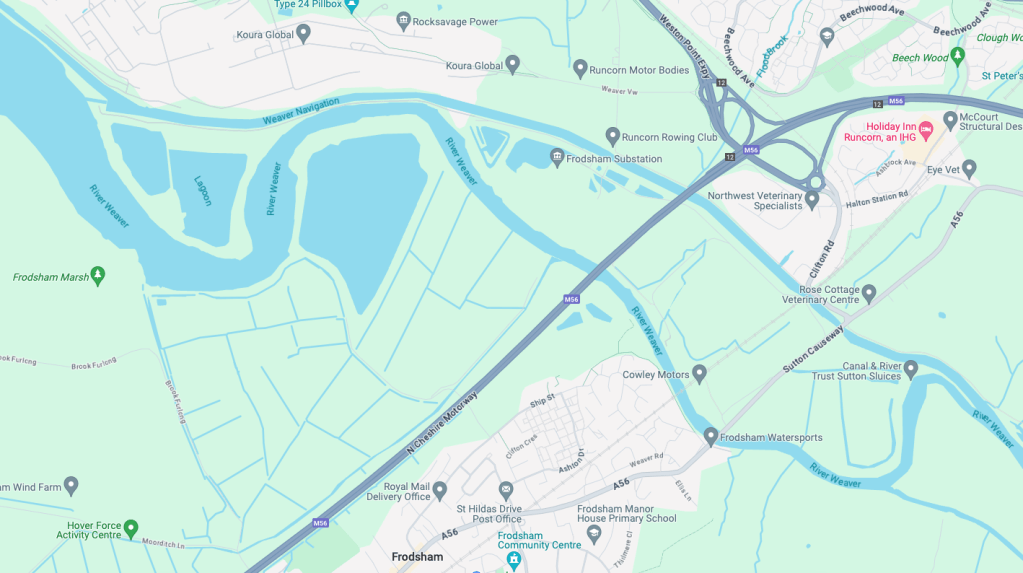
Along with my almost lifelong friend Mr Tim Rushton – I took a trip along a short stretch of the River Weaver, walking from east to west.
River Weaver – rising on the boundary between the counties of Shropshire and Cheshire and then flowing 45 miles north to reach the Irish Sea estuary of the River Mersey to the west of Runcorn.
Below Winsford, the course of the river has been altered several times, by the construction of cuts and locks, to enable small ships to trade on it. The river formerly joined the River Mersey at Weston Marsh, but since the construction of the Manchester Ship Canal, begun in 1887, it has flowed into the canal, from where surplus water enters the Mersey by the Weaver sluices, just upstream of the junction. The tidal river section below Frodsham has been bypassed by the Weston Canal since 1810 and is no longer navigable, as Frodsham Lock is derelict.
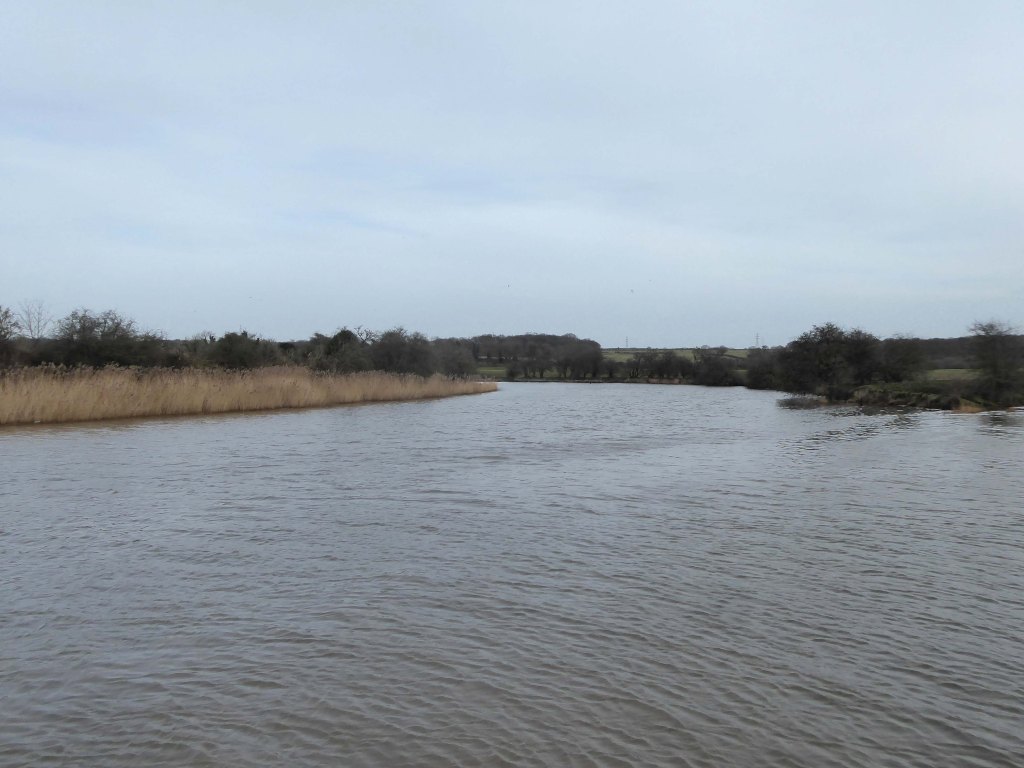





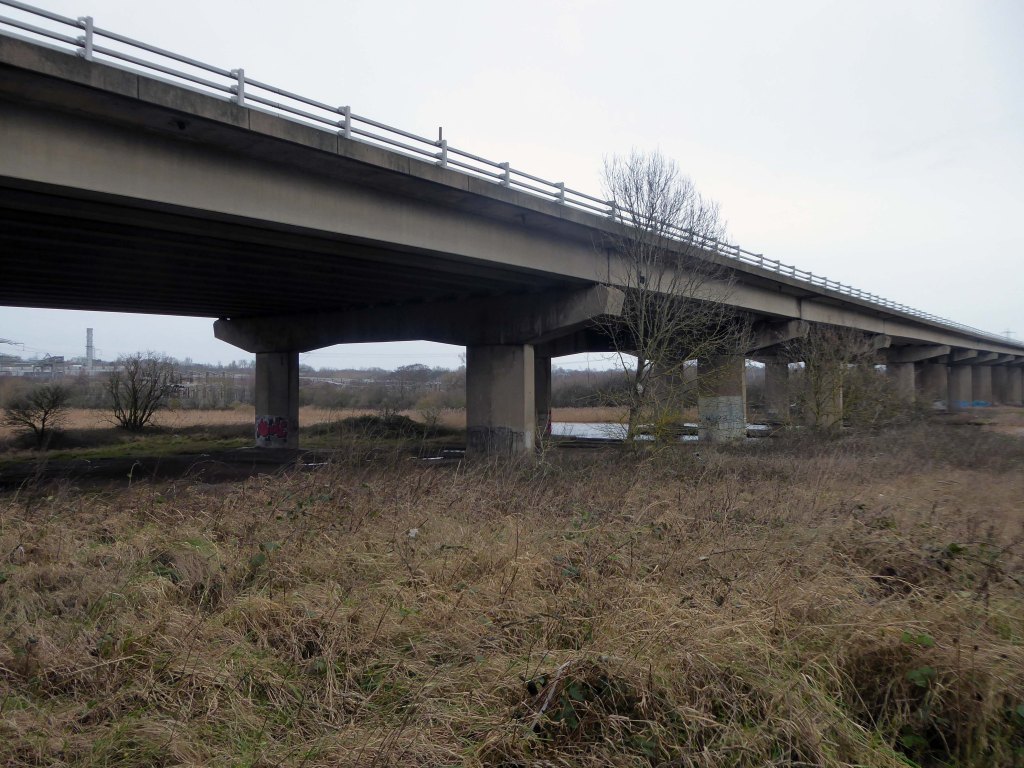
Railway viaduct over River Weaver and adjoining land by A Rendel Engineer and Thomas Brassey, contractor 1848-1850 – for Birkenhead Lancs & Cheshire Junction Railway Co.
Red sandstone, brown brick and cast iron, two segmental-arched iron spans of circa thirty metres over river; two round arches on west bank and twenty one on east bank. Piers to iron spans are rusticated tooled ashlar; the other spans have rusticated voussoirs, pier faces and quoins and rock-faced spandrels with brick reveals, cornice to iron-span piers, plainer imposts to others.
Top of central pier to river modified to take mid C20 concrete track bed.


Weaver Viaduct is one of the outstanding features of M56 and its design was approved by the Royal Fine Arts Commission. The three-quarter mile of elevated motorway and approach embankments over the River Weaver and Weaver Navigation Canal opened on 21 February 1971.
Design was by Husband and Co of Sheffield – acting for Department of Environment, who also supervised the project. The contractor was Christiani Shand with a tender price of £3,146,387 in March 1968.
Work began in April 1968 – the eventual cost was put at £3.5 million.
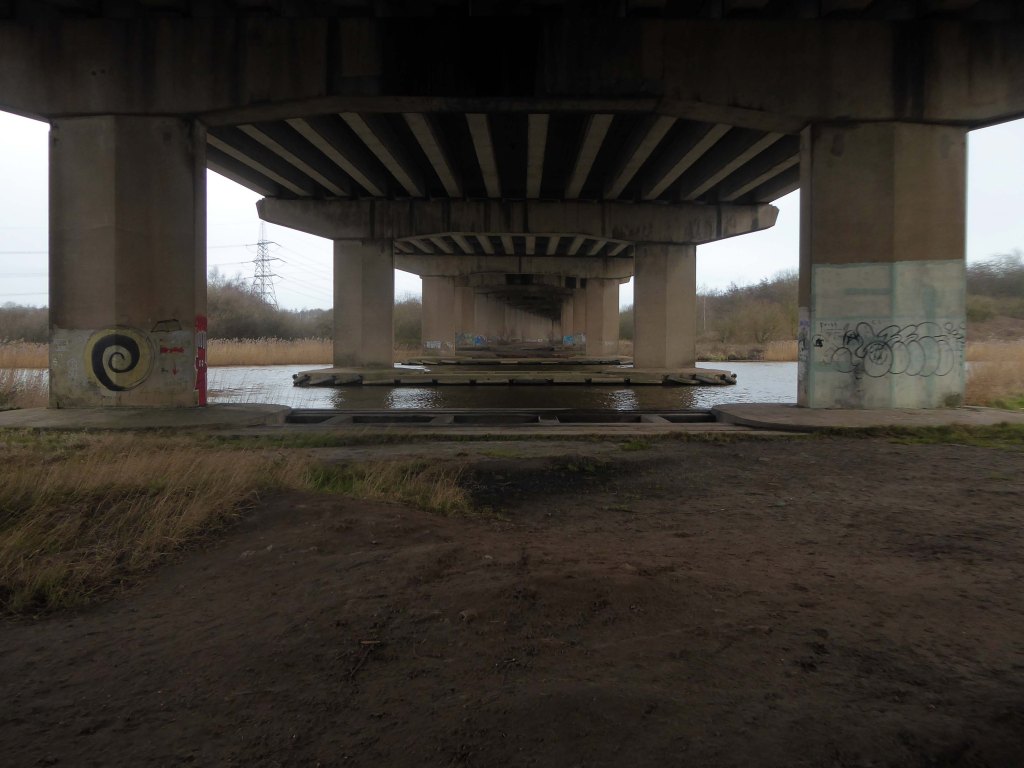




Thirty two 125-foot concrete 100-tonne beams were put into place in July 1970; the concrete beams were made by Matthews & Mumby of Windmill Lane Denton.
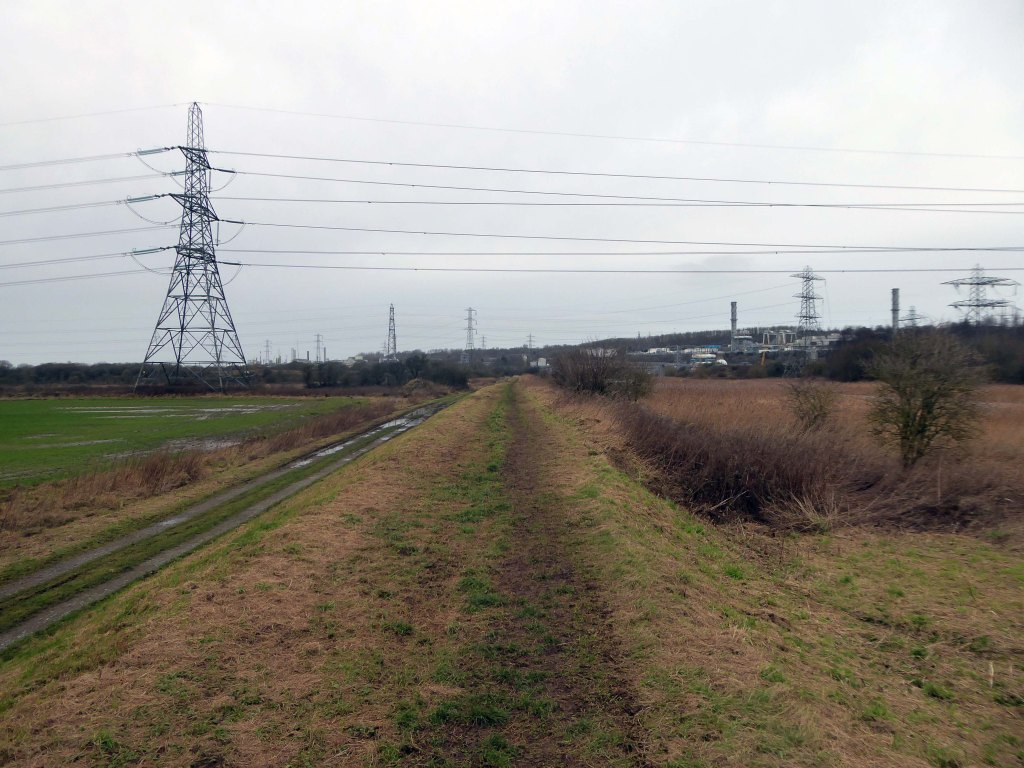


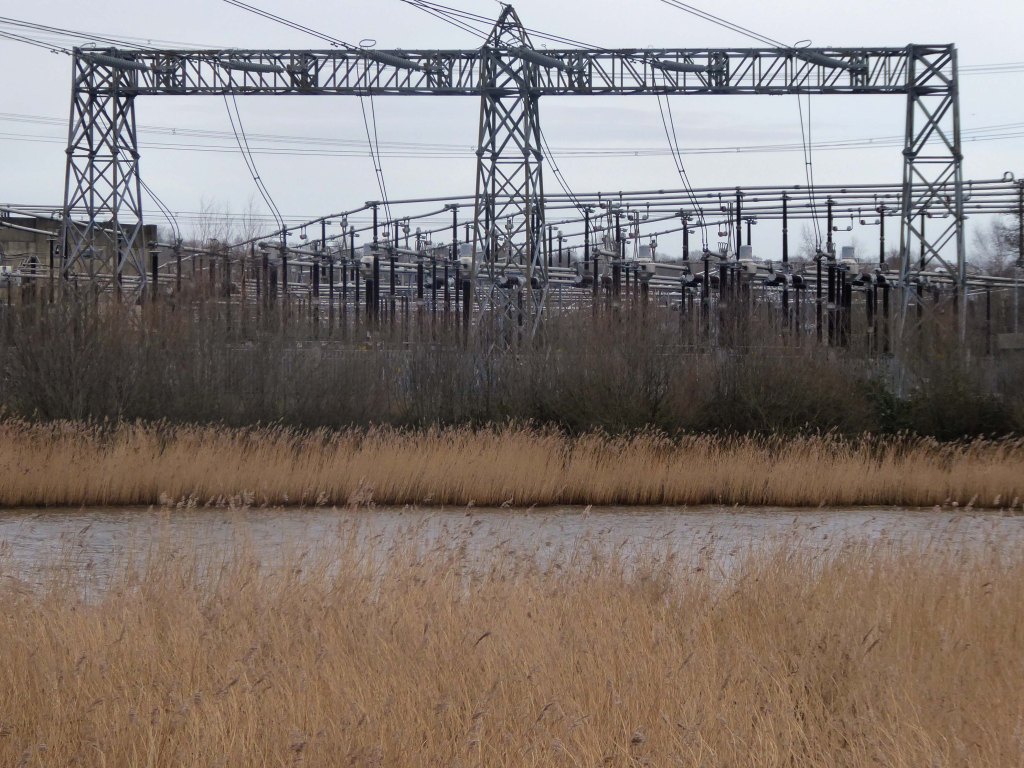
High-Voltage Frodsham Substation – Rock Savage power station
Rock Savage Power Station is an 800 MWe gas-fired power station.
It was opened by Queen Elizabeth II on 31 July 1998, and owned by InterGen, a company that is now jointly owned by Ontario Teachers’ Pension Plan and China Huaneng Group, it cost £375m.
It sponsors the Runcorn Jets baseball club, the Highfield Male Voice Choir and the Weston Angling Club.
The name comes from the nearby ruined Elizabethan mansion – Rocksavage.
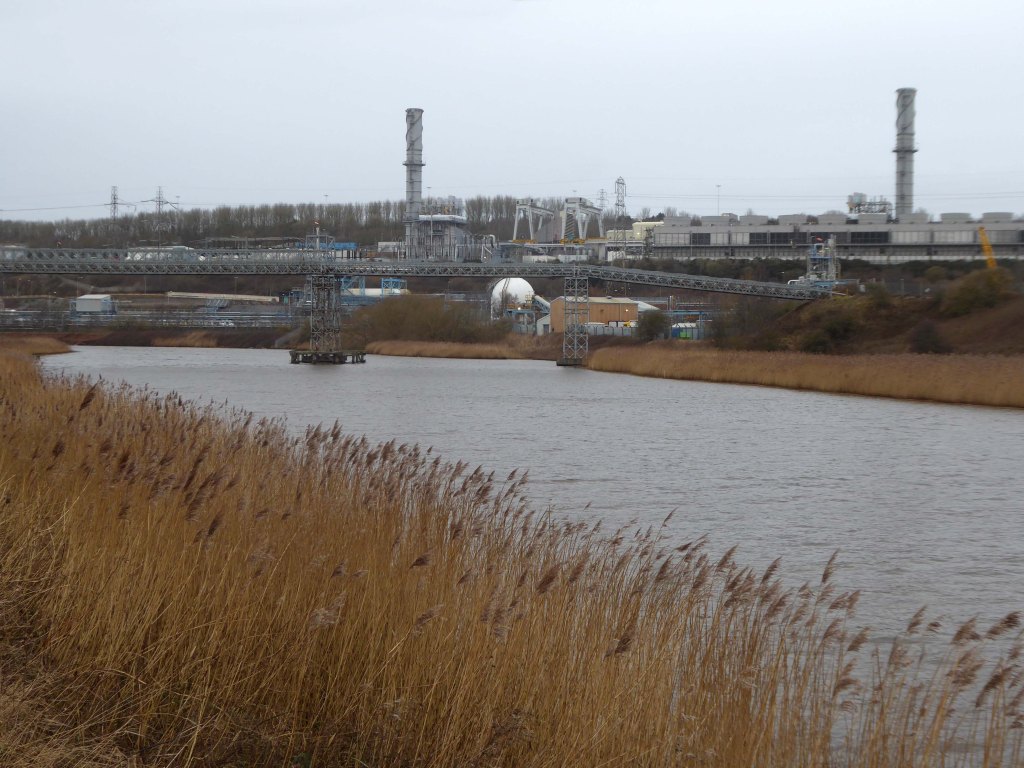





Koura Global – leader in the development, manufacture, and supply of fluoro products and technologies, opened a new HFA 152a production facility at their Runcorn site in the UK.
Chiesi, the international research-focused pharmaceuticals and healthcare group, signed a commercial agreement to use the new low carbon footprint medical propellant for inhalation product development and clinical trials in 2019.

Britain from Above 1948
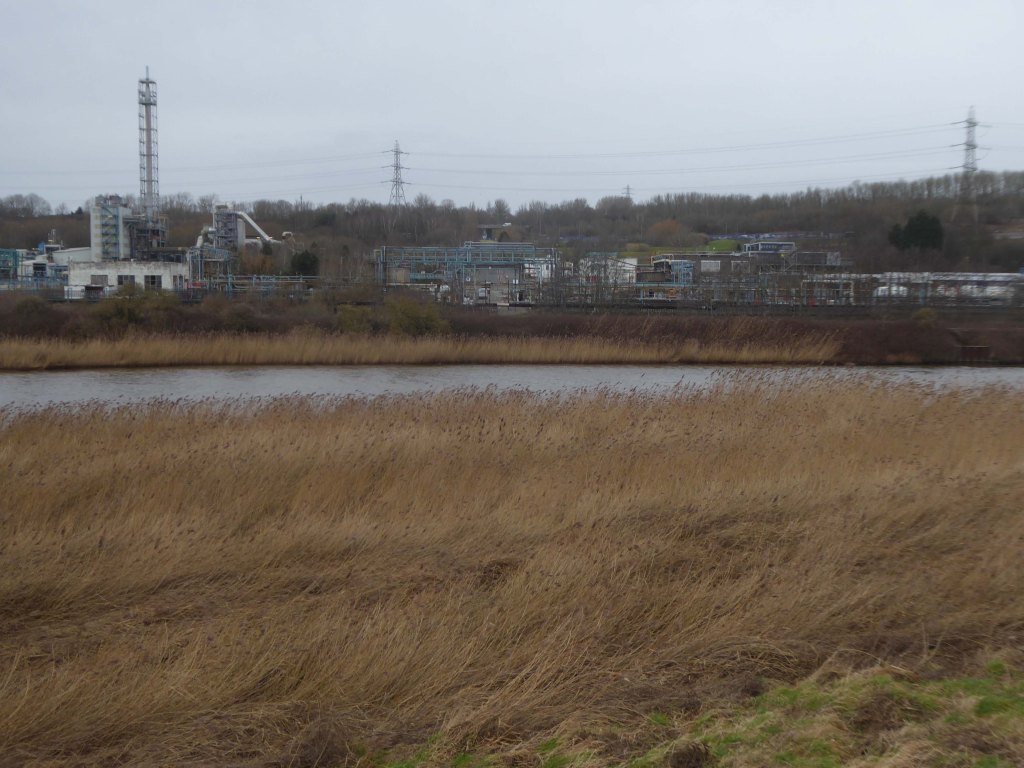
Ineos Chemical Complex formerly ICI Rocksavage Works on the banks of the River Mersey River Weaver and Manchester Ship Canal in Runcorn formerly ICI works of Rocksavage and Castner Kelner Works which produced fluorcarbons such as aerosol propellants dry cleaning solvents and chlorine UK January 2007
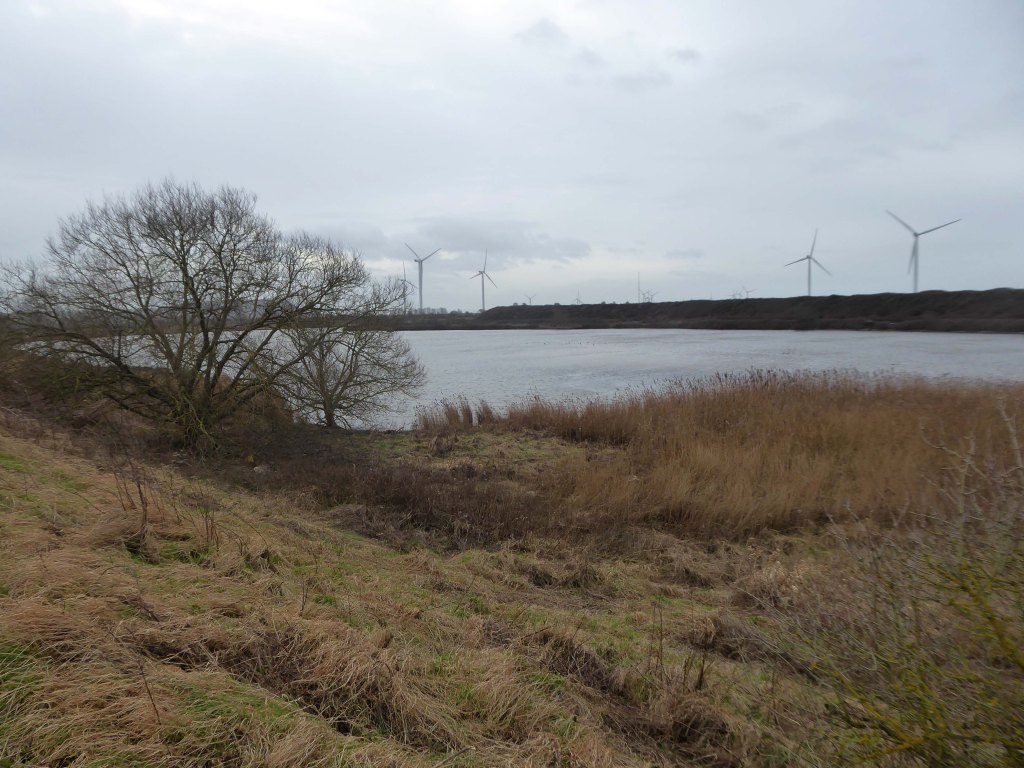
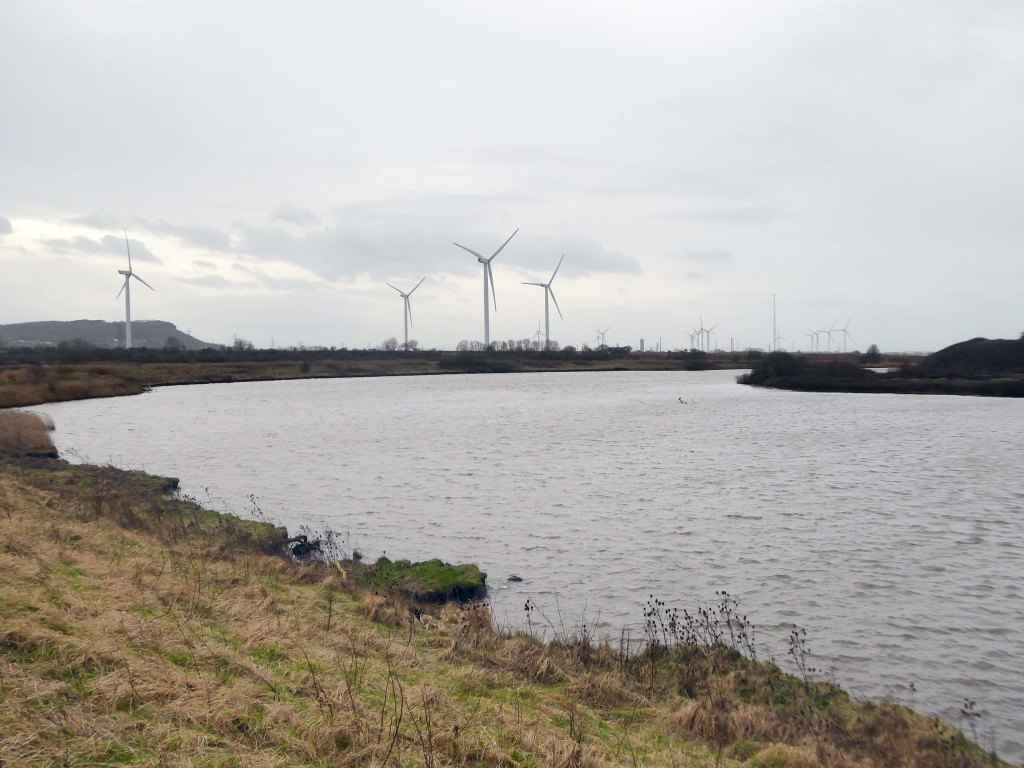
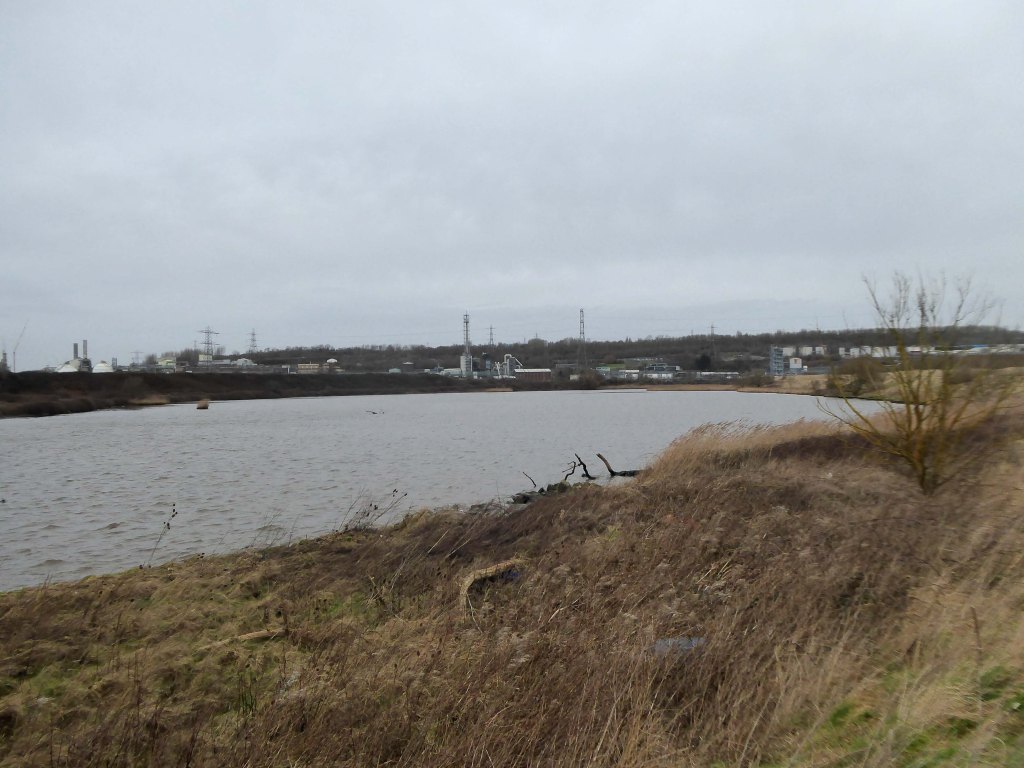
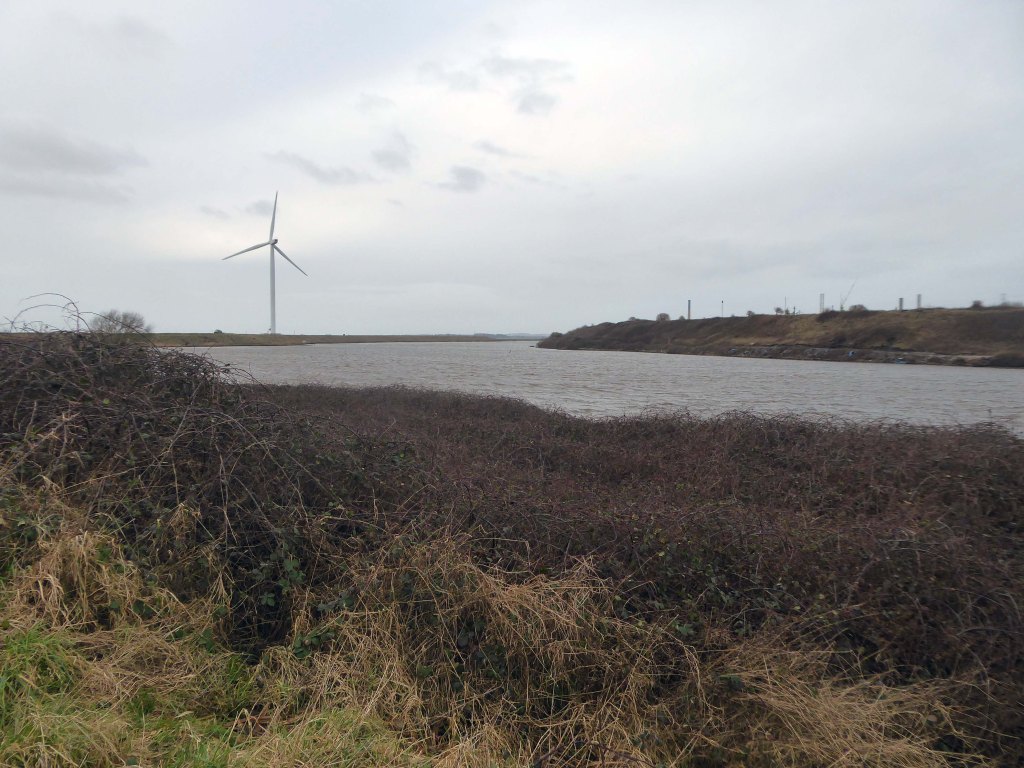









Frodsham Wind Farm is one of England’s largest onshore generating stations, and the largest in the Cheshire region, with an installed capacity of more than 50 MW. Construction of the wind farm began in March 2015 and became fully operational in February 2017.


Shore Lane Sheffield S10 3BU
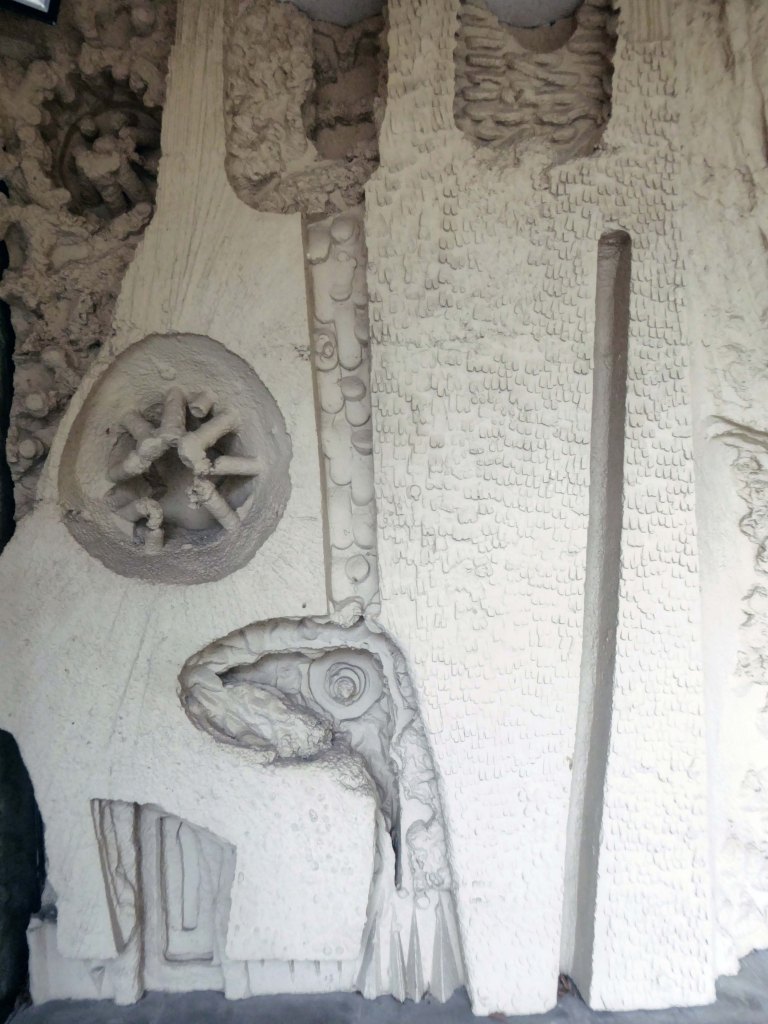
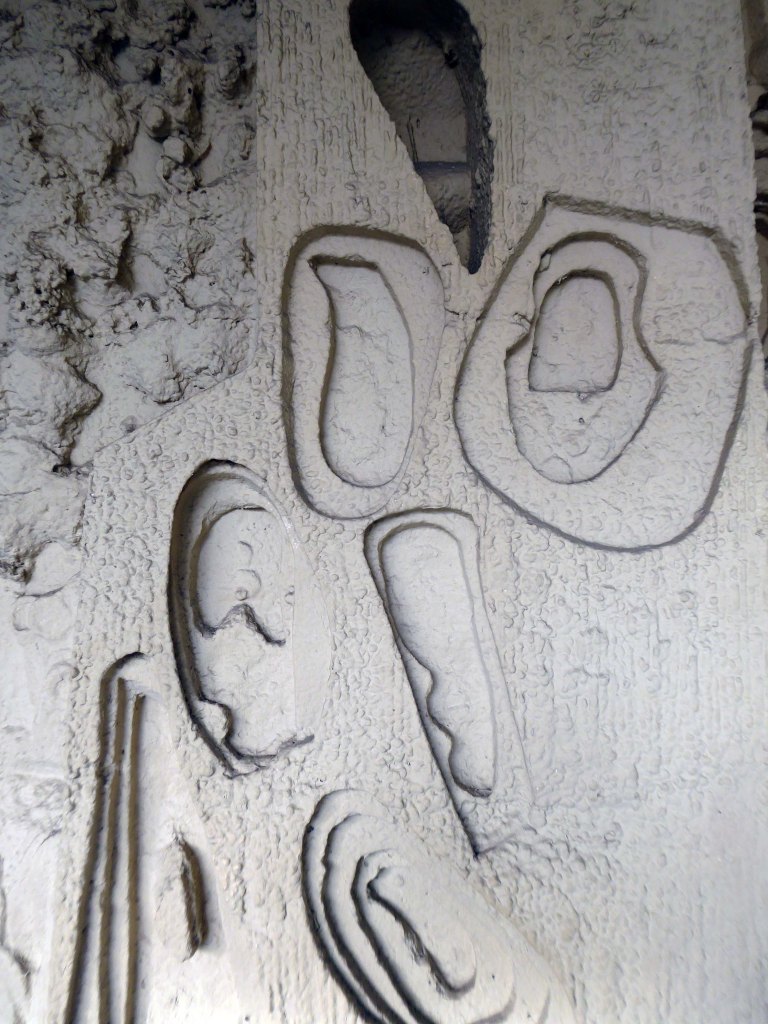
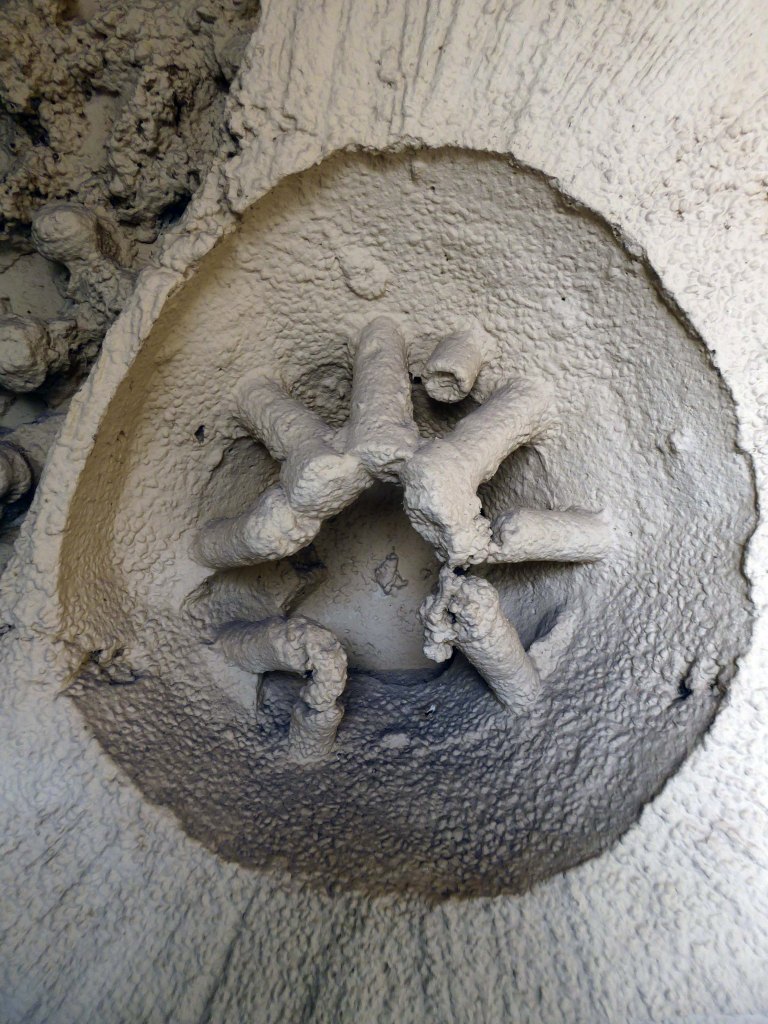
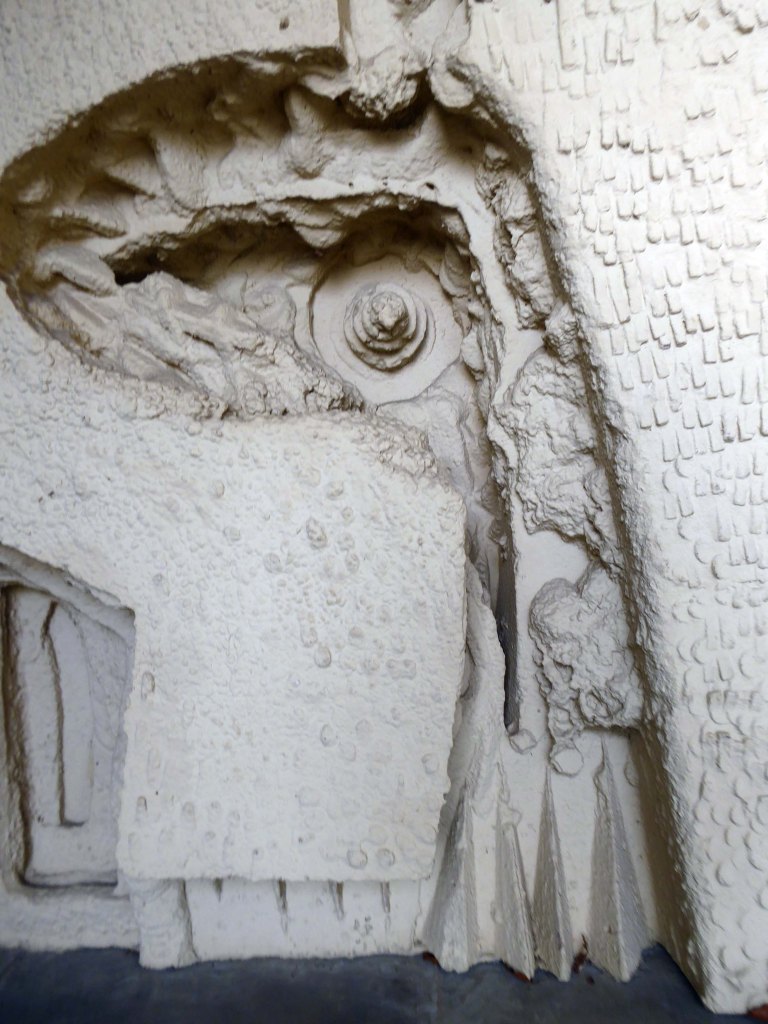
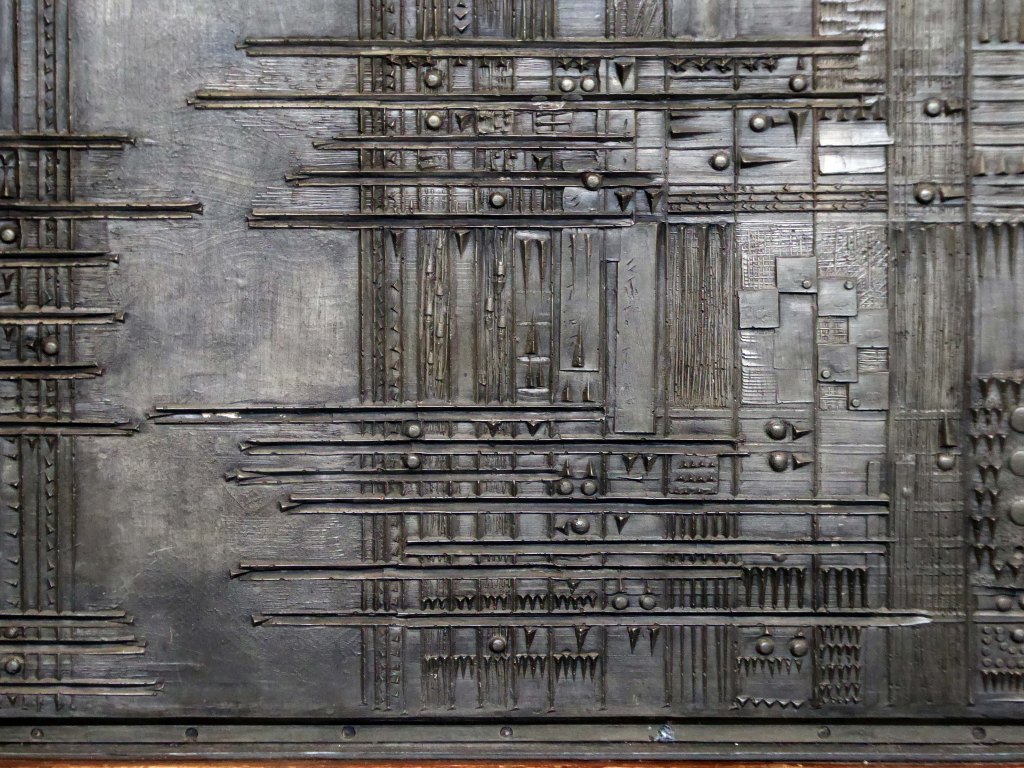
The Masonic Hall has an extension of 1967 by Hadfield Cawkson Davidson & Partners

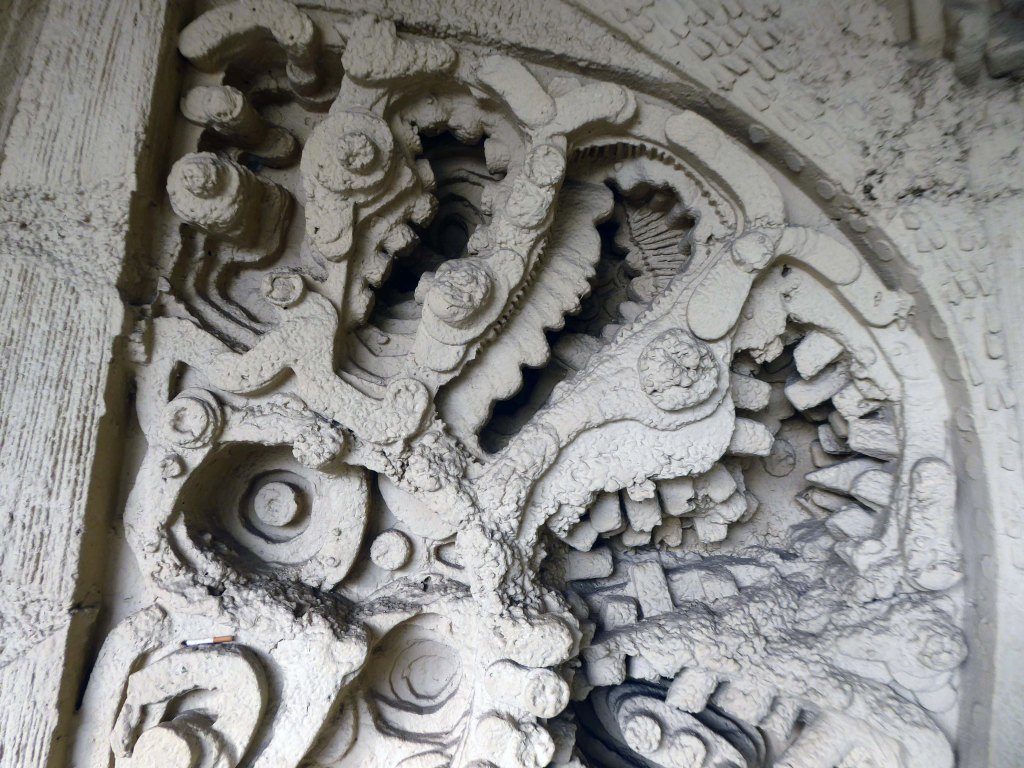
The Masonic Hall has an extension of 1967 has a concrete mural by William Mitchell.
Symbolising the turmoil and chaos of the outside world, contrasting with the order of the Masonic Temple – a Freemason told me so.
I thought to propose the idea that this may well be a false dichotomy – then thought I’d better not.

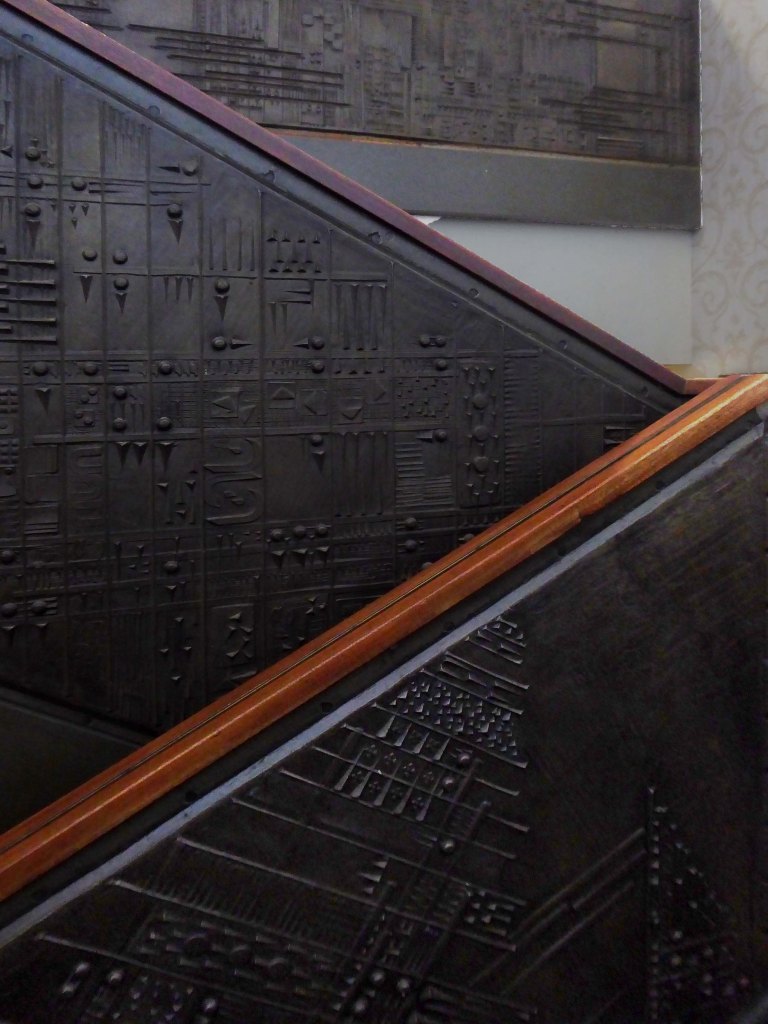
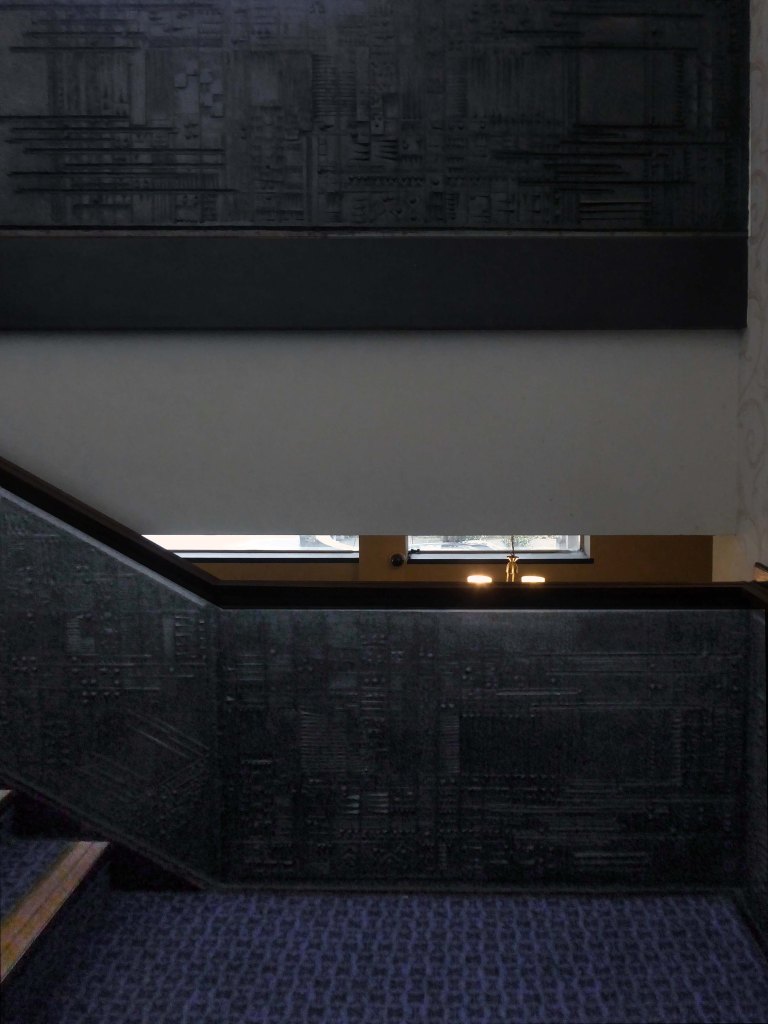
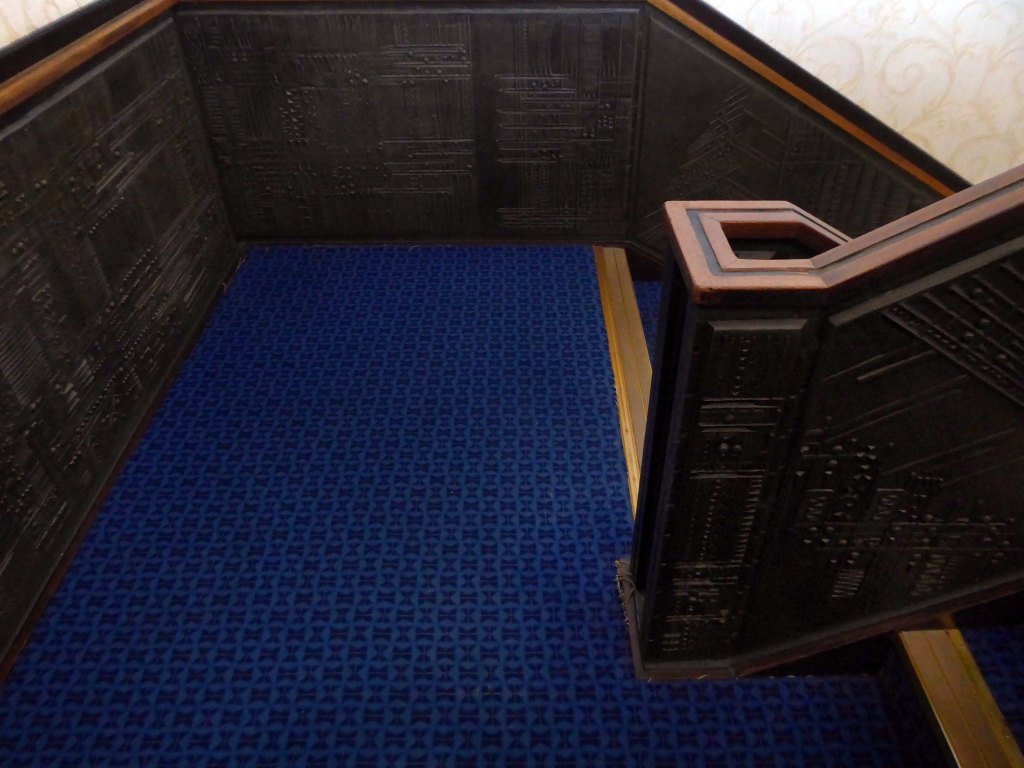
These are the constituent panels.
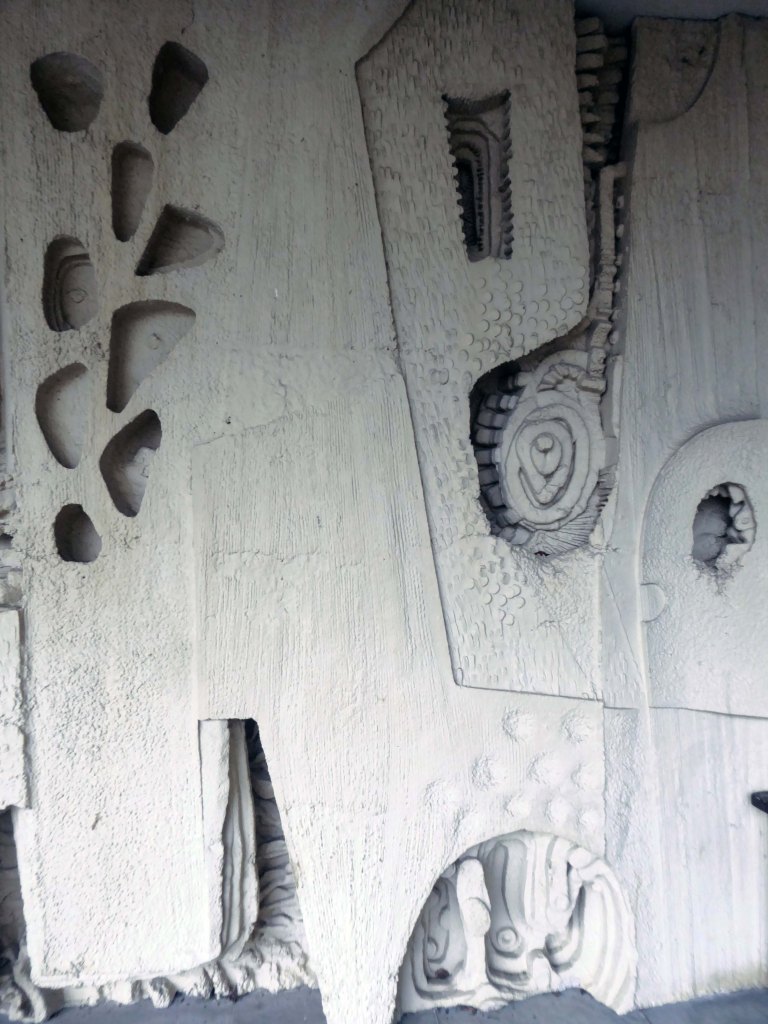
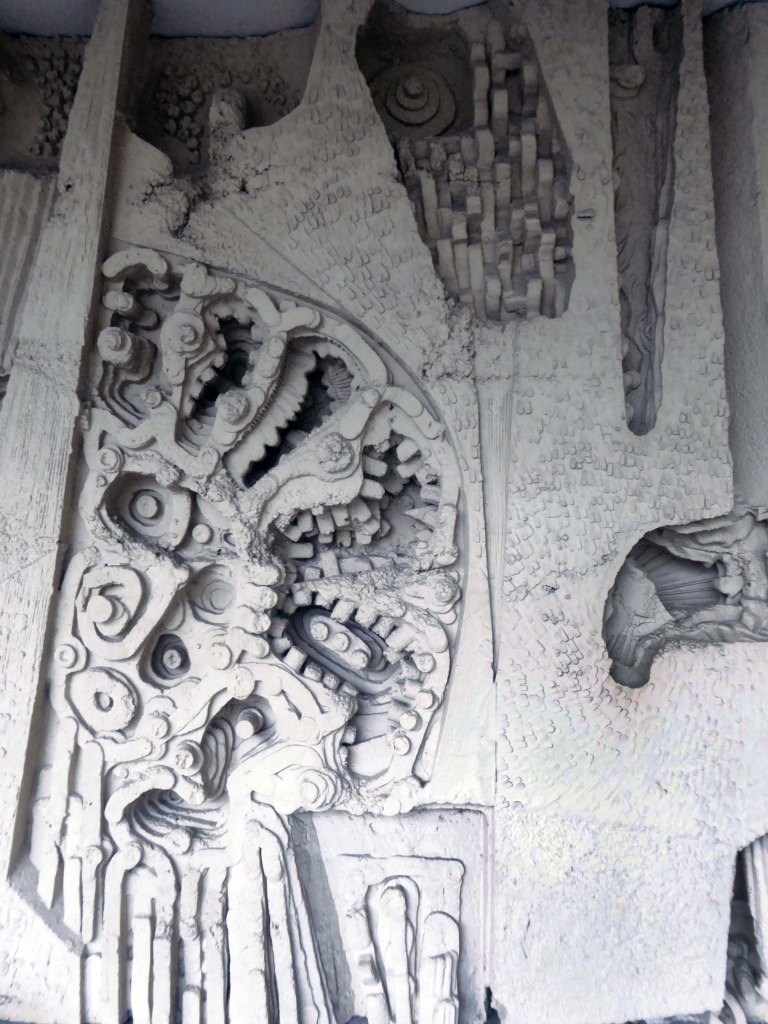
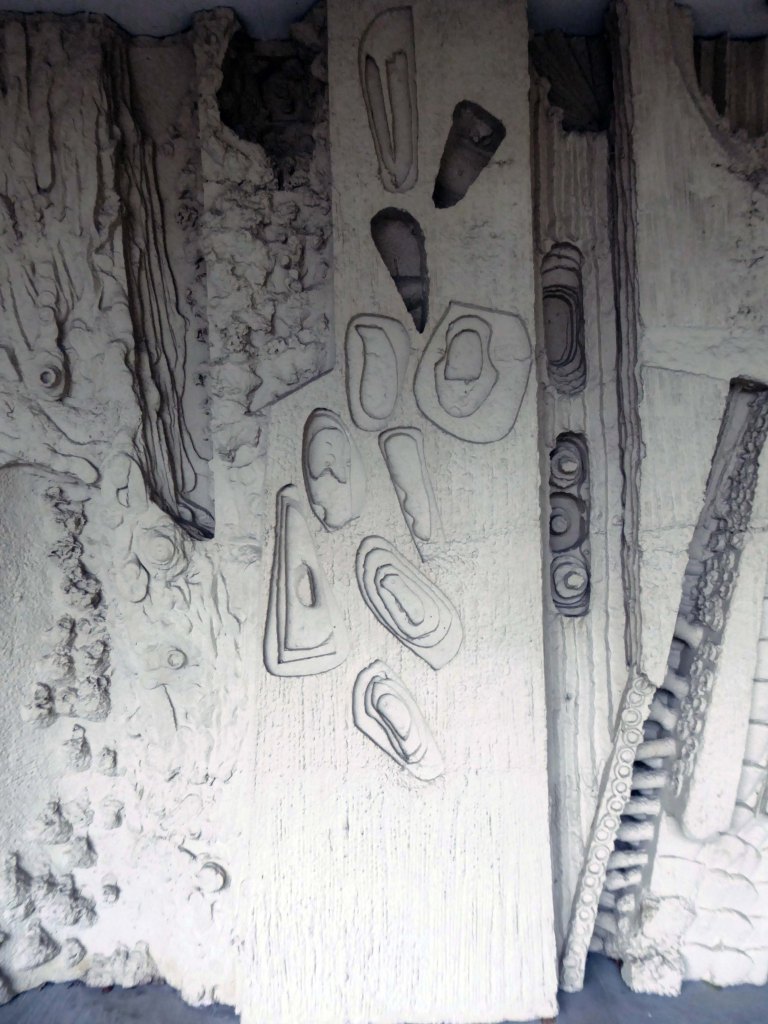






These are the details.
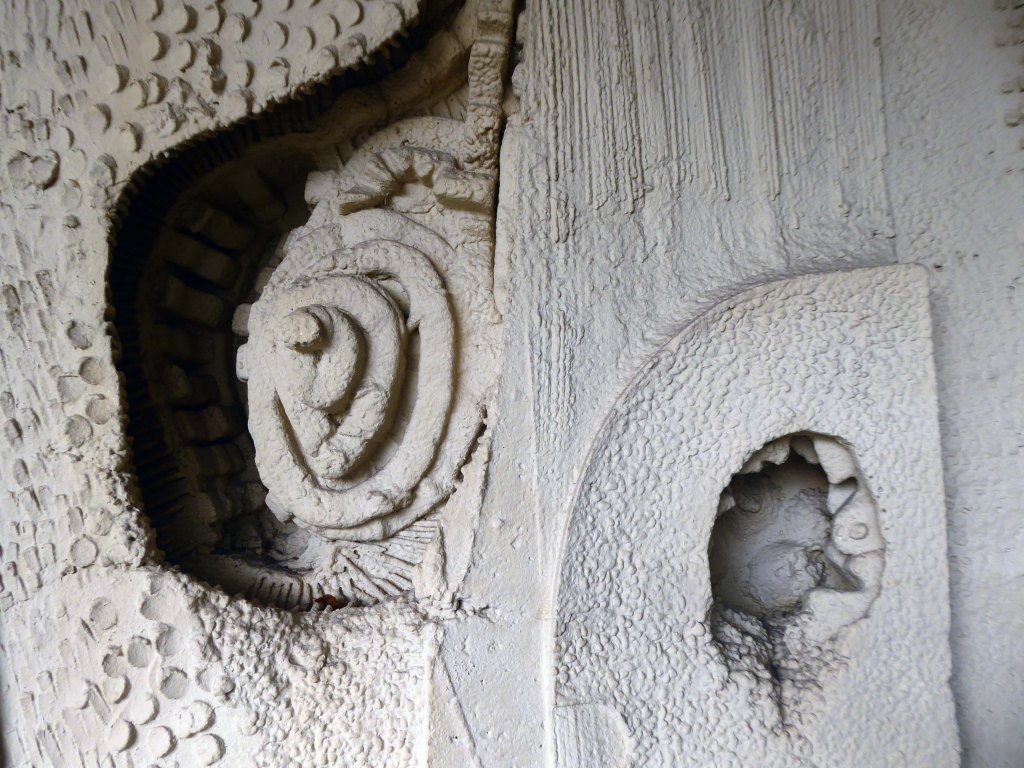
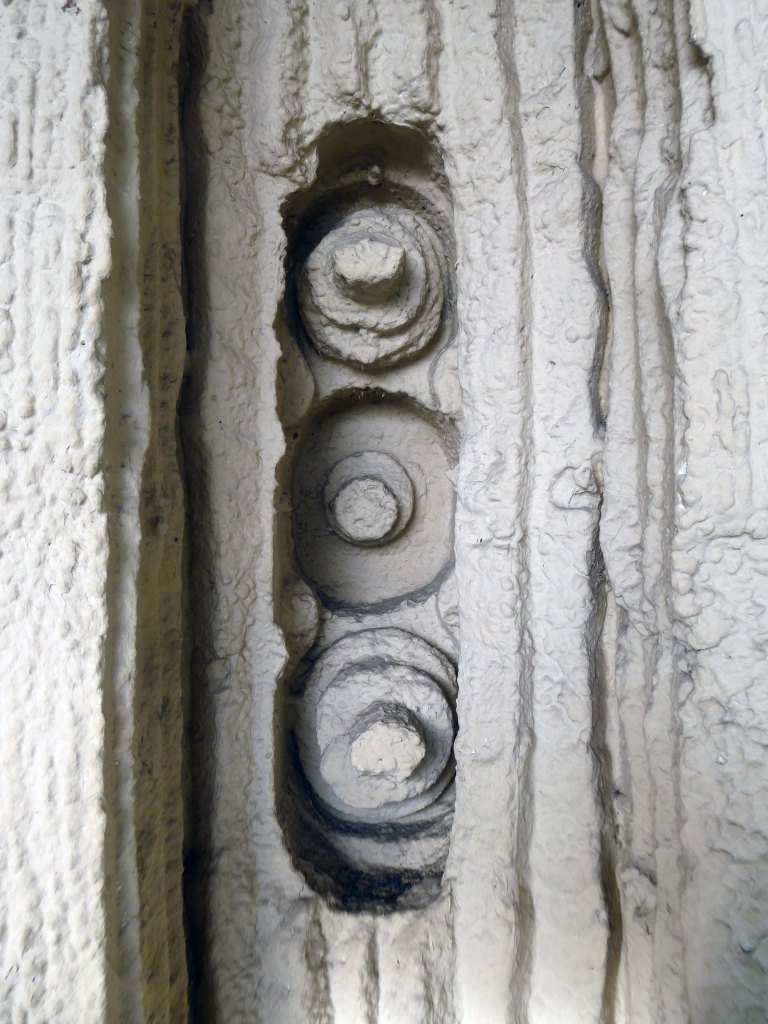






Having been asked to speak to the Sheffield University Alumni Women’s Group – on the subject of Modernist Sheffield, I had easy access to the interior space.
I was ever so excited to discover these decorative panels on the stairway – I assume that they are also the work of William Mitchell.
Nobody knew.
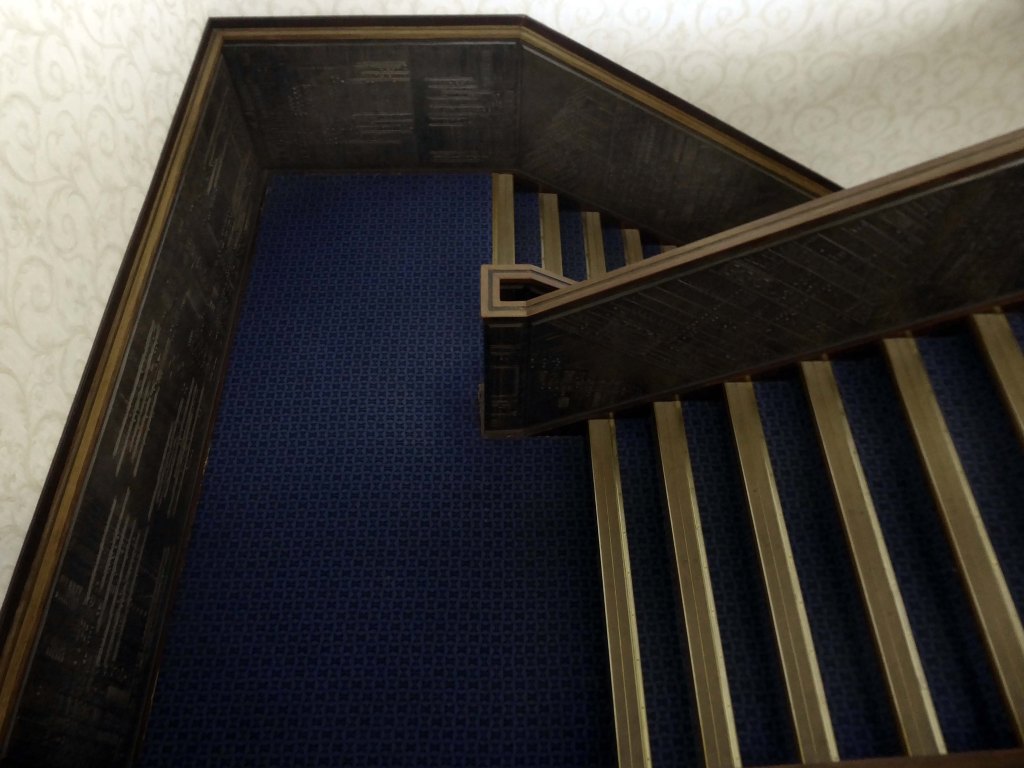










The Masonic Hall is now a venue in addition to being a Masonic Hall.

It was once the home of steel magnate Edward Vickers.
Vickers was a successful miller who invested his money in the railway industry. In 1828 he garnered control of his father-in-law’s steel foundry business, formerly Naylor & Sanderson, and renamed it Naylor Vickers & Co. He went on to be Alderman and the Mayor of Sheffield and was the first President of the Sheffield Chamber of Commerce before he died in 1897.

Having photographed the arterial roads of Manchester in 2014, I have resolved to return to the task in 2024.
Some things seem to have changed, some things seem to have stayed the same.
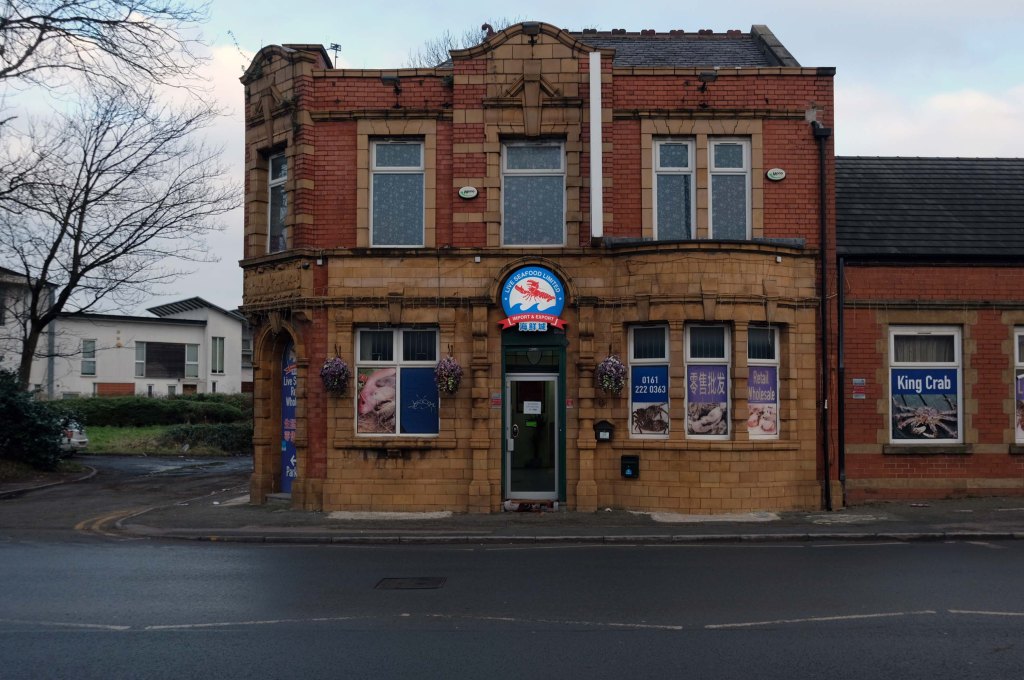
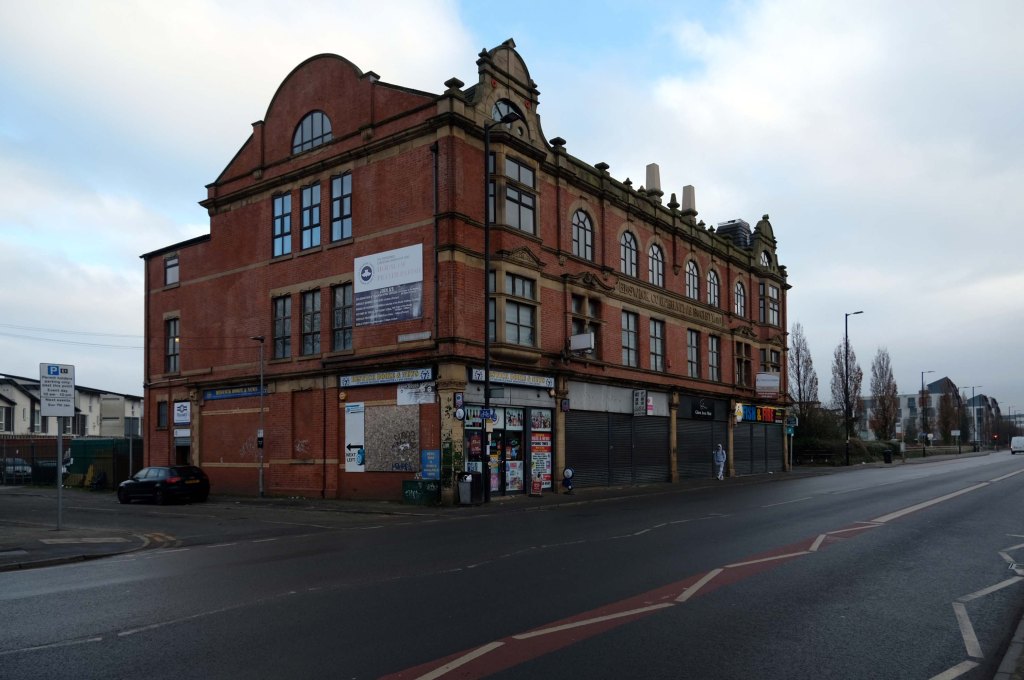
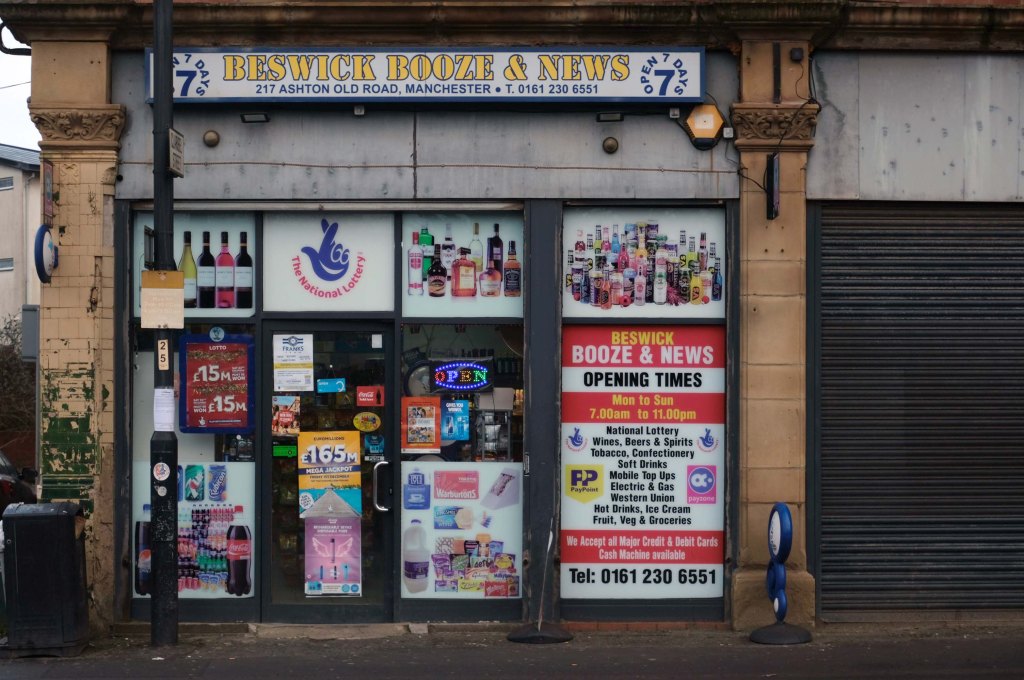
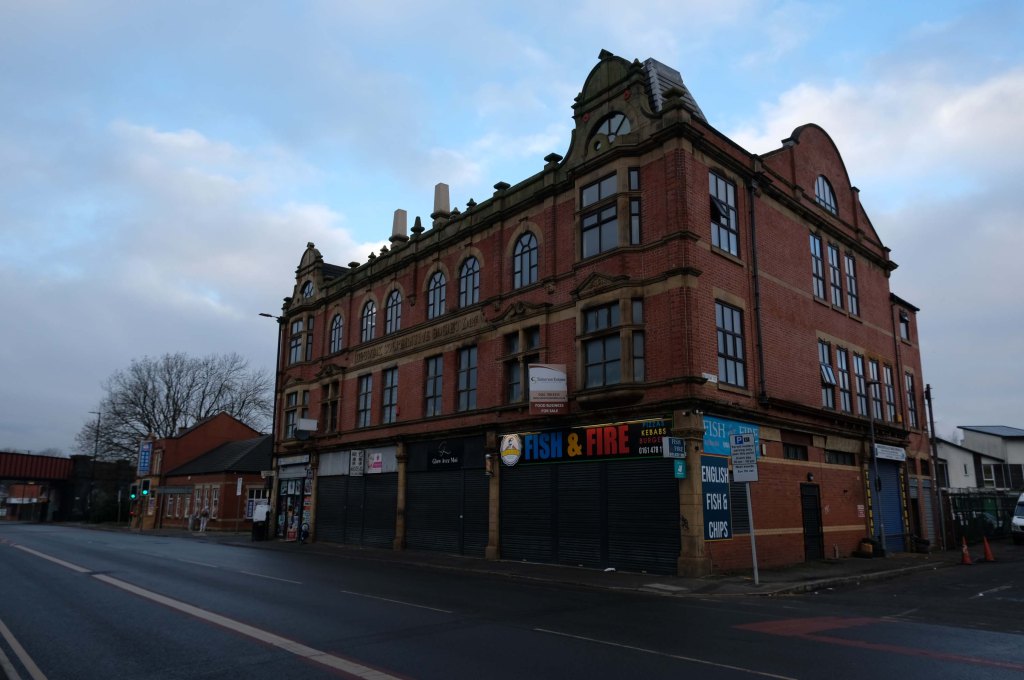
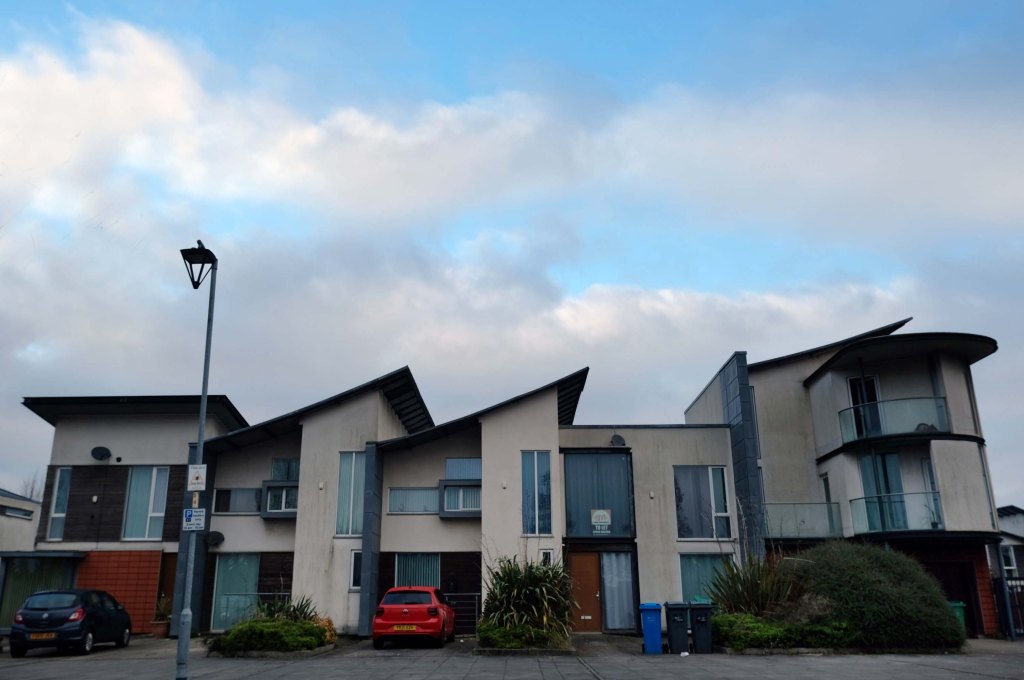
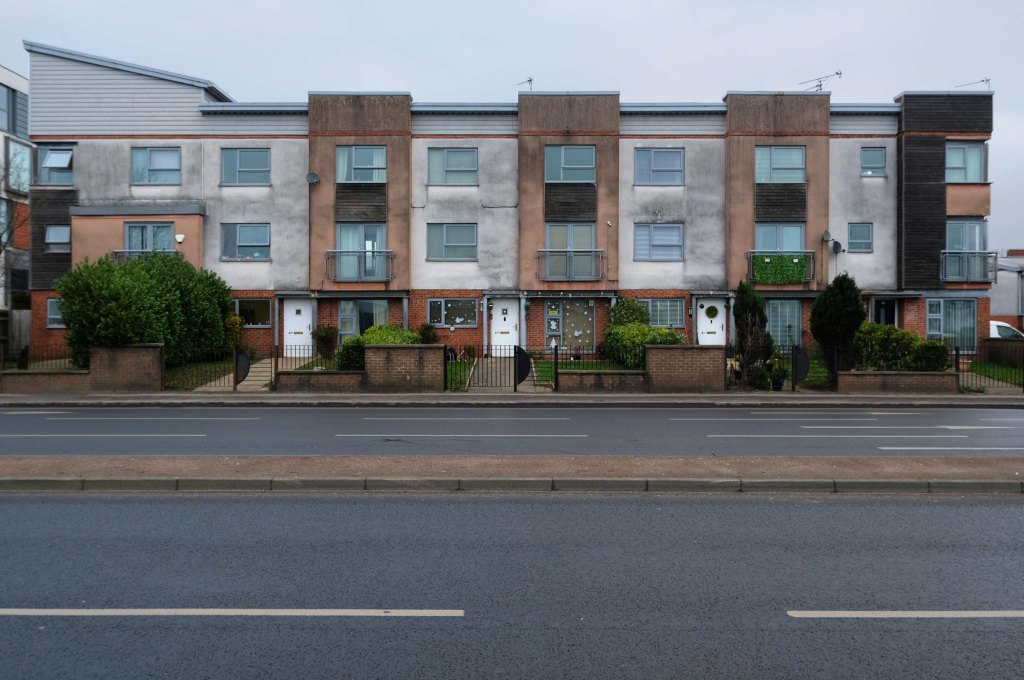
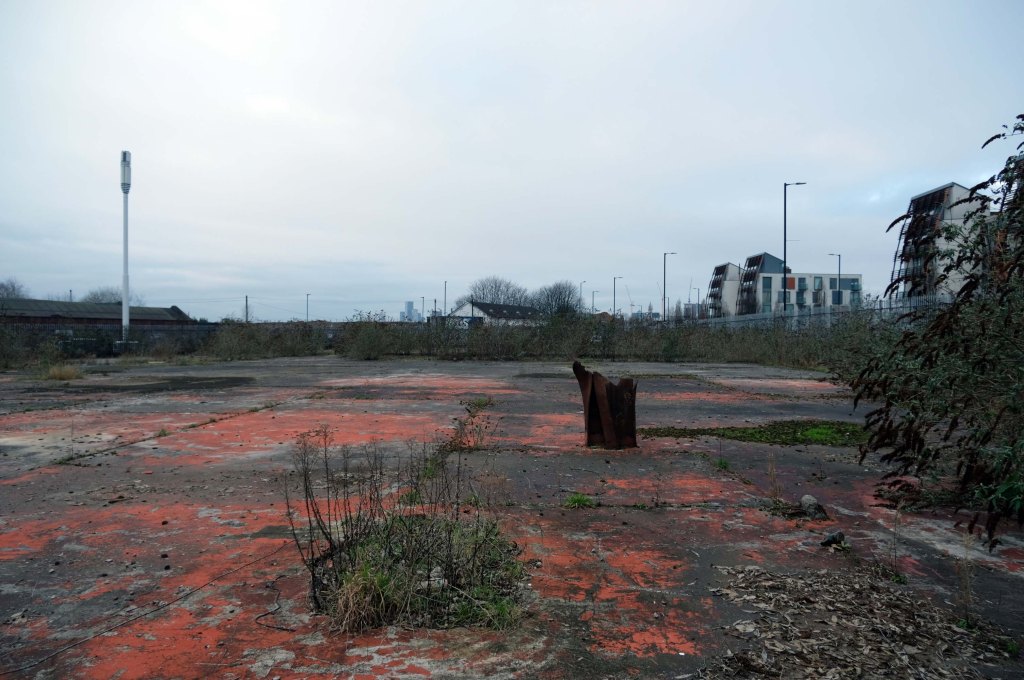
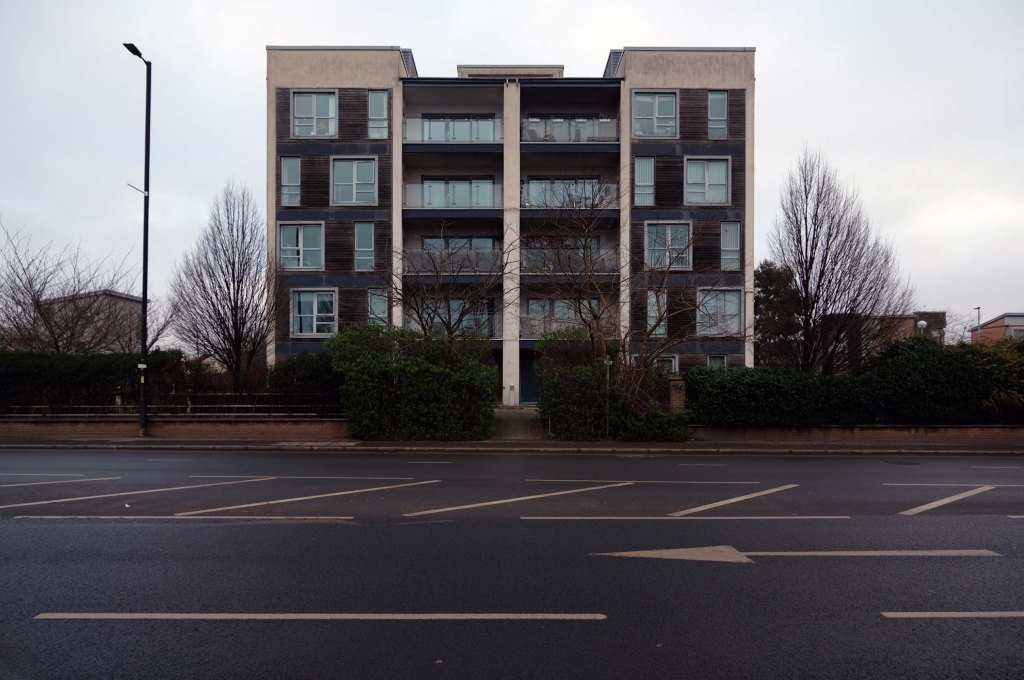
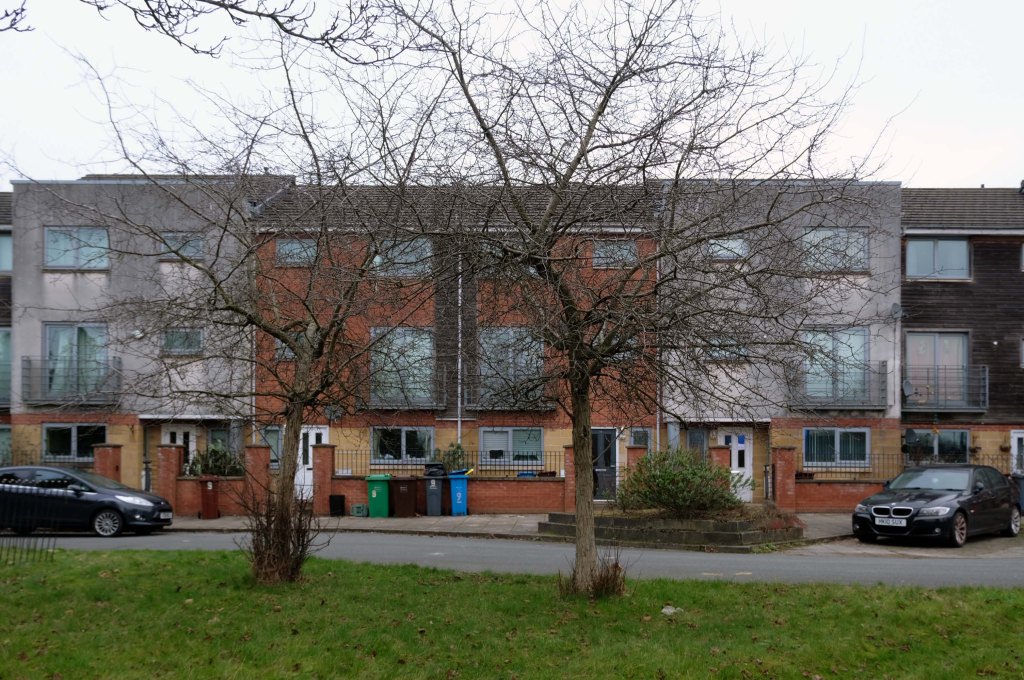
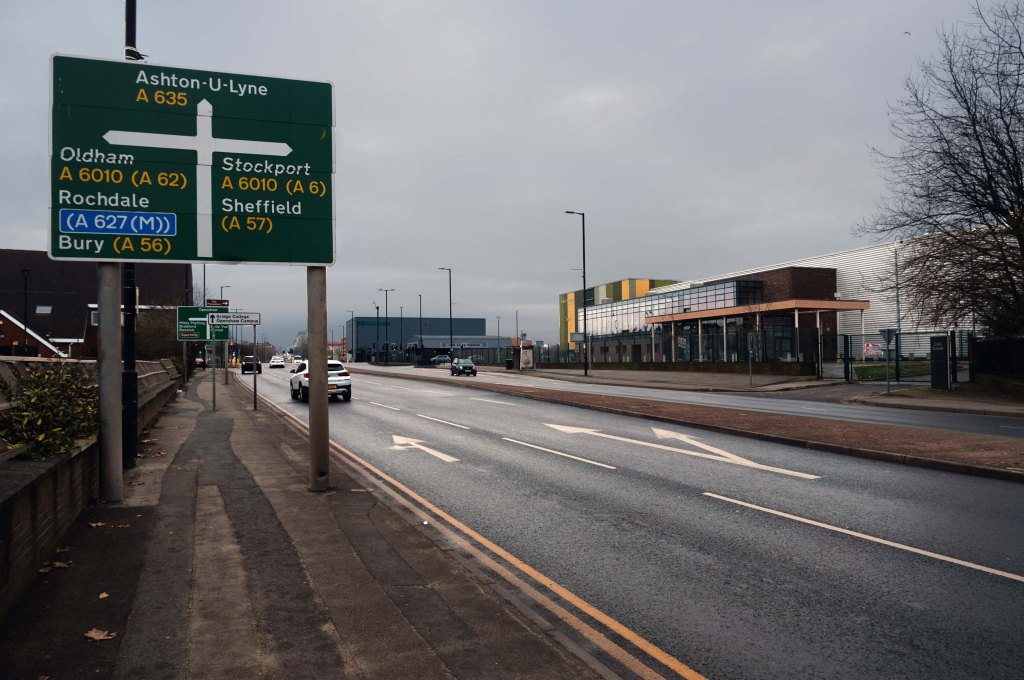
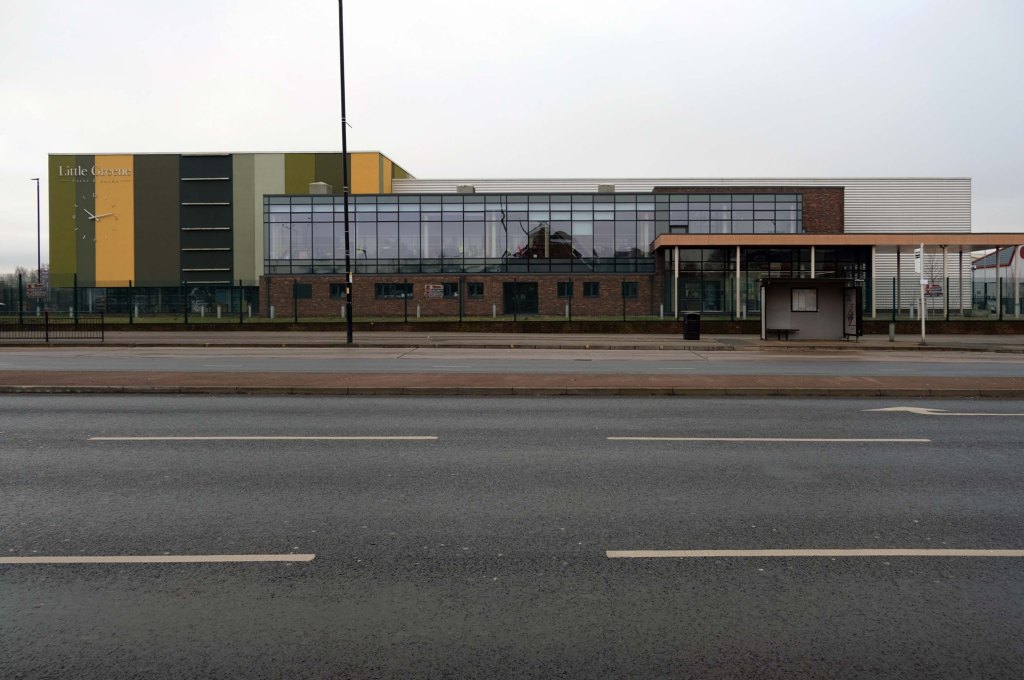
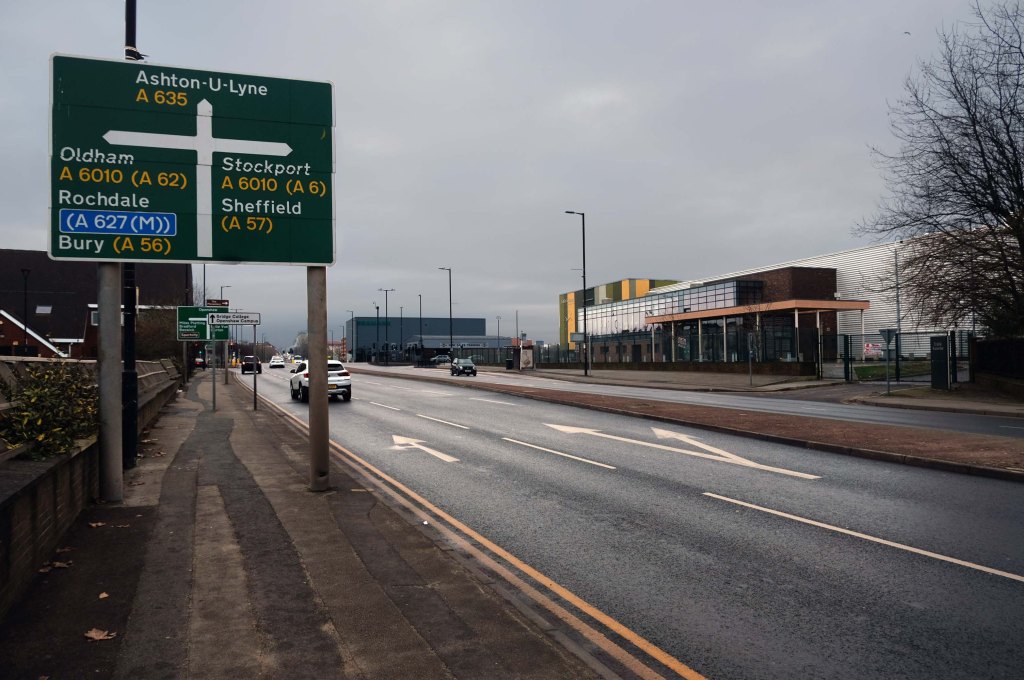
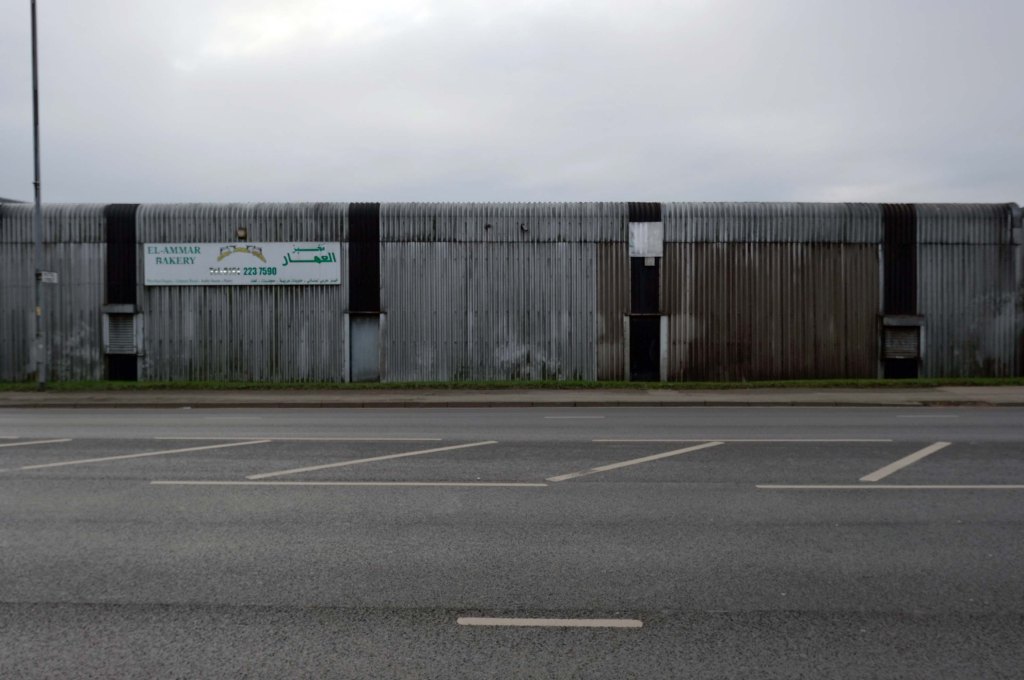
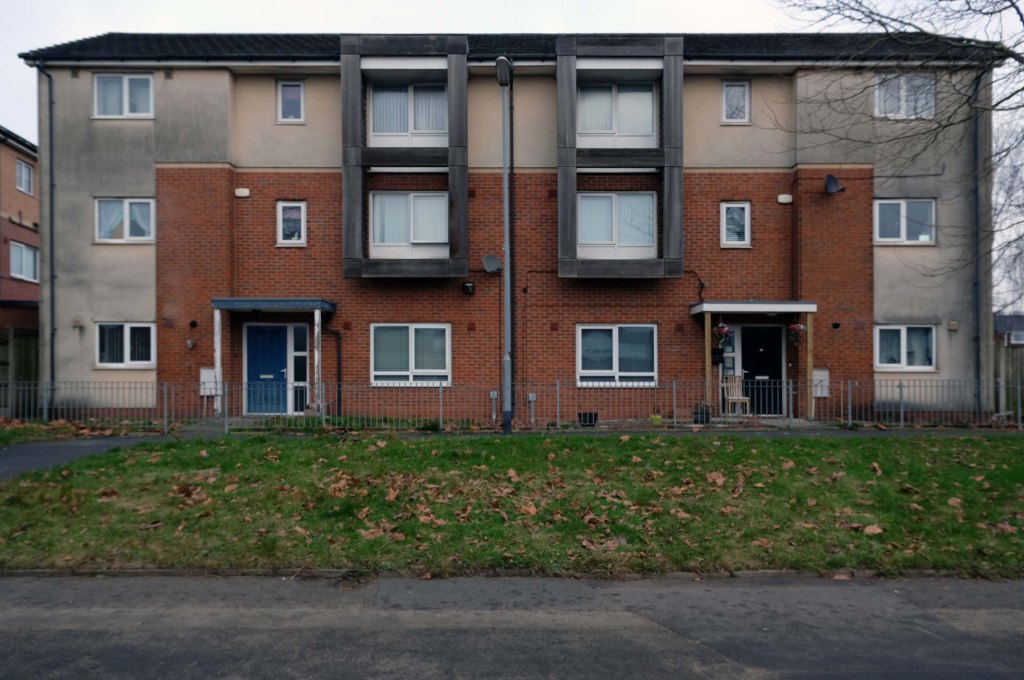
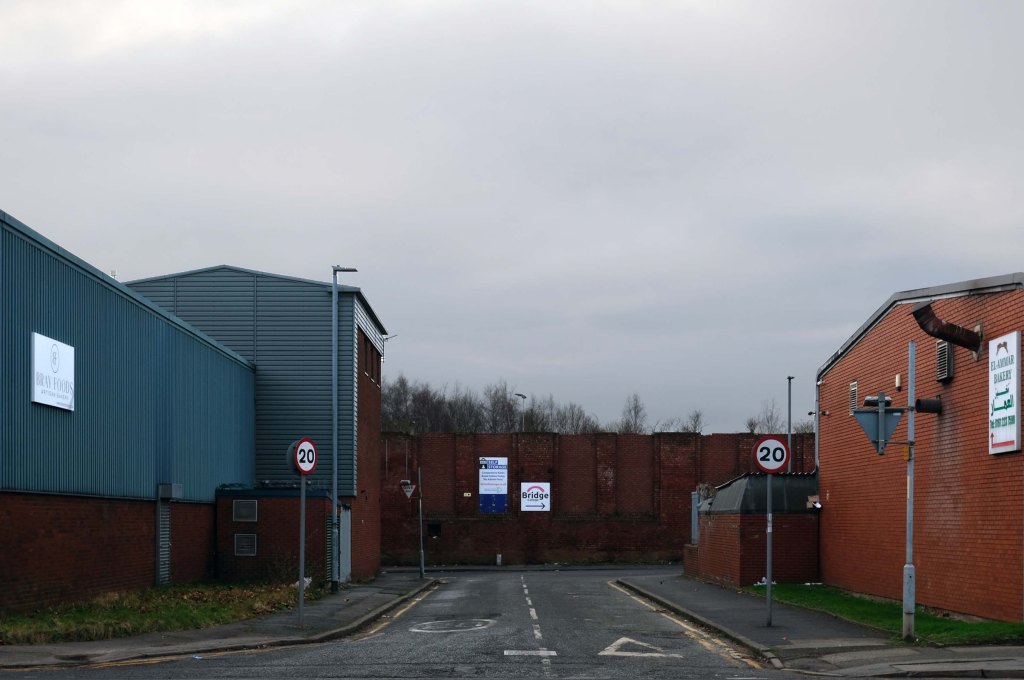
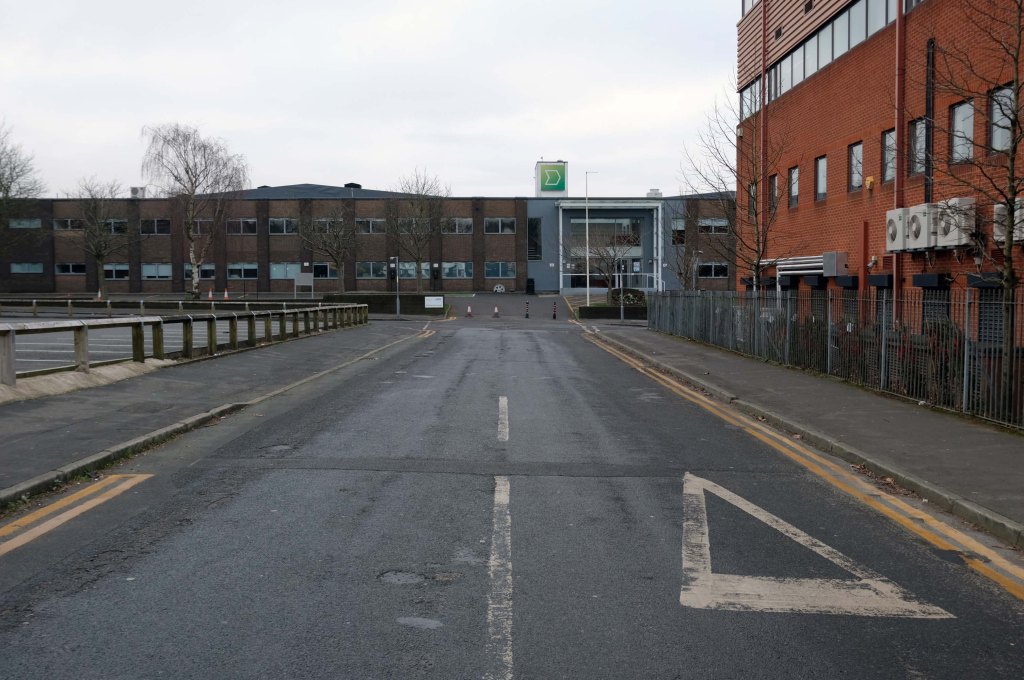
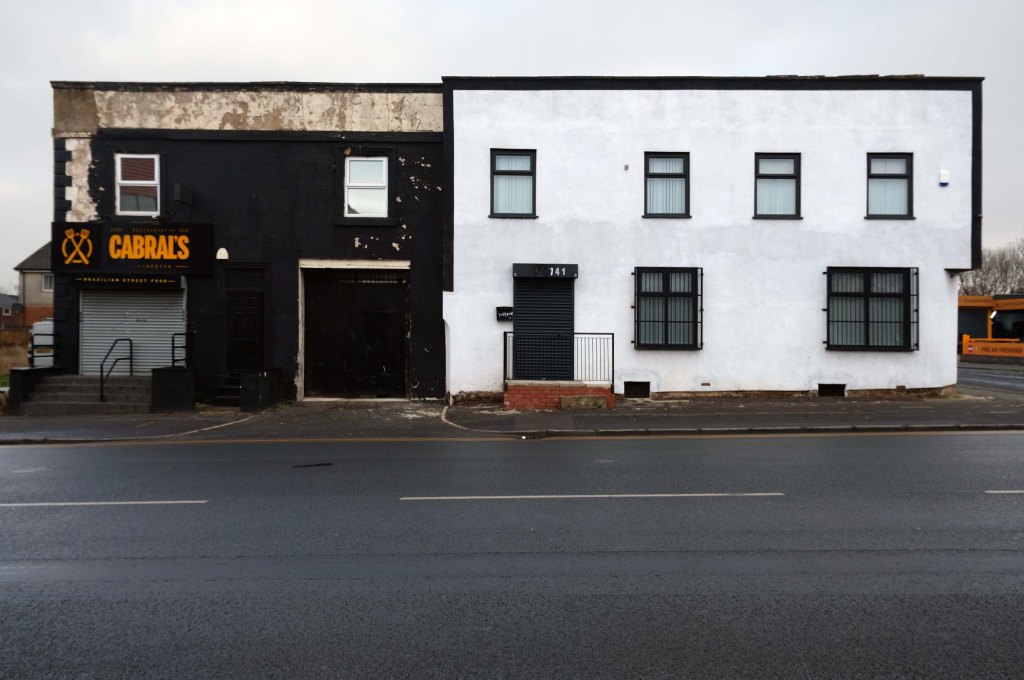
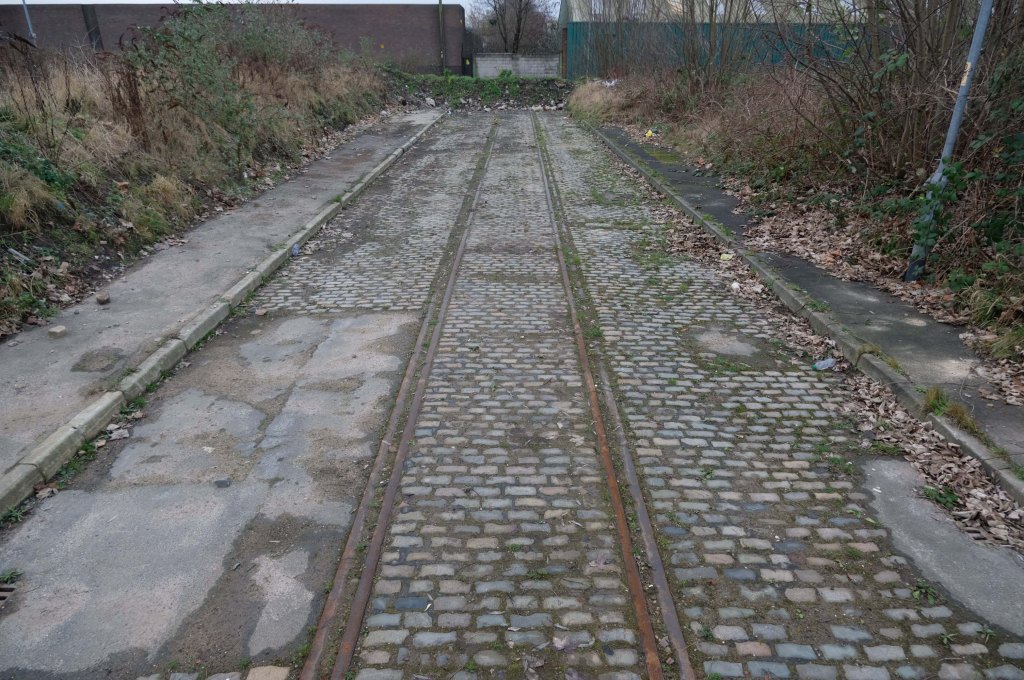
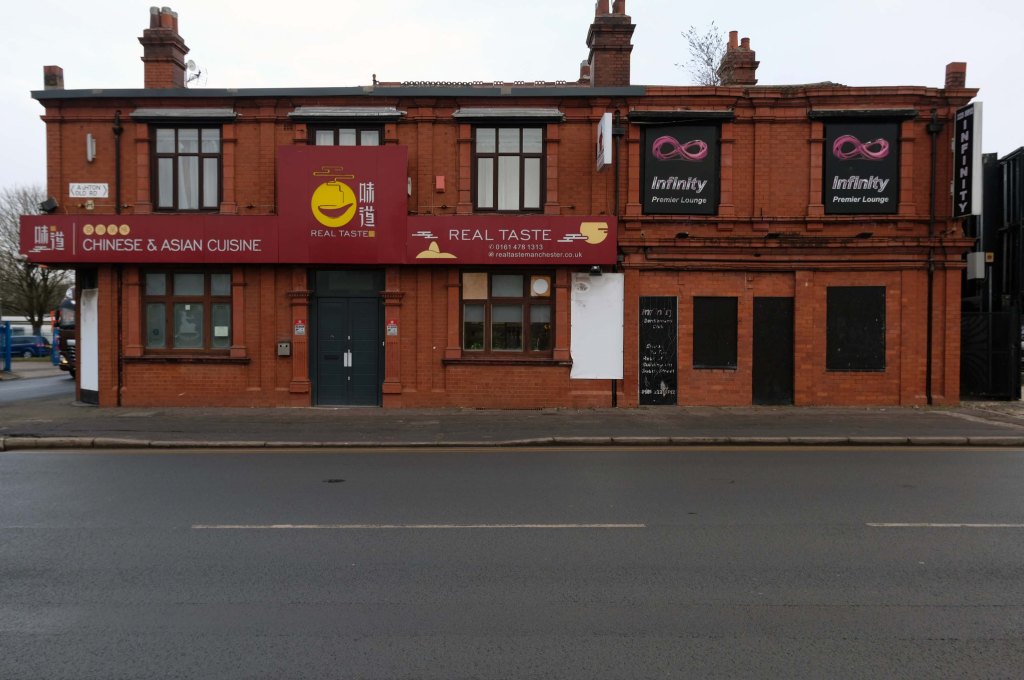
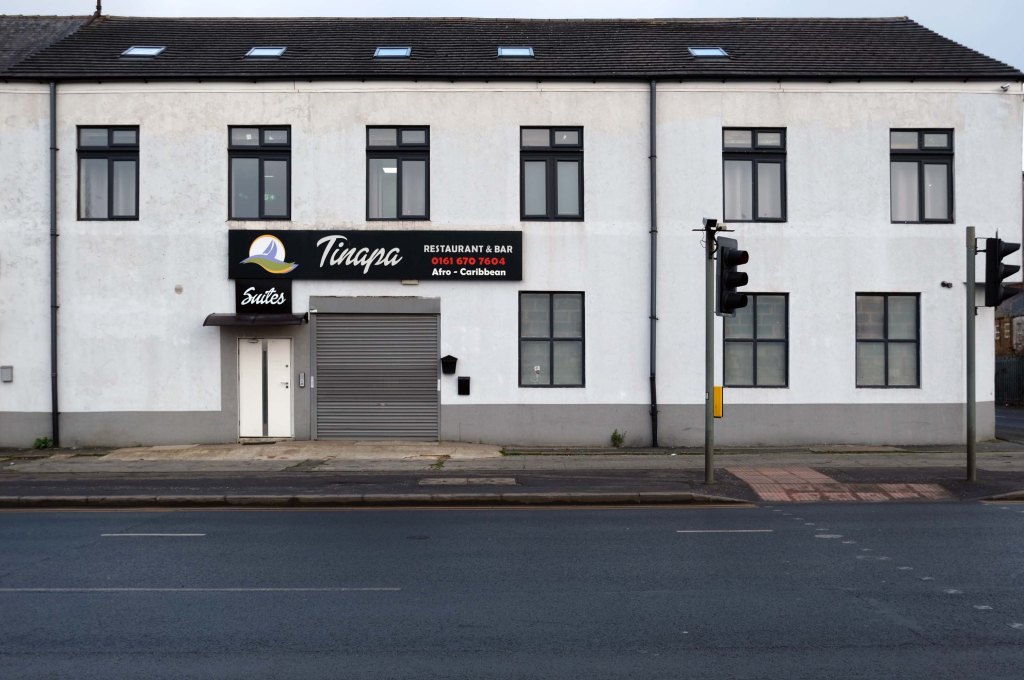
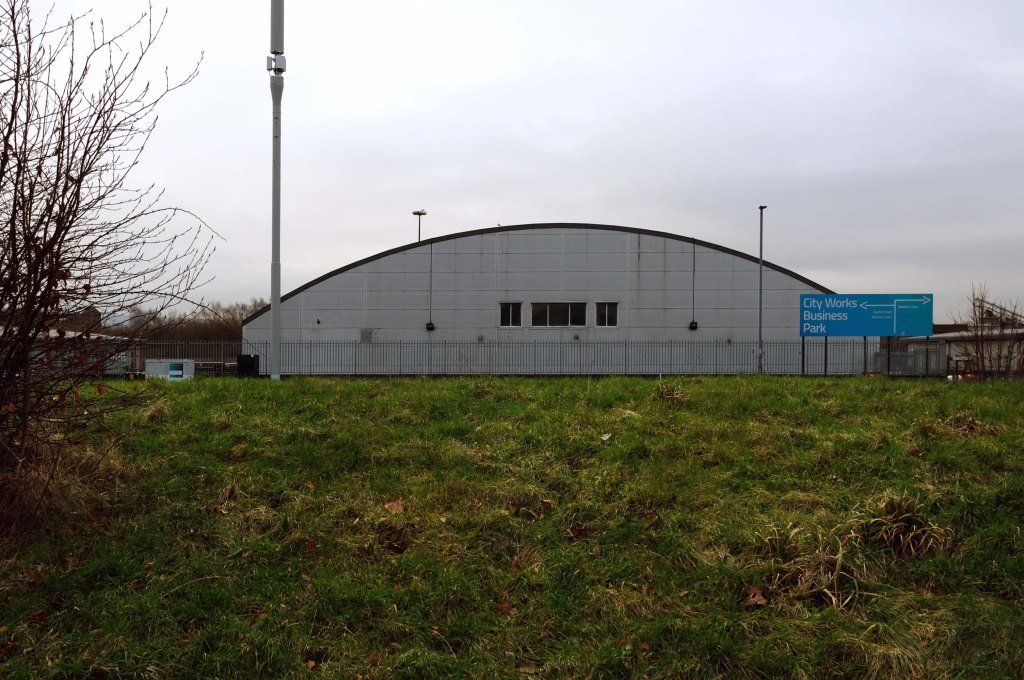
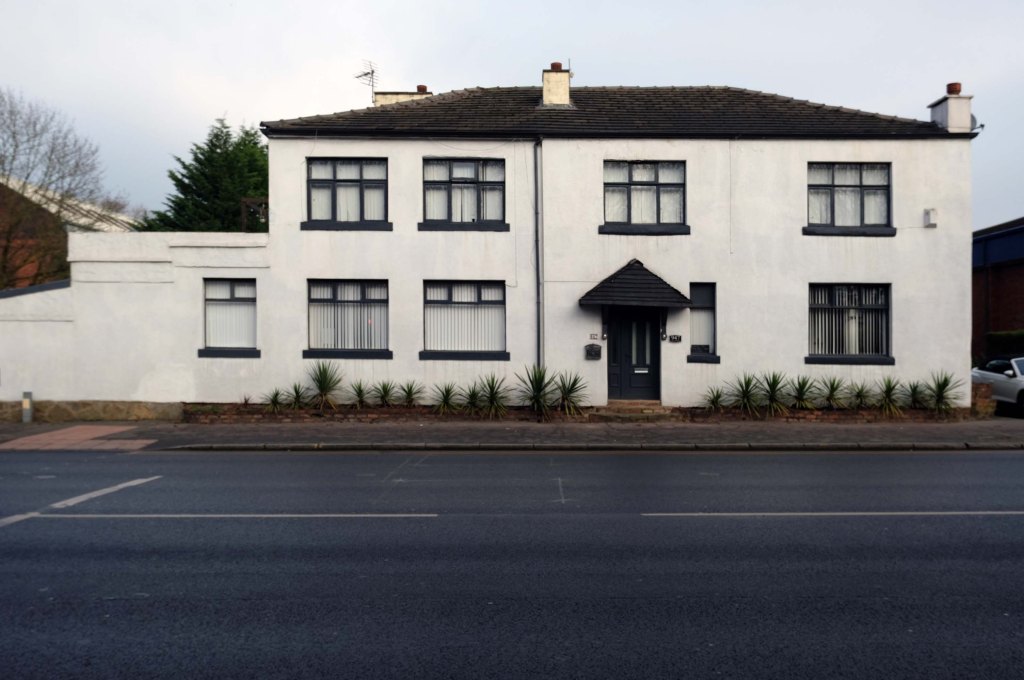
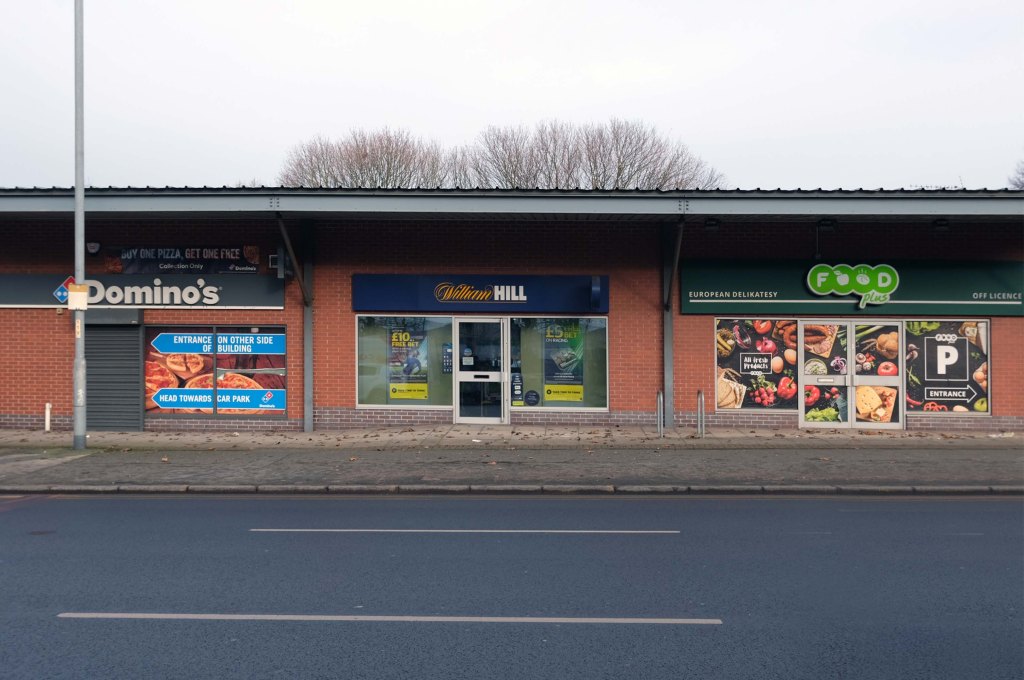
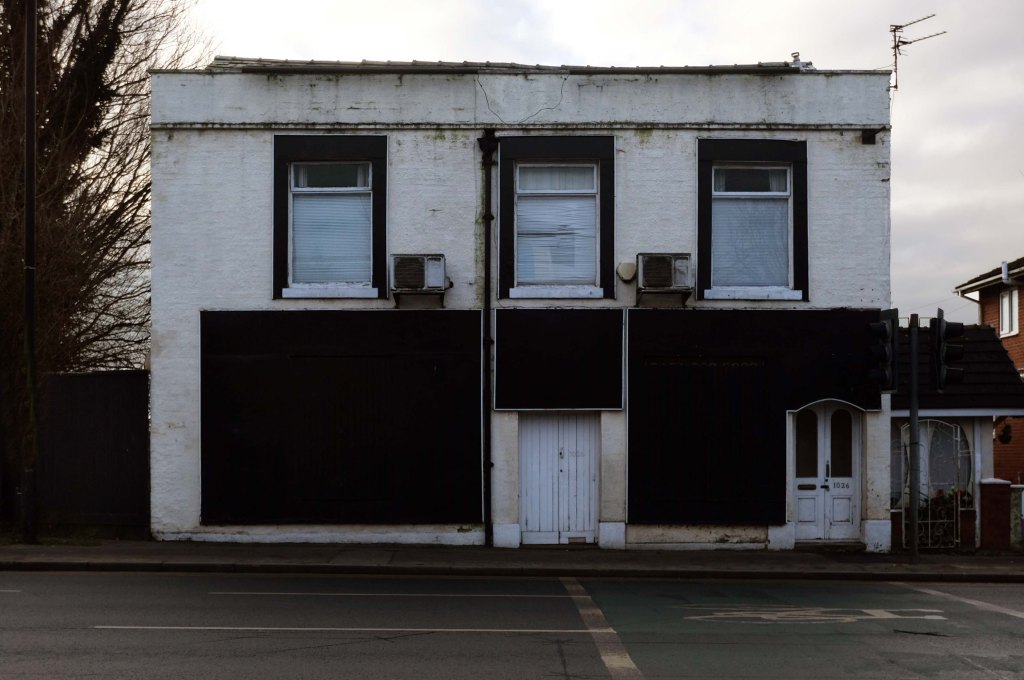
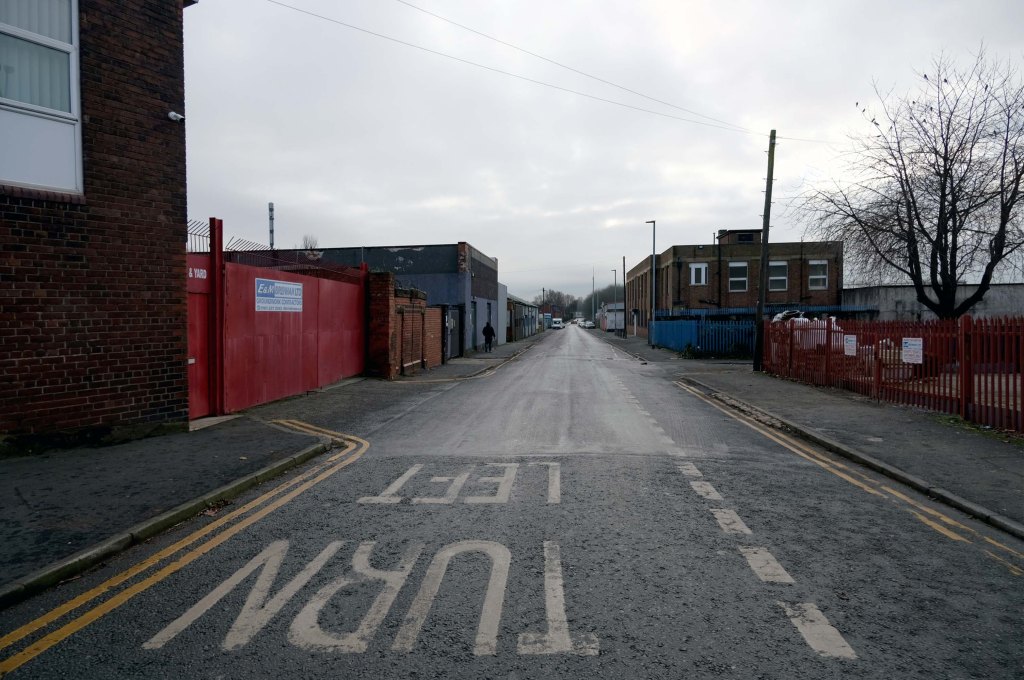
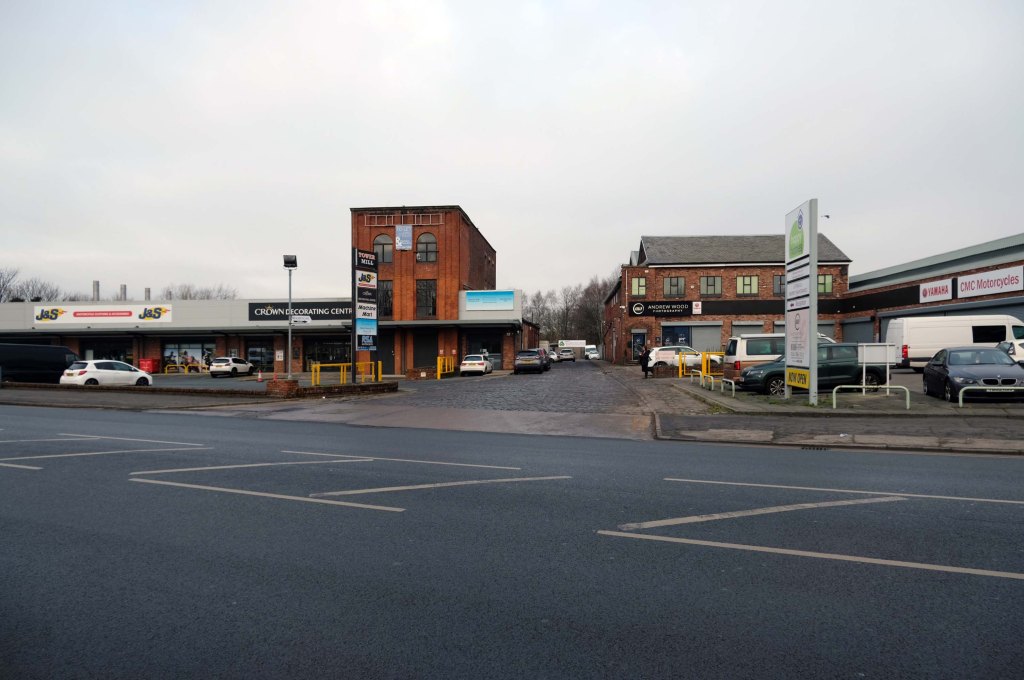
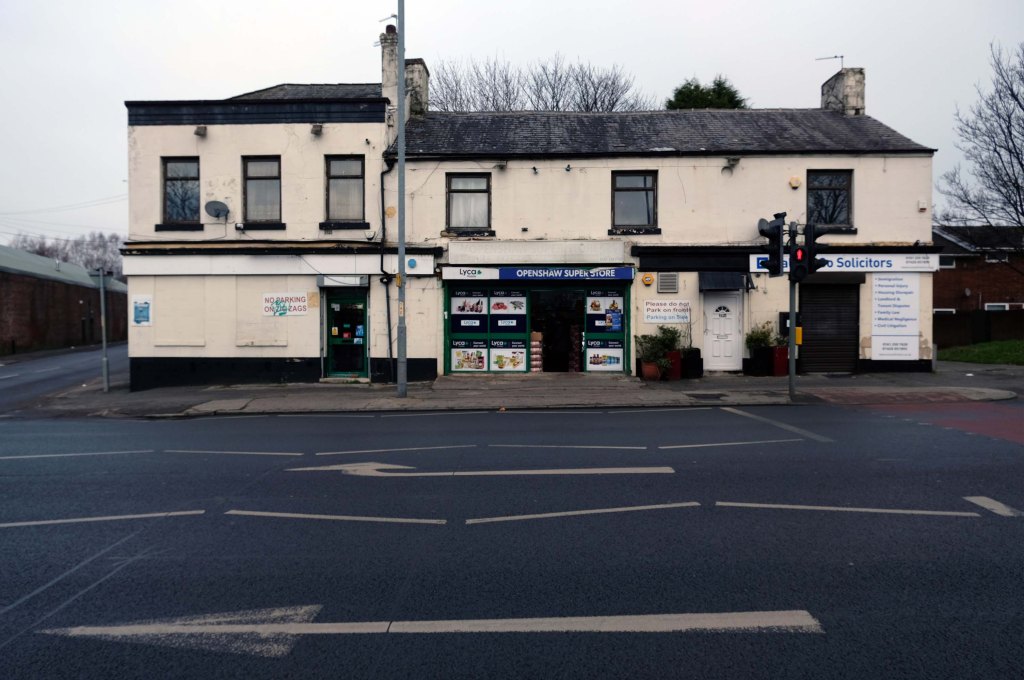
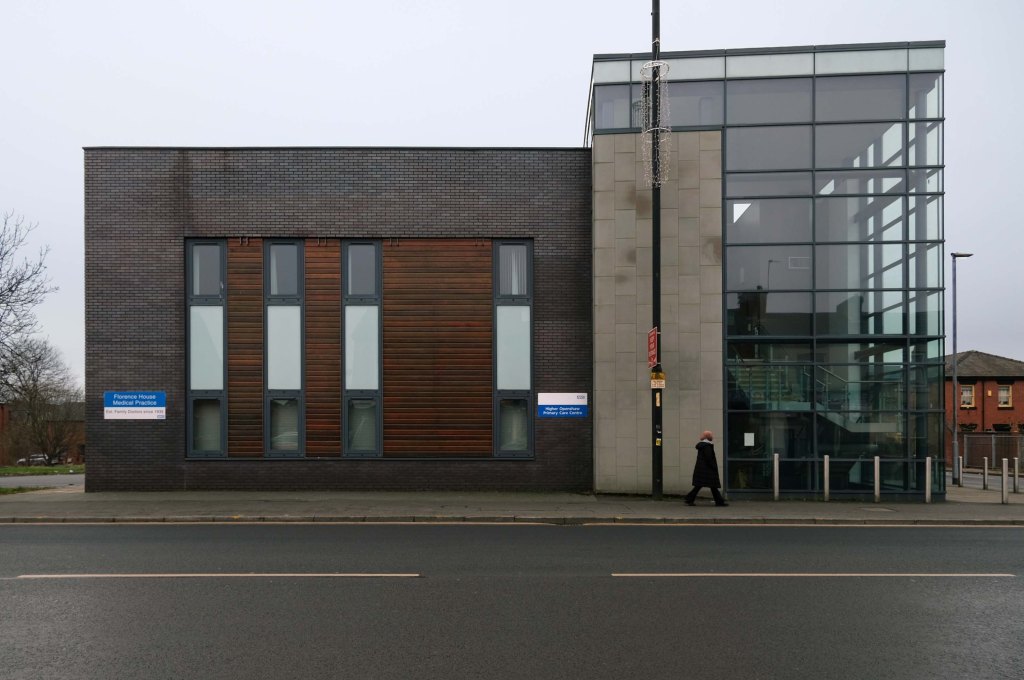
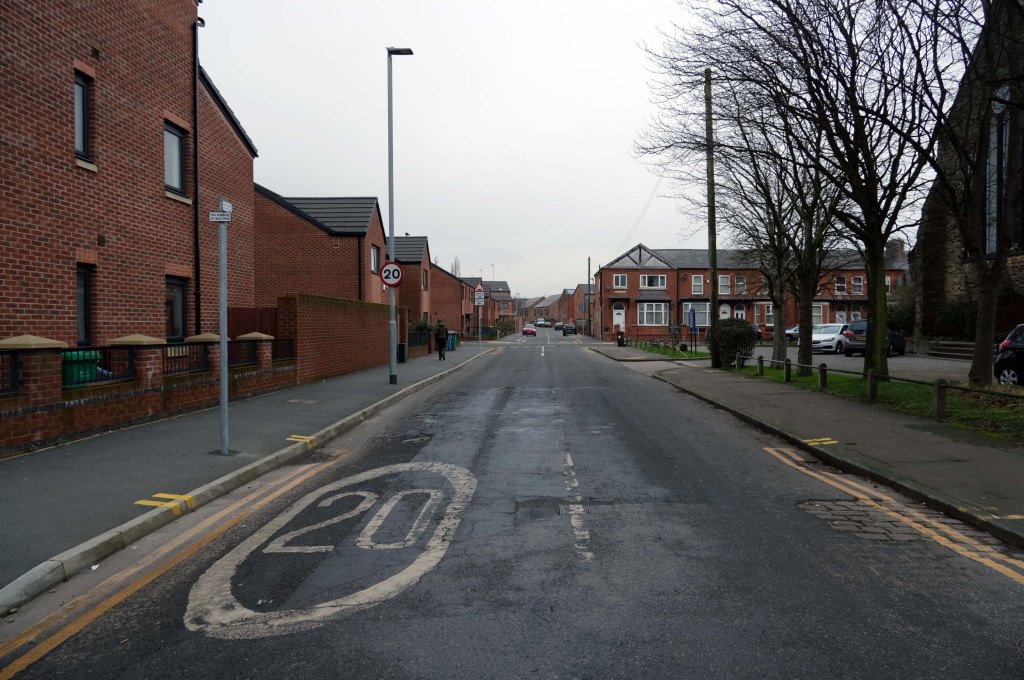
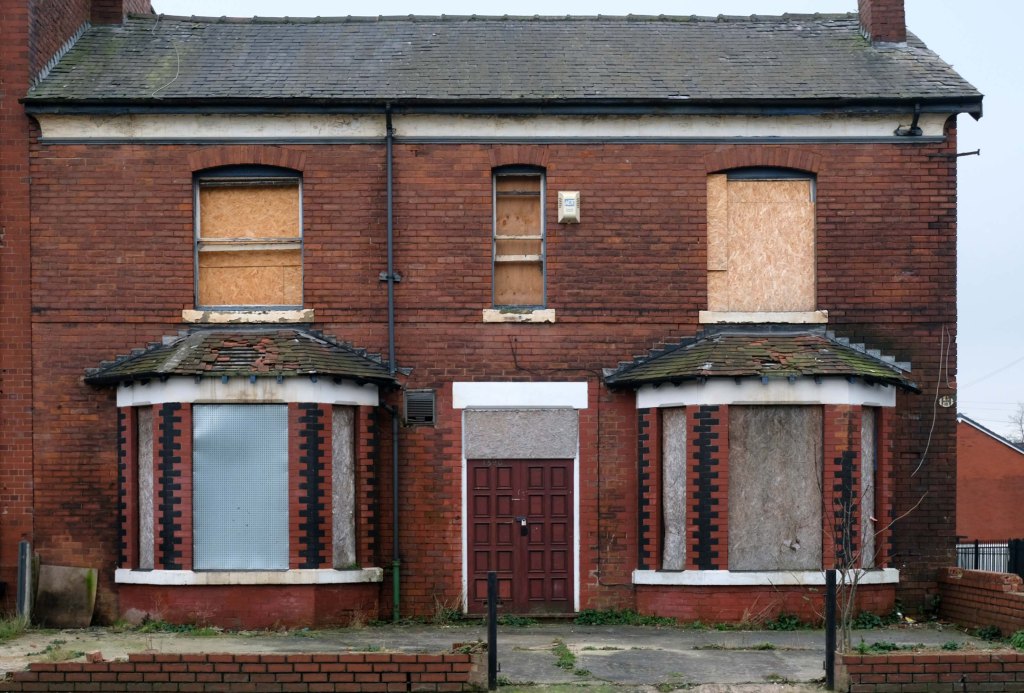
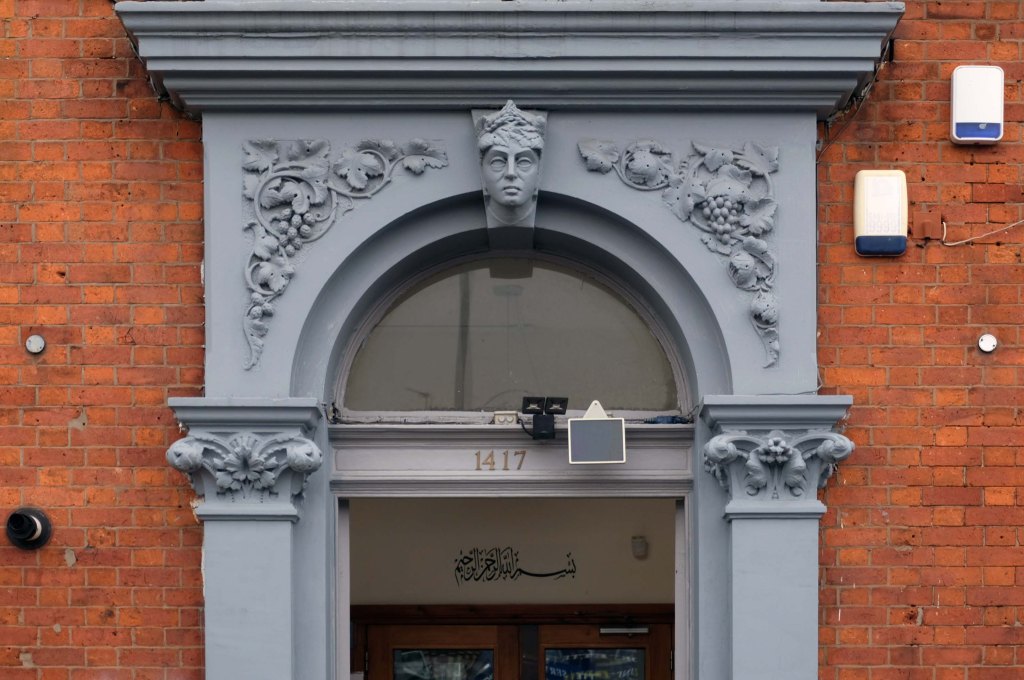
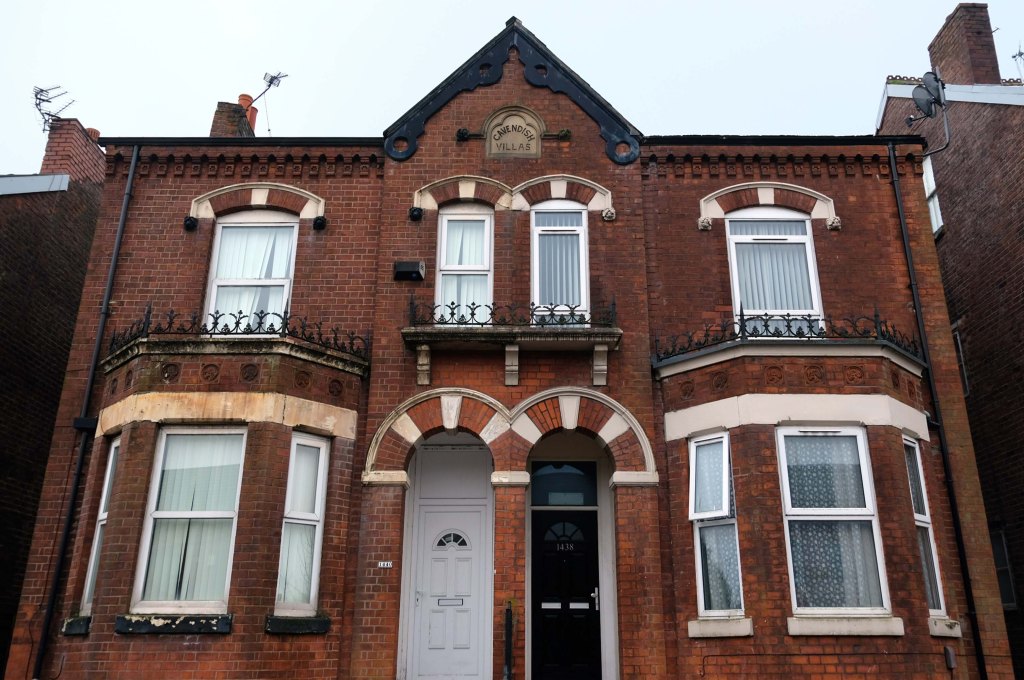
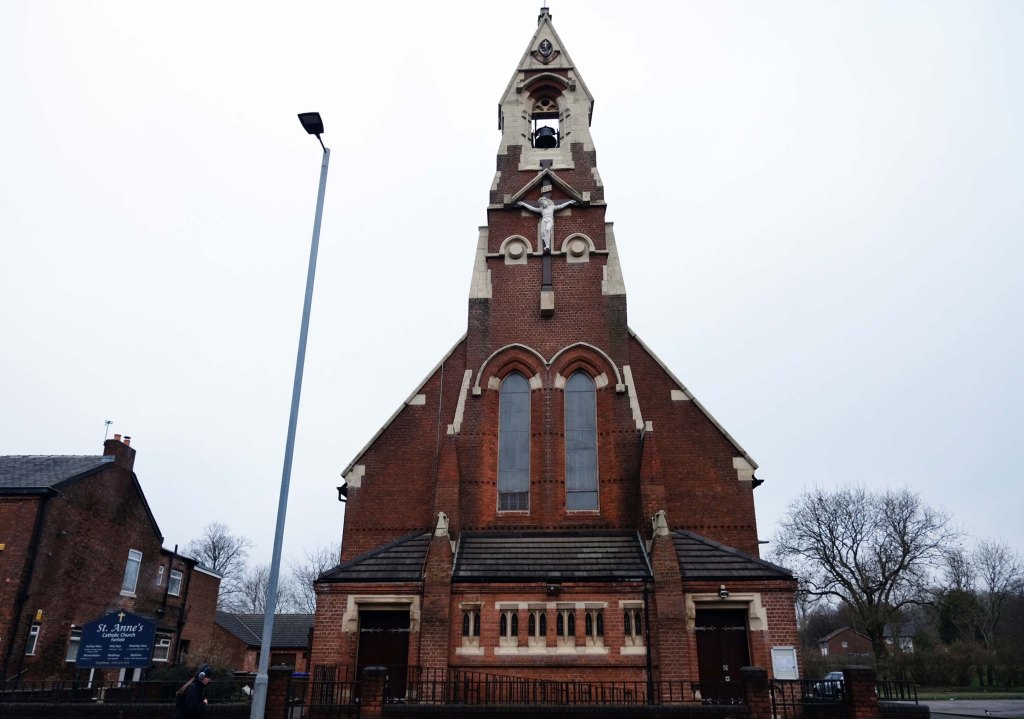
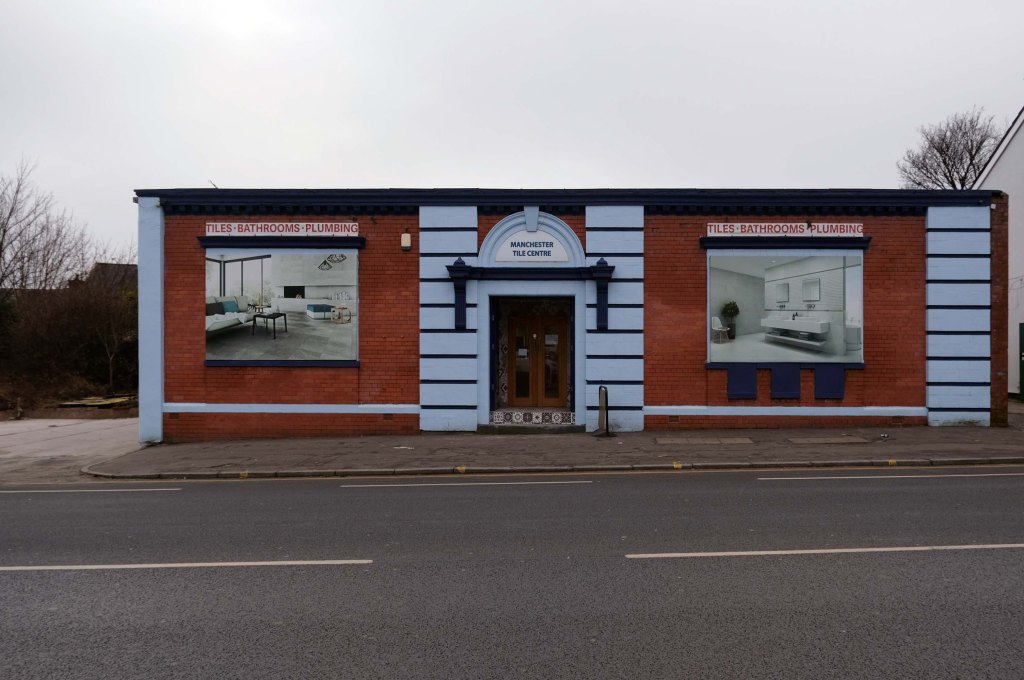
















































































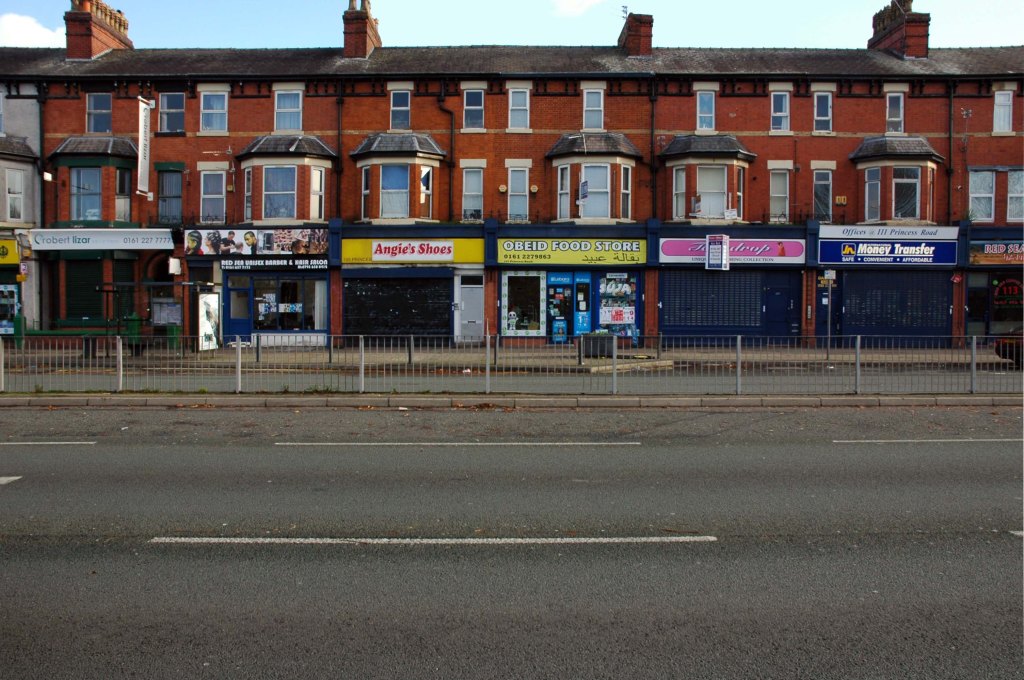
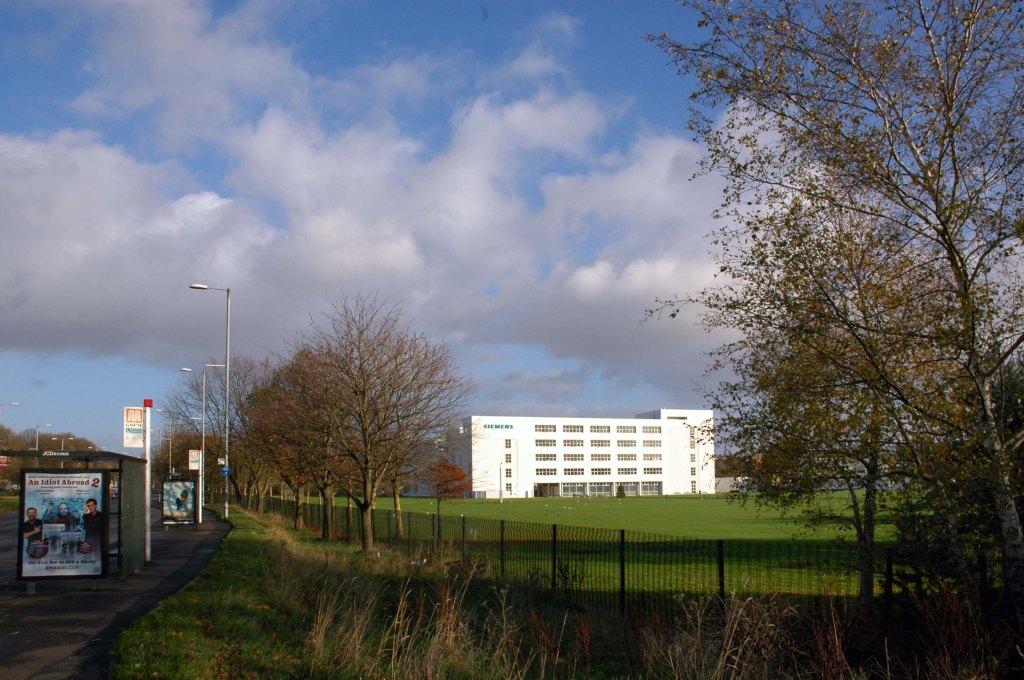
The A5103 is a major thoroughfare running south from Piccadilly Gardens in Manchester city centre to the M56 in Northenden. The road is two-lane dual carriageway with a few grade-separated junctions. It is used by many as a link to the airport and to the motorway network south.
The road starts at Piccadilly Gardens where it meets the A6. It heads along Portland Street – at one time it ran along the parallel Mosley Street, past fast-food outlets and off-licences and then meets the A34 Oxford Street. It multiplexes with that road north for 200 yards into St Peter’s Square and then turns left into Lower Mosley Street, initially alongside the tramlines and then past the former Manchester Central station, now a conference centre with the same name. The road becomes Albion Street and goes over the Bridgewater Canal and under the railway line east of Deansgate station. The road then meets the A57(M) Mancunian Way at a roundabout interchange. This is where most of the traffic joins and leaves.
The road is now 2×2 dual carriageway with the name Princess Road. It passes under the Hulme Arch, a grade-separated junction with the A5067, with an unusually large central reservation. This is presumably because of the proposed plans from the 1960s of a motorway. However, after passing under the junction, there are innumerate sets of traffic lights, with the B5219, the A6010 and the A5145, as well as many other unsigned roads. There are also many speed cameras set at 30 mph.
The road picks up pace as we exit the sprawl of South Manchester and the road becomes Princess Parkway, with a 50 mph speed limit. We cross the River Mersey and almost immediately hit the M60 at J5.
Except for the Manchester City Centre section – which was numbered A5068, this road did not exist on classification in 1922. Princess Road was built in 1932 to serve the new southwestern suburbs; initially it ran between the B5219 and A560 and was numbered B5290, with the road later extended north into the A5068 on the southern edge of the city centre and renumbered A5103.
The northern extension through Hulme initially followed previously existing roads, so followed a zigzag route. As part of the road’s upgrade and the reconstruction of Hulme in the 1970s the road was straightened and the original route can no longer be seen. The A5068 was severed around this time with the construction of the A57(M) and the A5103 took on its city-centre section, taking it to the A6.
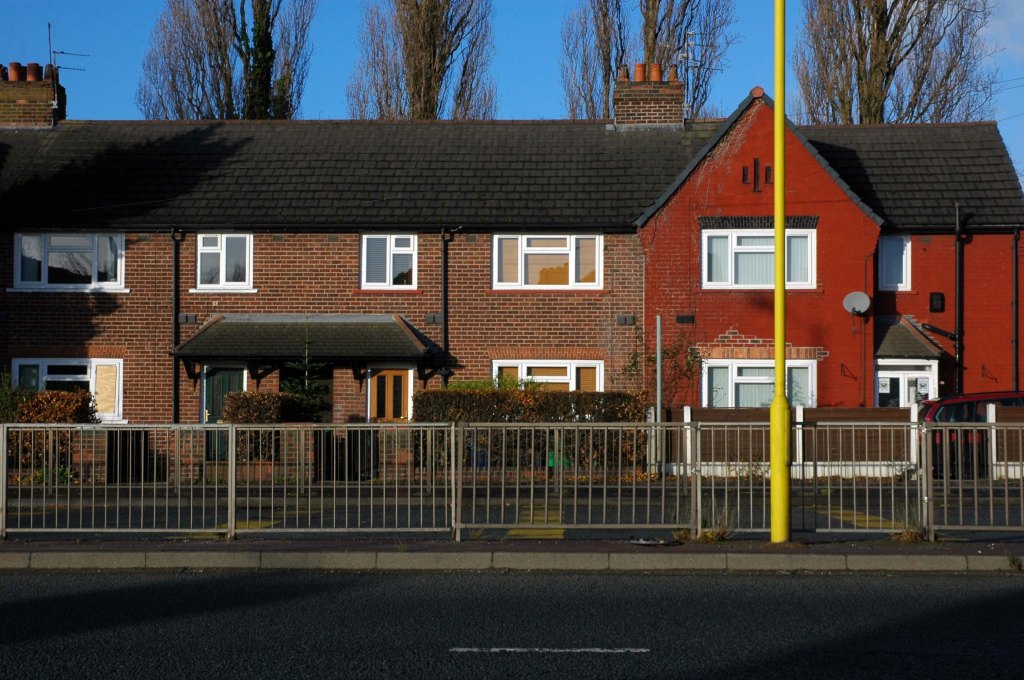
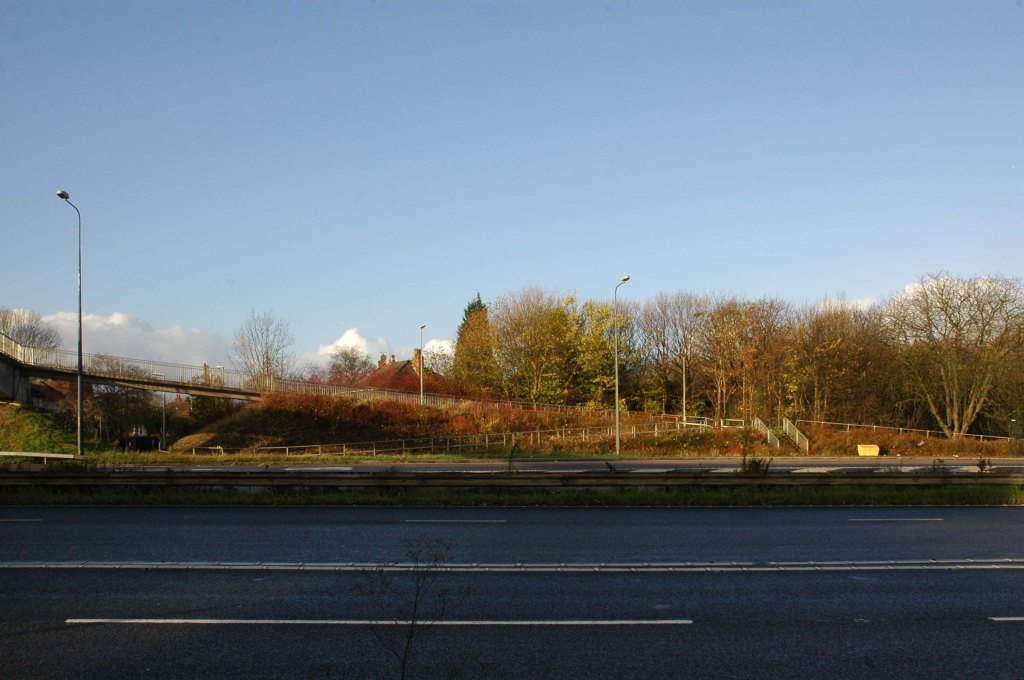


















































See also Bury New Road and Cheetham Hill Road and Rochdale Road and Oldham Road and Ashton New Road and Ashton Old Road and Hyde Road and Stockport Road and Kingsway.


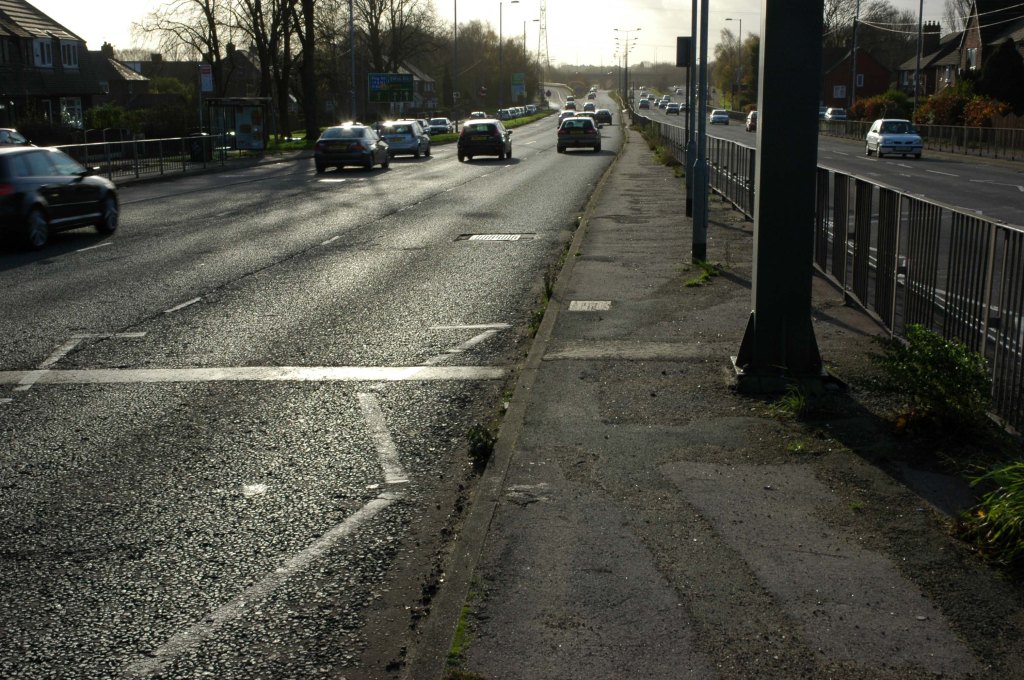
The A6 is Britain’s fourth longest road. Its route varies greatly from the lower lands of the South East, though the Peak District, right though the heart of Manchester city centre, then onwards towards Preston. It then goes though the historic city of Lancaster before skirting the Eastern fringe of the Lake District before ending in Carlisle, bang on the start of the A7.
North from Stockport towards Manchester, the A6 was a wide, four lane road, but still 30 mph, which usually flowed pretty well. According to Mudge, it looks like it has now been massacred by bus lanes and red paint. Shame. We meet the A57 from the east, just south of the city centre, and multiplex until we reach Mancunian Way, the A57 heading off as a short urban motorway, the A6 heading into the city centre via London Road/Piccadily, where it loses its number and vanishes. It would have gone straight down Piccadily/Market Street to meet Deansgate, and then across the River Irwell into Salford, and up Chapel Street, where the number reappears. Market Street has been pedestrianised for years, so the A6 has long ceased to be a through route.
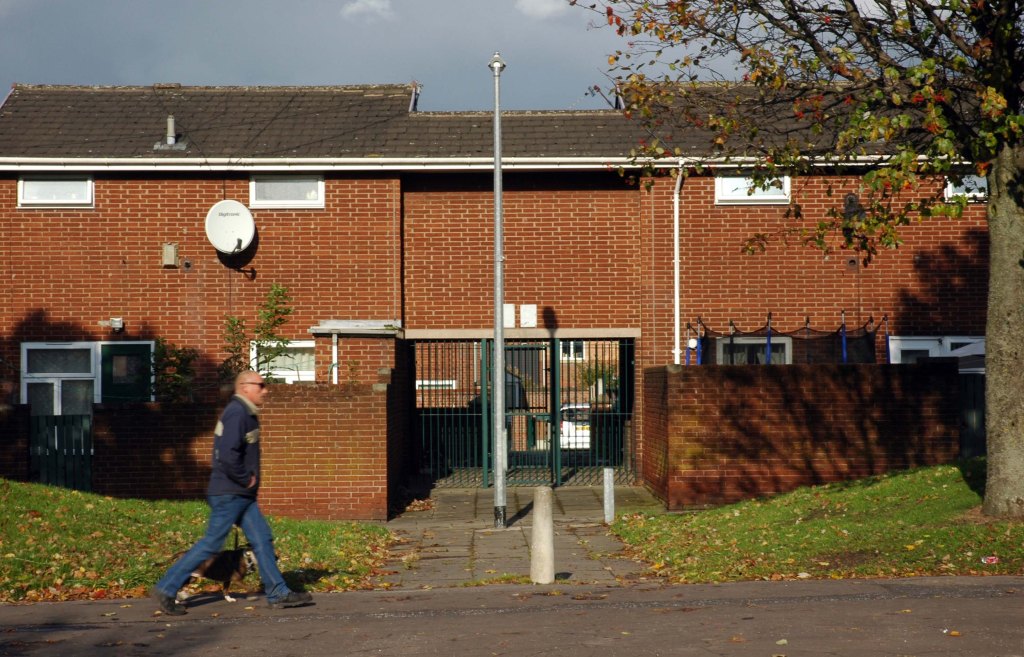
In 2014, having taken early retirement from teaching photography, I embarked on a series of walks along the arterial roads of Manchester.
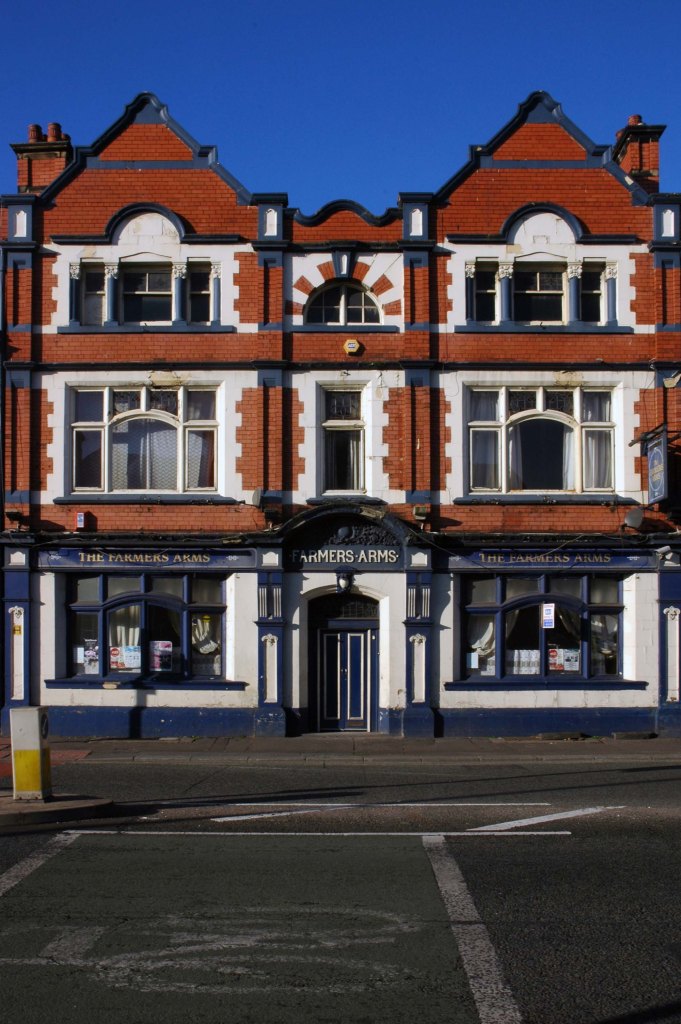
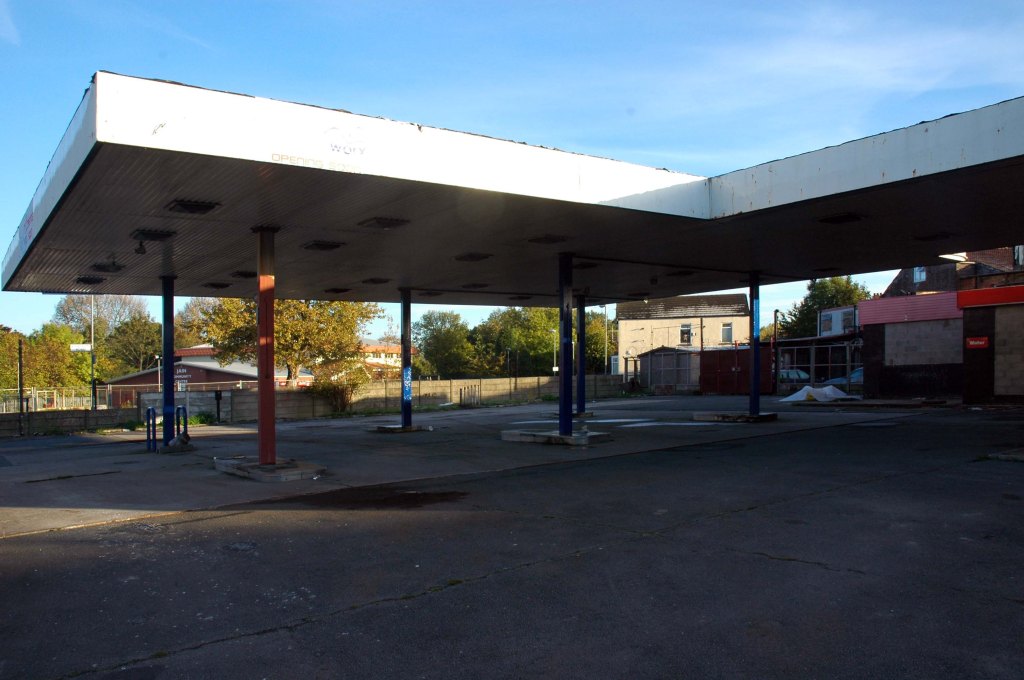
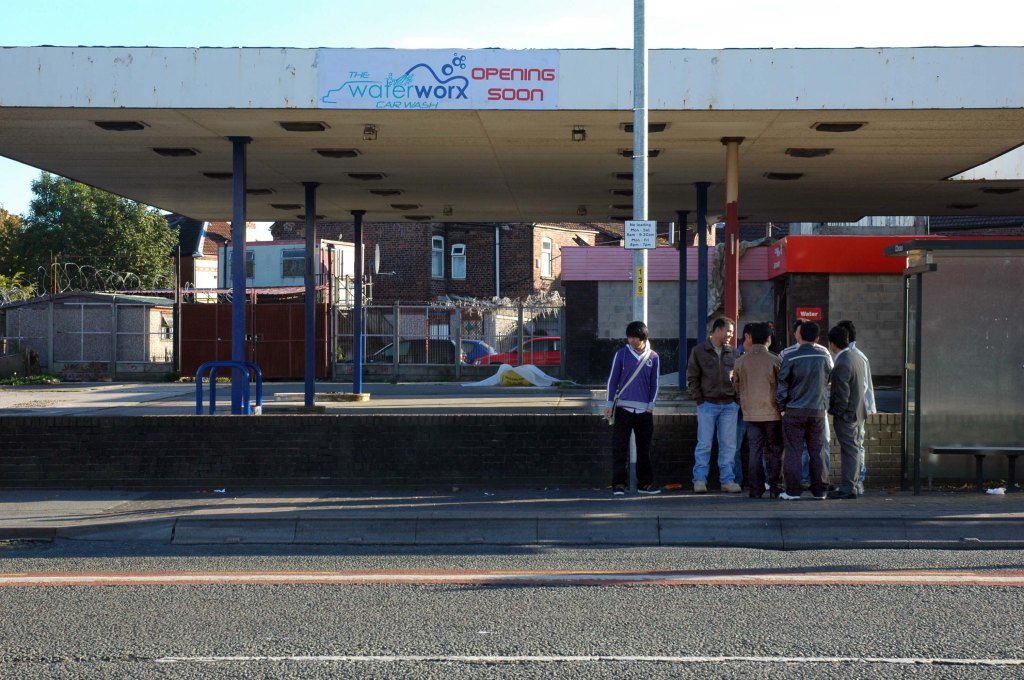
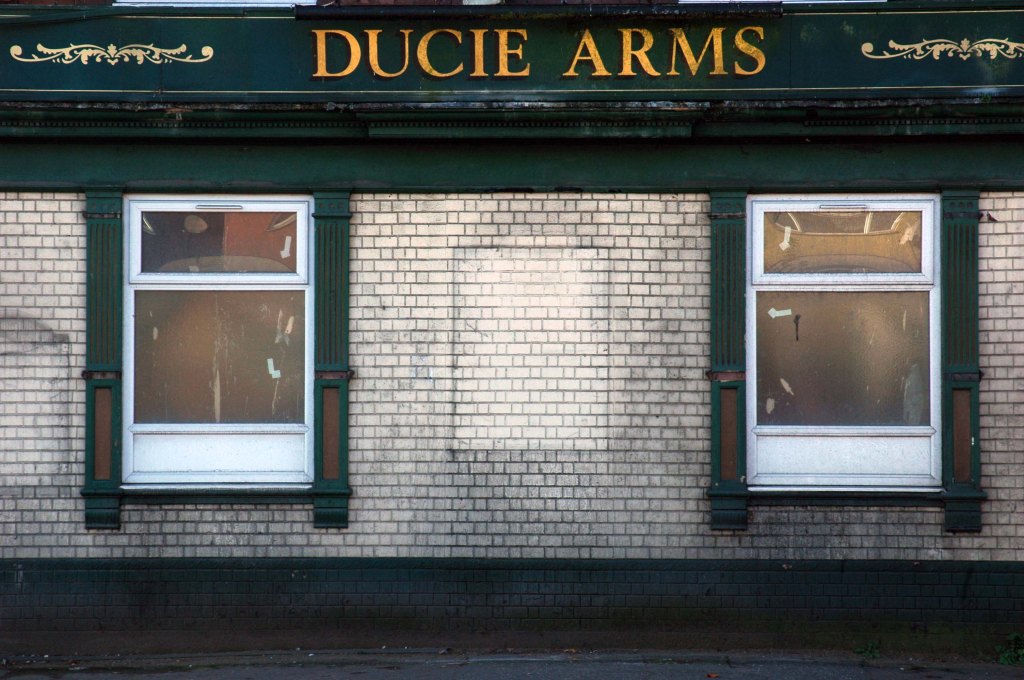
































See also Bury New Road and Cheetham Hill Road and Rochdale Road and Oldham Road and Ashton New Road and Ashton Old Road and Hyde Road.


The A57 was nearly a coast to coast route. It passes through three major city centres (Liverpool, Manchester, and Sheffield – with elevated sections in each) and several smaller ones, multiplexes with the A6 and the A1, follows the banks of two canals and negotiates the remotest part of the Peak District. In one city it part of it is a tram route, whilst in another its former route is also a tram route. After all these adventures, it sadly gives up just 40 miles short of the east coast, Lincoln apparently proving too big an obstacle.
The A57 crosses the River Irwell at Regent Bridge before entering its moment of motorway glory as the A57(M) Mancunian Way skirting the south of Manchester’s city centre on an elevated section and crossing the A56 and A34. This includes a half-completed exit that goes the wrong way up Brook Street – a one way street. The original A57 ran further north through the city centre along Liverpool Road (now the A6143) and Whitworth Street – B6469 as far as the A6 London Road which marked the start of a multiplex.
At the end of Mancunian Way, we reach a TOTSO, straight on being the short unsigned A635(M) and thence the A635 – for Saddleworth Moor, Barnsley and Doncaster whilst the A57 turns south, briefly multiplexing with the A6, and then branching off along Hyde Road. This section of road was extensively cleared for the westward extension for the M67, and consequently has seen a lot of redevelopment.
In 2014, having taken early retirement from teaching photography, I embarked on a series of walks along the arterial roads of Manchester.





















































See also Bury New Road and Cheetham Hill Road and Rochdale Road and Oldham Road and Ashton New Road and Ashton Old Road.


The road now begins slightly further south than it used to. Instead of starting on Fairfield Street in Manchester city centre, it begins immediately as the Mancunian Way ends, which at this point is the unsigned A635(M). The motorway flows directly into our route. There’s a TOTSO right at a set of lights, and we pick up the old alignment, which now starts as the B6469.
We can see the new City of Manchester Stadium on the left, site of the 2002 Commonwealth Games and now home to Manchester City FC. The road switches between S2 and S4 as it passes through the rather run-down urban areas of Ardwick and Gorton. A short one-way system at a triangular-shaped junction with the A662 leads onto a wider stretch as we near the M60 junction. This area is set to see significant industrial growth, with whole swathes of land either side of the now D3 road cleared and ready for development.
In 2014, having taken early retirement from teaching photography, I embarked on a series of walks along the arterial roads of Manchester.
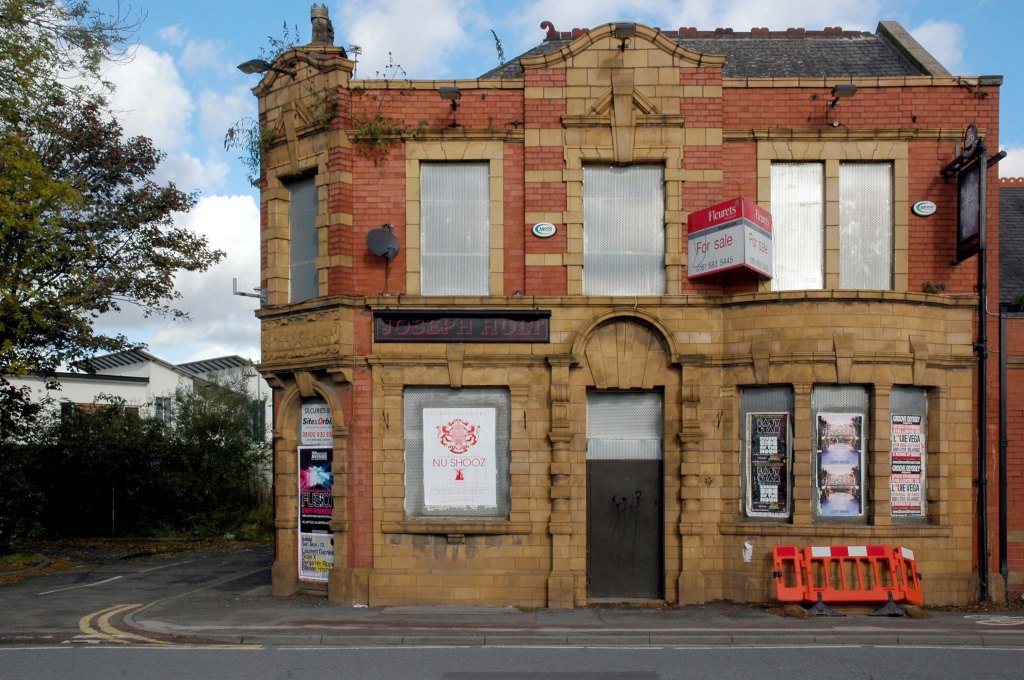
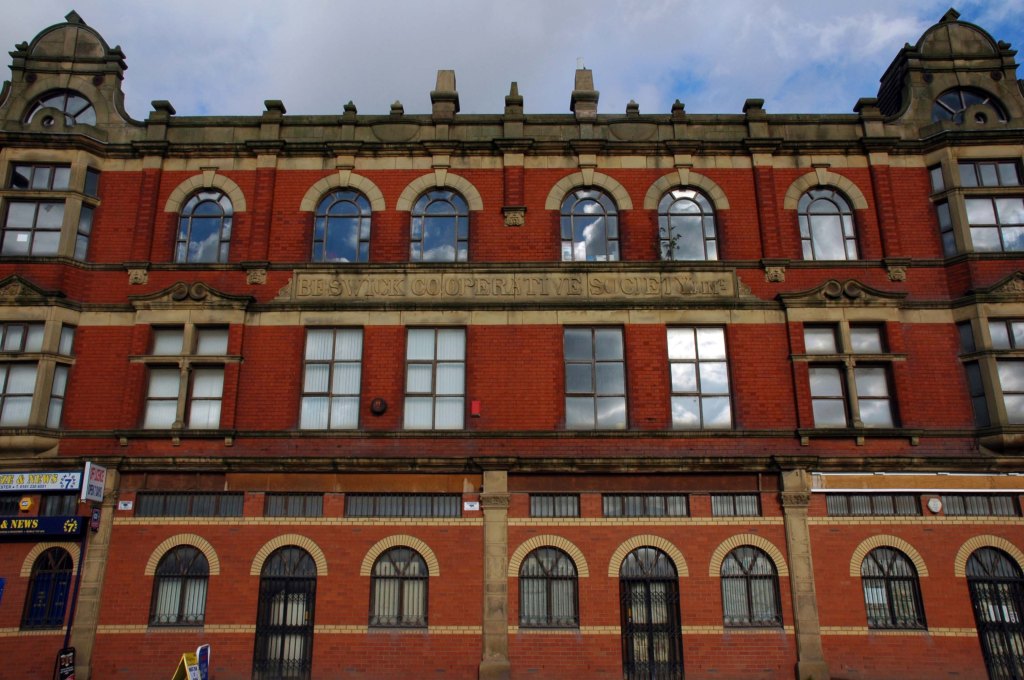
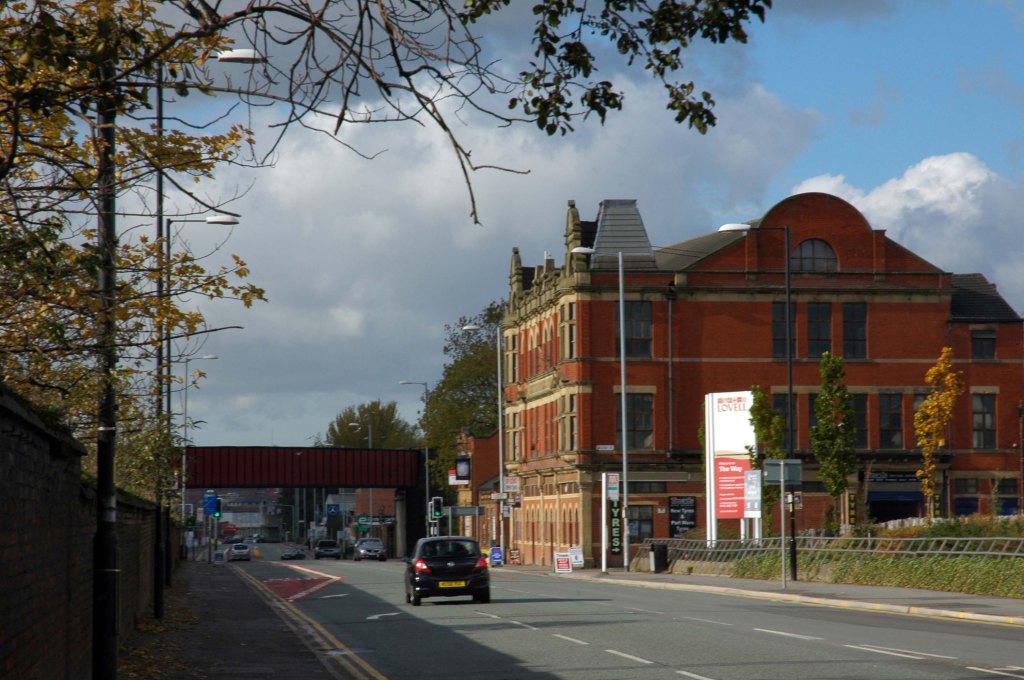
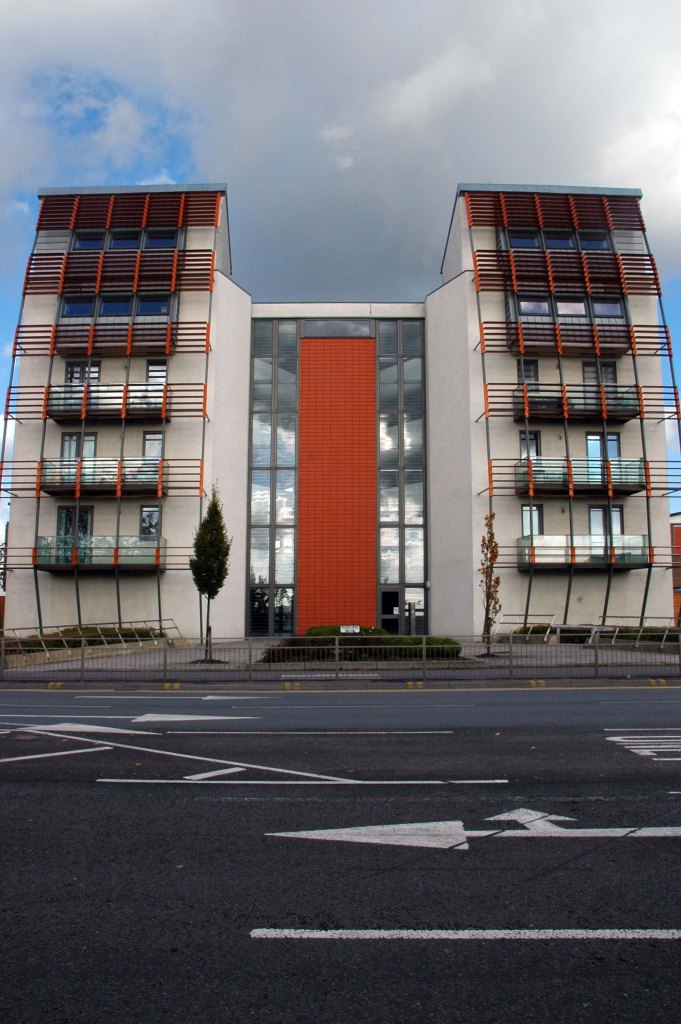
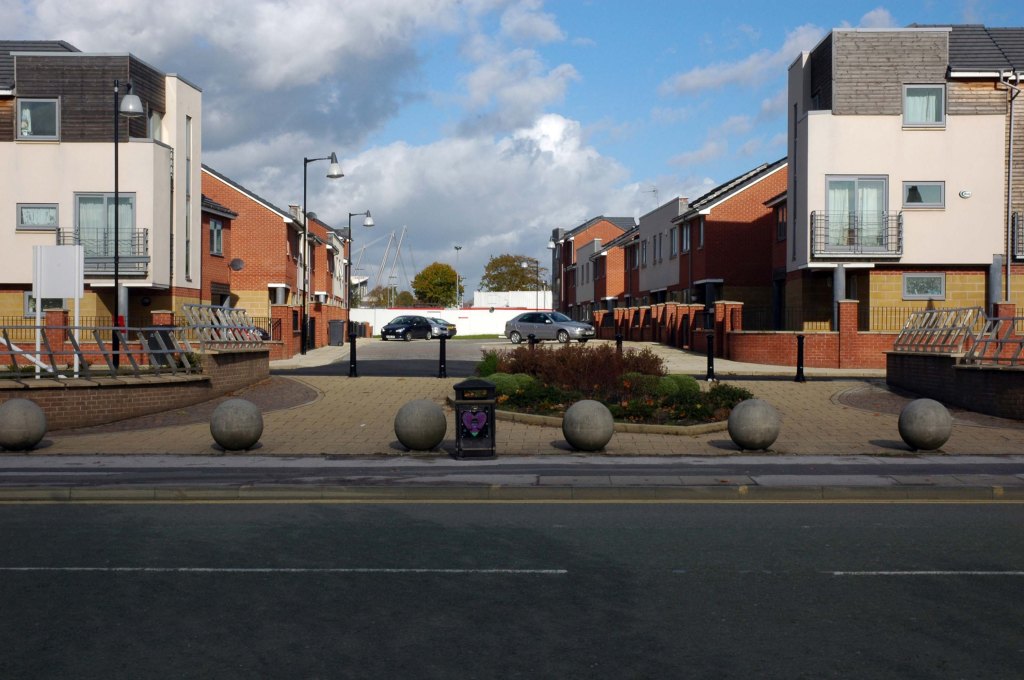
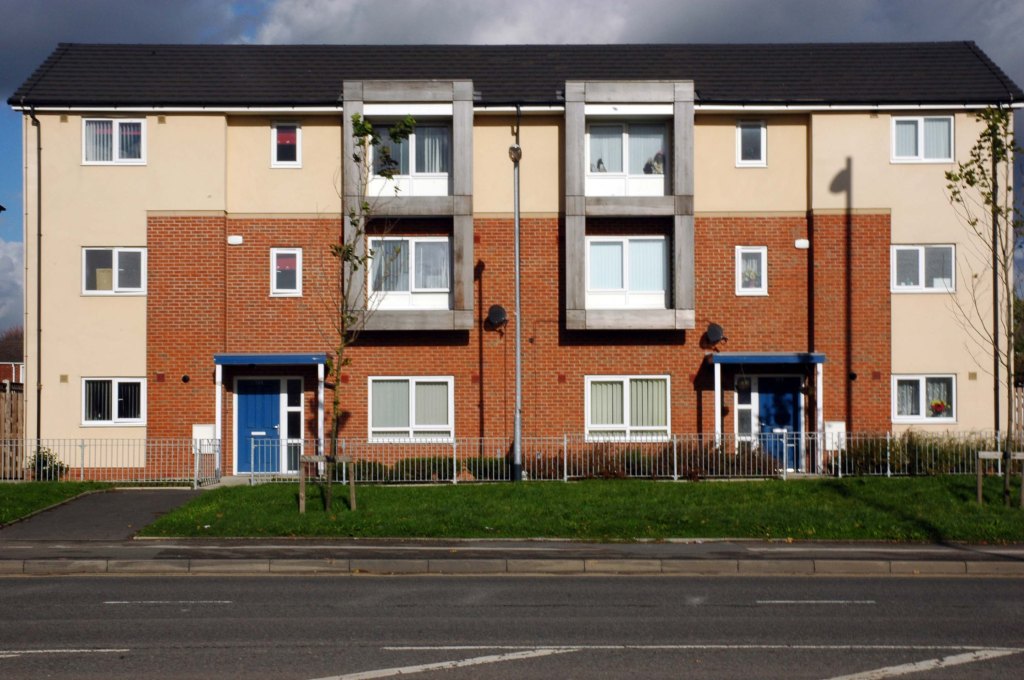
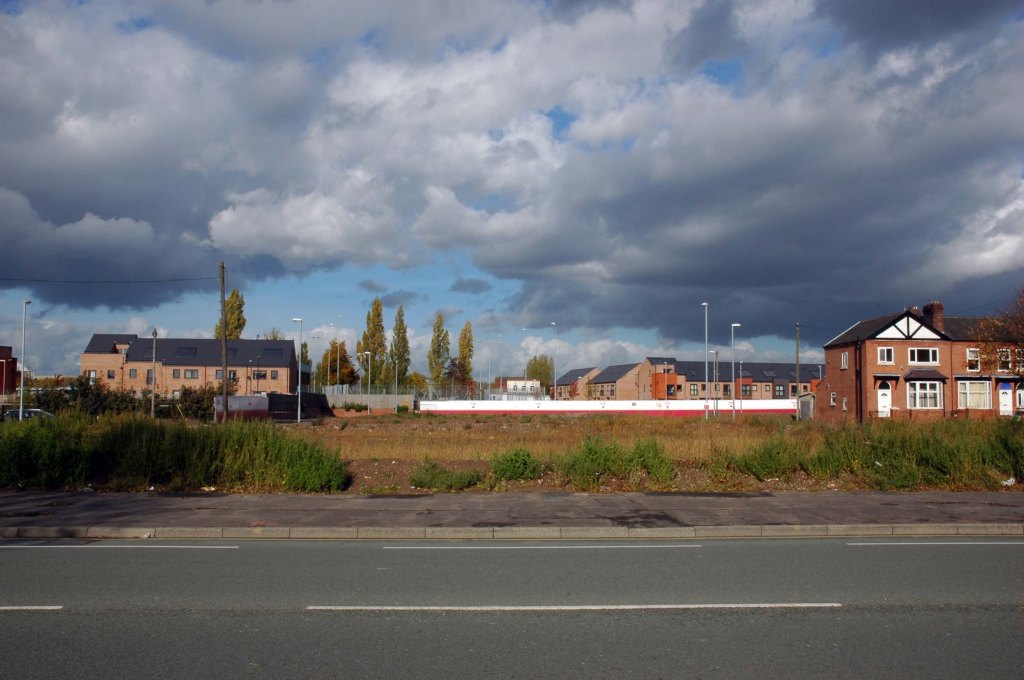
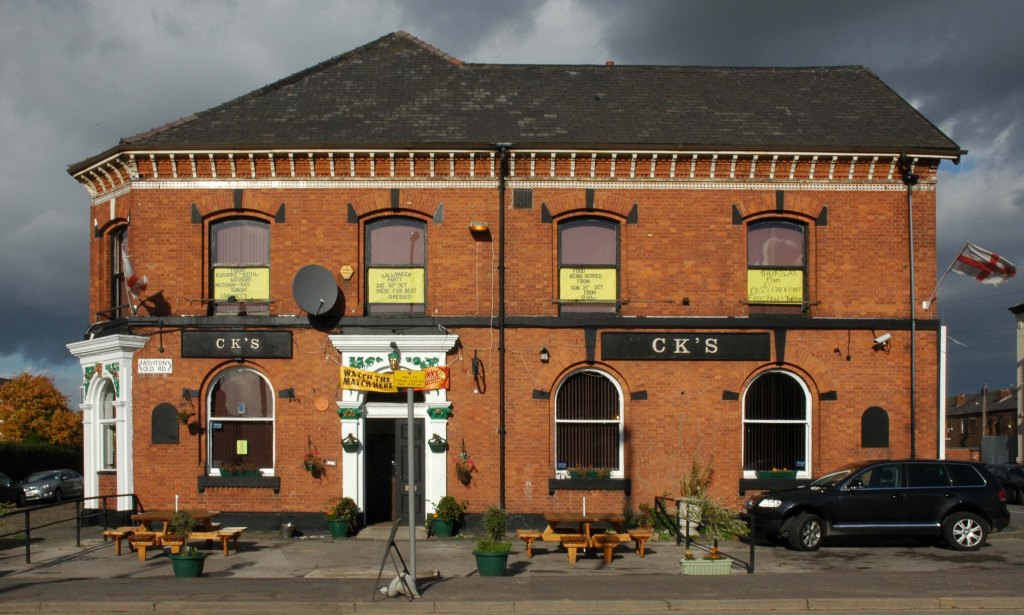
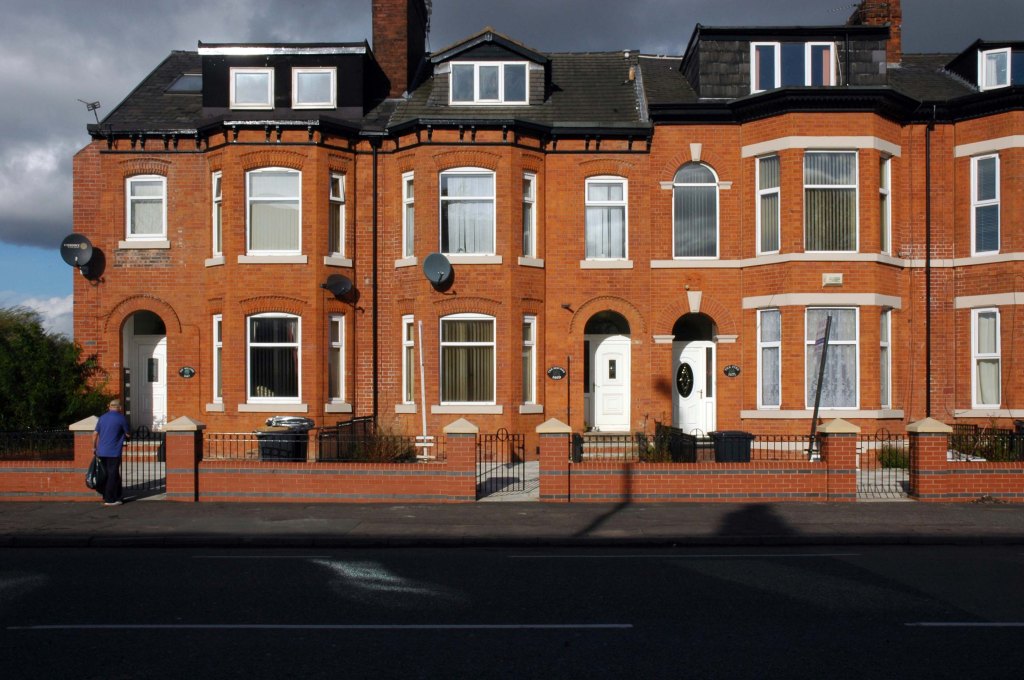
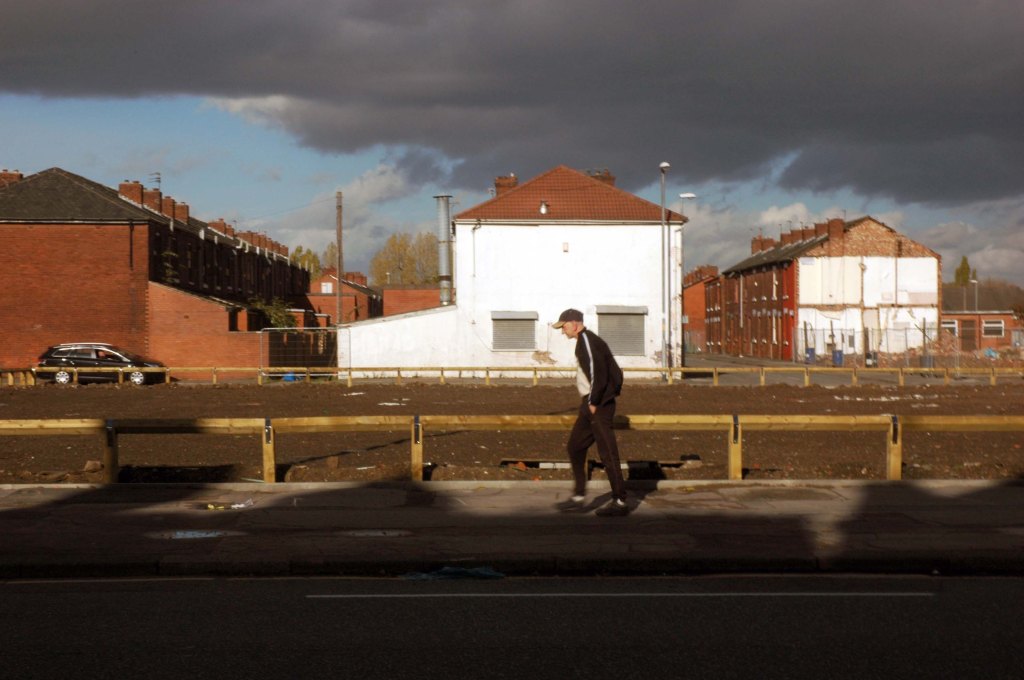




































See also Bury New Road and Cheetham Hill Road and Rochdale Road and Oldham Road and Ashton New Road


Starting at traffic lights on the A665 the road heads northeastwards, initially with the Metrolink on the left and a factory building on the right. The road then bears right at traffic lights marking the first section of on-street running for the trams, which lasts until just before a bridge over the River Medlock, after which the road passes to the south of the Sportcity complex whilst the tram line runs through the middle.
The A6010 is crossed at traffic lights, after which we see the tram lines on the left once more. We go over the Ashton Canal, then the tram lines at grade before bearing to the right to pass Clayton Park before another section of on-street running for the Metrolink begins, which continues for some distance. Just after crossing the Manchester city limit there is a set of traffic lights, after which the road becomes D2 for a short distance to allow a tram stop – Edge Lane, to be located in the central reservation. The tram leaves the road to the right for the next stop – Cemetery Road, and the stop in Droylsden town centre is once again in the central reservation. In all three cases the street running recommences after the stop.
In 2014, having taken early retirement from teaching photography, I embarked on a series of walks along the arterial roads of Manchester.
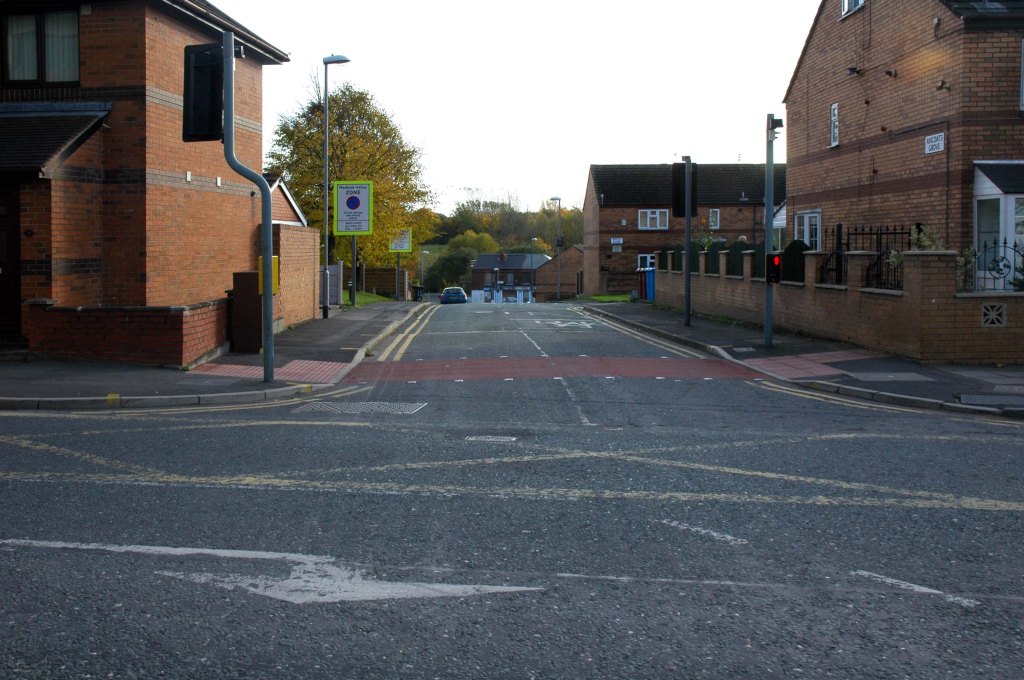
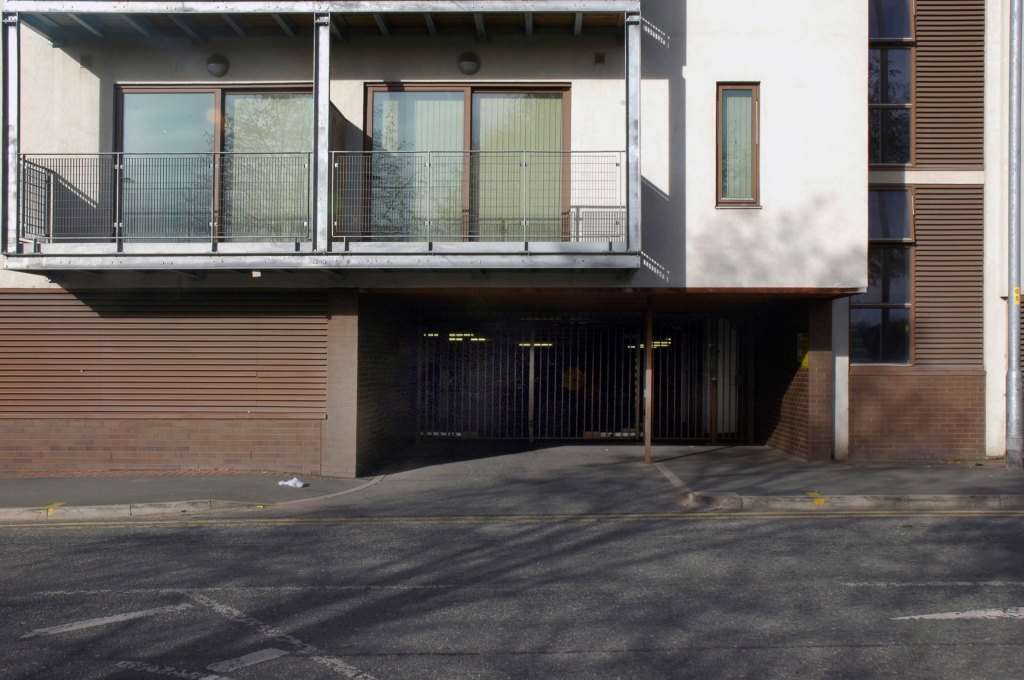
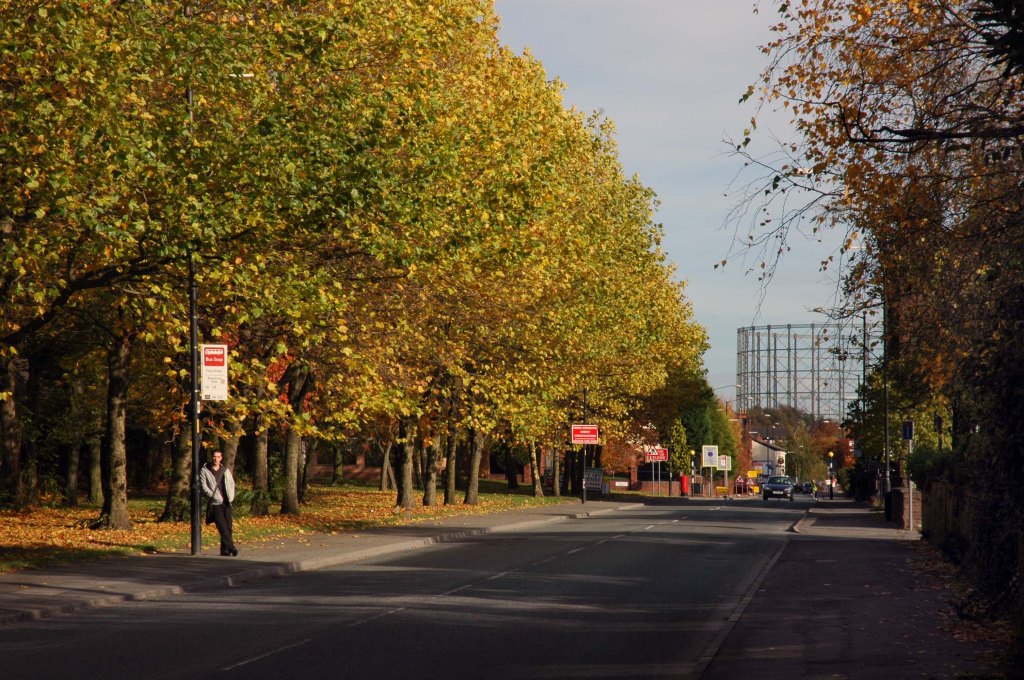
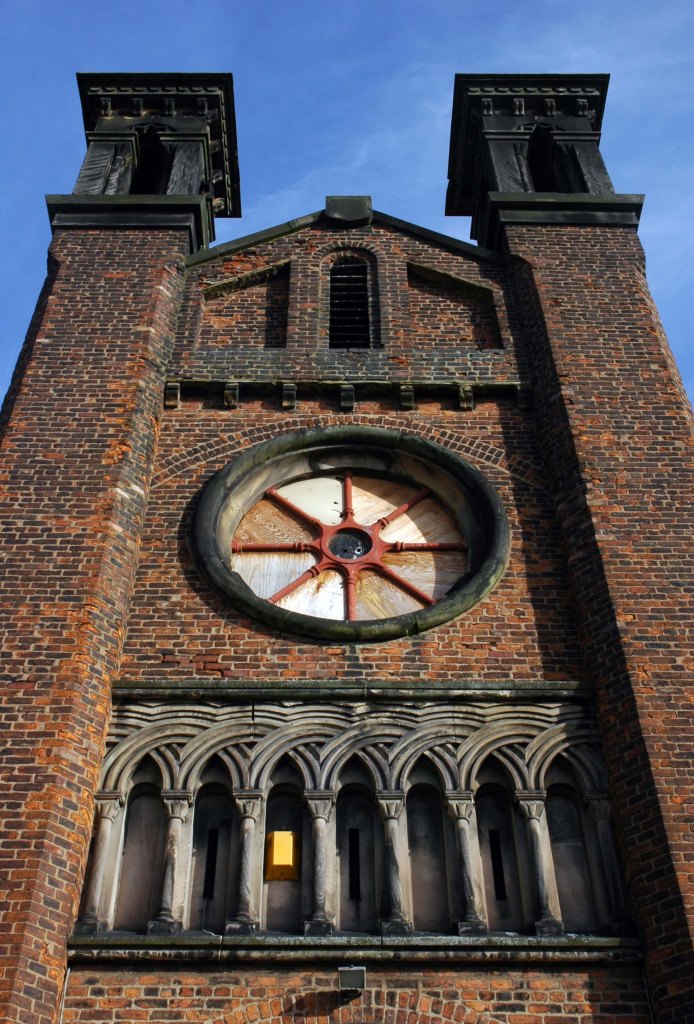
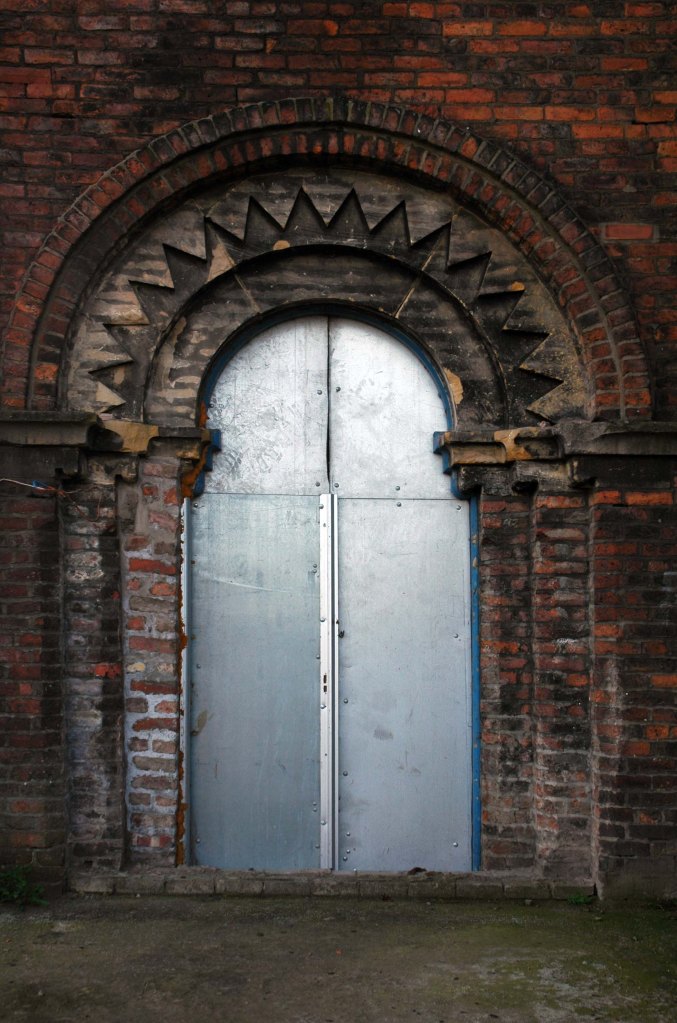
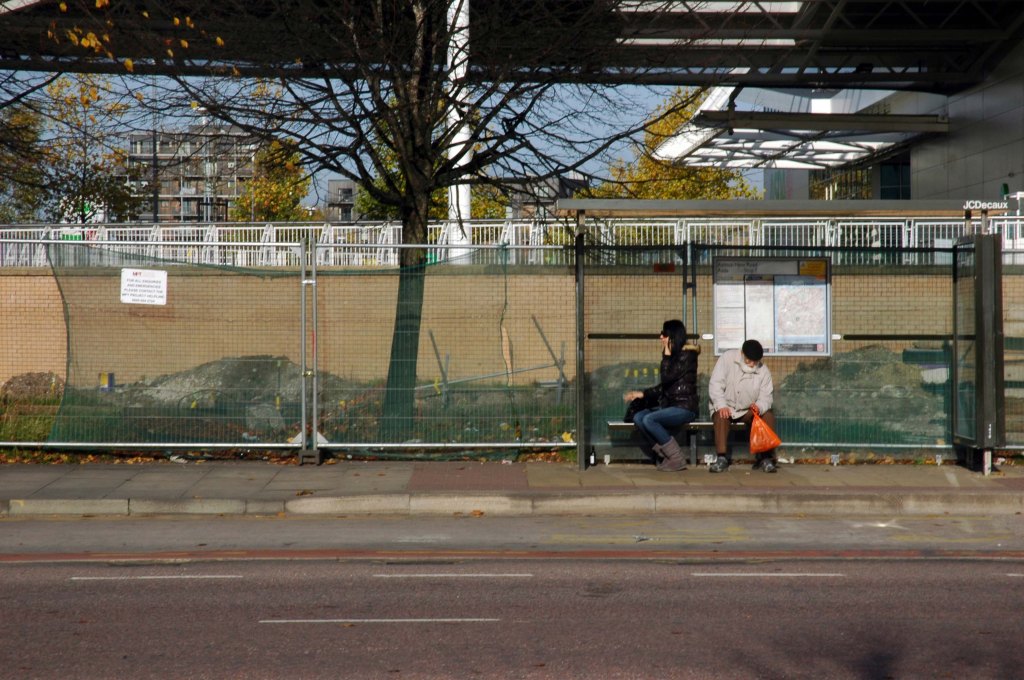
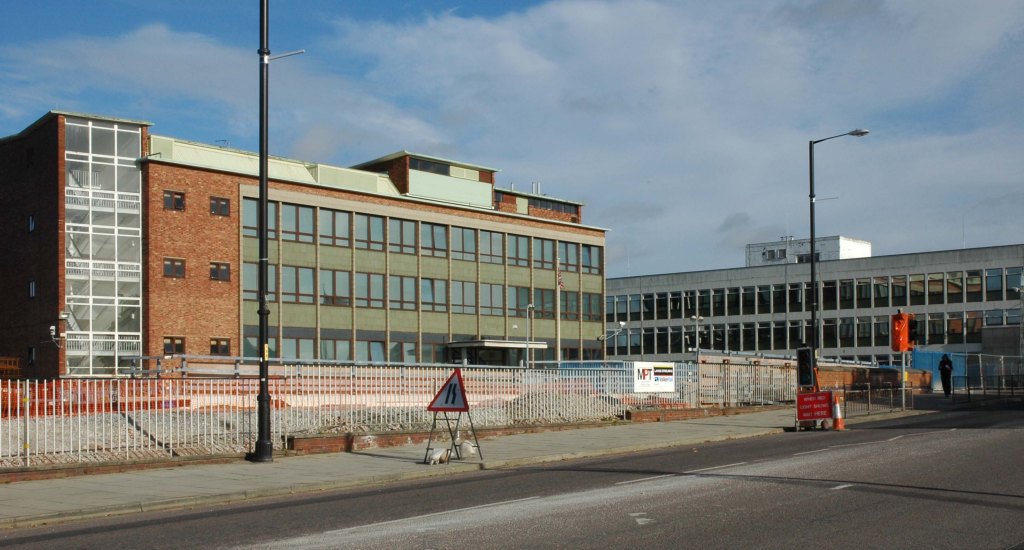
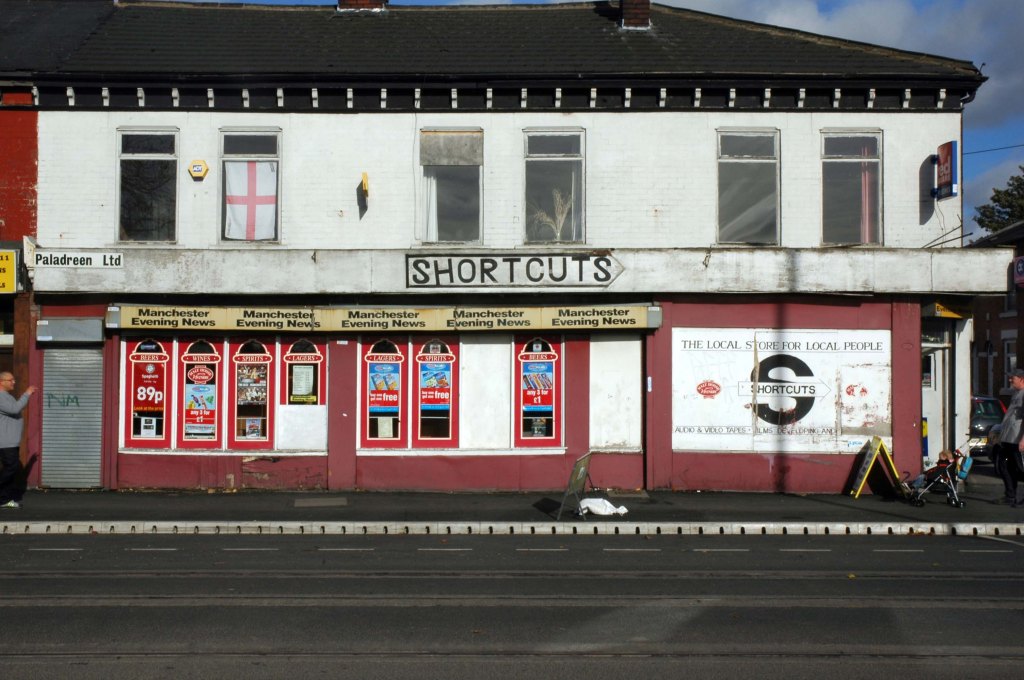






































See also Bury New Road and Cheetham Hill Road and Rochdale Road and Oldham Road.


The A62, which runs from Manchester to Leeds, via Oldham and Huddersfield, was once the main route across the Pennines, connecting the largest city in Lancashire with Yorkshire’s largest city. However with the completion of the M62 towards Leeds in the early 1970s it lost much of its importance and traffic to the motorway, which runs a few miles to the north. These days, the A62 serves as a busy primary route between Manchester and Oldham, an extremely very quiet route over the Pennines, and then a fairly busy local road linking Huddersfield with Leeds.
Most maps show that the A62 starts its journey in the middle of Manchester by leaving the A6 Piccadilly and running along Lever Street – the original route was the parallel Oldham Street. However, owing to a bus gate Lever Street is not generally accessible from Piccadilly. We head out easterly on a busy street – non–primary, until we meet the Ring Road where we pick up primary status that we retain until Oldham. We turn left at this point and then immediately right to start the A62 proper.
In 2014, having taken early retirement from teaching photography, I embarked on a series of walks along the arterial roads of Manchester.
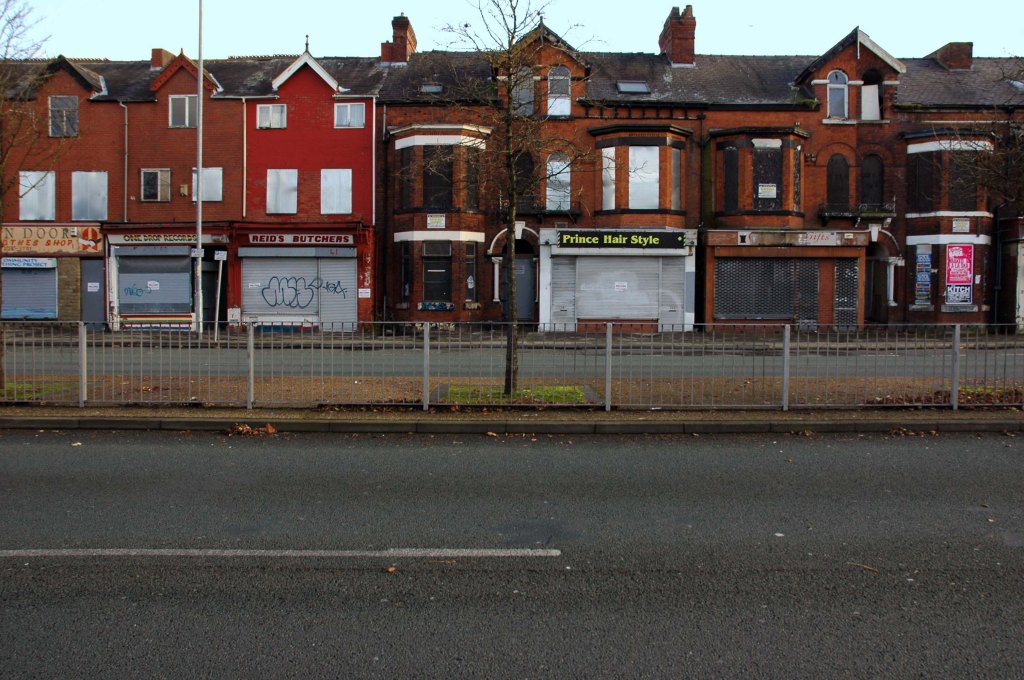
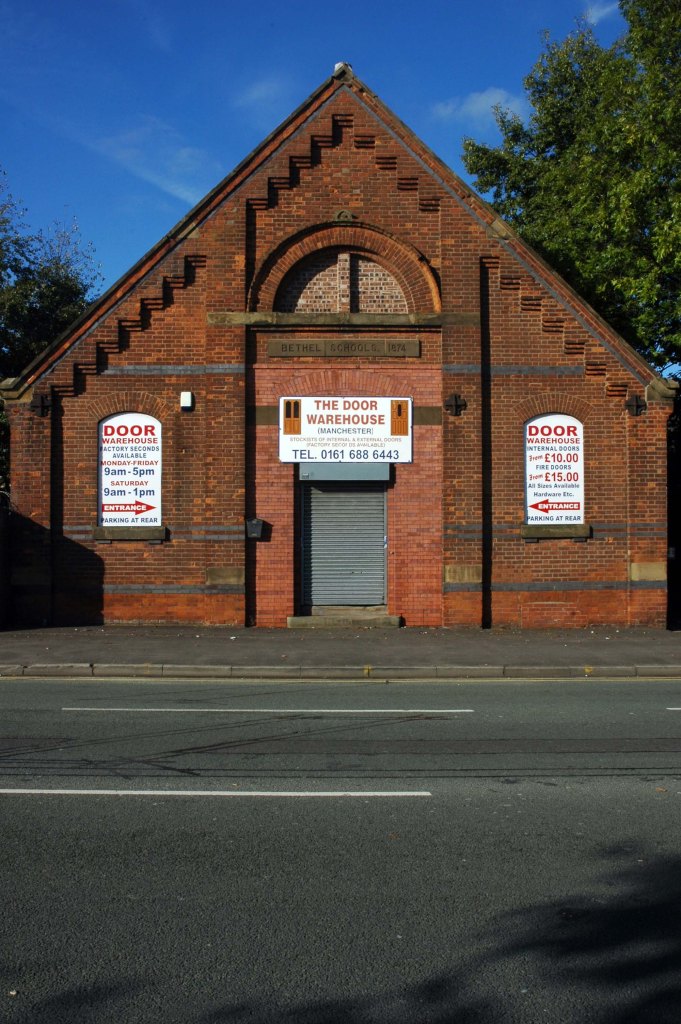
This whole undertaking was prompted in part by Charlie Meecham’s 1980’s Oldham Road project .
The work questions whether a sense of local identity can be maintained in an area of constant redevelopment and community displacement.
This area was first developed in the 19th century for cotton manufacture, coal extraction and later electrical and heavy engineering. The road was lined with shops and there was a vibrant community.
When I first started working on the project, most of the early industry had ceased operating and the mills were either abandoned or being dismantled. However, some had been refurbished either for new industrial use or later, made into apartments. Some run down areas were cleared making way for new housing. Clearance also provided opportunity to build new schools, trading estates and create green space. Most of the older community centres such as theatres and cinemas along the road were also abandoned and later cleared.
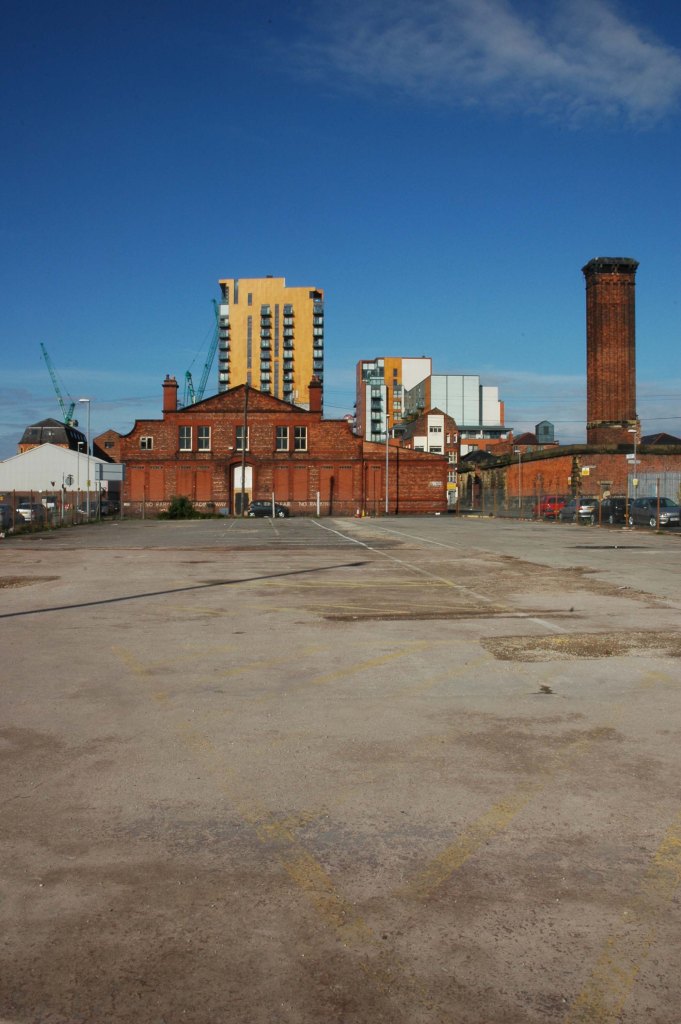
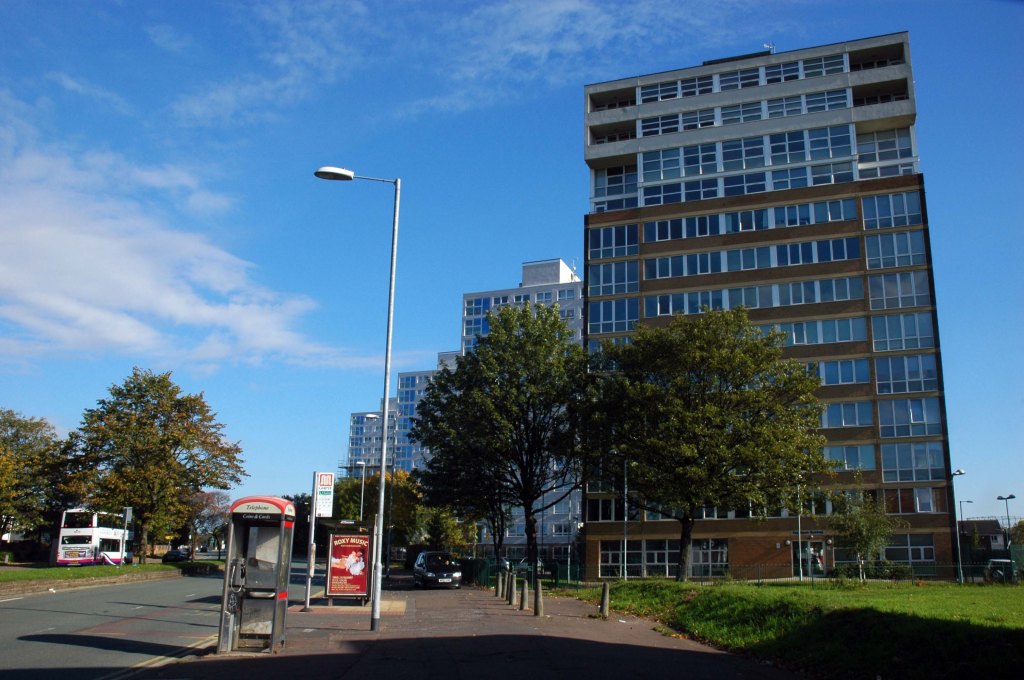
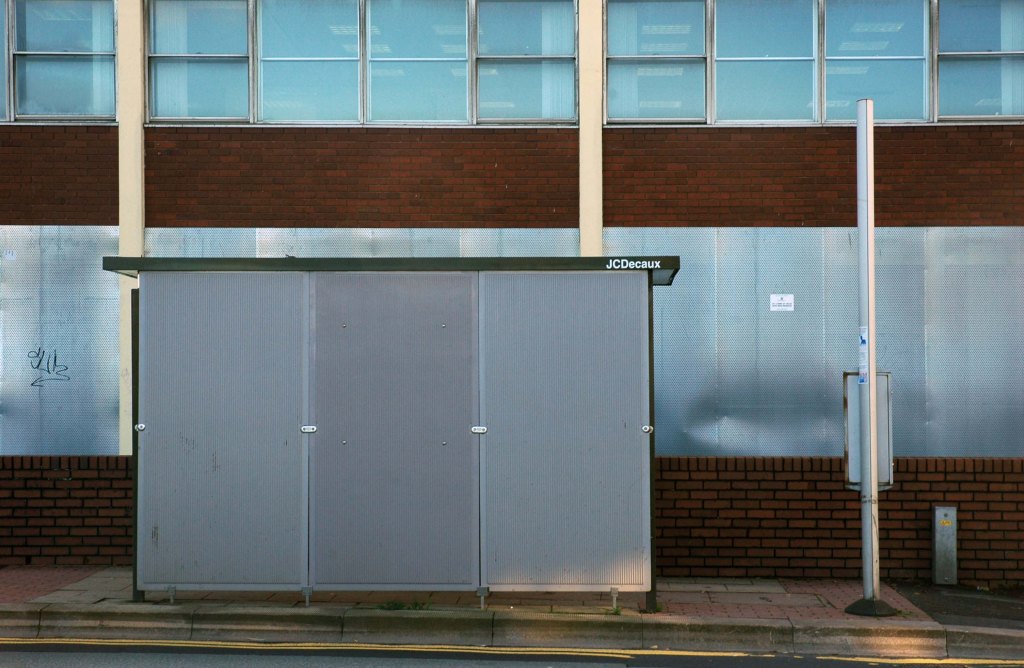
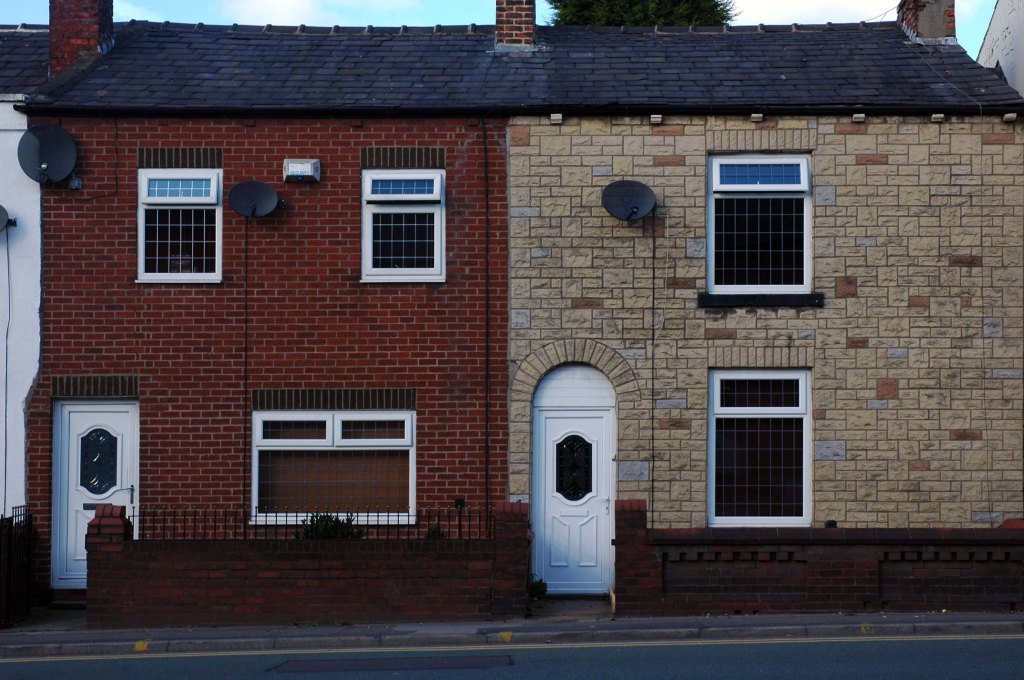
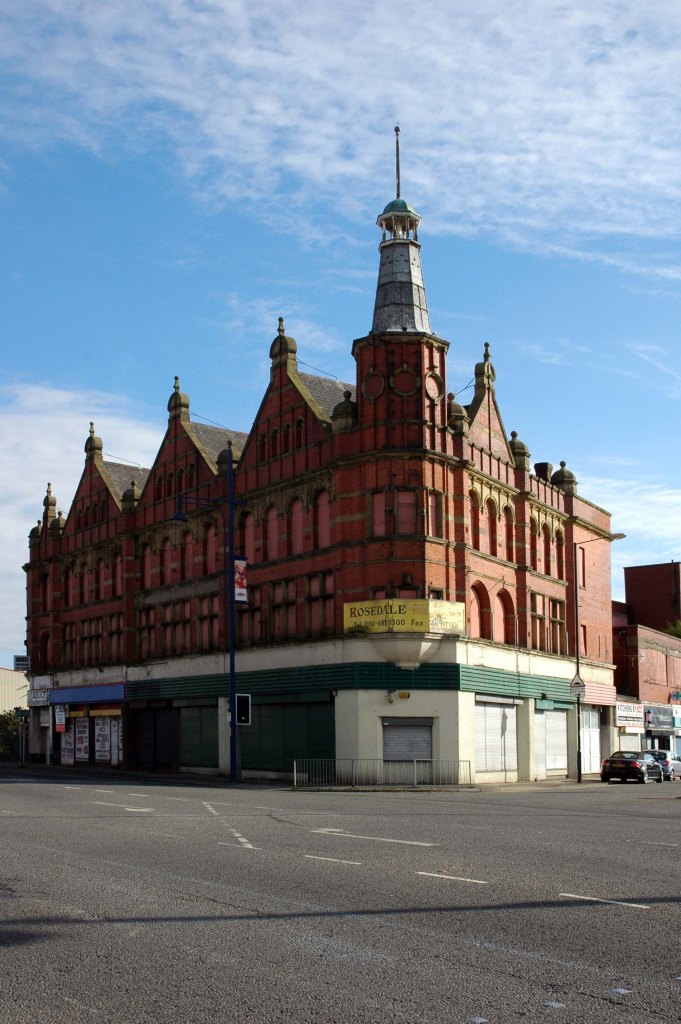
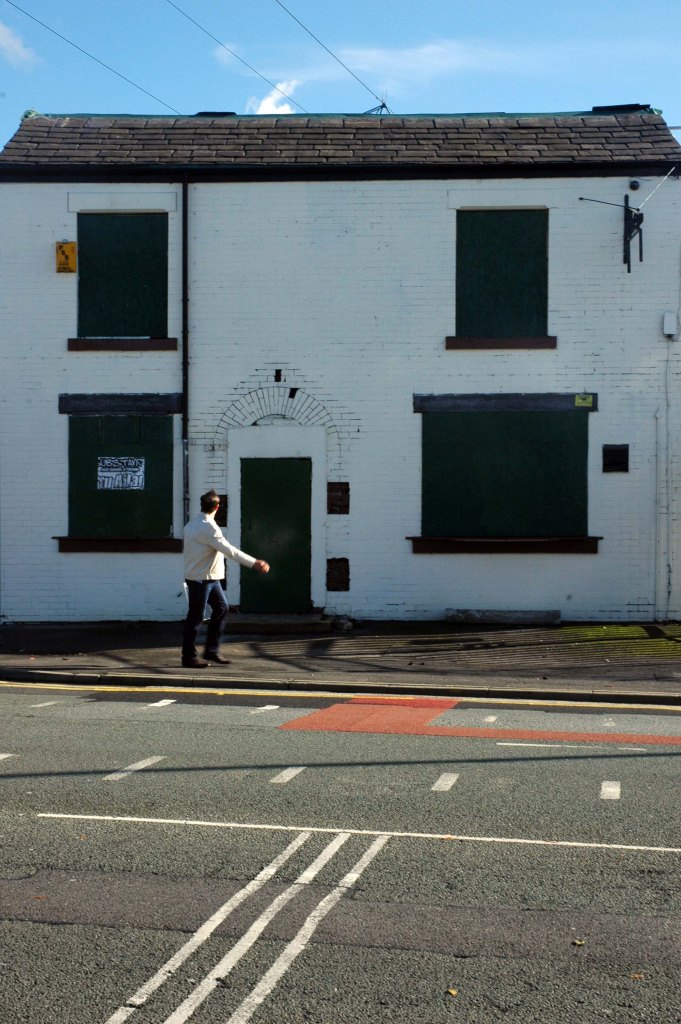







































See also Bury New Road and Cheetham Hill Road and Rochdale Road and Ashton New Road and Ashton Old Road and Hyde Road and Stockport Road and Kingsway and Princess Parkway.


First crossing the M60 Manchester Outer Ring Road at Junction 7 into Stretford.
The A56 takes the name of Chester Road and continues north-eastwards through Stretford and Hulme into Manchester city centre, where it takes on the name Deansgate, one of Manchester’s main shopping streets and thoroughfares. At the end of Deansgate, the A56 takes on the name of Victoria Street as it passes Manchester Victoria railway station. Since 2012, most of Victoria Street has been pedestrianised with planters, but the road markings still remain underneath.
In 2014, having taken early retirement from teaching photography, I embarked on a series of walks along the arterial roads of Manchester.






















June 2015 the last post of the lost last posts of Pomona.

April 2020 a history and appraisal of Pomona Gardens – the undergrowth having recently having had a trim.

What were once opulent Pleasure Gardens now await the Midas touch of Peek Holdings.
What knows what fates awaits you?
Long-awaited plans to redevelop the 26-acre swathe of land will not come forward until Peel L&P and Trafford Council reach an accord on the level of affordable housing to be provided on a separate project.
In 2021, Peel lodged plans for a 162-apartment build-to-rent scheme on part of Pomona Island.
The project featured no on-site affordable housing provision – although Peel did offer a ‘significant financial contribution’ towards off-site affordable housing – and Trafford Council subsequently recommended the development be refused.
This promoted Peel to withdraw the £35m proposals before they were discussed at committee.
Place Northwest 2022

The 2023 iteration of the project, part of the developer’s Manchester Waters masterplan, also features no on-site affordable homes.
However, as part of the proposals, Peel will be making a contribution equivalent to 20% affordable housing within Trafford, the developer said. The earlier iteration proposed 5%.
Place Northwest 2023

The proposed nature reserve seem like a distant dream
Despite suggestions that Pomona could become the Eden Project of the north, 3,000 homes are planned for the site by owners Peel L&P and the first development, Pomona Wharf, is already complete.
This green space could have been a globally significant urban park, and a powerful statement of Manchester’s commitment to fighting climate change and protecting green spaces.
Unfortunately, the city chose more apartments and financial growth over the natural world and not for the first time – Luke Blazejewski.
So once again we venture down the rabbit hole of a hole in the fence by Cornbrook.
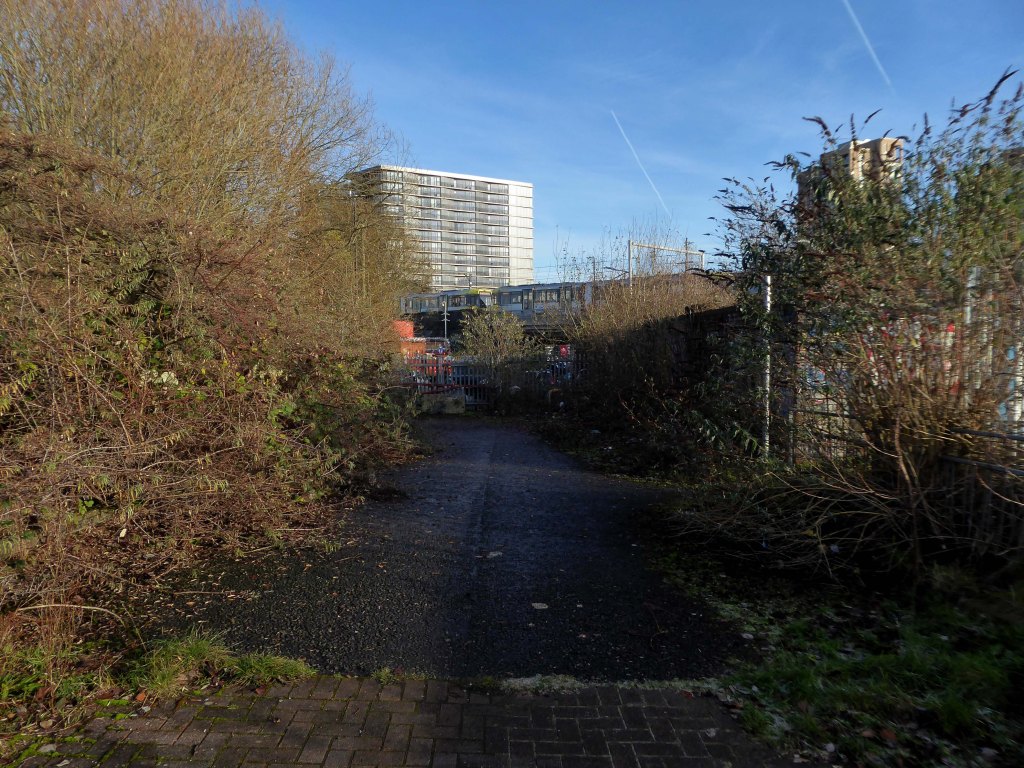
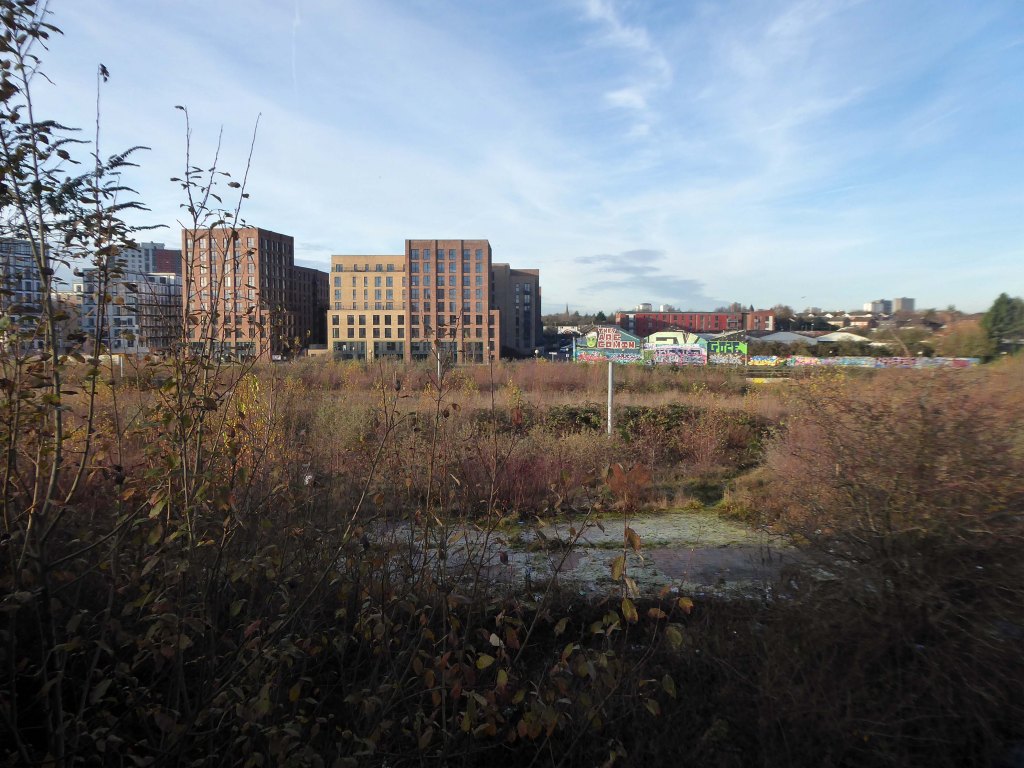
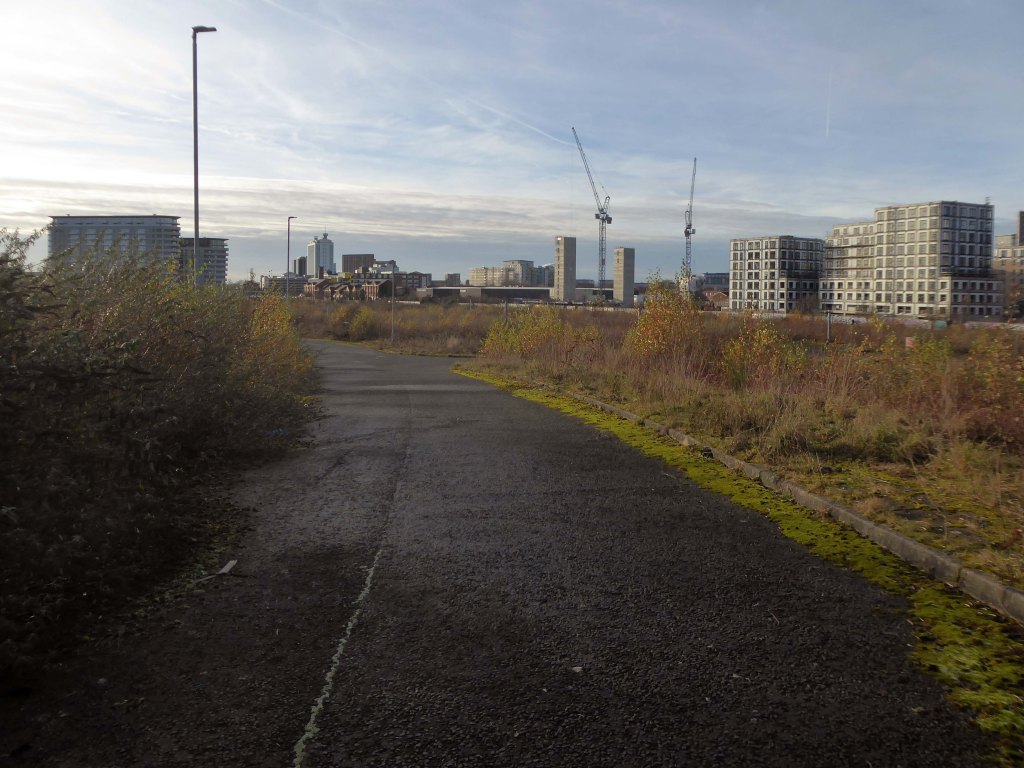
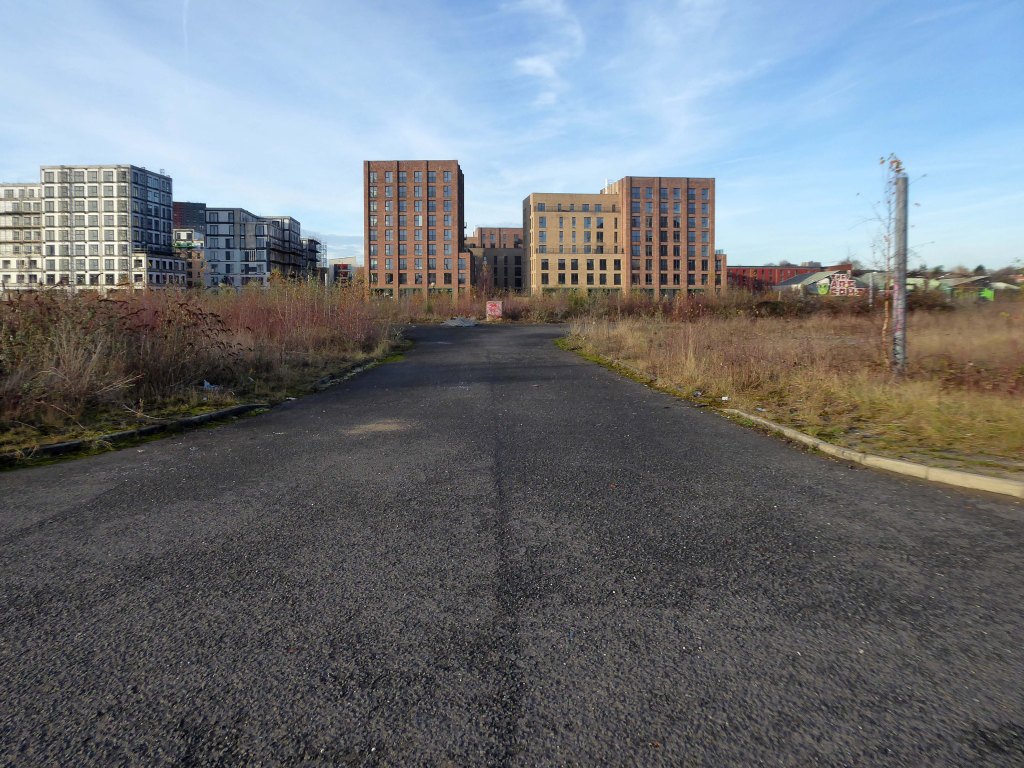
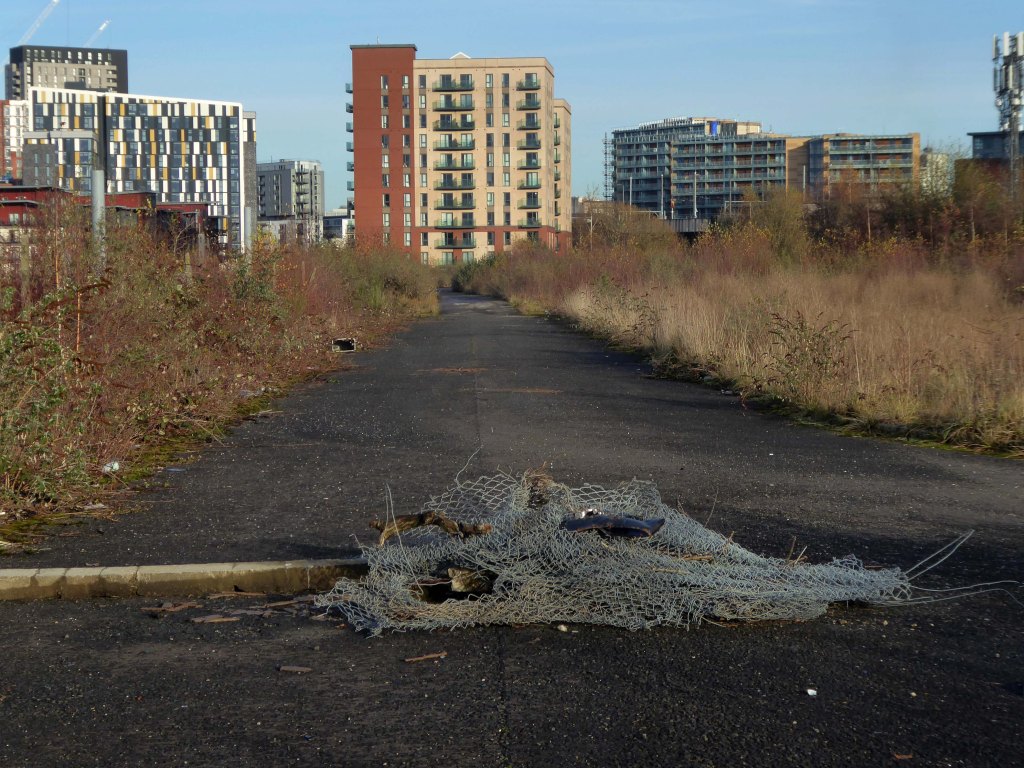
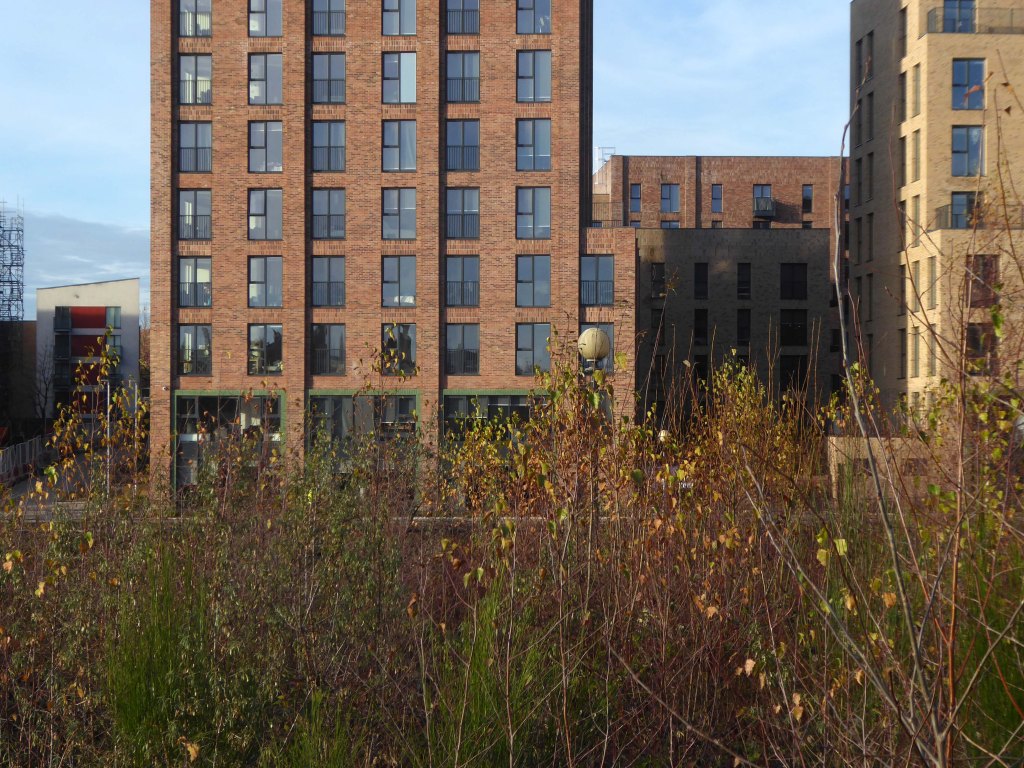
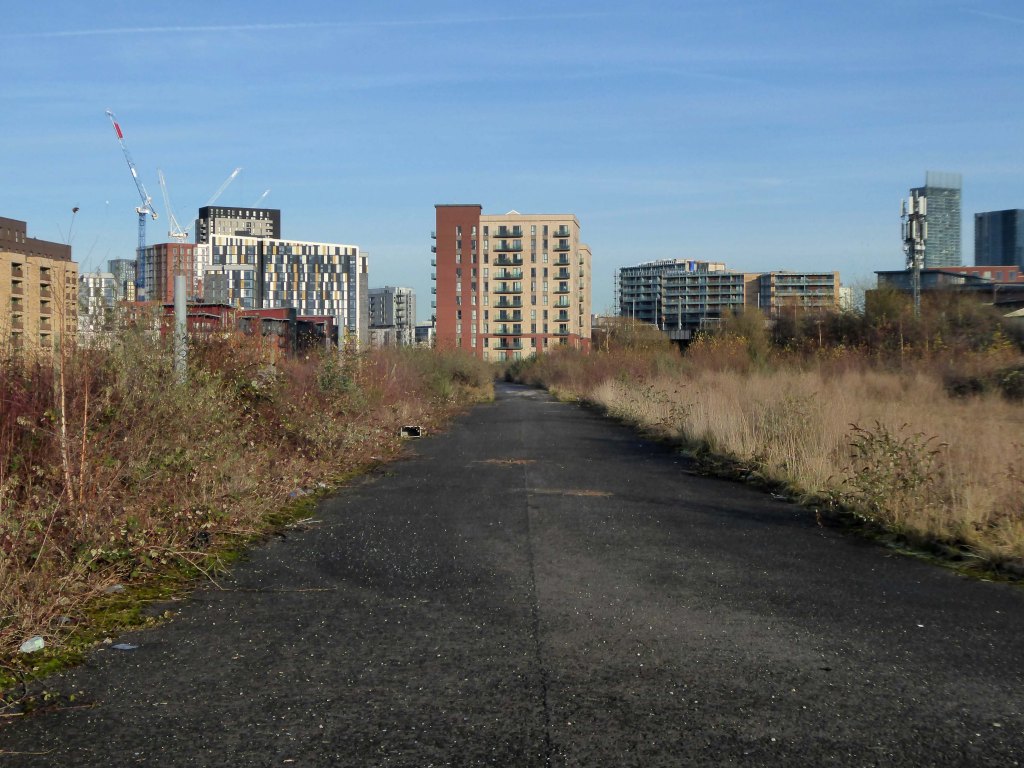
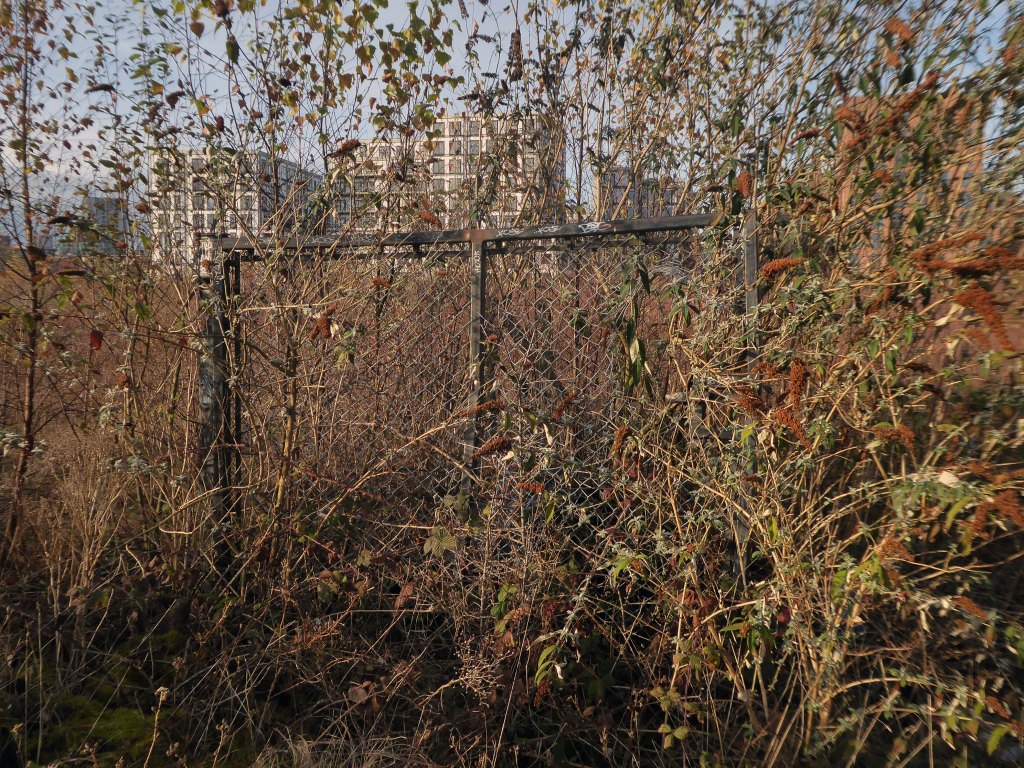
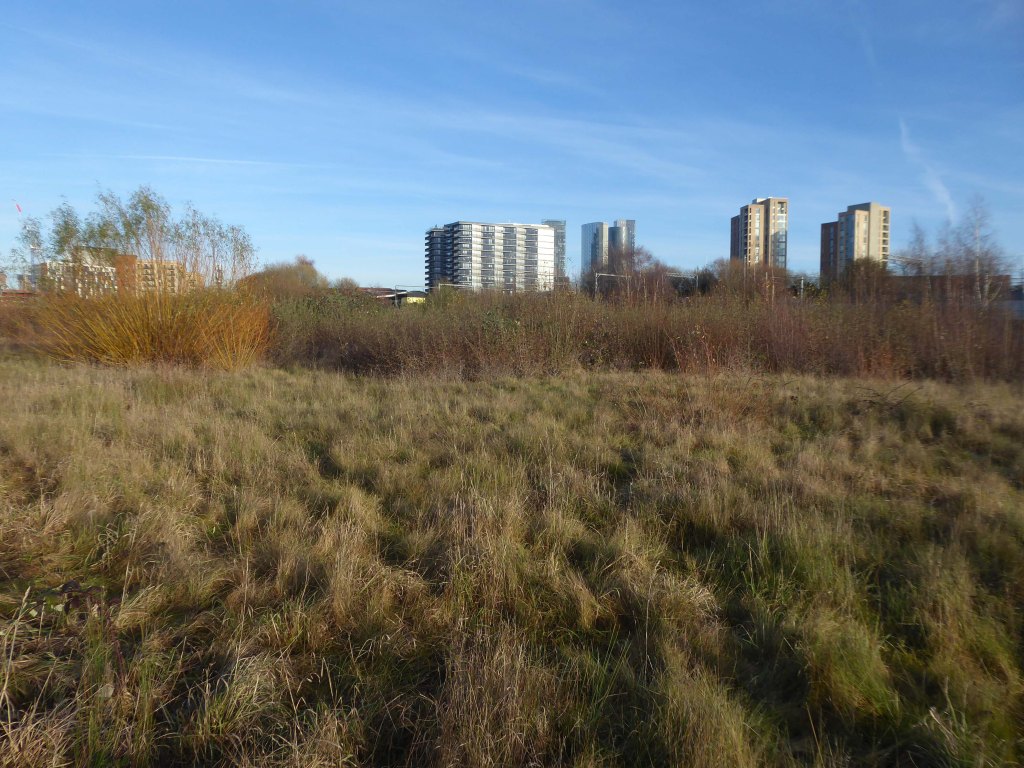
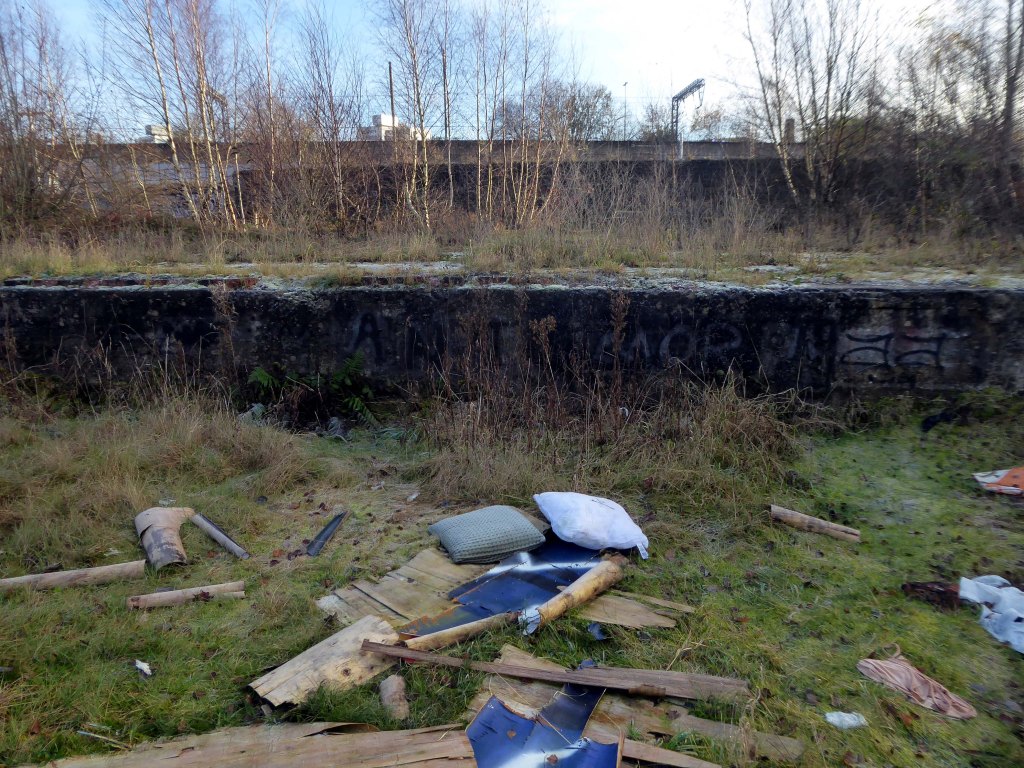
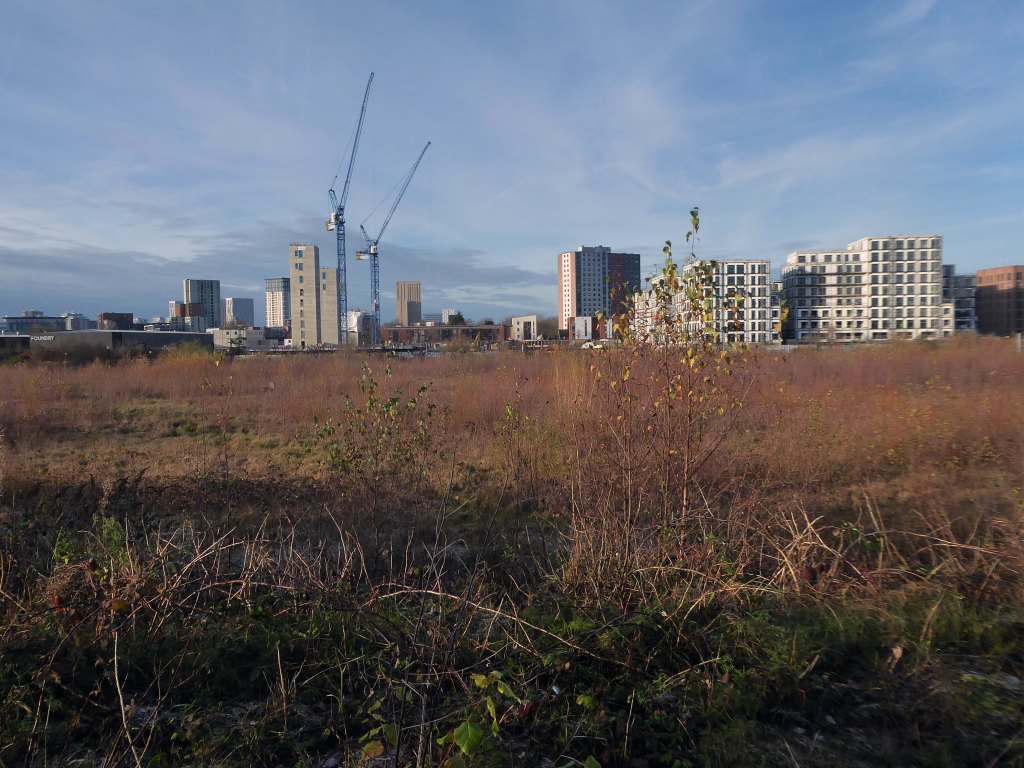
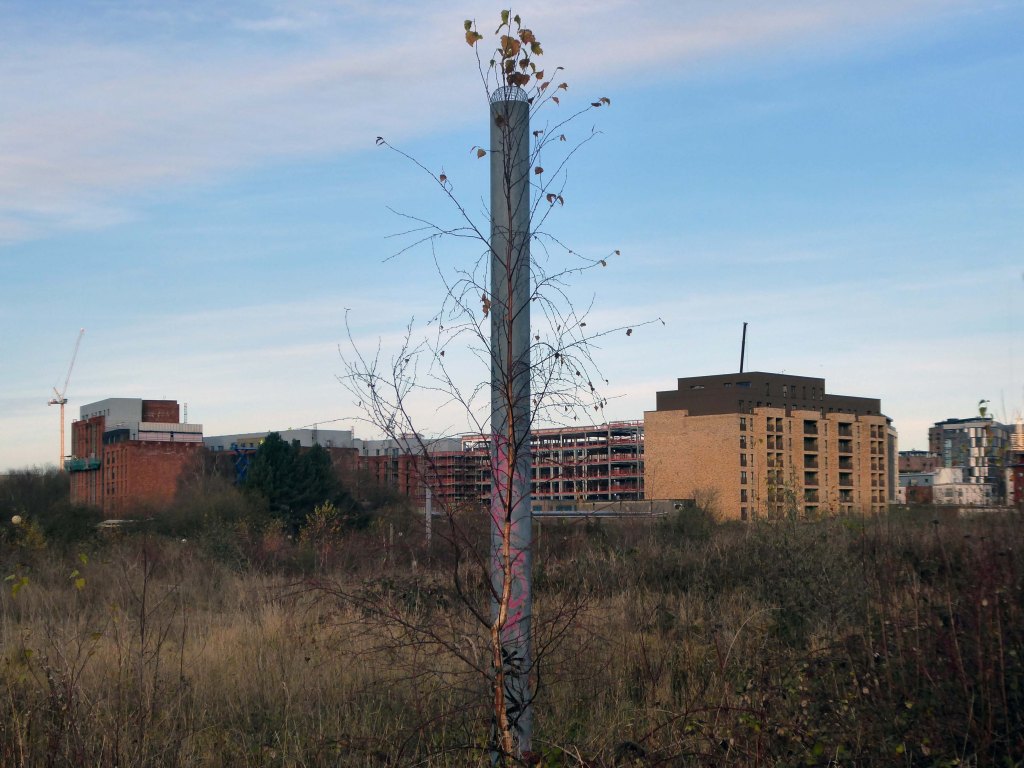



























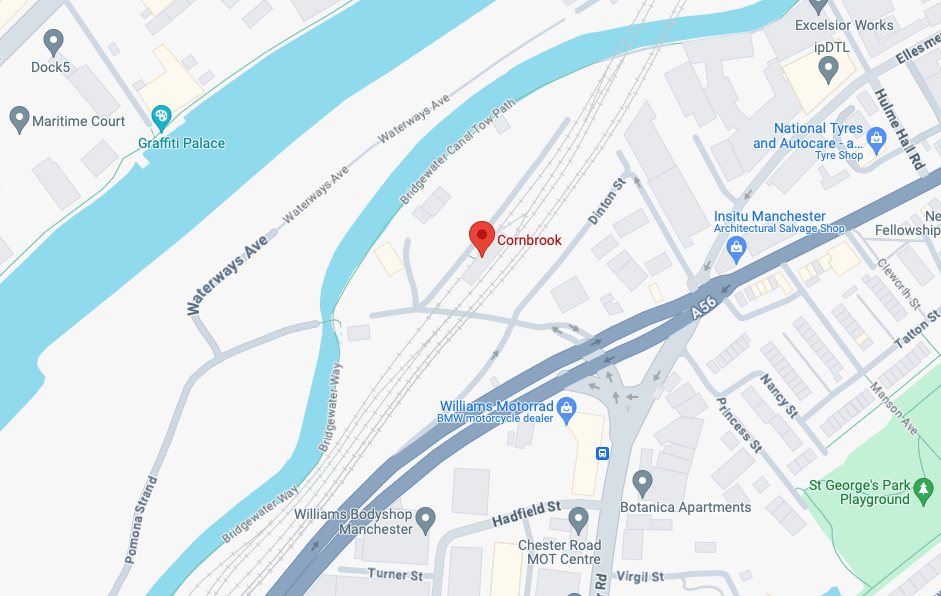
The Cornbrook drains the urban area South of the River Medlock, it rises in Gorton and follows a tortous path through Manchester’s Southern ‘inner city’ suburbs and empties itself into the Manchester Ship Canal at the Pomona Docks.

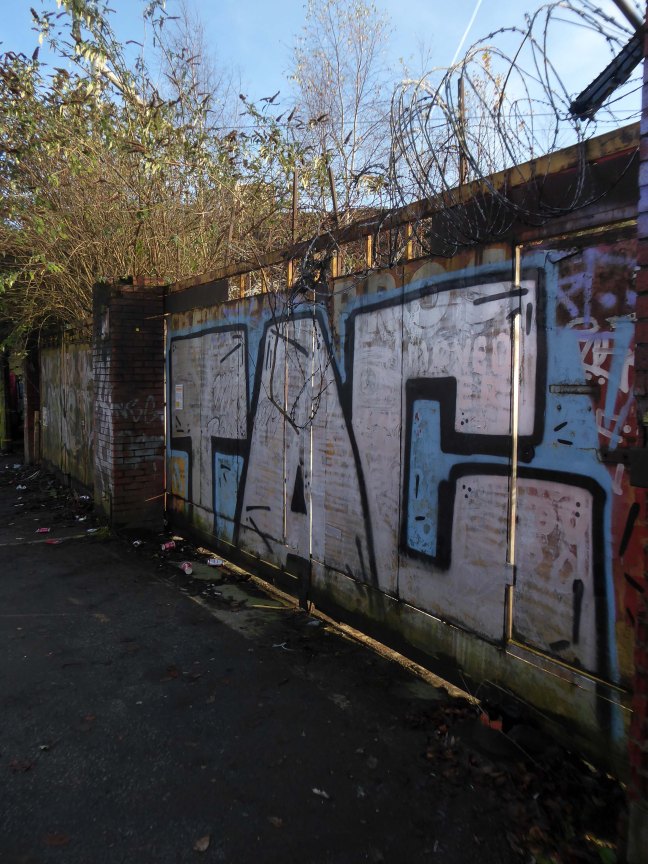
It’s a tram stop – primarily an interchange, though the brand new shiny residential new build has produced a brave band of brand new shiny residents in transit. Slipping and sliding ‘neath the bridge, skating over the age old accretion of filth, oil, diesel and detritus produced by the surrounding scrap yards.
The market leader is Bennett Brothers:
We are one of the first recycling companies operating in the North West, Bennett Bros was founded in 1948 by Francis William Bennett and Bernard Bennett, and remains a family-run business to this day. Bennett Bros was originally involved in loaning ponies to the many rag and bone men who collected unwanted household items and sold them to merchants, and while the recycling industry has now embraced modern technology, we are very proud of our heritage as innovators in what was then a new industry.
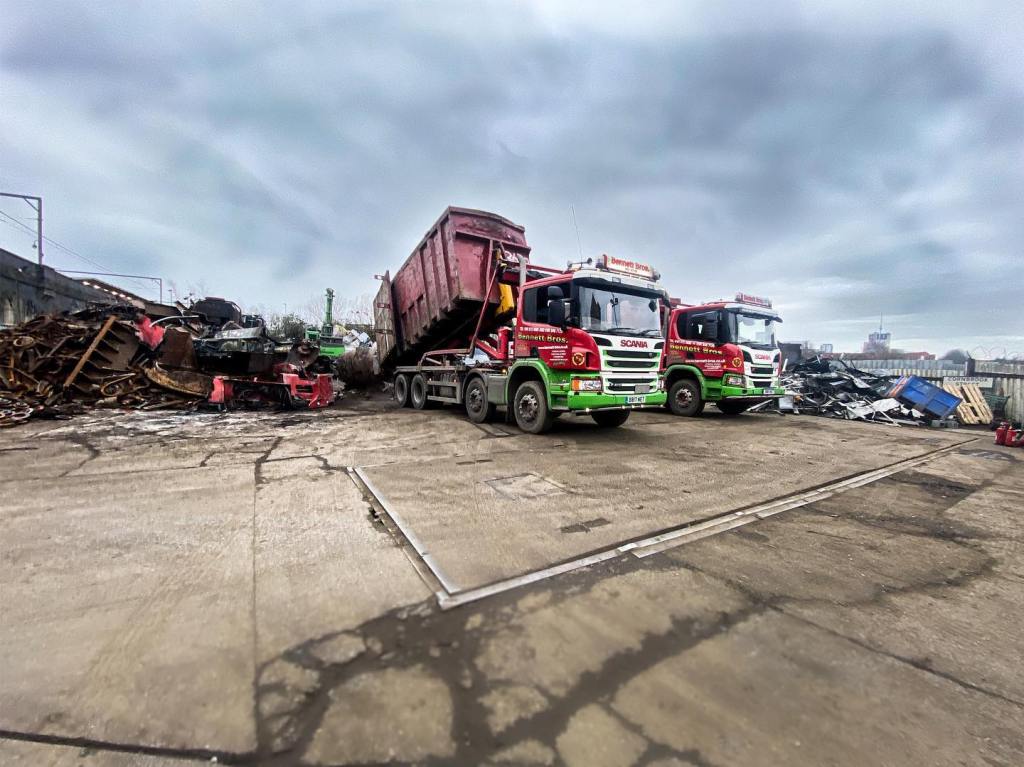

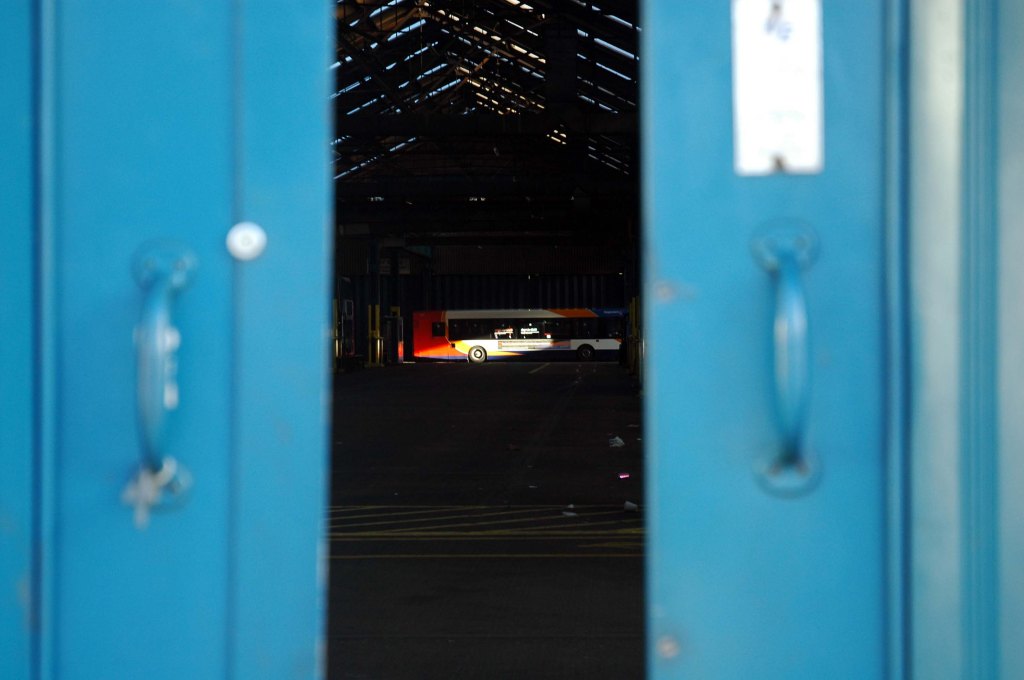
In 2017 I visited the area to snap the gates of their older site – as they had moved the business just across the street.

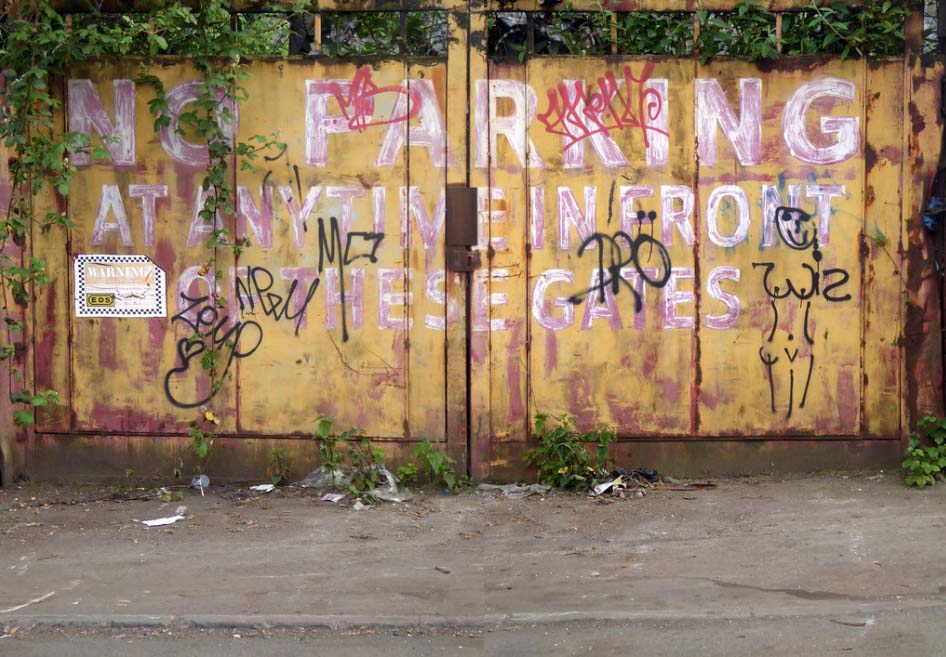
I returned in December 2023 to discover what had become of the gates.
Remnants of the drop shadow block lettering remain, beneath a palimpsest of tags and grime.
Here’s what I saw.
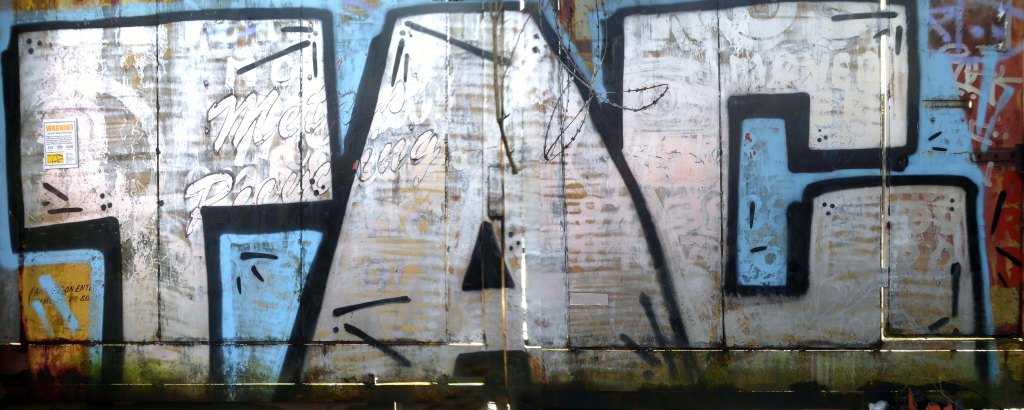
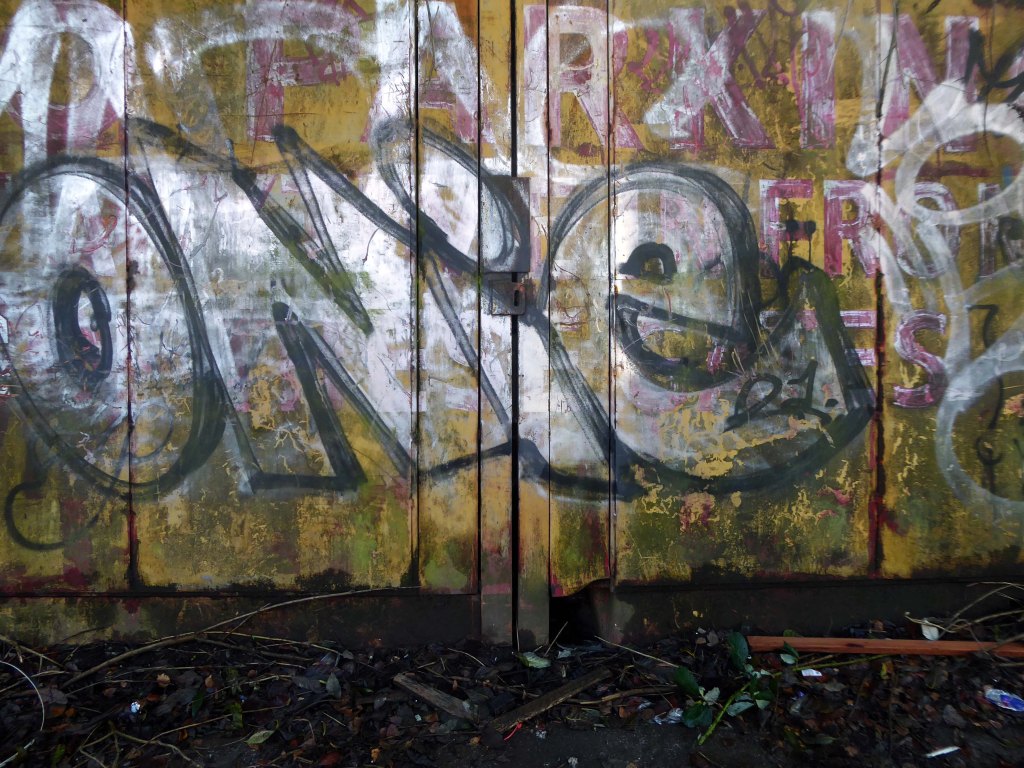
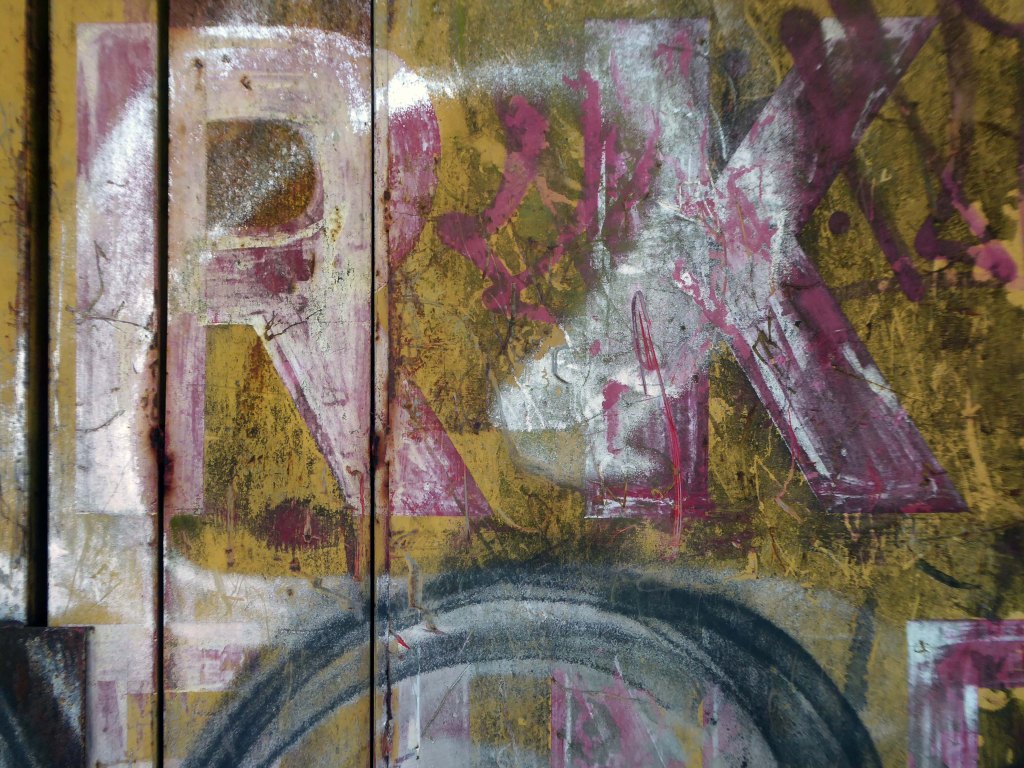
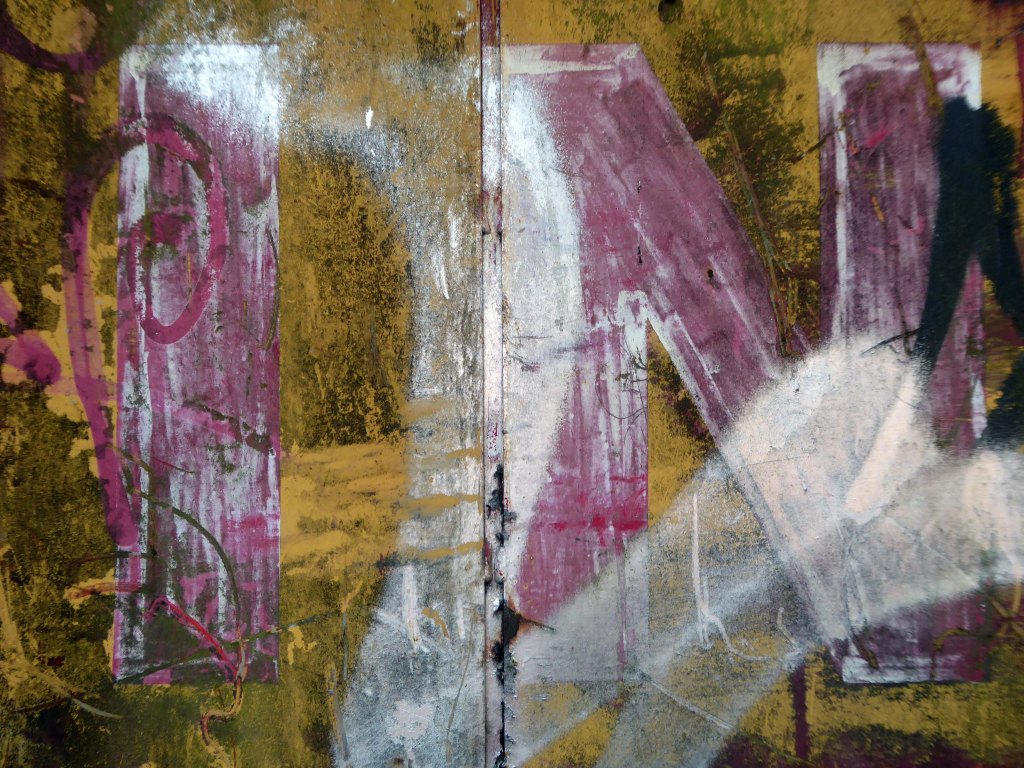
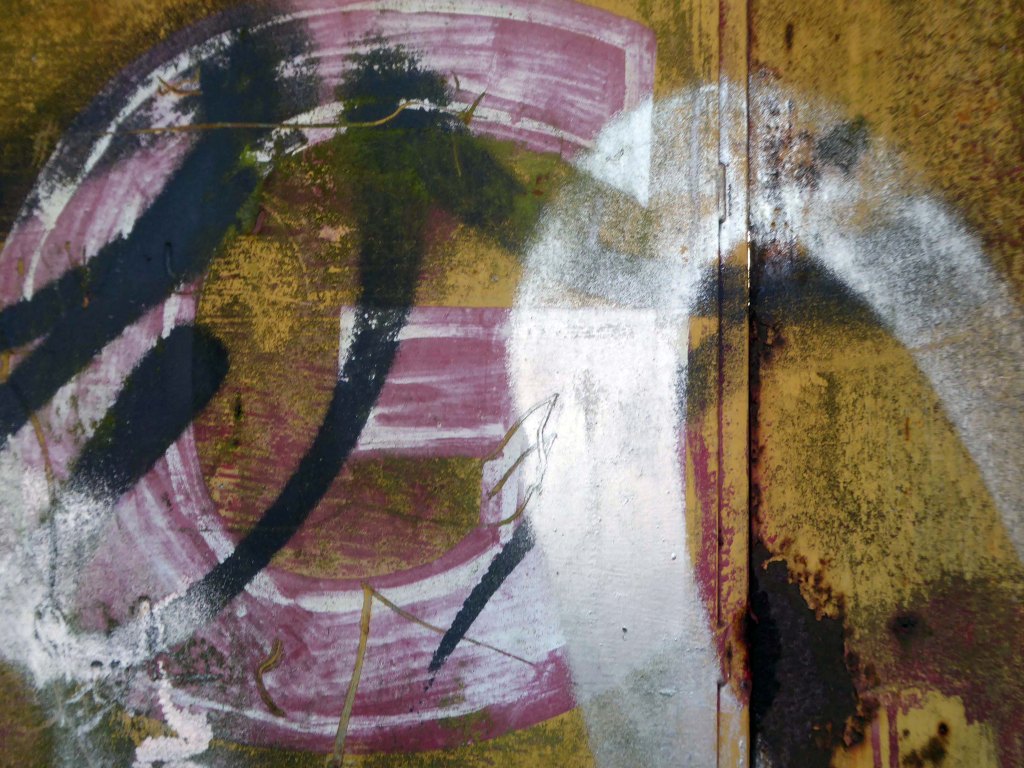
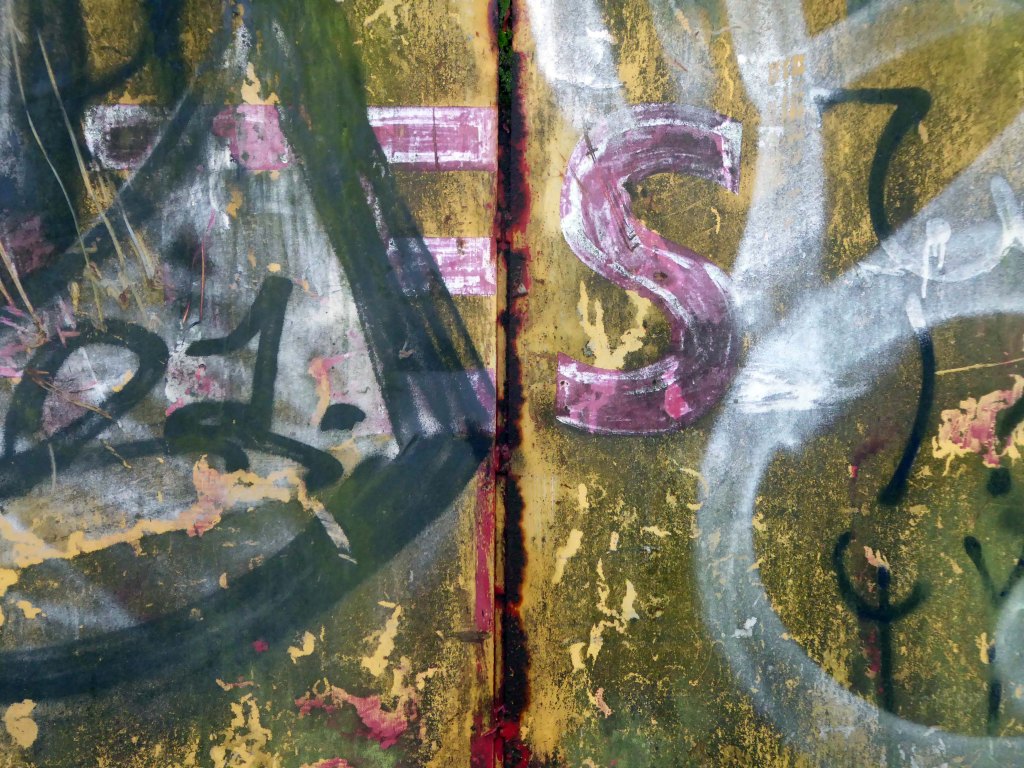







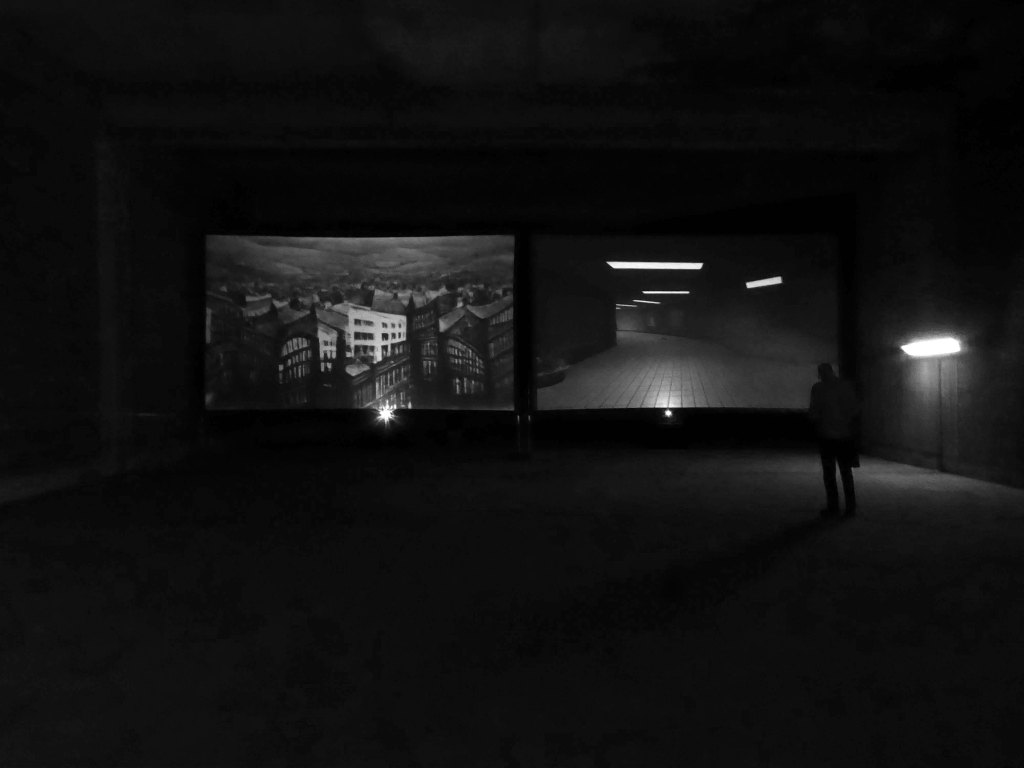
The outline of a presentation for Photonorth – November 16th 2023.

I was asked to talk about the photographs which Sean Madner had selected for exhibition on behalf of the Sheffield Modernists.
Illustrating a wide range of building types in and around Sheffield sheltering beneath the broad umbrella of Modernism.
By way of context the photographs are all Topographic in nature – in which a landscape subject is photographed, devoid of people, framed orthogonally and lacking artifice or effect.
Practiced most famously by the 1970s New Topographics photographers, including Robert Adams, Lewis Baltz, Nicholas Nixon, and Bernd and Hilla Becher.

Bernd and Hilla’s photographs lead us to:
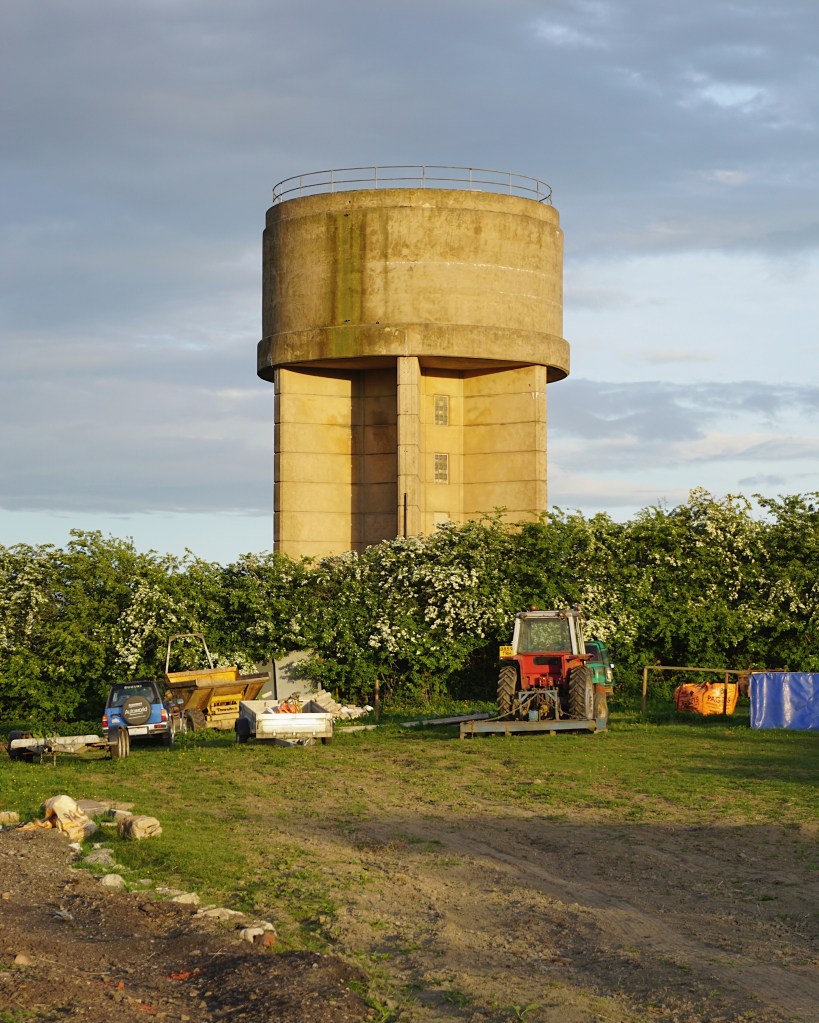
1 Potter Hill Water Tower
The British Water Tower Appreciation Society

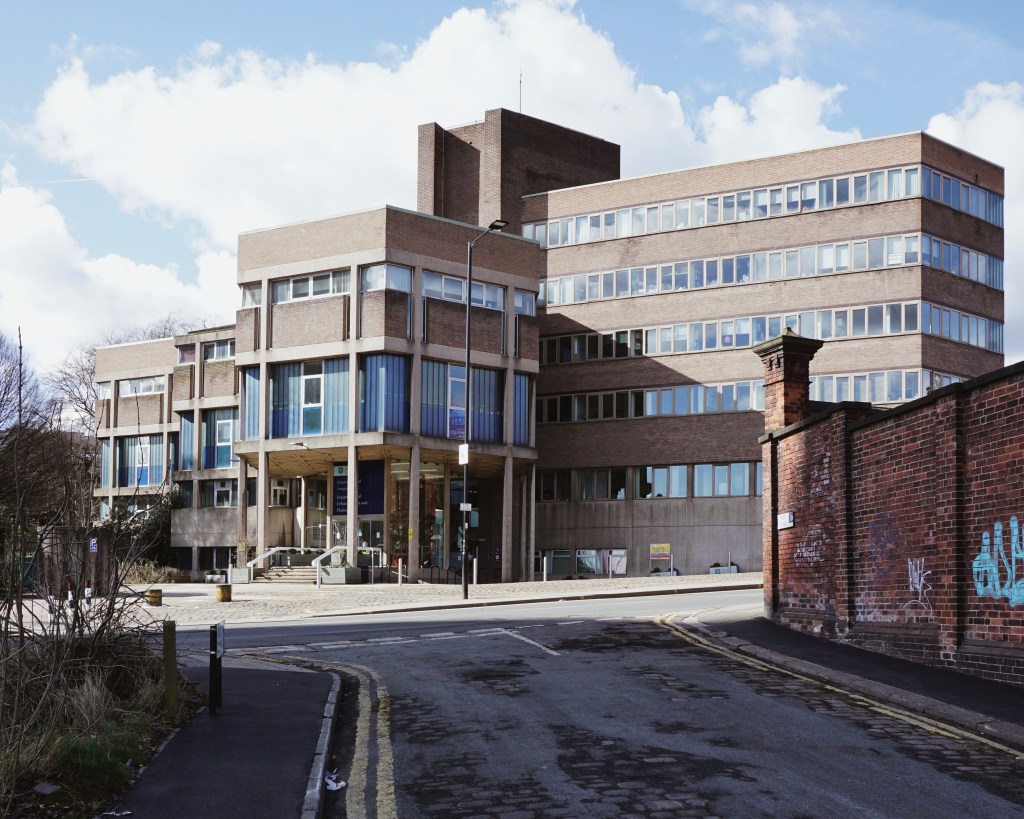
2 Geography Building 1970 Sir William Whitfield
Alterations made 2022

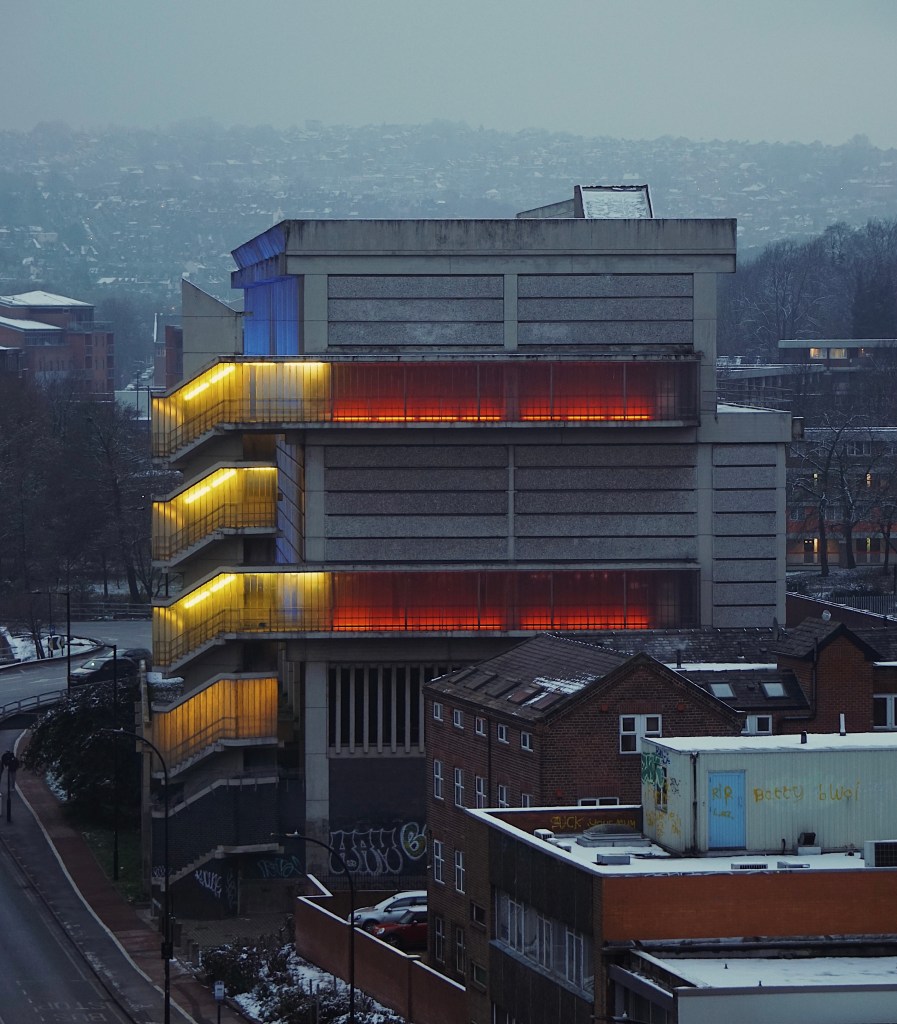
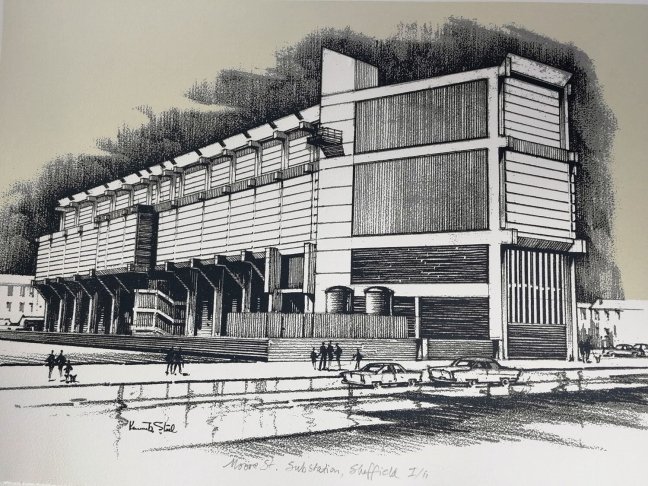
3 Moore Street Substation 1968 Jefferson Sheard
Owen Hatherley describes it as:
A shocking paroxysm of a building, an explosion in reinforced concrete, a bunker built with an aesthete’s attention to detail, a building which is genuinely Brutalist in both senses of the term.

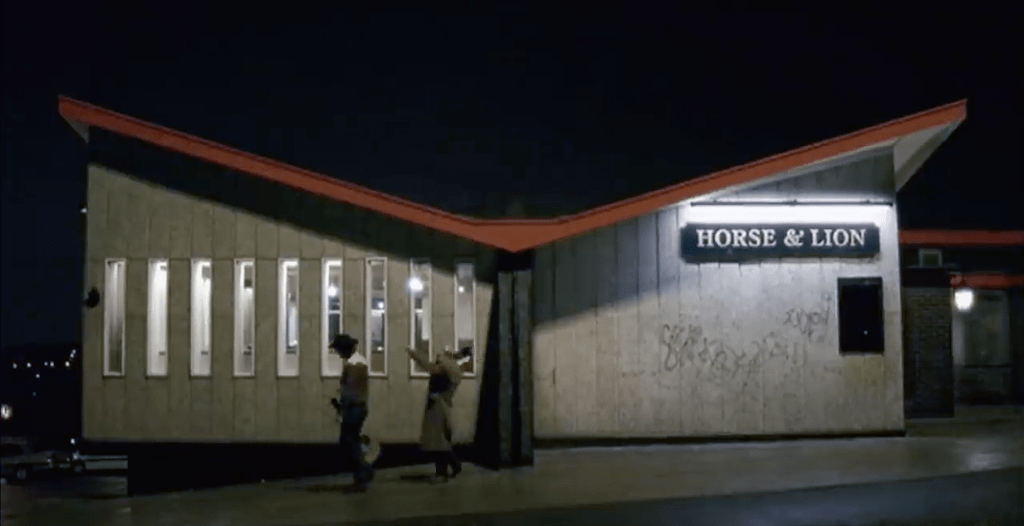
4 Horse and Lion Pub – Bass Charringtons
Prime example of a so-called Estate Pub.
With a hyper parabolic roof a doubly-curved surface that resembles the shape of a saddle, that is, it has a convex form along one axis, and a concave form on along the other.

Featured in the video for the Arctic Monkeys’ 2006 number one hit – When the Sun Goes Down at 1.21.

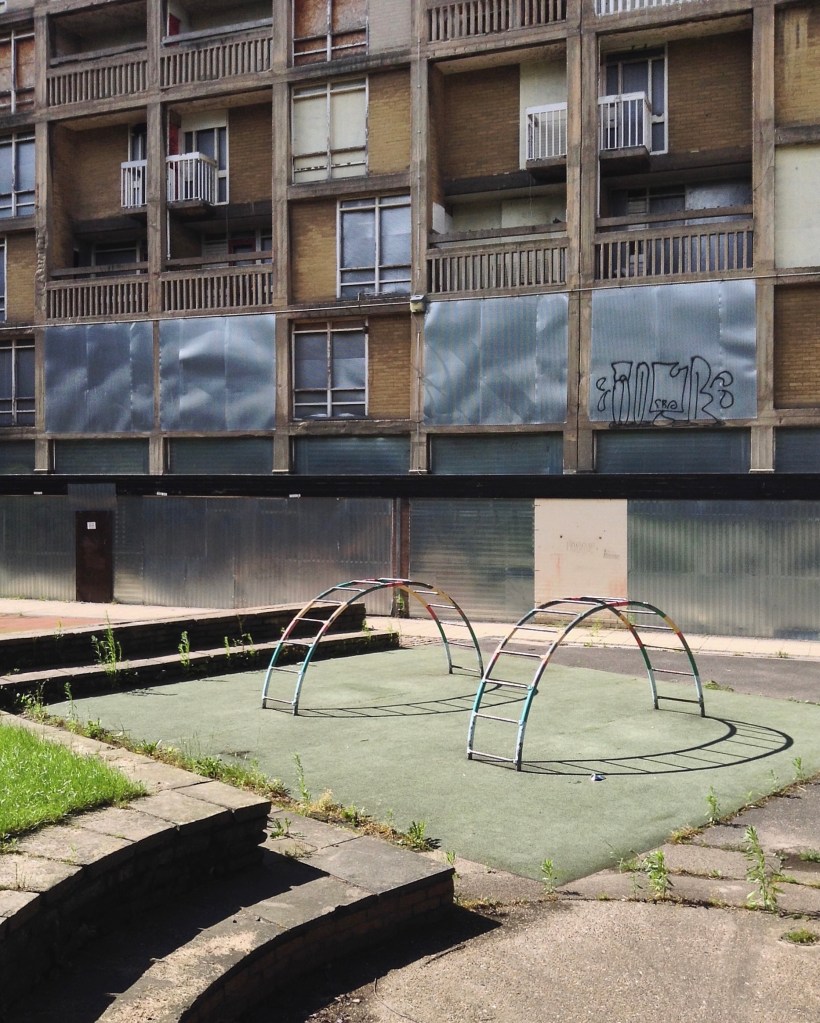
5 Park Hill – 1957 and 1961 Jack Lynn and Ivor Smith under the supervision of JL Womersley,
Grace Owen Nursery – with two Wicksteed climbing frames
The Play Ground should not be put in a corner behind railings, but in a conspicuous and beautiful part of a Park, free to all, where people can enjoy the play and charming scenery at the same time; where mothers can sit, while they are looking on and caring for their children.
Charles Wicksteed

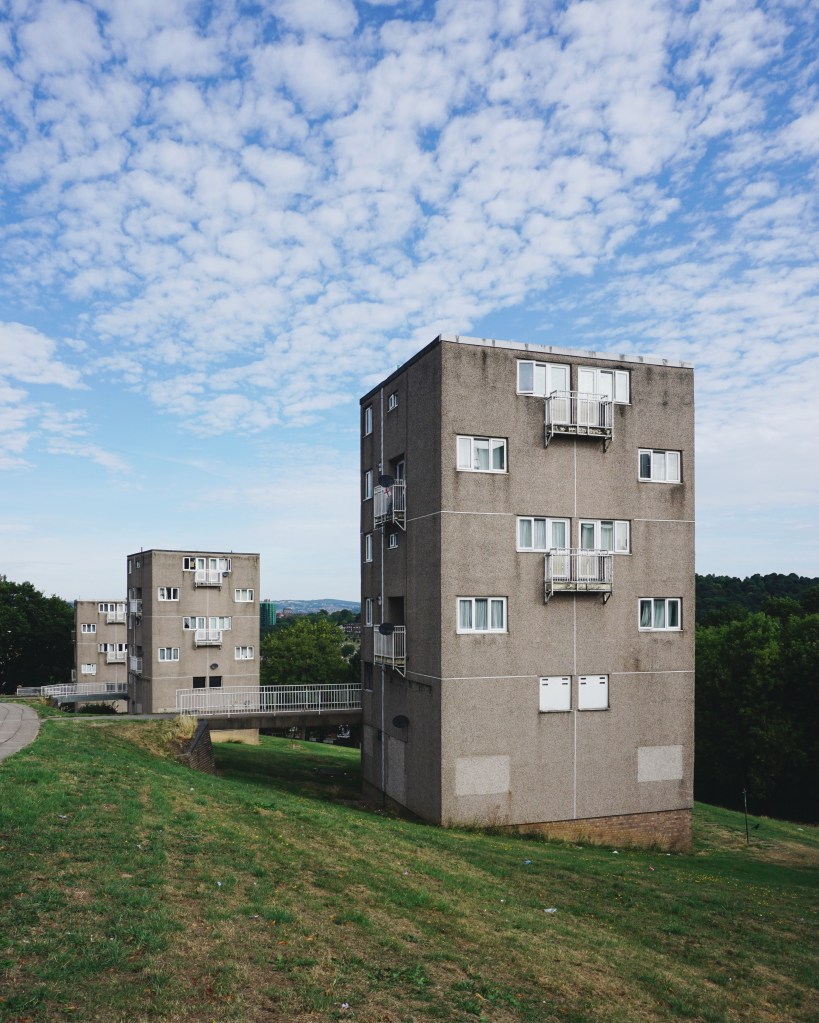
6 Gleadless Estate 1963 Lewis Wormersley City Architect
The Sheffield Blitz in December 1940 killed almost 700 and damaged some 82,000 homes, over half the city’s housing stock. As the city looked to rebuilding, its 1952 Development Plan estimated the need to replace 20,000 unfit homes and build a further 15,000 to cater for the natural increase of population.
Supreme, but often overlooked, achievement … is the Gleadless Valley Estate which combined urban housing types and the natural landscape so effectively that it still looks stunning, especially on a bright winter’s day.
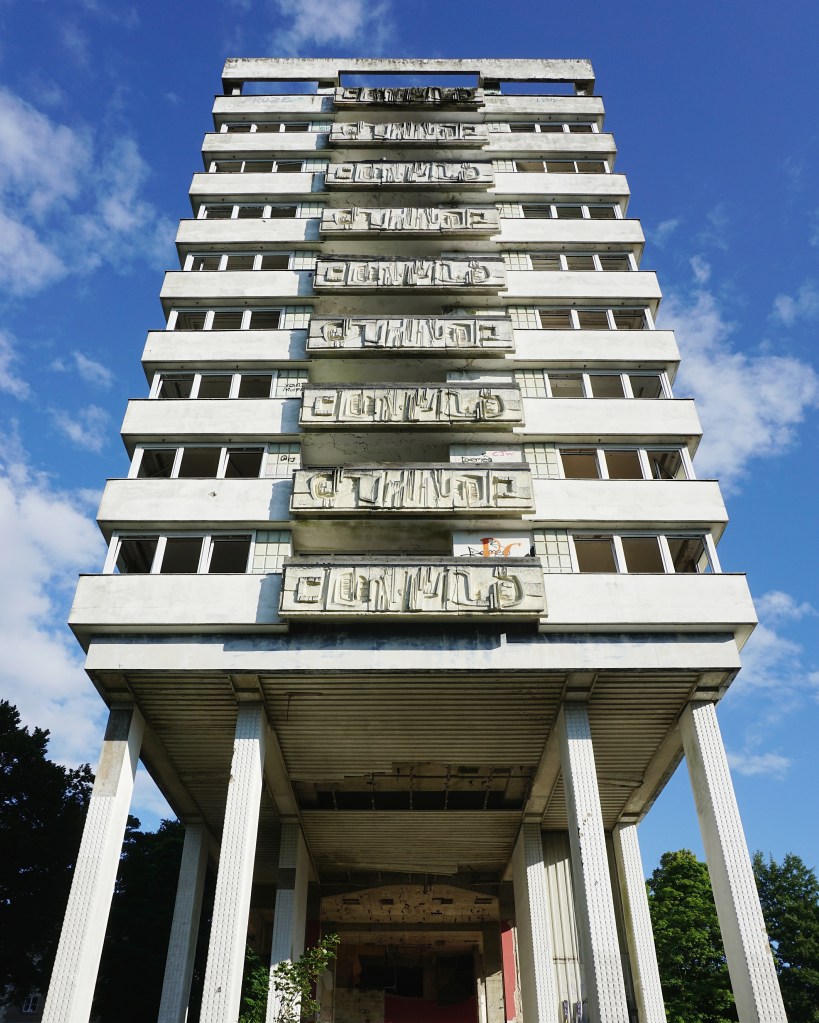



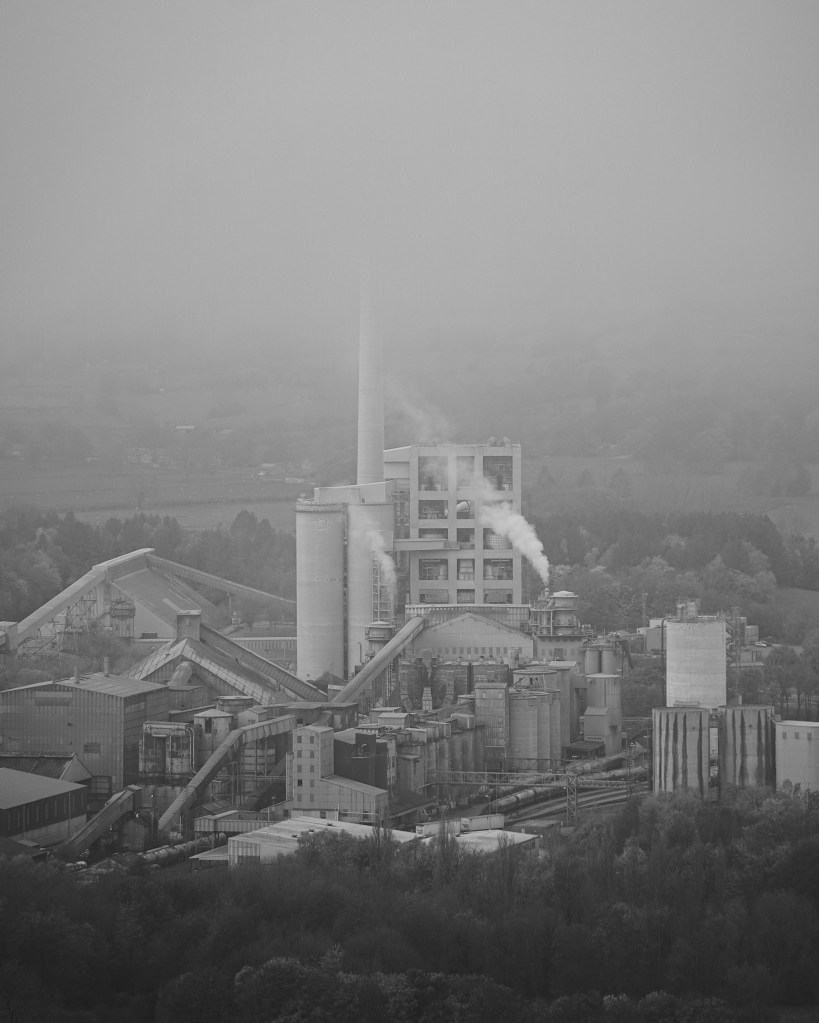
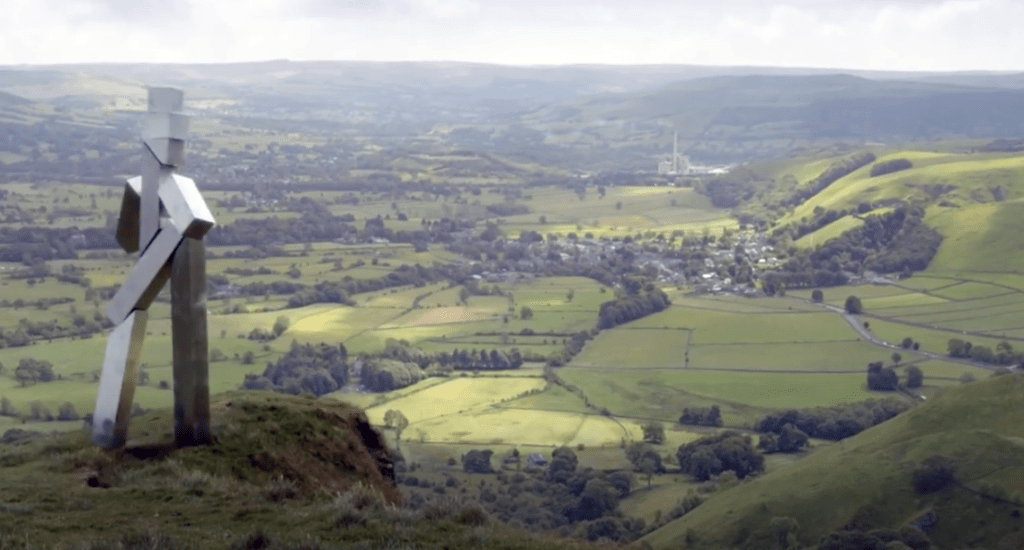
The plant started its first full year of production in 1929
The plant was located at Hope, because it is at the edge of where carboniferous limestone of the Monsal Dale Group, meets Edale Shale, the two main components of finished cement.
Since 1951, when the Peak District National Park was created, most of the outbound traffic from the plant has been exported by rail.

As seen in the Channel 4 TV ident.

The same location used in Shelagh Delaney’s A taste of Honey.

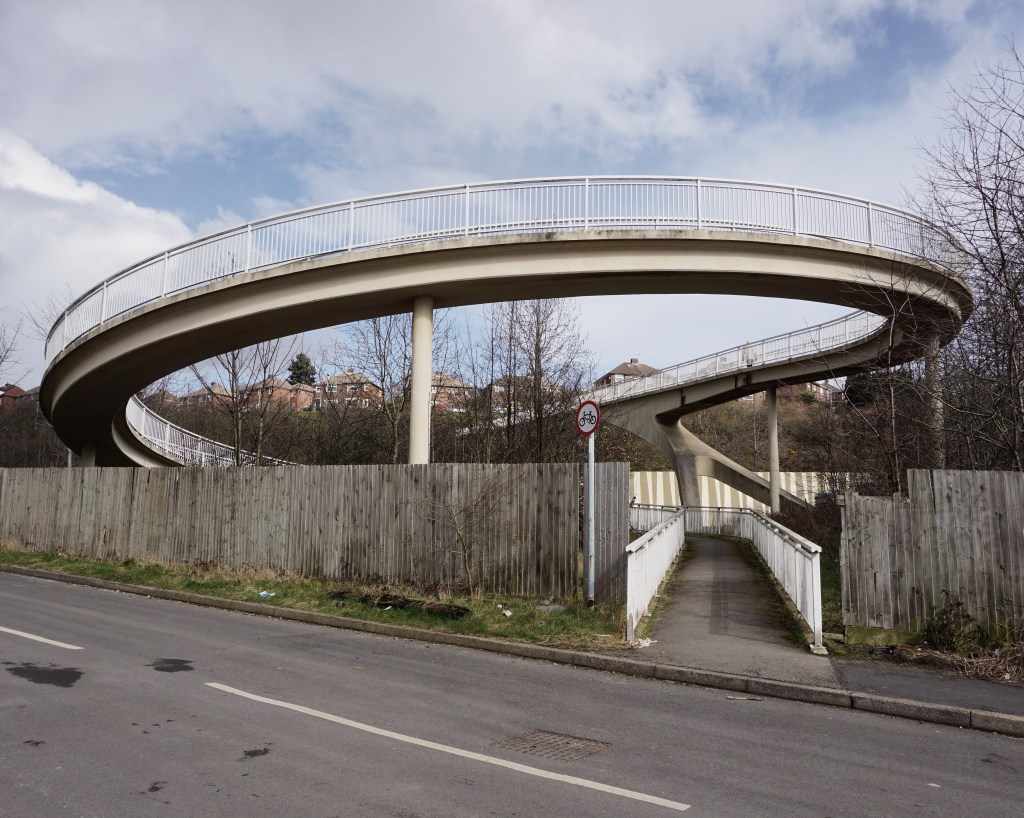
9 Droppingwell Footbridge – West Riding County Architect Colonel Stuart Maynard
Colleagues in the team included Bill Varley, Ron Bridle, Sri Sriskandan and FA Joe Sims. The team was responsible for the introduction of a great deal of new computing technology into bridge design, as well as for some of the most imaginative bridge engineering going on anywhere in the country. Their design efforts were supported by close involvement in research and testing work, for example, on half-joints and concrete hinges. All the above named engineers went on to considerable seniority, some in the Department of Transport, and Sims and Bridle in particular have published various papers and contributed to books on the history of Britain’s motorway development.

10 Beeversleigh Rotherham 1968-71 Main contractors J Finnegan
It’s thirteen storeys high – housing forty eight dwellings.

11 Park House School 1964 Lyons Israel Ellis Gray
Listed in 2017 – then demolished.
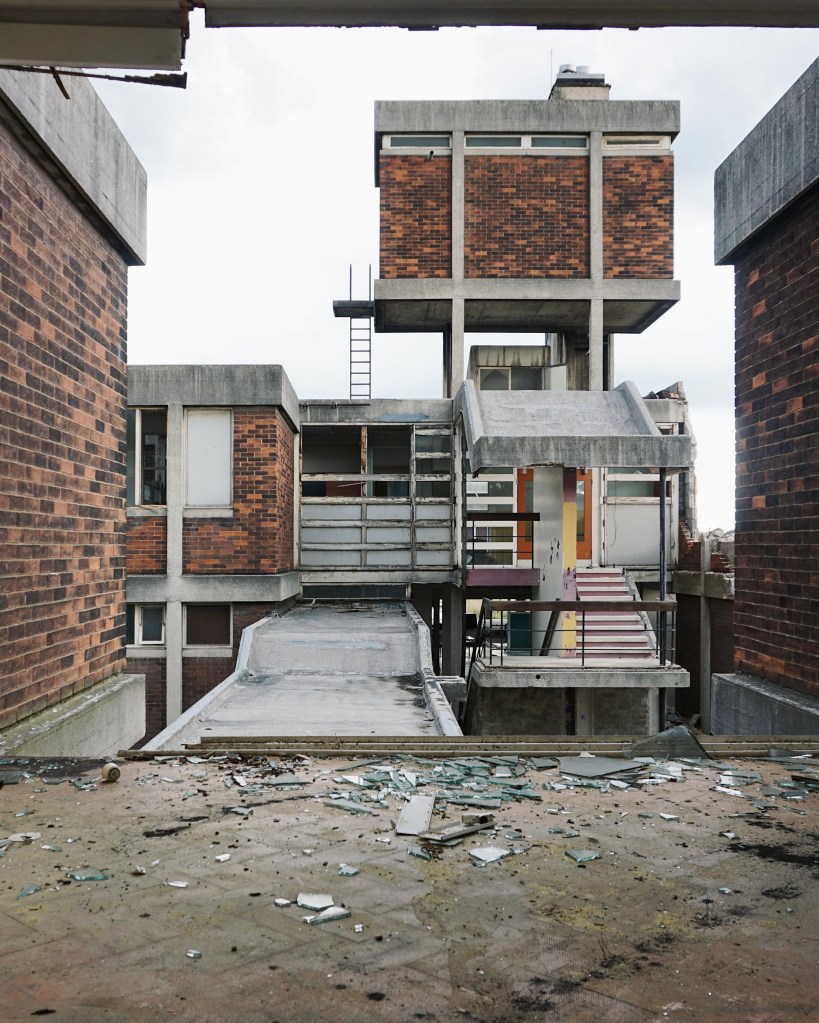

12 Magistrates Court 1978 B Warren City Architect
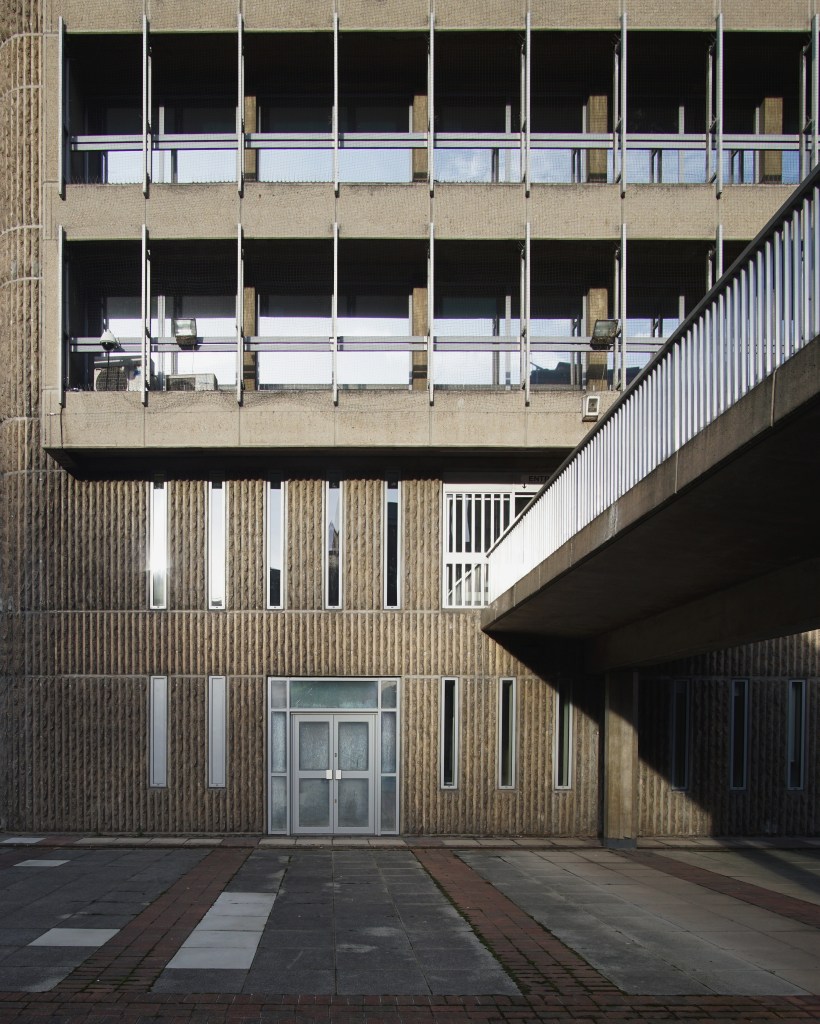

Built using a structure developed by EM Wincher in Pittsburgh 1930.


14 Westfield Estate Mosborough
Formerly Waterthorpe Farm Estate a rural township which was subsumed by Sheffield’s expanding housing schemes.
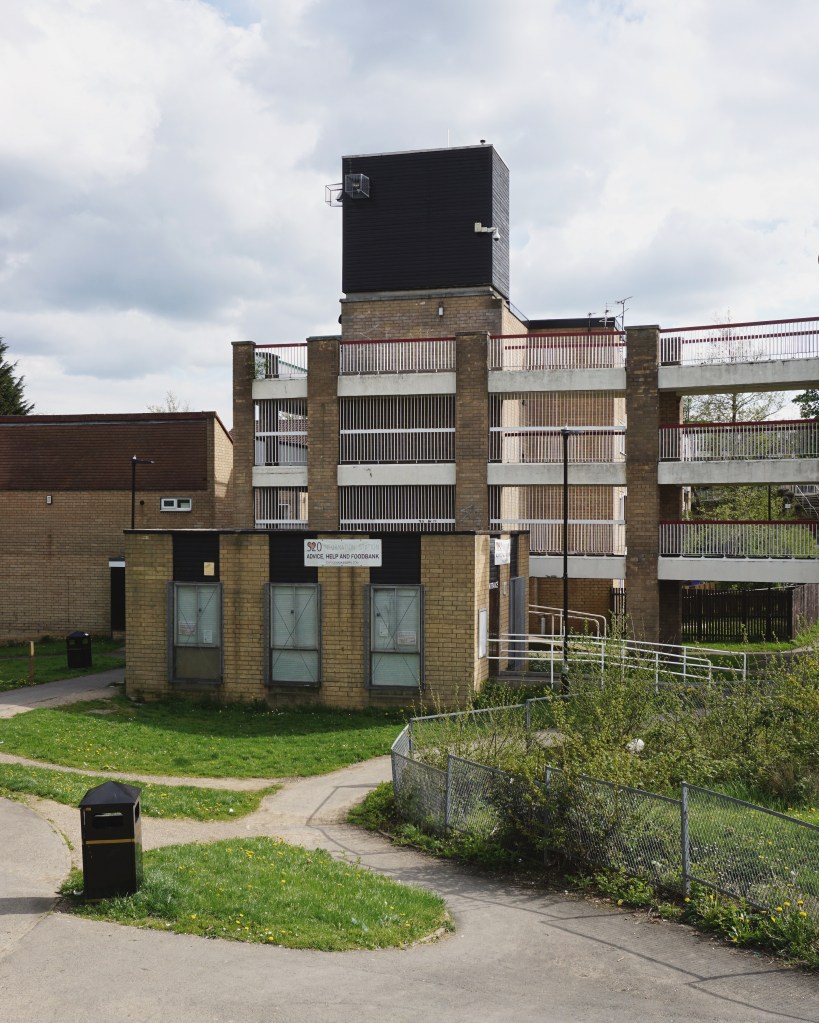

I have walked around the exterior on more than one occasion.
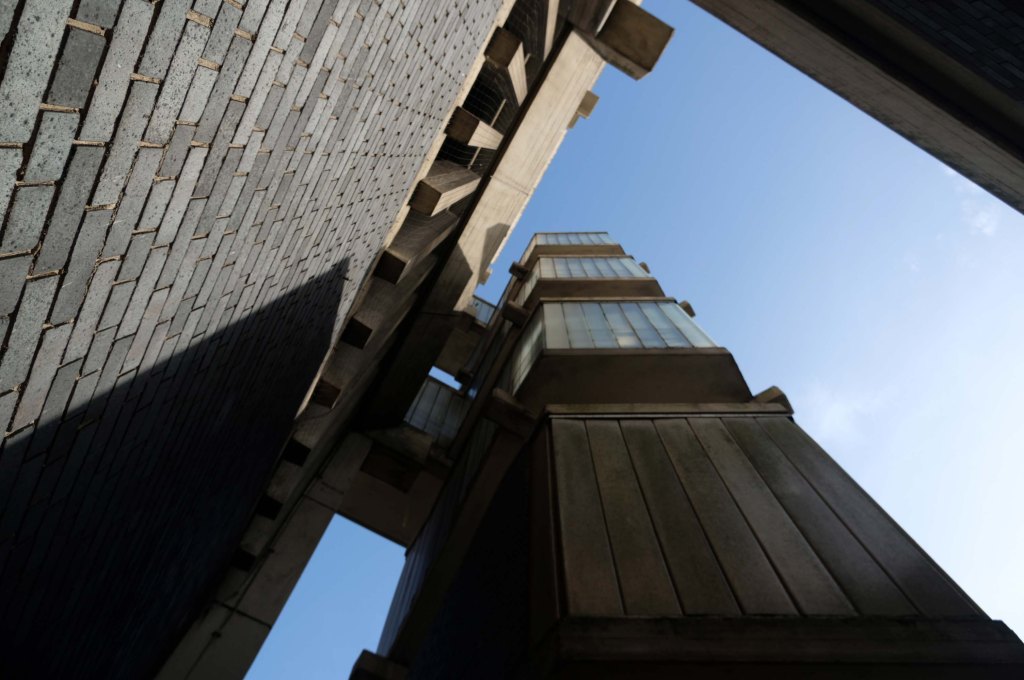
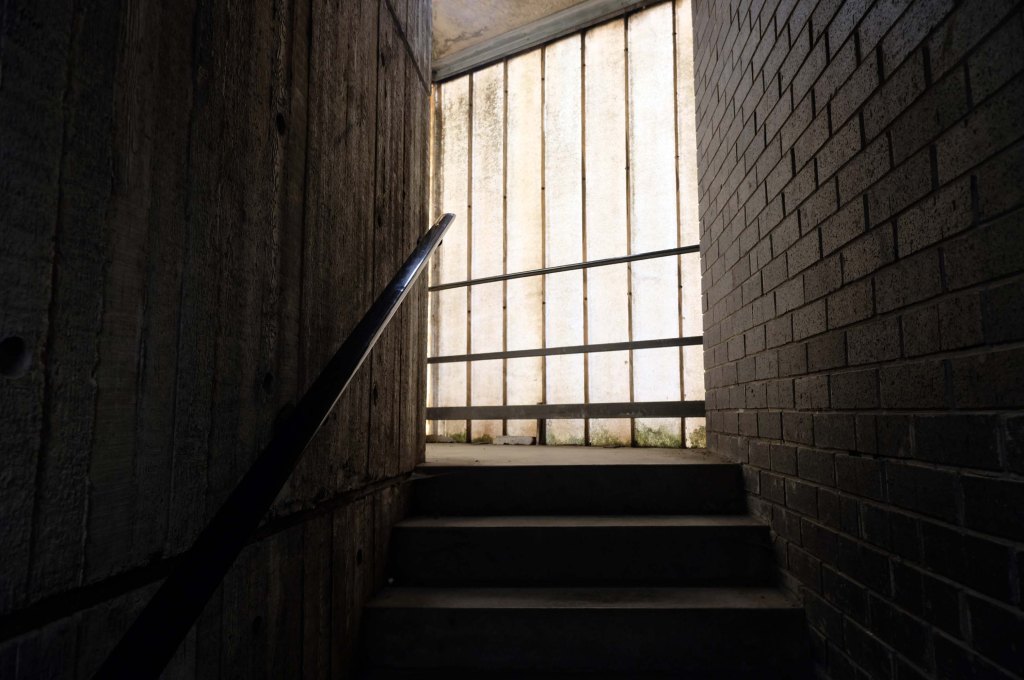
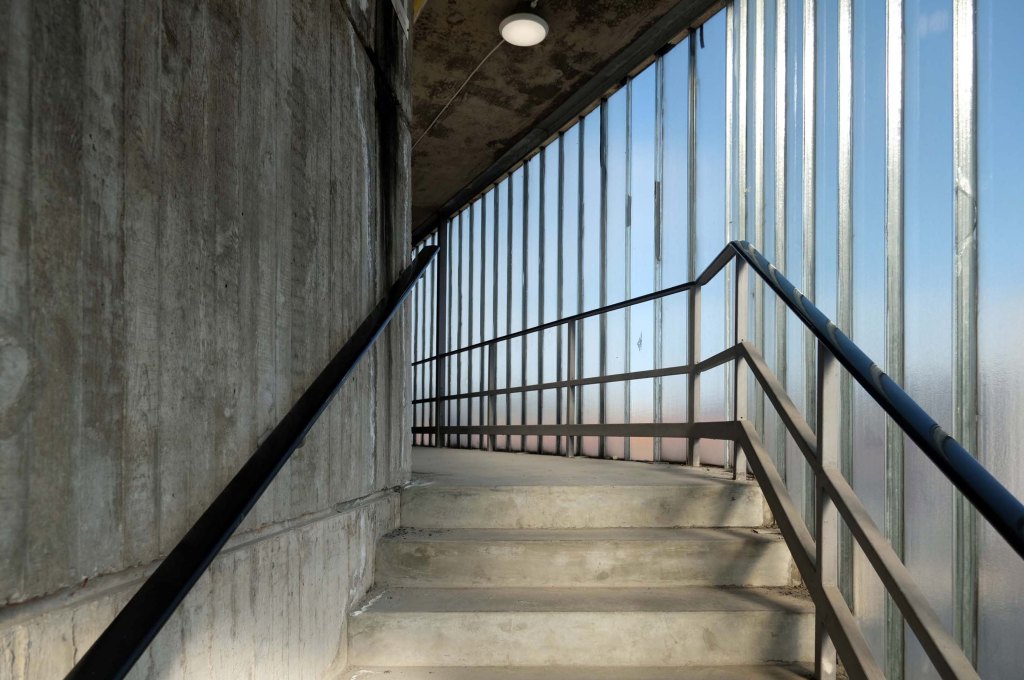
This concrete enclosed, collection of transformers and switchgear.
Electricity substation. 1968 to designs by consulting architects Jefferson, Sheard and Partners, Sheffield, led by Bryan Jefferson, in association with the Regional Civil Engineers’ Department of the CEGB North East Region. Contractors, Longden & Sons Ltd, Sheffield. Reinforced concrete frame with board-marked finish with formwork bolt marks, construction and daywork joints emphasised, concrete floor slabs, blue engineering facing bricks, cladding panels of Cornish granite aggregate.
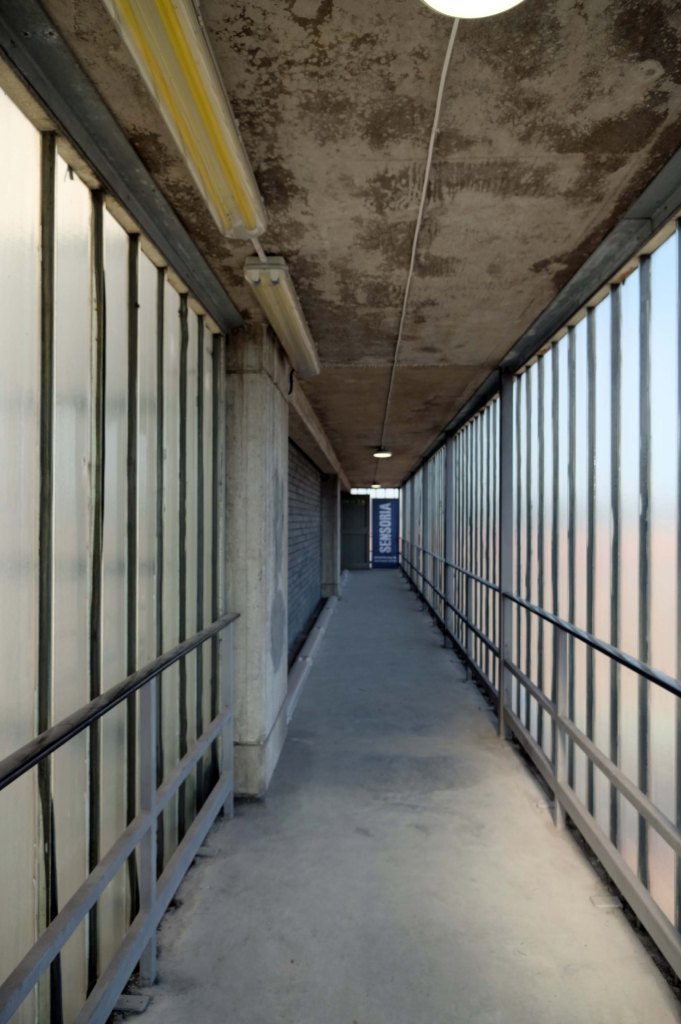
The good folk at Sensoria and The Black Dog staged My Brutal Life inside the building – using the void created by the non-expansion of expanded demand for electricity.

The exhibition features work by Bill Stephenson, Mick Jones, Mandy Payne, Martin Dust, Scott Amoeba, Richard Davis, Jen Orpin, Alun Cocks, Human Studio, Sean Madner, Helen Angell and The Black Dog.
Let’s take a look outside inside out.
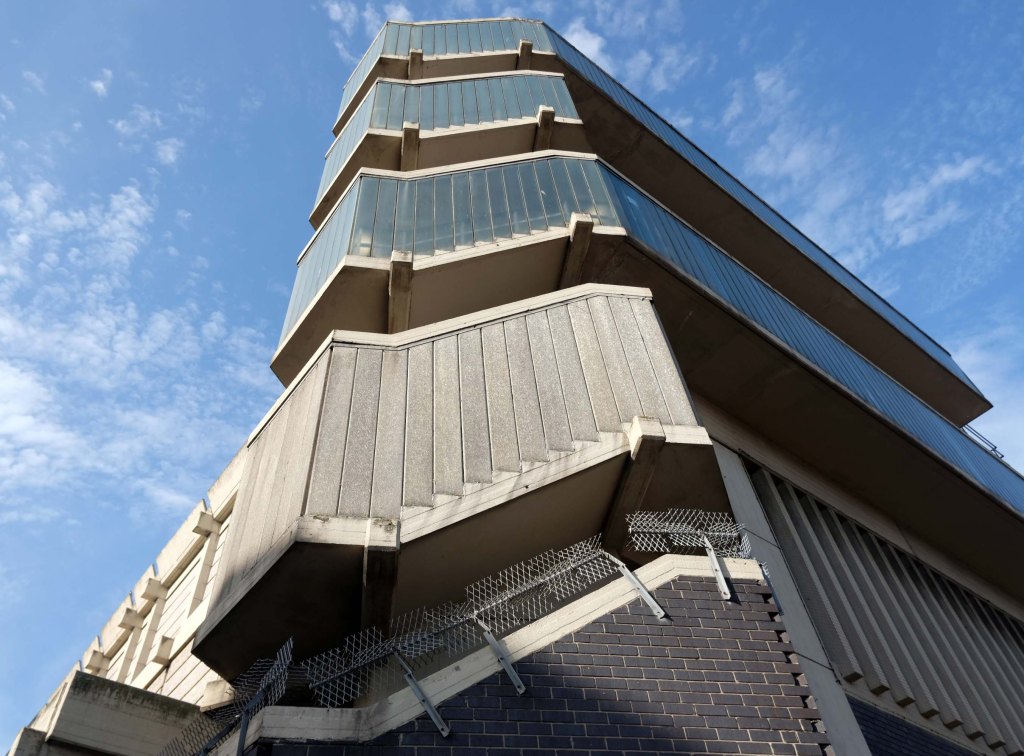
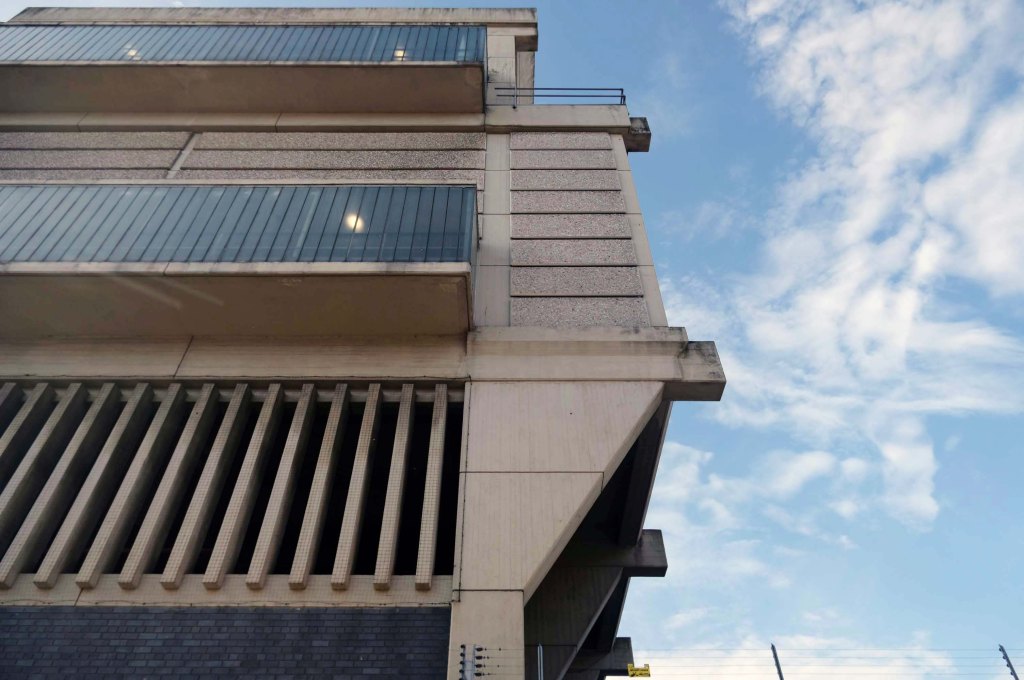
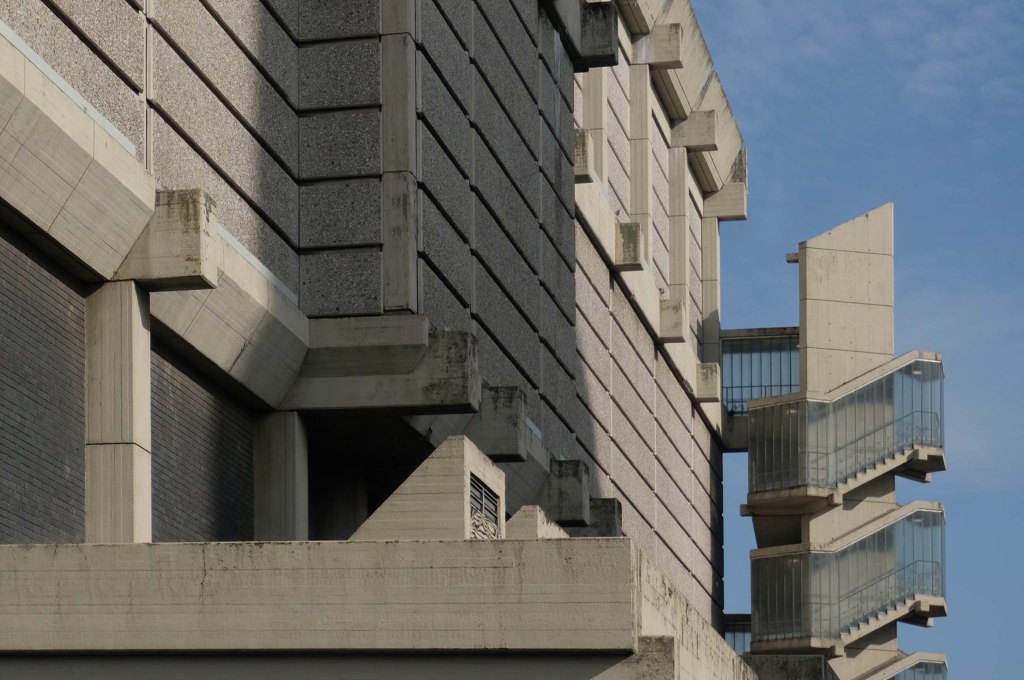



















Thanks.
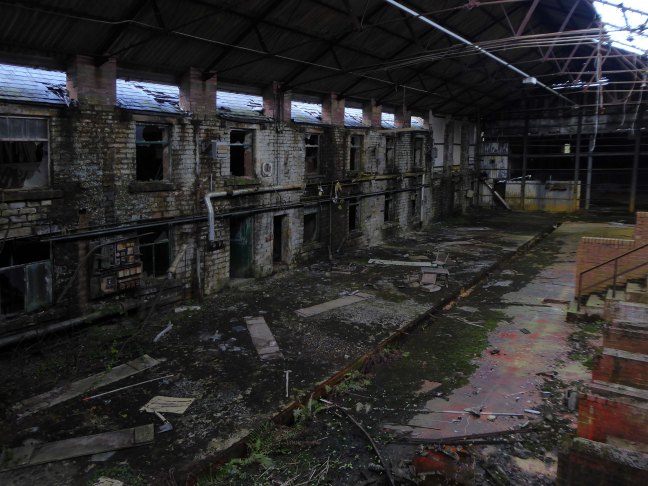

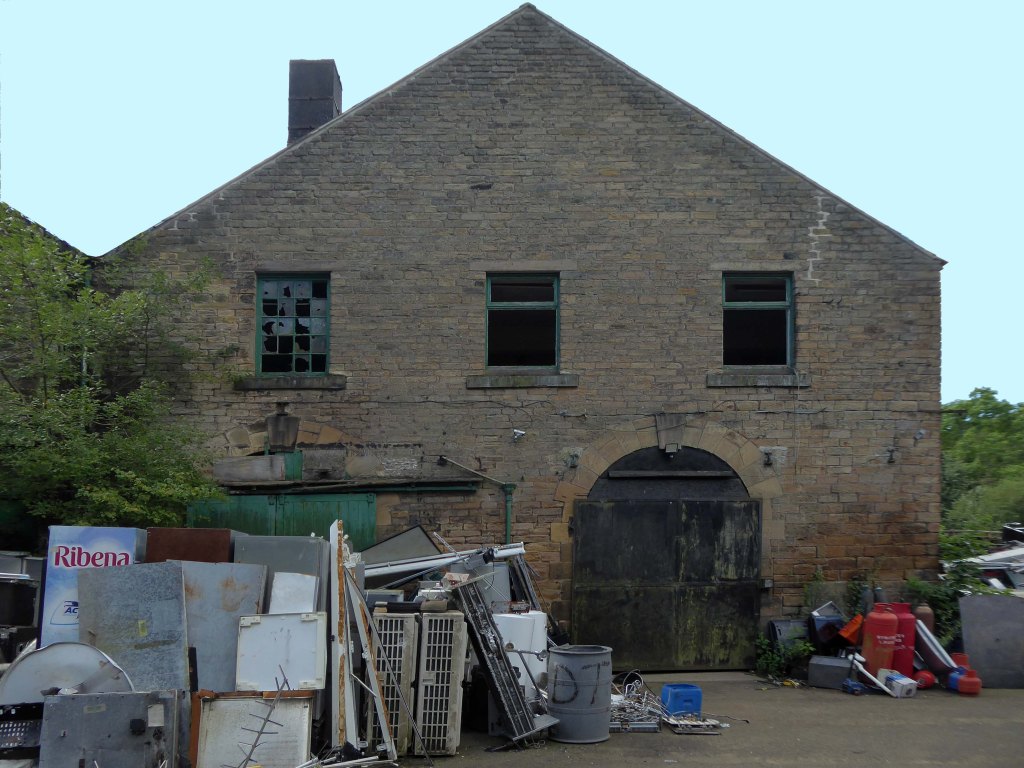
Chisworth Works Coombes Lane Holehouse Charlesworth and Chisworth SK13 5DQ
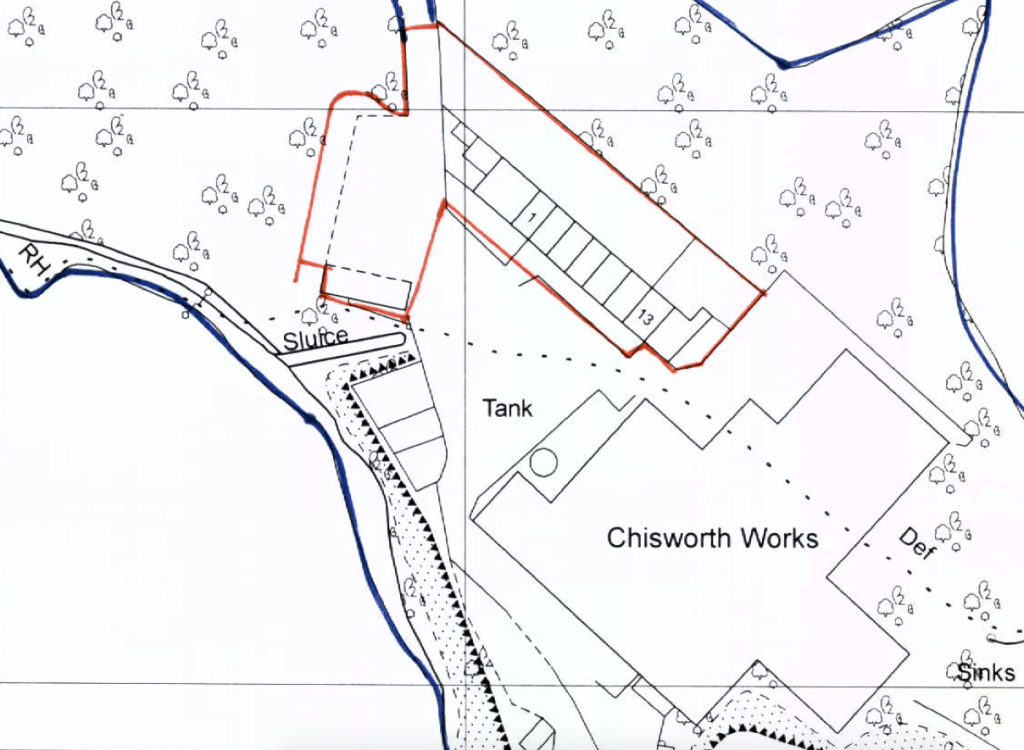
Built at the end of the 18th or in the early 19th centuries; Chisworth Works was as a cotton band manufactory. During these times, the site was called Higher Mill.
It was referred to as Higher Mill, as there was a lower works, Mouse Mill in Holehouse, owned by the Booth family.

Keiner & Co., at Charlesworth, employ over 100 people and are engaged principally in the production of synthetic and chrome tanning extracts.
Glossop Official Handbook 1948
It has been a longstanding, low-lying object of interest to those intrepid Urban Explorers.
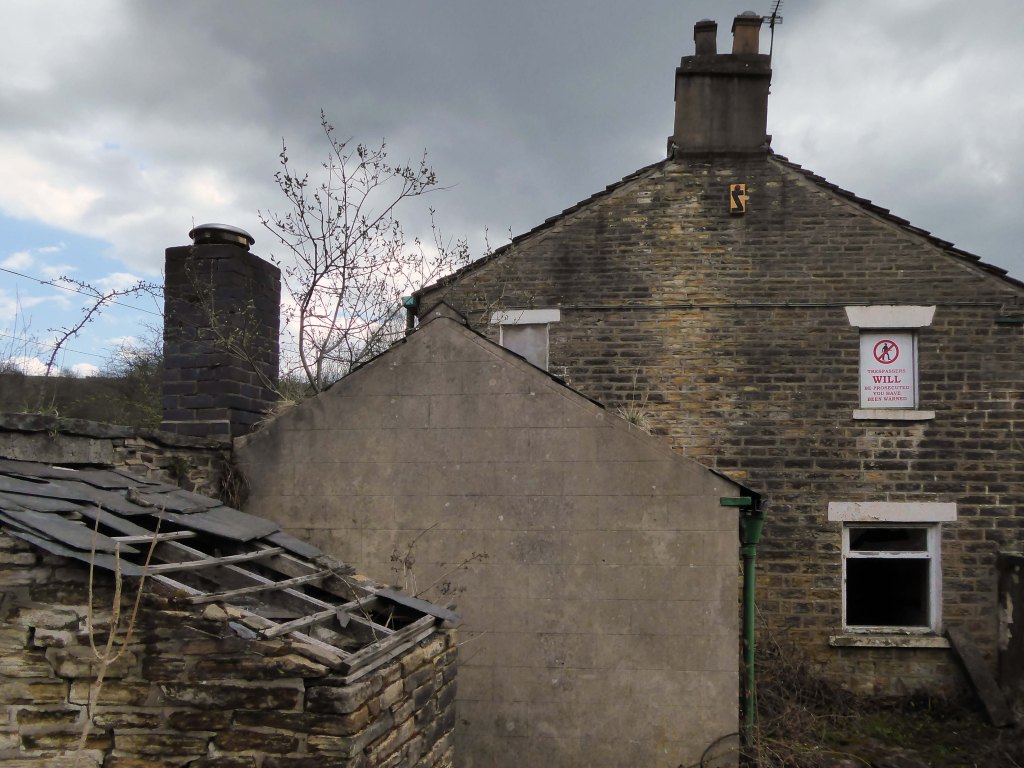
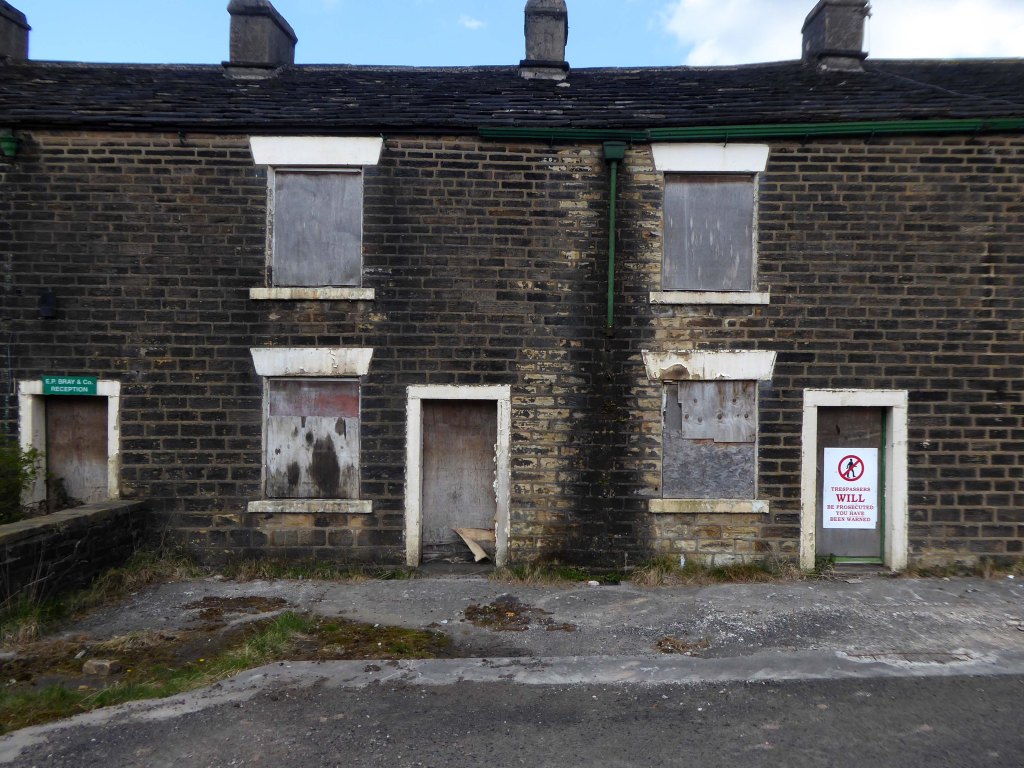
A planning application of 2009 was submitted for redevelopment of the terraced cottages.
Proposed alterations and change of use to form ten two bedroom cottages from existing five dwellings and vacant office accommodation.
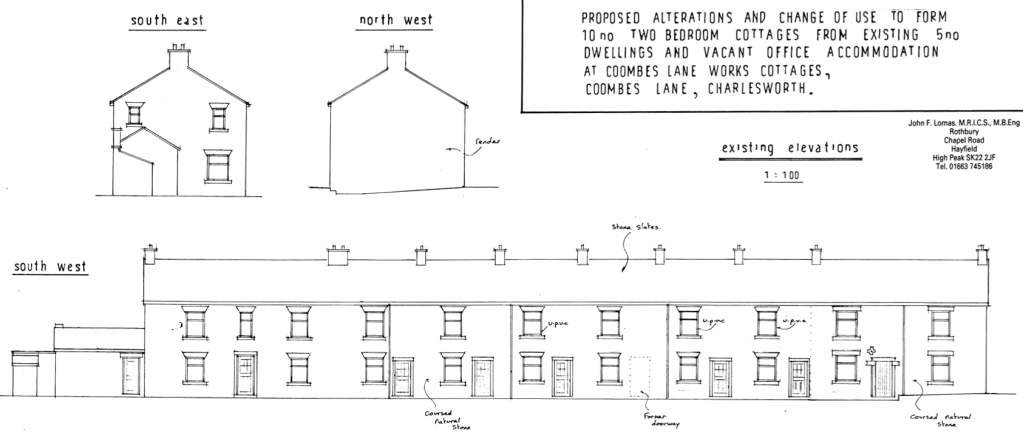
This was the state of play in April 2021 – the interior photographs were taken through an open aperture.





Lead Chromate can affect you when inhaled or swallowed. Contact can irritate and burn the skin and eyes. Prolonged skin contact may cause blisters and deep ulcers.
Inhaling Lead Chromate can irritate the nose, throat and lungs.Exposure can cause headache, irritability, and muscle and joint pain. Repeated exposure can cause Lead poisoning with metallic taste, colic and muscle cramps.
Inhaling Lead Chromate can cause a sore and/or a hole in the septum.
Lead Chromate may cause a skin allergy.
Lead Chromate may damage the nervous system. Exposure may cause kidney and brain damage, and anemia.
The building was subsequently owned by EP Bray.

Wherever the choice has had to be made between the man of reason and the madman, the world has unhesitatingly followed the madman.
Aldous Huxley – Crome Yellow
Chrome yellow is a derivative of Lead Chromate.
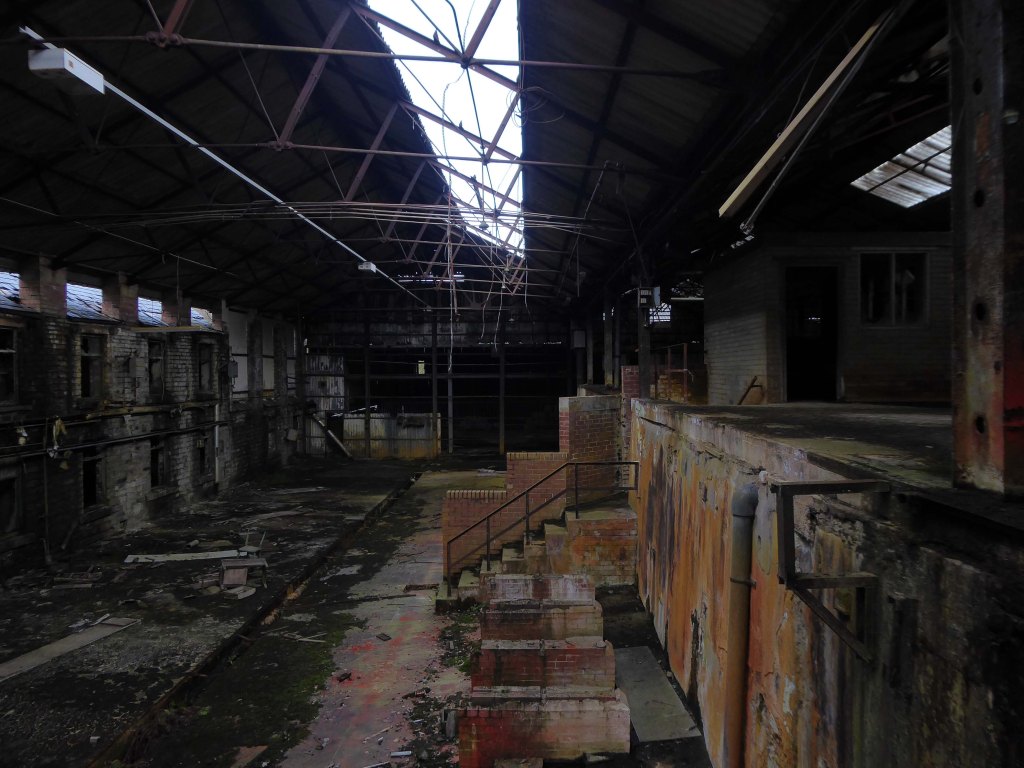
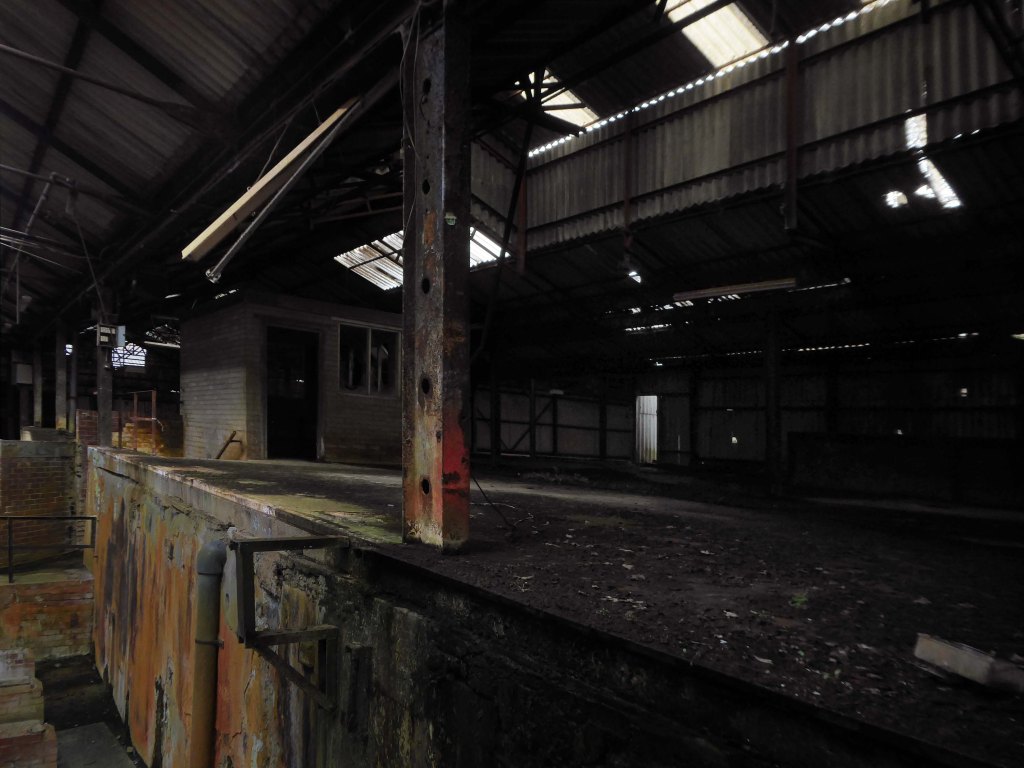


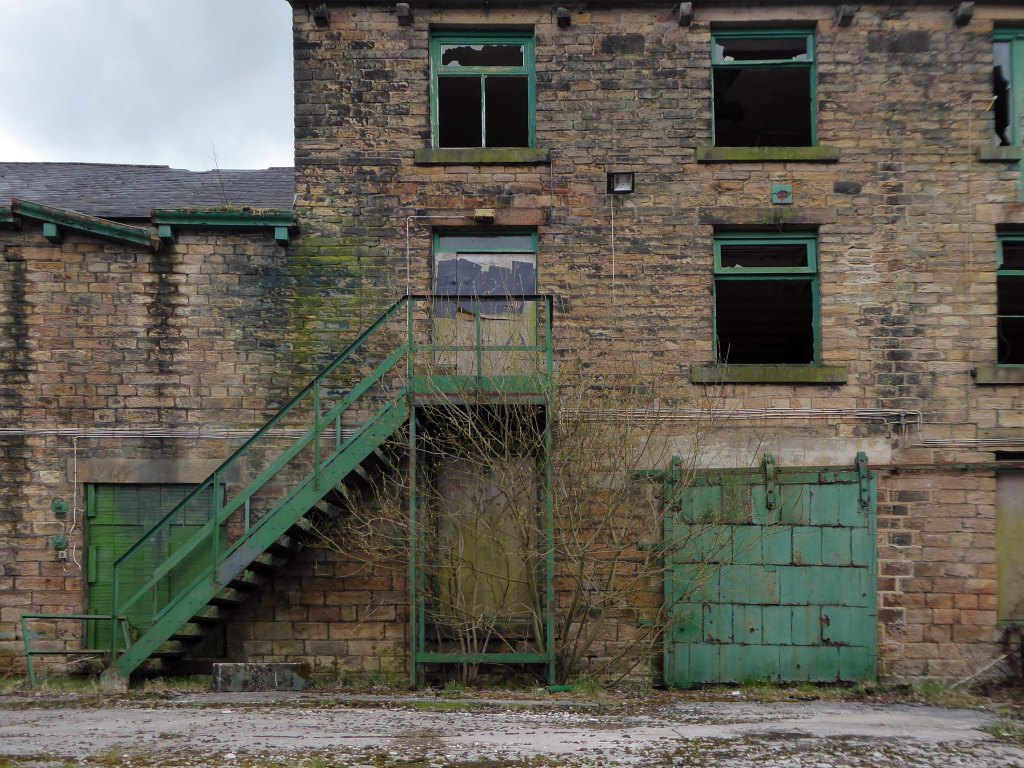
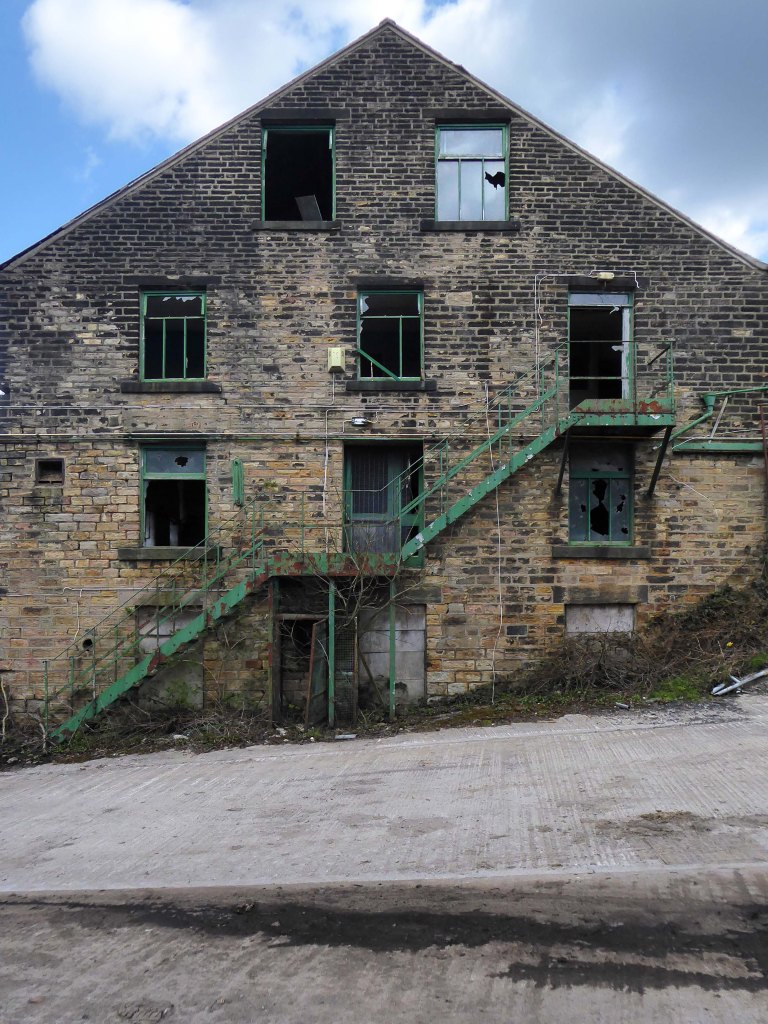
For over two hundred years the site has been a place of toil, dangerous toil taking its toll.
The valleys which inevitably fed the Mersey, were home to the origins of the Industrial Revolution – people and water powered.
This is a toxic landscape, nestled in the heart of ancient post-glacial earth movements:
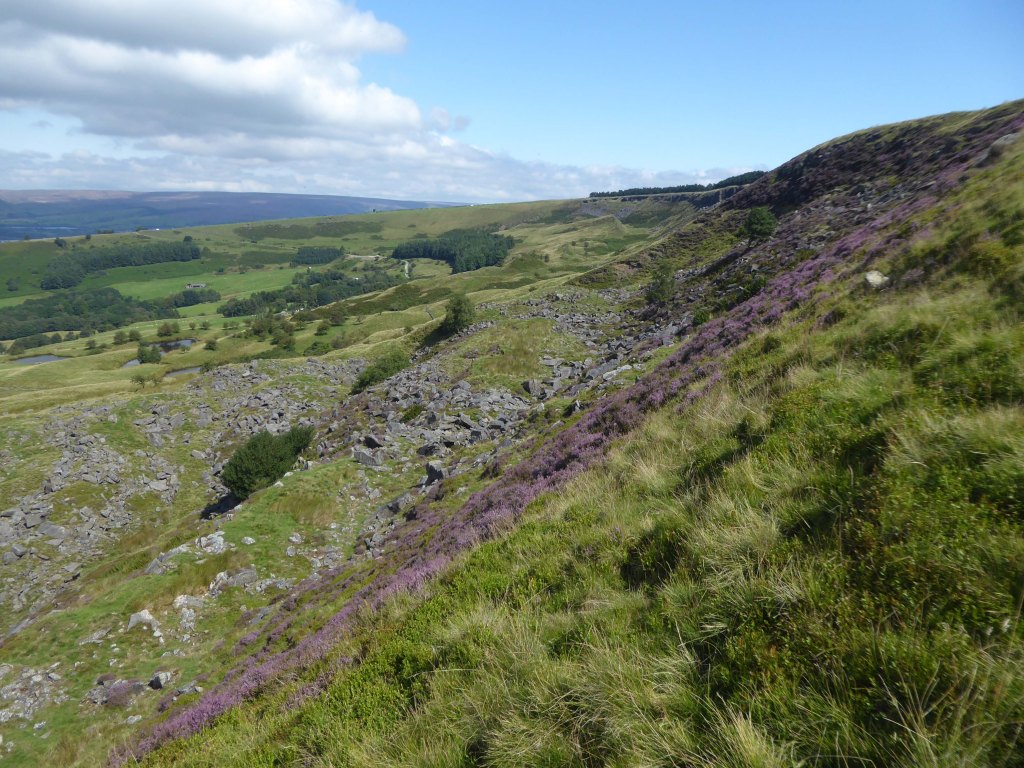

Geomorphological investigations of two landslide areas on the Cown Edge escarpment showed that slope failure was primarily the result of local stratigraphic and lithological conditions and not of past climatic vicissitudes or changes in the form of the relief. Failure on each occasion took place by shearing along the same line of weakness: shales either within a calcareous shale band or in close proximity to it became decomposed and unable to bear the weight of the slope forming material above it. Each displacement resulted in a bank slip failure and the formation of a block glide landslide. The morphology indicates that slip movements has occurred several times and the periods when these took place have been determined using palynological methods. These results indicate that the Cown Edge landslides date from a post-glacial period.
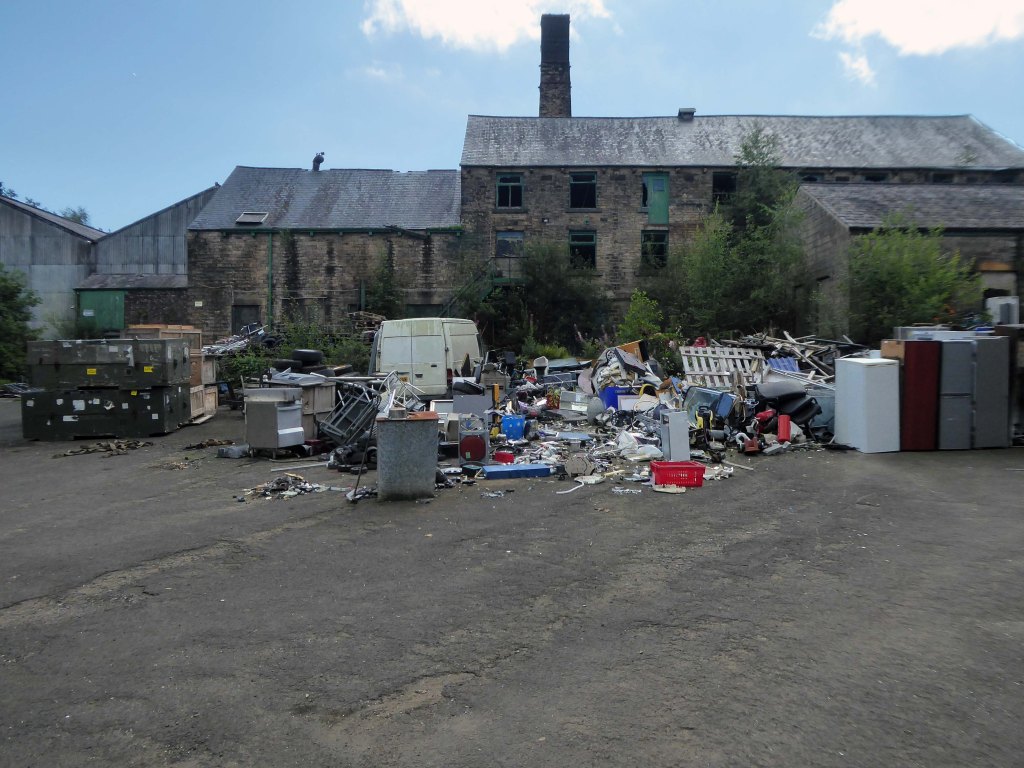
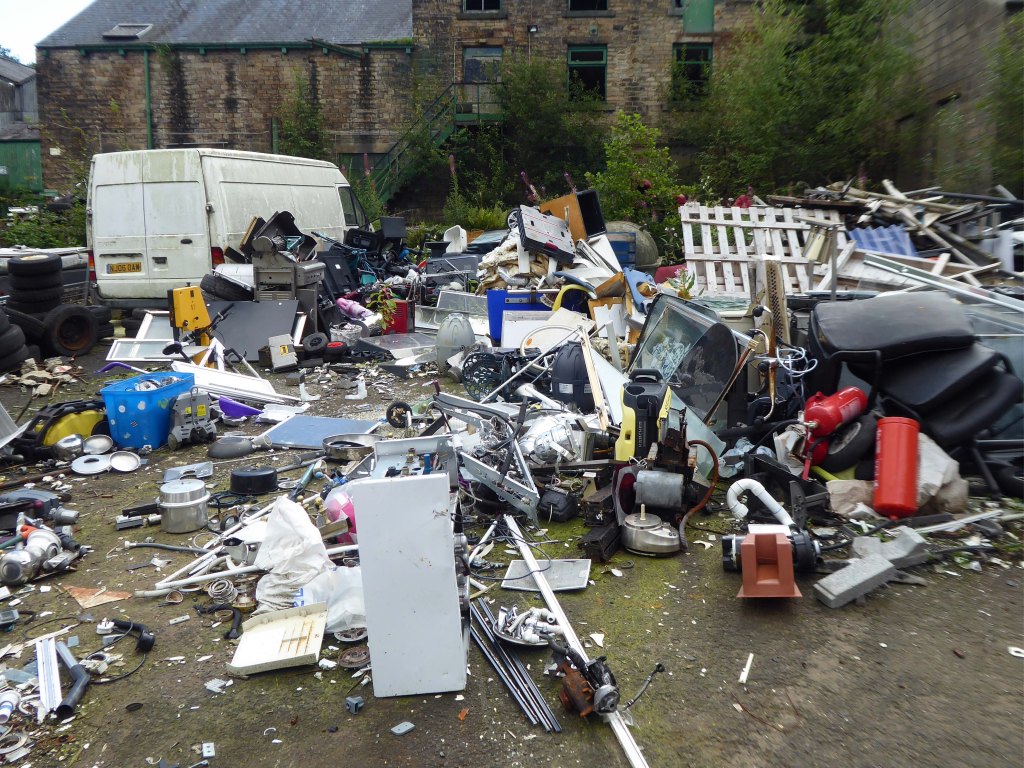
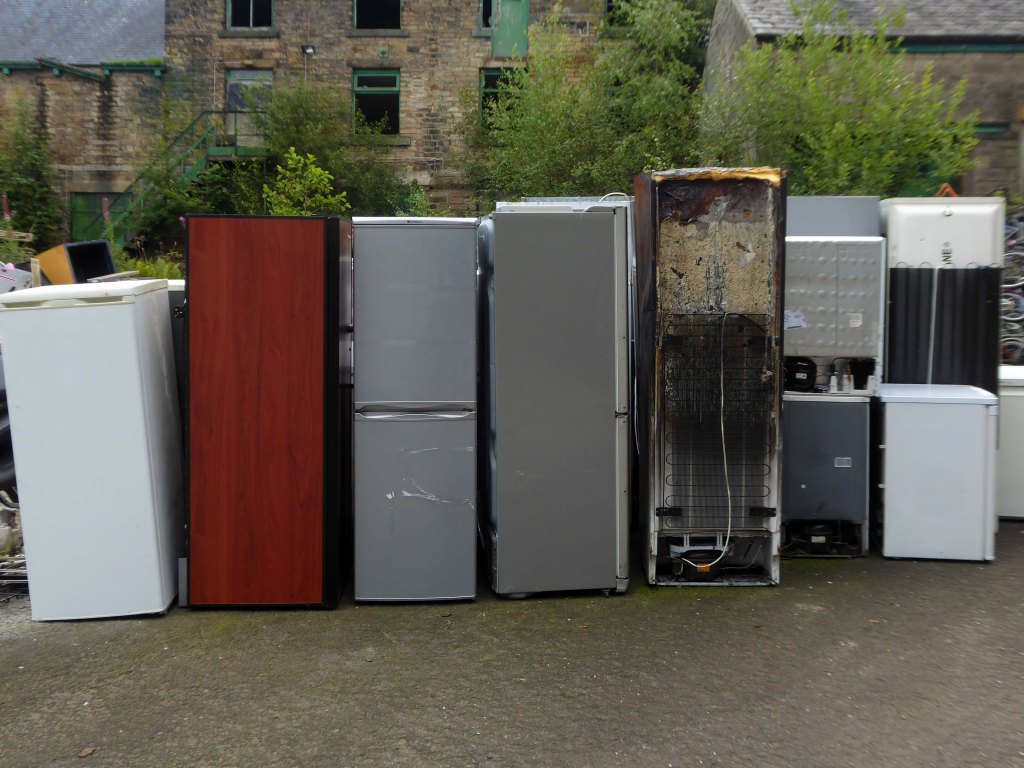
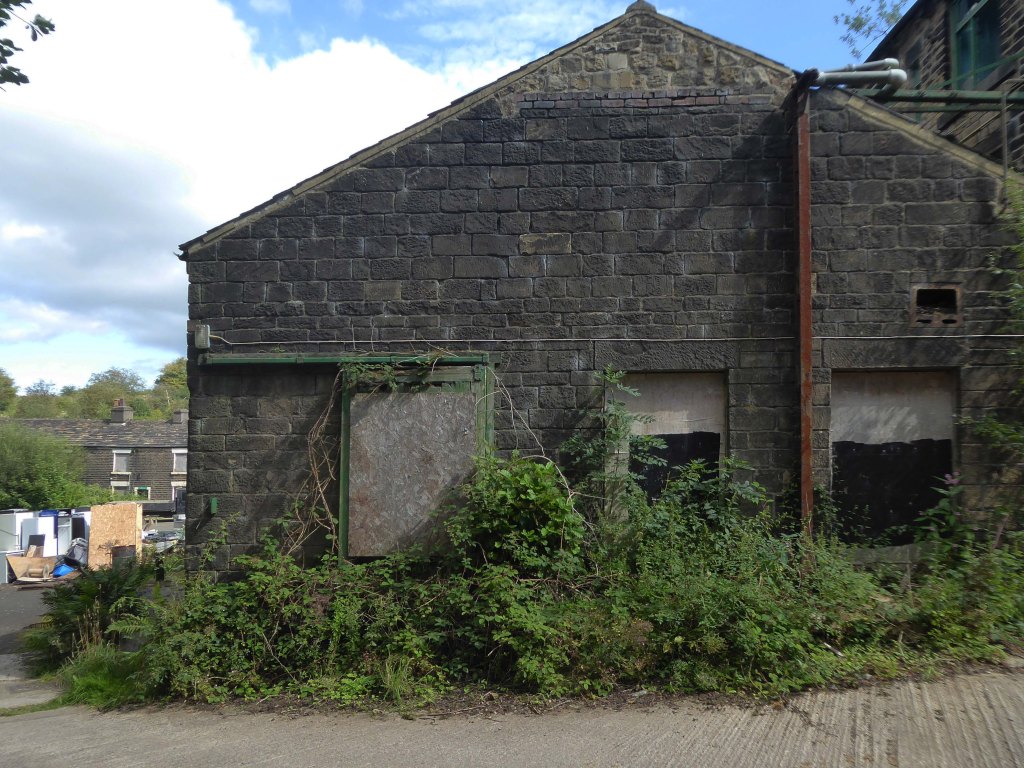
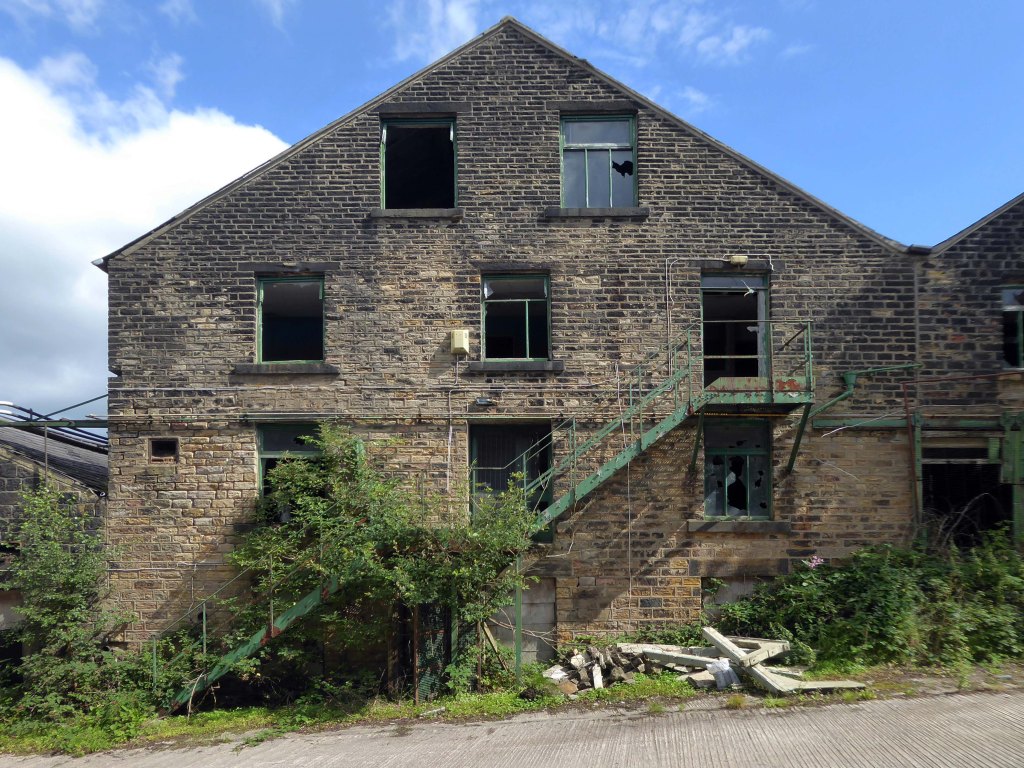
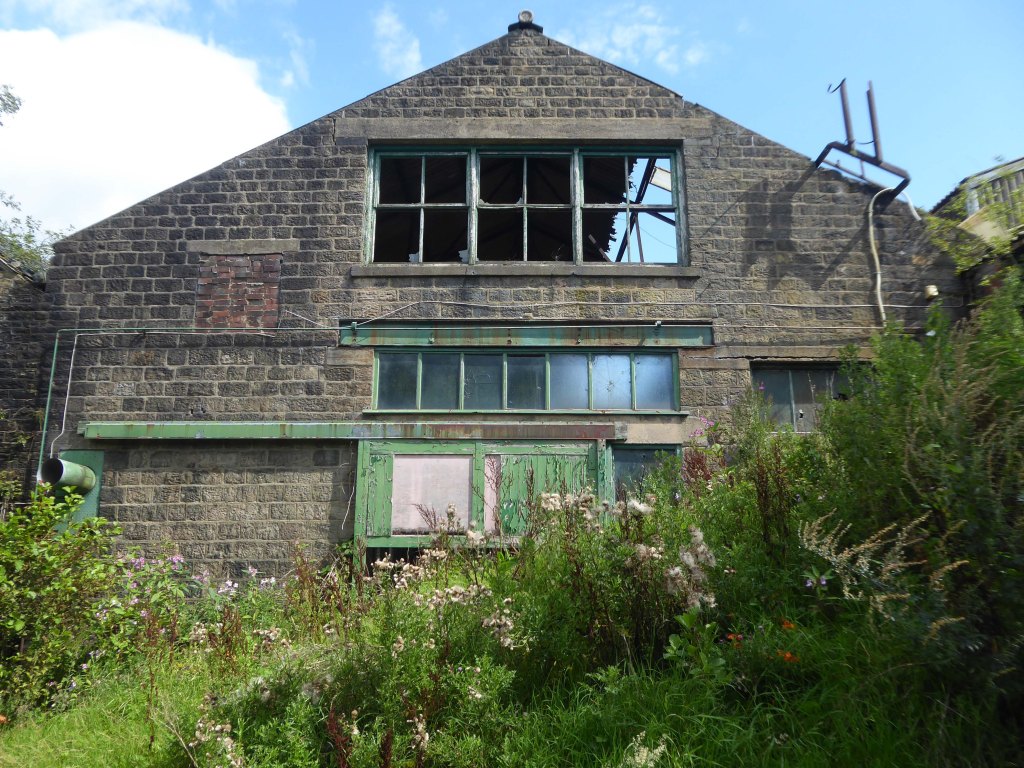
As of August 2023 the terraces remain un-rehabilitated.
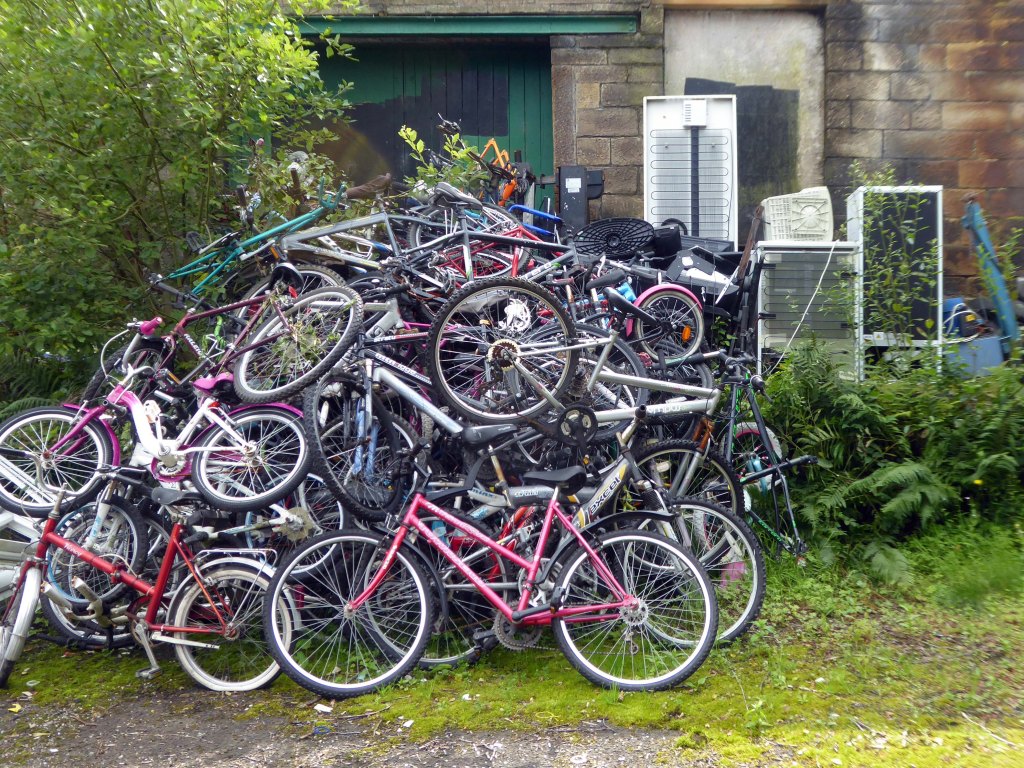
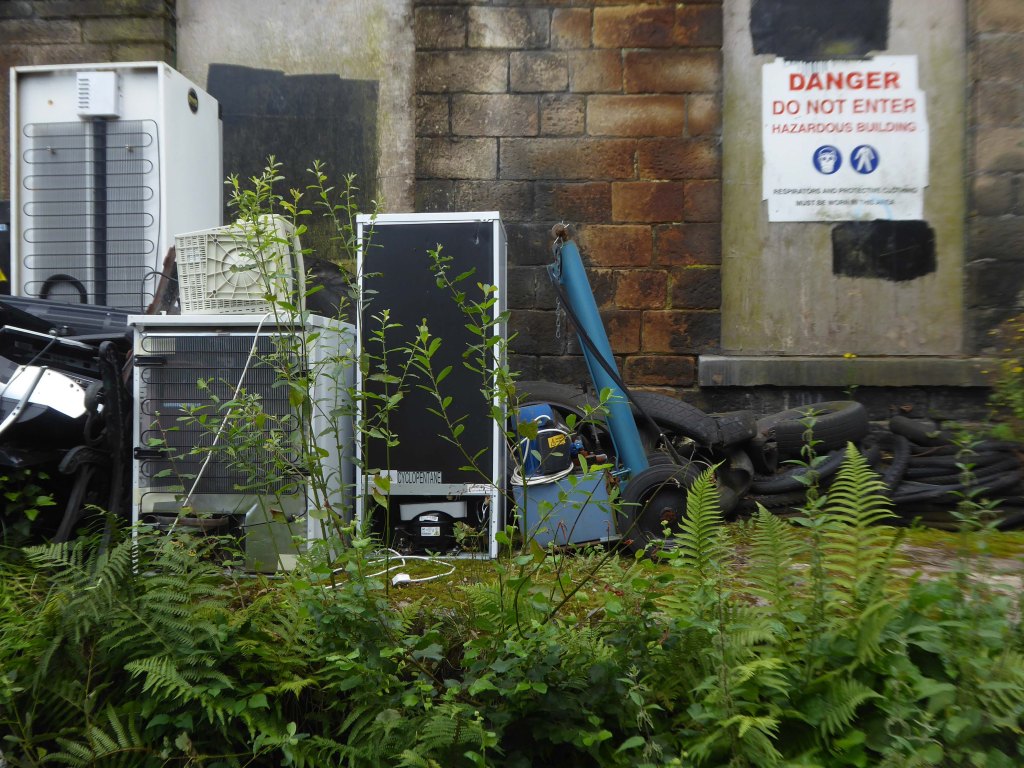
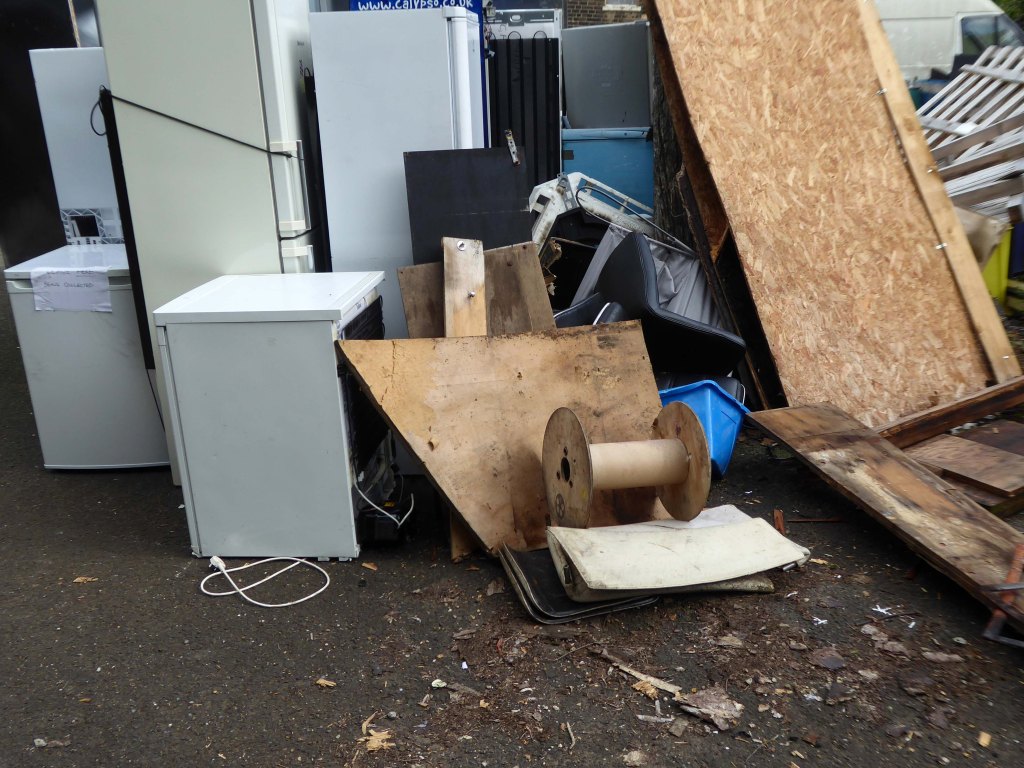
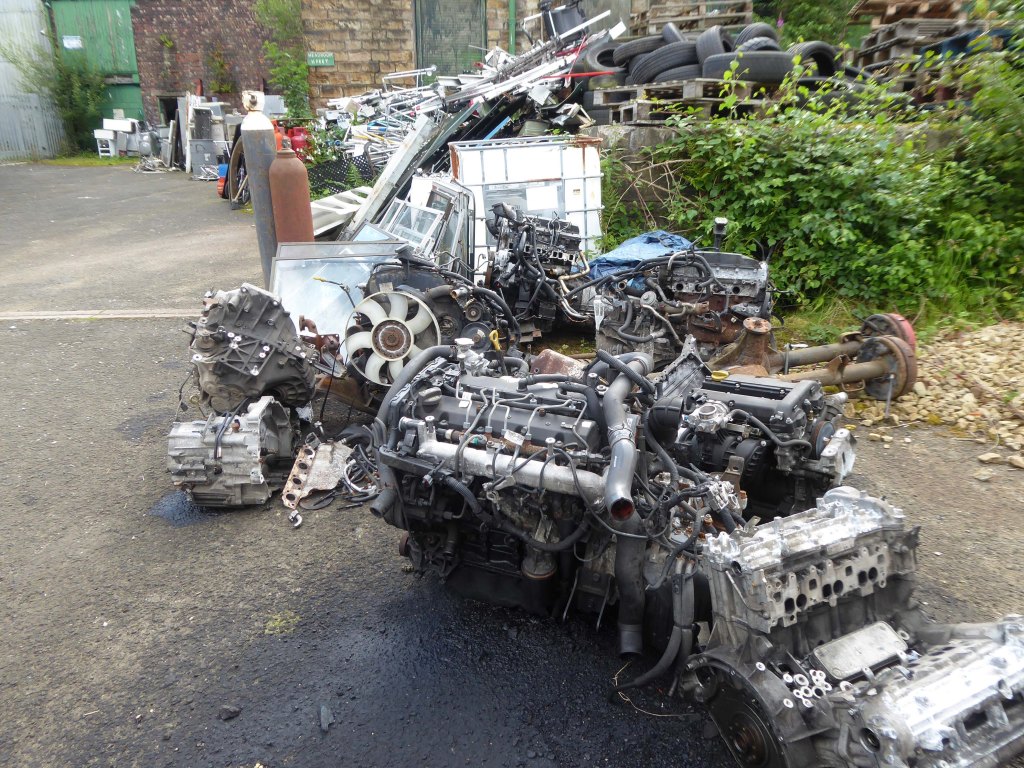
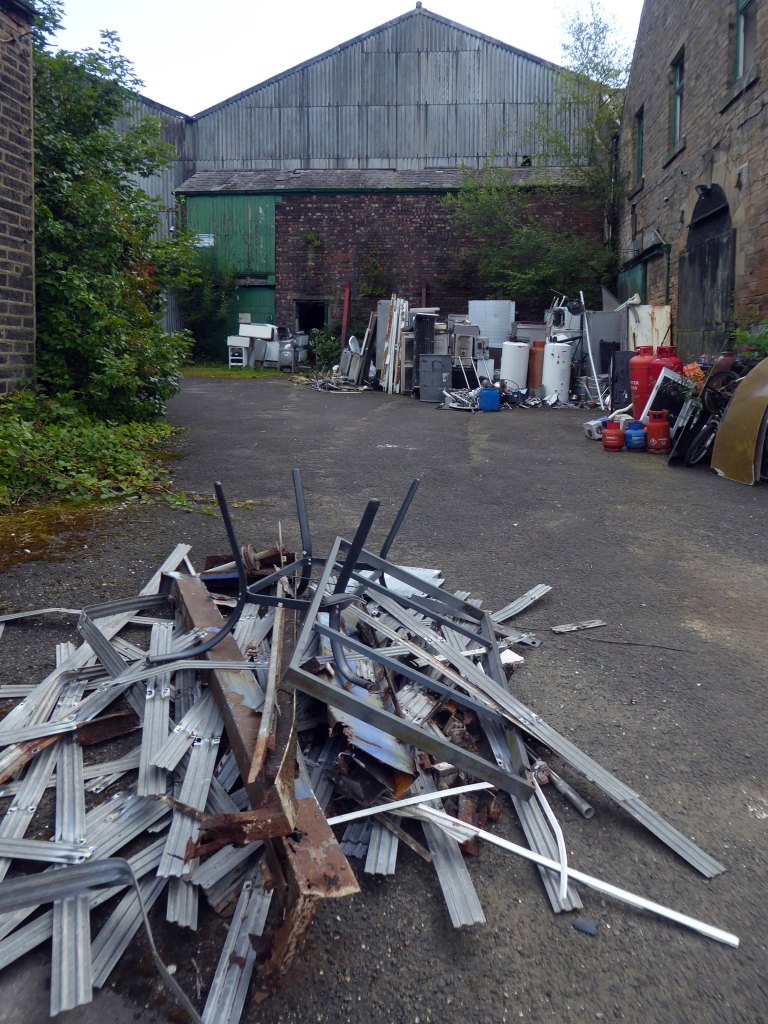
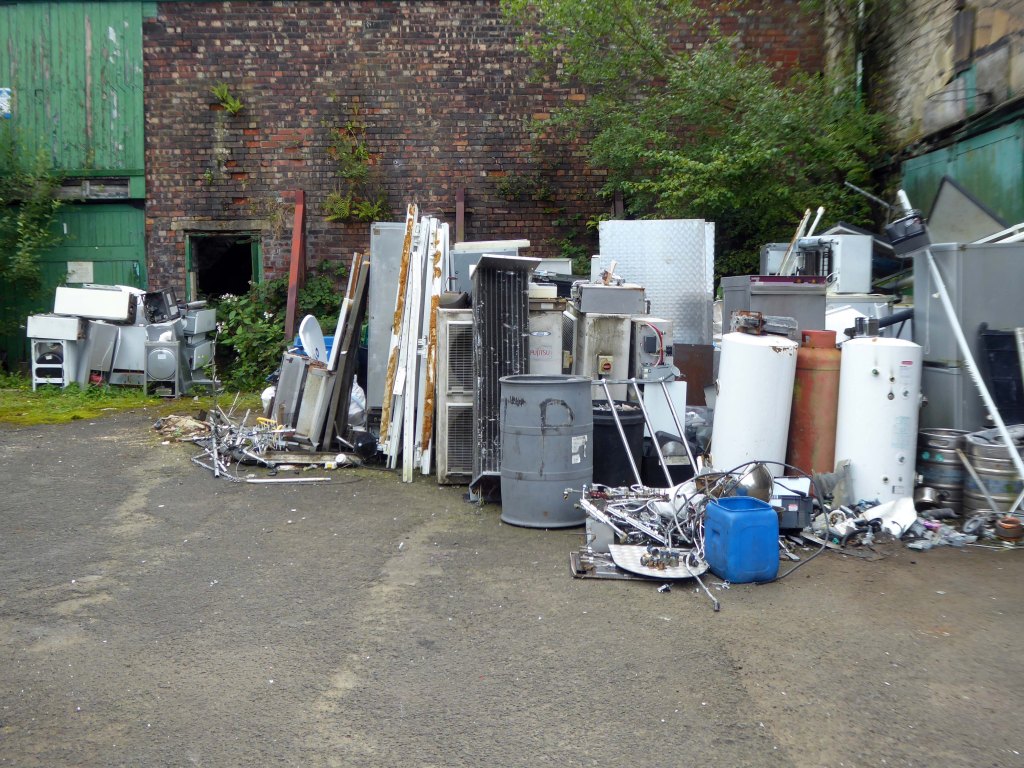
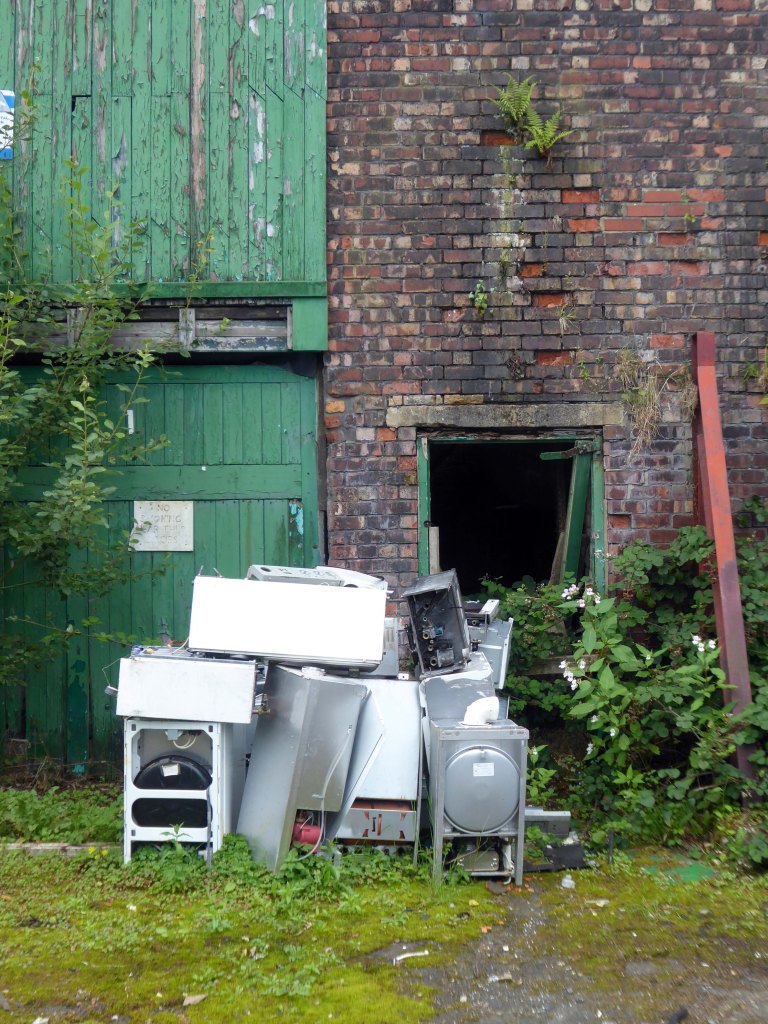
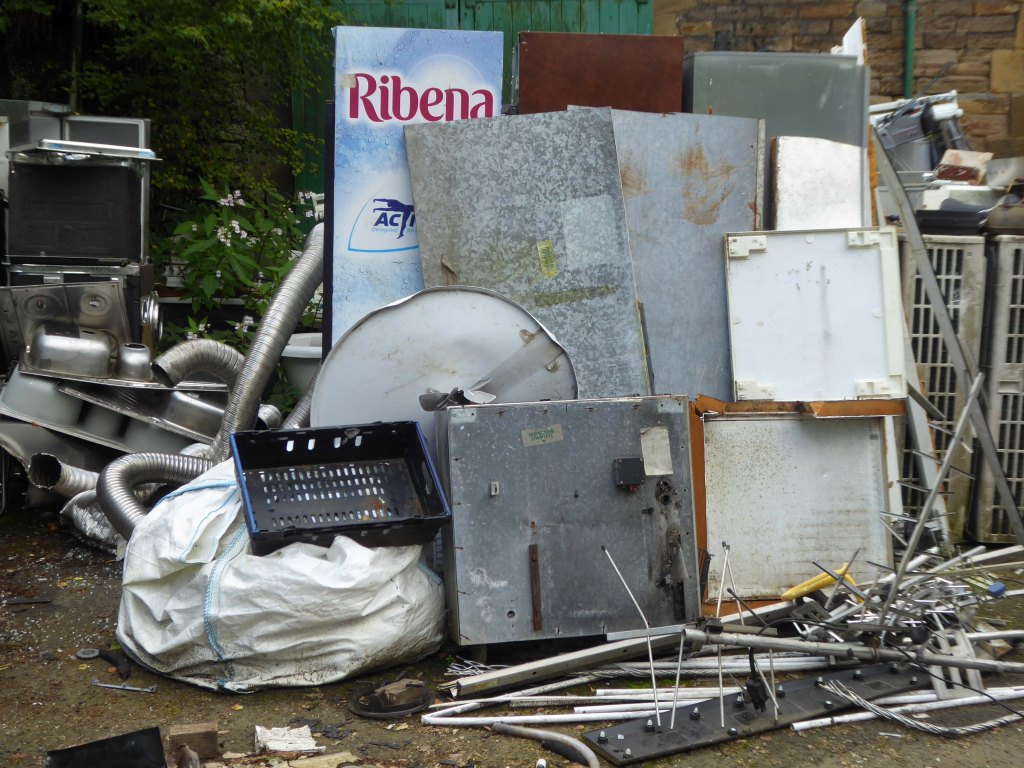
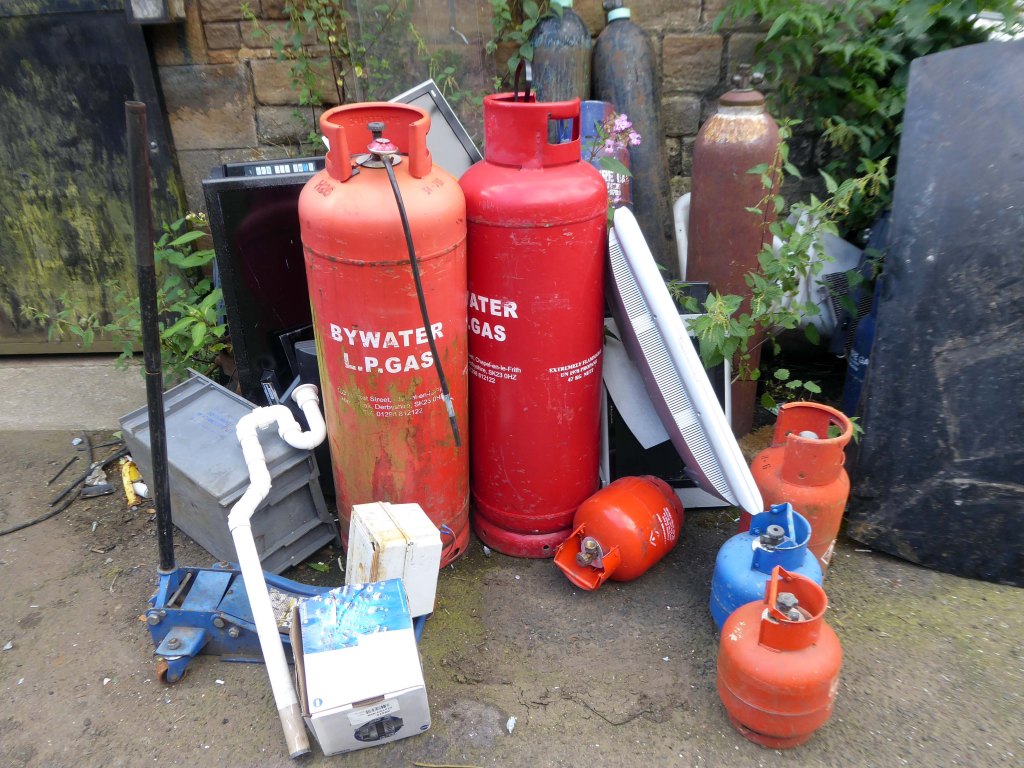
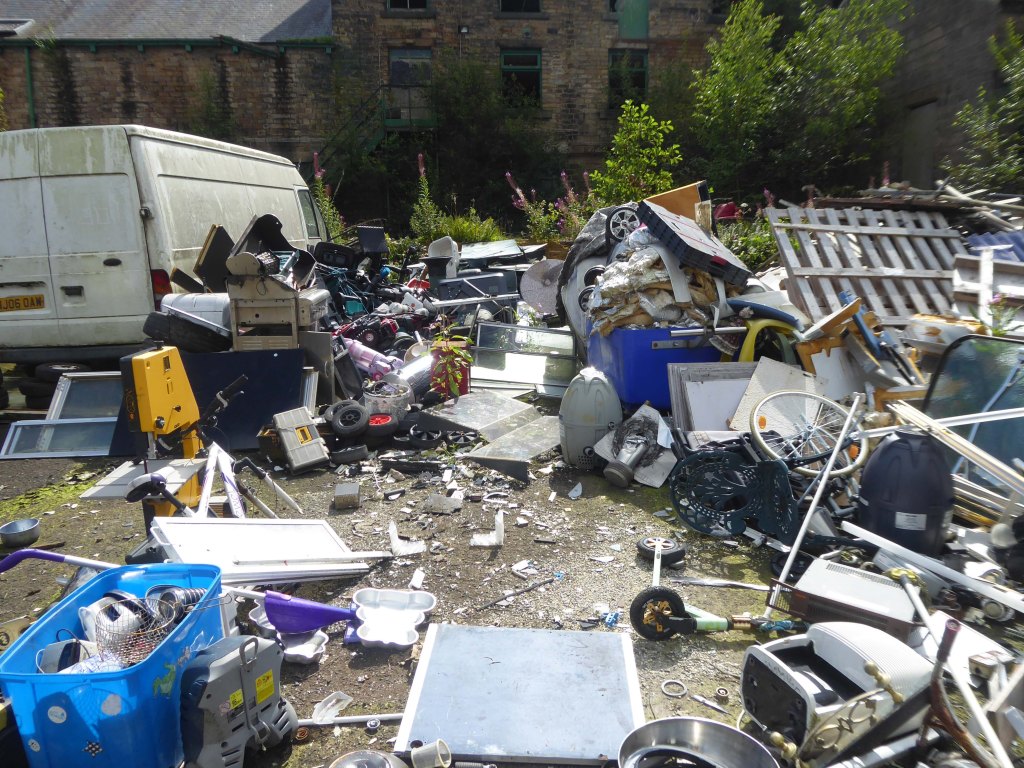
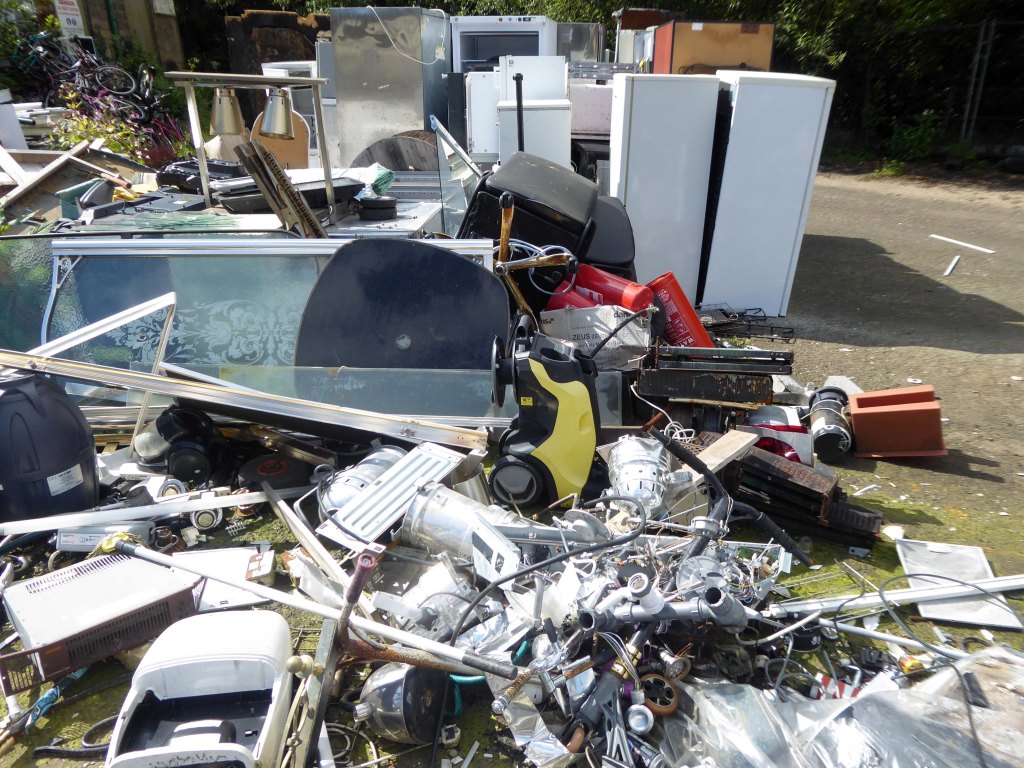
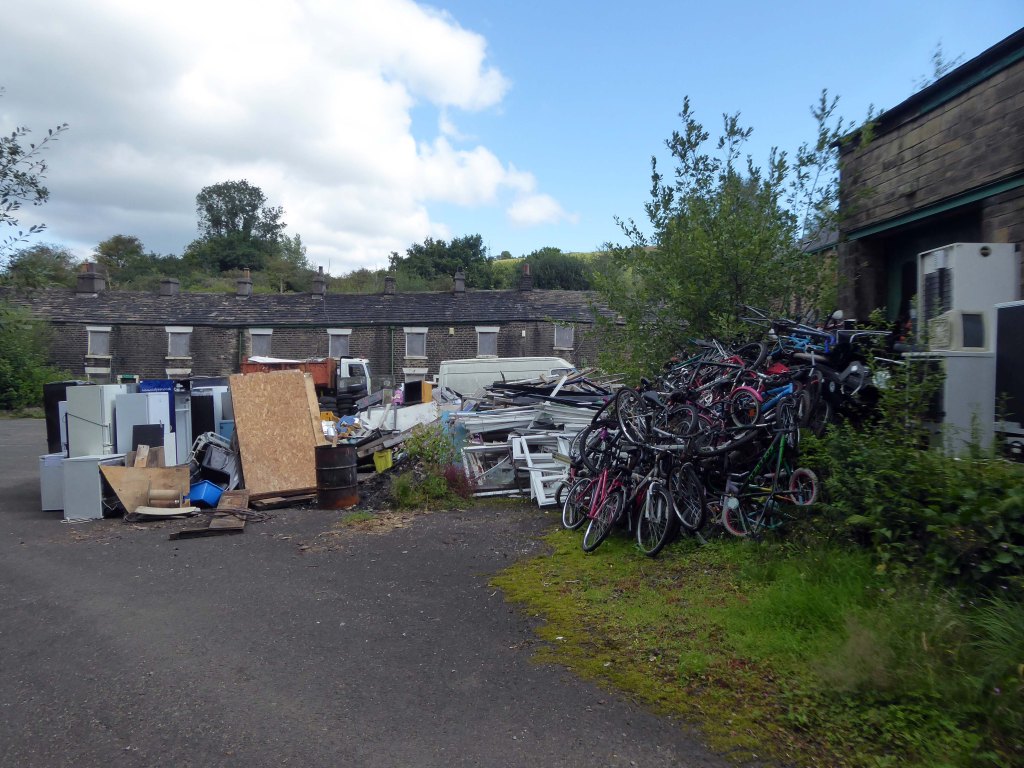
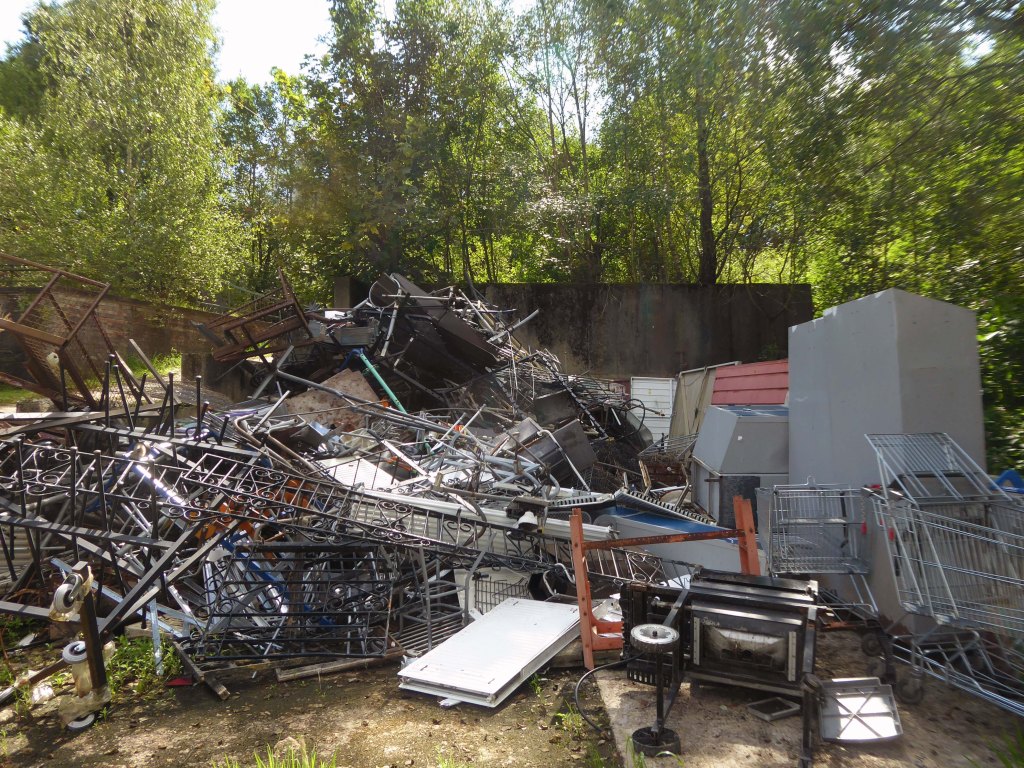
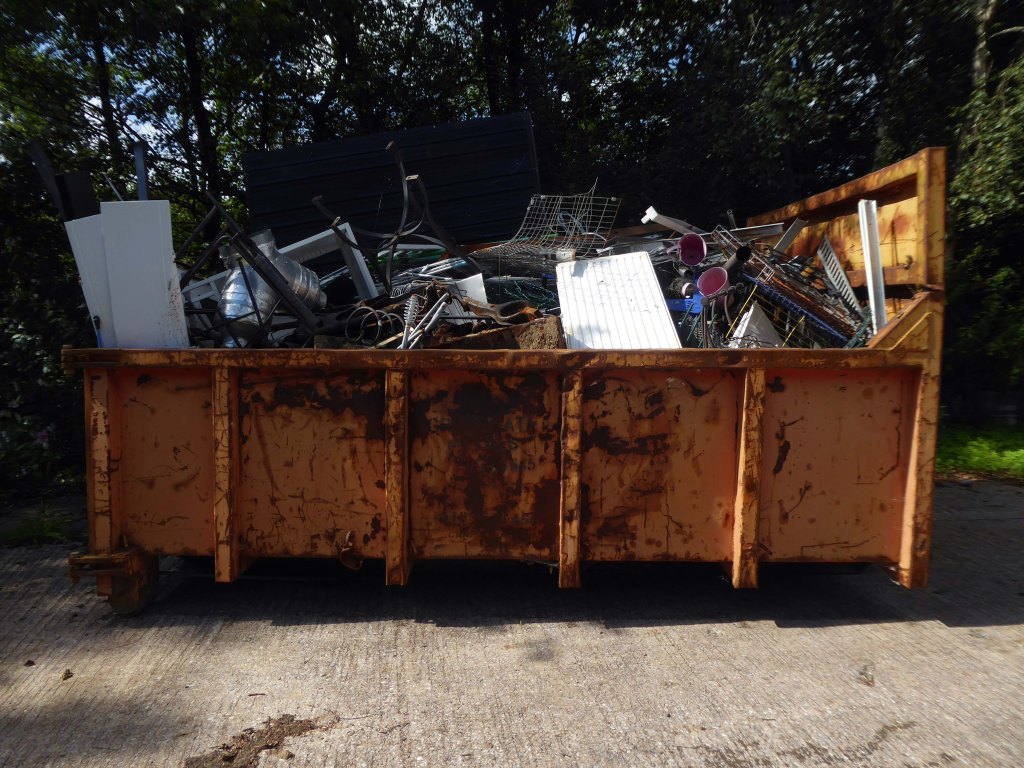
The forecourt of the factory is currently strewn with the detritus of an ever more wasteful world.






























Available online here or call in the Modernist Shop on Port Street Manchester.
Tameside Moderne
By Steve Marland
A comprehensive guide to the Borough’s modern architecture.
Almost two years in the making.
Tameside east of Manchester – a volcanic explosion of concrete, glass, steel, brick and wood!
From sacred sites to suburban substations, a rollercoaster ride through provincial style.
Softcover, 84pages,
B&W
148 x 210xmm – landscape
£10 well spent – be quick these will fly!





